BP神经网络进行分类任务
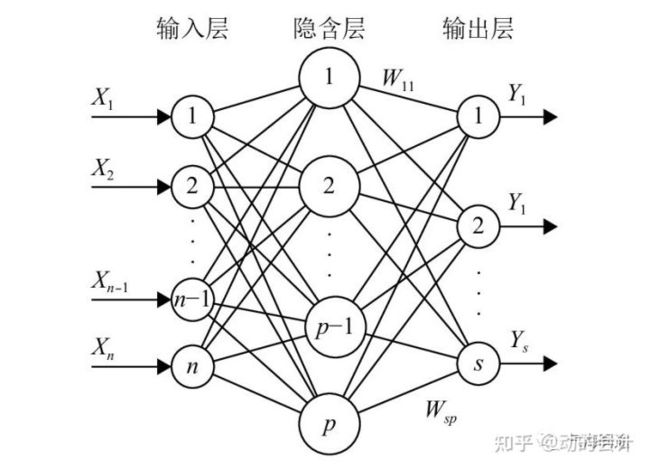
BP(Back Propagation)神经网络是一种按误差逆传播算法训练的多层前馈网络,它的学习规则是使用梯度下降法,通过反向传播来不断调整网络的权值和阈值,使网络的误差平方和最小。BP神经网络模型拓扑结构包括输入层(input)、隐层(hiddenlayer)和输出层(output layer)。BP网络的学习过程,由信息的正向传播和误差的反向传播两个过程组成。
BP神经网络示意图
下面以鸢尾花数据集为例,使用pytorch实现BP神经网络:
1 鸢尾花数据介绍Iris 鸢尾花数据集是一个经典数据集,在统计学习和机器学习领域都经常被用作示例。数据集内包含 3 类共 150 条记录,每类各 50 个数据,每条记录都有 4 项特征:花萼长度、花萼宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度,通过这4个特征预测鸢尾花卉属于(iris-setosa, iris-versicolour, iris-virginica)中的哪一品种。
2 超参数设置超参数无法通过训练得到,只能经验给定,或遍历求最佳组合。
lr = 0.02 #学习率
epochs = 300
n_feature = 4 # 输入特征(鸢尾花四个特征)
n_hidden = 20 # 隐含层
n_output = 3 # 输出(鸢尾花三种类别)3 数据准备将数据分类训练集(80%)和测试集(20%),训练集训练得到网络的权重,测试集评估网络的泛化误差。对数据进行归一化,测试集的数据归一化必须使用训练集上得到的最大最小值。最后将数据转化为Tensor类型,以便能够进行训练。
iris = datasets.load_iris() # 下载并导入数据
# 划分数据集和测试集
x_train0, x_test0,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(iris.data,iris.target,test_size=0.2,random_state= 22)
# 归一化
x_train = np.zeros(np.shape(x_train0))
x_test = np.zeros(np.shape(x_test0 ))
for i in range(4):
xMax = np.max(x_train0[:,i])
xMin = np.min(x_train0[:,i])
x_train[:,i] = (x_train0[:,i] - xMin)/(xMax - xMin)
x_test[:,i] = (x_test0[:,i] - xMin)/(xMax - xMin)
# 数据类型转换为tensor
x_train = torch.FloatTensor(x_train)
y_train = torch.LongTensor (y_train)
x_test = torch.FloatTensor(x_test )
y_test = torch.LongTensor (y_test )4 定义BP神经网络定义三层神经网络,即1输入层,1隐含层,1输出层,激活函数使用softmax。
class bpnnModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(bpnnModel, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # 定义隐藏层网络
self.out = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # 定义输出层网络
def forward(self, x):
x = Fun.relu(self.hidden(x)) # 隐藏层的激活函数,采用relu,也可以采用sigmod,tanh
out = Fun.softmax(self.out(x), dim=1) # 输出层softmax激活函数
return out5 定义优化器损失函数优化器使用Adam,损失函数使用交叉熵(对于分类问题常用)。
net = bpnnModel(n_feature=n_feature, n_hidden=n_hidden, n_output=n_output)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr) # 优化器选用随机梯度下降方式
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 对于多分类一般采用的交叉熵损失函数6 训练和测试此过程即循环epochs=300遍,每一次循环都遍历训练集的全部数据,并通过误差反向传播更新权重。
loss_steps = np.zeros(epochs) # 保存每一轮epoch的损失函数值
accuracy_steps = np.zeros(epochs) # 保存每一轮epoch的在测试集上的精度
for epoch in range(epochs):
y_pred = net(x_train) # 前向过程
loss = loss_func(y_pred, y_train) # 输出与label对比
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 使用梯度优化器
loss_steps[epoch] = loss.item() # 保存loss
# 下面计算测试机的精度,不需要求梯度
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = net(x_test) # 测试集预测
correct = (torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1) == y_test).type(torch.FloatTensor)
accuracy_steps[epoch] = correct.mean() # 测试集精度
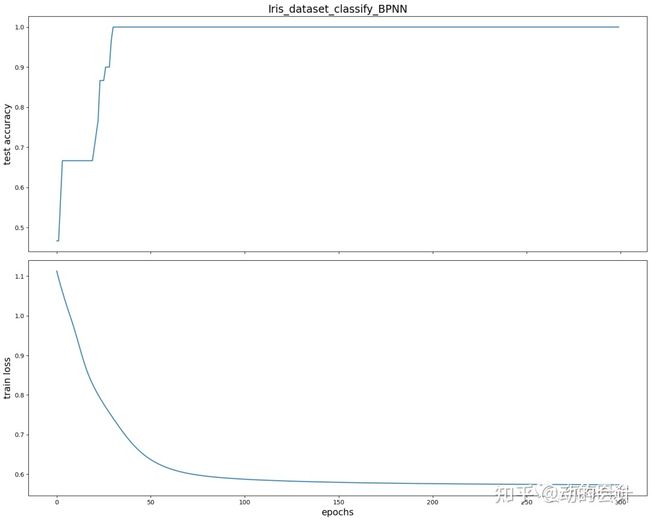
print("测试集莺尾花预测准确率",accuracy_steps[-1])损失函数和精度曲线,训练开始,随着损失函数降低,测试集上的精度也在不断降低,但是训练在100轮以后,基本不再提升。
以下为全部代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split #引入训练集、测试集划分函数
import torchimport torch.nn.functional as Fun
