pytorch 建立LSTM模型实现股价预测
本文参考了这篇知乎文章:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/128927771,并对其中部分代码进行修改,使其更有可读性。
原版代码和数据见此链接:https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//github.com/yhannahwang/stock_prediction
本文通过jupyter notebook转化成markdown文件,再放到这里,代码和文字可能会有部分有背景色
阅读本文之前,需要知道LSTM的原理,还有pytorch中LSTM的接口定义,否则读起来很吃力。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
导入数据,并进行处理
dates = pd.date_range('2010-10-11','2017-10-11',freq = 'B') # 生成时间序列,频率为工作日
# 生成一个只含索引的DataFrame
df_main = pd.DataFrame(index = dates)
df_main
| 2010-10-11 |
|---|
| 2010-10-12 |
| 2010-10-13 |
| 2010-10-14 |
| 2010-10-15 |
| ... |
| 2017-10-05 |
| 2017-10-06 |
| 2017-10-09 |
| 2017-10-10 |
| 2017-10-11 |
1828 rows × 0 columns
df_aaxj = pd.read_csv("data/ETFs/aaxj.us.txt", index_col=0)
df_aaxj
| Open | High | Low | Close | Volume | OpenInt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | ||||||
| 2008-08-15 | 44.886 | 44.886 | 44.886 | 44.886 | 112 | 0 |
| 2008-08-18 | 44.564 | 44.564 | 43.875 | 43.875 | 28497 | 0 |
| 2008-08-19 | 43.283 | 43.283 | 43.283 | 43.283 | 112 | 0 |
| 2008-08-20 | 43.918 | 43.918 | 43.892 | 43.892 | 4468 | 0 |
| 2008-08-22 | 44.097 | 44.097 | 44.017 | 44.071 | 4006 | 0 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2017-11-06 | 75.900 | 76.530 | 75.890 | 76.530 | 1313730 | 0 |
| 2017-11-07 | 76.490 | 76.580 | 76.090 | 76.185 | 1627277 | 0 |
| 2017-11-08 | 76.370 | 76.590 | 76.290 | 76.570 | 681128 | 0 |
| 2017-11-09 | 76.040 | 76.200 | 75.580 | 76.110 | 1261567 | 0 |
| 2017-11-10 | 76.110 | 76.150 | 75.870 | 76.080 | 619687 | 0 |
2325 rows × 6 columns
# 数据拼接
df_main = df_main.join(df_aaxj)
df_main
| Open | High | Low | Close | Volume | OpenInt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010-10-11 | 55.971 | 56.052 | 55.863 | 56.052 | 268544.0 | 0.0 |
| 2010-10-12 | 55.676 | 55.792 | 55.362 | 55.667 | 817951.0 | 0.0 |
| 2010-10-13 | 56.472 | 56.867 | 56.401 | 56.569 | 999413.0 | 0.0 |
| 2010-10-14 | 56.733 | 56.742 | 56.293 | 56.579 | 661897.0 | 0.0 |
| 2010-10-15 | 56.893 | 56.893 | 56.194 | 56.552 | 245001.0 | 0.0 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2017-10-05 | 73.500 | 74.030 | 73.500 | 73.970 | 2134323.0 | 0.0 |
| 2017-10-06 | 73.470 | 73.650 | 73.220 | 73.579 | 2092100.0 | 0.0 |
| 2017-10-09 | 73.500 | 73.795 | 73.480 | 73.770 | 879600.0 | 0.0 |
| 2017-10-10 | 74.150 | 74.490 | 74.150 | 74.480 | 1878845.0 | 0.0 |
| 2017-10-11 | 74.290 | 74.645 | 74.210 | 74.610 | 1168511.0 | 0.0 |
1828 rows × 6 columns
# 绘制收盘价格走势图
df_main[['Close']].plot()
plt.ylabel("stock_price")
plt.title("aaxj ETFs")
plt.show()
# 筛选四个变量,作为数据的输入特征
sel_col = ['Open', 'High', 'Low', 'Close']
df_main = df_main[sel_col]
df_main.head()
| Open | High | Low | Close | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010-10-11 | 55.971 | 56.052 | 55.863 | 56.052 |
| 2010-10-12 | 55.676 | 55.792 | 55.362 | 55.667 |
| 2010-10-13 | 56.472 | 56.867 | 56.401 | 56.569 |
