Self-adaptive Differential Evolution with Neighborhood Search
0、论文背景
本文是在SaDE和NSDE的基础上,结合二者的特点,提出了SaNSDE算法。
Yang Z, Tang K, Yao X. Self-adaptive differential evolution with neighborhood search[C]//2008 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence). IEEE, 2008: 1110-1116.
1、SaNSDE
有关SaDE和NSDE,请参见博客:NSDE,SaDE。
SaNSDE与NSDE、SaDE不同点在于以下几个方面:
- 突变策略自适应。SaNSDE采用了与SaDE相同的方法。提供选择的策略有两个:DE/rand/1 和 DE/current to best/2。
- F值自适应。采用了NSDE里面获取F值的方式,但不同的地方是,这里的fp不是固定值0.5,而是通过突变策略自适应中调整p值的方式来调整fp值的。
- CR值自适应。采用了SaDE里面自适应调整CR值的方式来获取CR值,但是这里给每个向量的CR值前面乘了一个权重系数,每个权重系数与成功保留到下一代的点与之前点对应的适应度值差值成正比。
![]()
2、算法的实现与简单实验
function [globalBest, globalBestFitness, FitnessHistory] = SaNSDE(popsize, maxIteration,dim, LB, UB, Fun)
% 种群的初始化和计算适应度值
Sol(popsize, dim) = 0; % Declare memory.
Fitness(popsize) = 0;
for i = 1:popsize
Sol(i,:) = LB+(UB-LB).* rand(1, dim);
Fitness(i) = Fun(Sol(i,:));
end
% 获得全局最优值以及对应的种群向量
[fbest, bestIndex] = min(Fitness);
globalBest = Sol(bestIndex,:);
globalBestFitness = fbest;
% 策略学习初始化值的设置
p1 = 0.5;p3 = 0.5;
ns1 = 0;ns2 = 0;nf1 = 0;nf2 = 0;
fns1 = 0;fns2 = 0;fnf1 = 0;fnf2 = 0;
CRm = 0.5;
CRQ = normrnd(CRm,0.1,[popsize,1]);
CRRecord = [];
RecRecord = [];
% 开始迭代
for time = 1:maxIteration
for i = 1:popsize
% 突变
if rand() >= p3
pd = makedist('tLocationScale','mu',0,'sigma',1,'nu',1);
F = random(pd,1,1);%生成1个柯西随机数
tag1 = 1;
else
F = normrnd(0.5,0.3);%生成1个高斯随机数
tag1 = 2;
end
if rand() <= p1
r = randperm(popsize, 3); %策略1
mutantPos = Sol(r(1),:) + F * (Sol(r(2),:) - Sol(r(3),:));%在1~pop中随机选择3个数组成一个数组
tag0 = 1;
else
r = randperm(popsize, 2); %策略2
mutantPos = Sol(i,:) + F * (globalBest - Sol(i,:)) + F * (Sol(r(1),:) - Sol(r(2),:));
tag0 = 2;
end
% 交叉
jj = randi(dim); % 选择至少一维发生交叉
CR = CRQ(i,1);
for d = 1:dim
if rand() < CR || d == jj
crossoverPos(d) = mutantPos(d);
else
crossoverPos(d) = Sol(i,d);
end
end
% 检查是否越界.
crossoverPos(crossoverPos>UB) = UB(crossoverPos>UB);
crossoverPos(crossoverPosclear;clc;clearvars;
% 初始化变量维度,种群数,最大迭代次数,搜索区间,F,CR
dim = 20;
popsize = 100;
maxIteration = 1000;
LB = -5.12 * ones(1, dim);
UB = 5.12 * ones(1, dim);
F = 1;
CR = 0.9;
%Griewank[-600,600] Ackley[-32.768,32.768] Rastrigin[-5.12,5.12]
[globalBest3, globalBestFitness3, FitnessHistory3] = SaNSDE(popsize, maxIteration,dim, LB, UB, @(x)Rastrigin(x));
[globalBest, globalBestFitness, FitnessHistory] = DE(popsize, maxIteration,dim, LB, UB, F, CR, @(x)Rastrigin(x));
[globalBest1, globalBestFitness1, FitnessHistory1] = NSDE(popsize, maxIteration,dim, LB, UB, CR, @(x)Rastrigin(x));
[globalBest2, globalBestFitness2, FitnessHistory2] = SaDE(popsize, maxIteration,dim, LB, UB, @(x)Rastrigin(x));
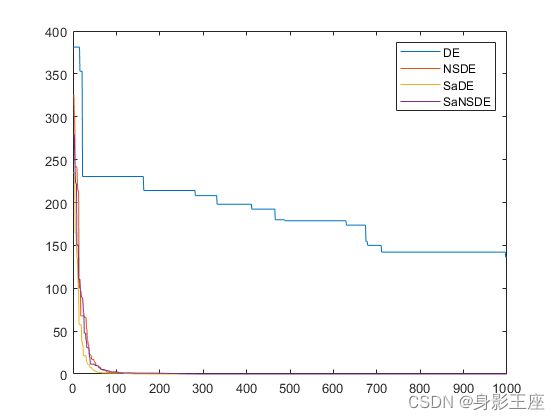
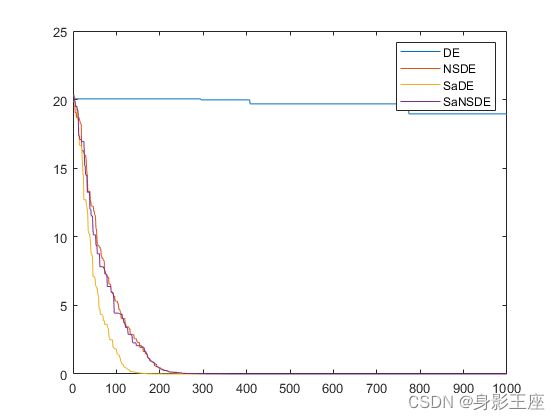
plot(FitnessHistory);
hold on;
plot(FitnessHistory1);
hold on;
plot(FitnessHistory2);
hold on;
plot(FitnessHistory3);
legend('DE','NSDE','SaDE','SaNSDE','Location', 'northeast');
Griewank函数的测试结果:
Ackley函数的测试结果:
Rastrigin函数的测试结果:
如有错误,还望批评改正!