# 0. 超参数设置
lr = 0.02
epochs = 300
n_feature = 4
n_hidden = 20
n_output = 3
# 1. 数据准备
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x_train0, x_test0,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(iris.data,iris.target,test_size=0.2,random_state= 22)
x_train = np.zeros(np.shape(x_train0))
x_test = np.zeros(np.shape(x_test0 ))
for i in range(4):
xMax = np.max(x_train0[:,i])
xMin = np.min(x_train0[:,i])
x_train[:,i] = (x_train0[:,i] - xMin)/(xMax - xMin)
x_test[:,i] = (x_test0[:,i] - xMin)/(xMax - xMin)
x_train = torch.FloatTensor(x_train)
y_train = torch.LongTensor(y_train)
x_test = torch.FloatTensor(x_test )
y_test = torch.LongTensor(y_test )
# 2. 定义BP神经网络
class bpnnModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(bpnnModel, self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # 定义隐藏层网络
self.out = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # 定义输出层网络
def forward(self, x):
x = Fun.relu(self.hidden(x))# 隐藏层的激活函数,采用relu,也可以采用sigmod,tanh
out = Fun.softmax(self.out(x), dim=1) # 输出层softmax激活函数
return out
# 3. 定义优化器损失函数
net = bpnnModel(n_feature=n_feature, n_hidden=n_hidden, n_output=n_output)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr) # 优化器选用随机梯度下降方式
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 对于多分类一般采用的交叉熵损失函数
# 4. 训练数据
loss_steps = np.zeros(epochs)
accuracy_steps = np.zeros(epochs)
for epoch in range(epochs):
y_pred = net(x_train) # 前向过程
loss = loss_func(y_pred, y_train) # 输出与label对比
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 使用梯度优化器
loss_steps[epoch] = loss.item() # 保存loss
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = net(x_test)
correct = (torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1) == y_test).type(torch.FloatTensor)
accuracy_steps[epoch] = correct.mean()
print("测试集莺尾花预测准确率",accuracy_steps[-1])
# 5 绘制损失函数和精度
fig_name = 'Iris_dataset_classify_BPNN'
fontsize = 15
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, figsize=(15, 12), sharex=True)
x1.plot(accuracy_steps)
ax1.set_ylabel("test accuracy", fontsize=fontsize)
ax1.set_title(fig_name, fontsize='xx-large')
ax2.plot(loss_steps)
ax2.set_ylabel("train loss", fontsize=fontsize)
ax2.set_xlabel("epochs", fontsize=fontsize)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(fig_name+'.png')
plt.show()参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/52b86c774b0b
文章来源:气海同途公众号水文、生态、遥感、人工智能、大气等方向视频教程汇总![]() https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzUzMTczMDMwMw==&mid=2247500552&idx=4&sn=0d68a31fcdac77b47f1aec2c04e65f78&chksm=fabc9918cdcb100e706da62a720d2343106238ca2fc4a4aac001bad3e01d066d1355284fa6bd&token=1597410074&lang=zh_CN#rd
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzUzMTczMDMwMw==&mid=2247500552&idx=4&sn=0d68a31fcdac77b47f1aec2c04e65f78&chksm=fabc9918cdcb100e706da62a720d2343106238ca2fc4a4aac001bad3e01d066d1355284fa6bd&token=1597410074&lang=zh_CN#rd