| 2010-10-14 | 56.733 | 56.742 | 56.293 | 56.579 |
| 2010-10-15 | 56.893 | 56.893 | 56.194 | 56.552 |
# 查看是否有缺失值
np.sum(df_main.isnull())
Open 65
High 65
Low 65
Close 65
dtype: int64
# 缺失值填充
df_main = df_main.fillna(method='ffill') # 缺失值填充,使用上一个有效值
np.sum(df_main.isnull())
Open 0
High 0
Low 0
Close 0
dtype: int64
# 数据缩放
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1))
for col in sel_col: # 这里不能进行统一进行缩放,因为fit_transform返回值是numpy类型
df_main[col] = scaler.fit_transform(df_main[col].values.reshape(-1,1))
# 将下一日的收盘价作为本日的标签
df_main['target'] = df_main['Close'].shift(-1)
df_main.head()
| Open | High | Low | Close | target | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010-10-11 | -0.089800 | -0.135104 | -0.074936 | -0.106322 | -0.129274 |
| 2010-10-12 | -0.107350 | -0.150977 | -0.104289 | -0.129274 | -0.075502 |
| 2010-10-13 | -0.059996 | -0.085348 | -0.043415 | -0.075502 | -0.074905 |
| 2010-10-14 | -0.044469 | -0.092979 | -0.049742 | -0.074905 | -0.076515 |
| 2010-10-15 | -0.034950 | -0.083761 | -0.055543 | -0.076515 | -0.068407 |
df_main.dropna() # 使用了shift函数,在最后必然是有缺失值的,这里去掉缺失值所在行
df_main = df_main.astype(np.float32) # 修改数据类型
建立LSTM模型
import torch.nn as nn
input_dim = 4 # 数据的特征数
hidden_dim = 32 # 隐藏层的神经元个数
num_layers = 2 # LSTM的层数
output_dim = 1 # 预测值的特征数
#(这是预测股票价格,所以这里特征数是1,如果预测一个单词,那么这里是one-hot向量的编码长度)
class LSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, output_dim):
super(LSTM, self).__init__()
# Hidden dimensions
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
# Number of hidden layers
self.num_layers = num_layers
# Building your LSTM
# batch_first=True causes input/output tensors to be of shape (batch_dim, seq_dim, feature_dim)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, batch_first=True)
# Readout layer 在LSTM后再加一个全连接层,因为是回归问题,所以不能在线性层后加激活函数
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
# Initialize hidden state with zeros
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()
# 这里x.size(0)就是batch_size
# Initialize cell state
c0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_dim).requires_grad_()
# One time step
# We need to detach as we are doing truncated backpropagation through time (BPTT)
# If we don't, we'll backprop all the way to the start even after going through another batch
out, (hn, cn) = self.lstm(x, (h0.detach(), c0.detach()))
out = self.fc(out)
return out
按照模型的接口组织数据
# 创建两个列表,用来存储数据的特征和标签
data_feat, data_target = [],[]
# 设每条数据序列有20组数据
seq = 20
for index in range(len(df_main) - seq):
# 构建特征集
data_feat.append(df_main[['Open', 'High', 'Low', 'Close']][index: index + seq].values)
# 构建target集
data_target.append(df_main['target'][index:index + seq])
# 将特征集和标签集整理成numpy数组
data_feat = np.array(data_feat)
data_target = np.array(data_target)
训练集与测试集的划分
# 这里按照8:2的比例划分训练集和测试集
test_set_size = int(np.round(0.2*df_main.shape[0])) # np.round(1)是四舍五入,
train_size = data_feat.shape[0] - (test_set_size)
print(test_set_size) # 输出测试集大小
print(train_size) # 输出训练集大小
366
1442
trainX = torch.from_numpy(data_feat[:train_size].reshape(-1,seq,4)).type(torch.Tensor)
# 这里第一个维度自动确定,我们认为其为batch_size,因为在LSTM类的定义中,设置了batch_first=True
testX = torch.from_numpy(data_feat[train_size:].reshape(-1,seq,4)).type(torch.Tensor)
trainY = torch.from_numpy(data_target[:train_size].reshape(-1,seq,1)).type(torch.Tensor)
testY = torch.from_numpy(data_target[train_size:].reshape(-1,seq,1)).type(torch.Tensor)
print('x_train.shape = ',trainX.shape)
print('y_train.shape = ',trainY.shape)
print('x_test.shape = ',testX.shape)
print('y_test.shape = ',testY.shape)
x_train.shape = torch.Size([1442, 20, 4])
y_train.shape = torch.Size([1442, 20, 1])
x_test.shape = torch.Size([366, 20, 4])
y_test.shape = torch.Size([366, 20, 1])
建立数据导入器(略)
# 因为数据量不大,所以这里就不再划分batch,即认为batch_size=1442,
# 这里只是演示一下数据导入器,我们并不使用
batch_size=1442
train = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(trainX,trainY)
test = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(testX,testY)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=test,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False)
训练模型
# 实例化模型
model = LSTM(input_dim=input_dim, hidden_dim=hidden_dim, output_dim=output_dim, num_layers=num_layers)
# 定义优化器和损失函数
optimiser = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01) # 使用Adam优化算法
loss_fn = torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=True) # 使用均方差作为损失函数
# 设定数据遍历次数
num_epochs = 100
# 打印模型结构
print(model)
LSTM(
(lstm): LSTM(4, 32, num_layers=2, batch_first=True)
(fc): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
# 打印模型各层的参数尺寸
for i in range(len(list(model.parameters()))):
print(list(model.parameters())[i].size())
torch.Size([128, 4])
torch.Size([128, 32])
torch.Size([128])
torch.Size([128])
torch.Size([128, 32])
torch.Size([128, 32])
torch.Size([128])
torch.Size([128])
torch.Size([1, 32])
torch.Size([1])
# train model
hist = np.zeros(num_epochs)
for t in range(num_epochs):
# Initialise hidden state
# Don't do this if you want your LSTM to be stateful
# model.hidden = model.init_hidden()
# Forward pass
y_train_pred = model(trainX)
loss = loss_fn(y_train_pred, trainY)
if t % 10 == 0 and t !=0: # 每训练十次,打印一次均方差
print("Epoch ", t, "MSE: ", loss.item())
hist[t] = loss.item()
# Zero out gradient, else they will accumulate between epochs 将梯度归零
optimiser.zero_grad()
# Backward pass
loss.backward()
# Update parameters
optimiser.step()
Epoch 10 MSE: 0.01842750422656536
Epoch 20 MSE: 0.008485360071063042
Epoch 30 MSE: 0.004656758159399033
Epoch 40 MSE: 0.0032537723891437054
Epoch 50 MSE: 0.002434148220345378
Epoch 60 MSE: 0.0020096886437386274
Epoch 70 MSE: 0.0018414082005620003
Epoch 80 MSE: 0.0017679394222795963
Epoch 90 MSE: 0.0017151187639683485
# 计算训练得到的模型在训练集上的均方差
y_train_pred = model(trainX)
loss_fn(y_train_pred, trainY).item()
0.0016758530400693417
测试模型
# make predictions
y_test_pred = model(testX)
loss_fn(y_test_pred, testY).item()
0.004057767800986767
# 从结果来看,有些过拟合
绘制效果图
"训练集效果图"
# 无论是真实值,还是模型的输出值,它们的维度均为(batch_size, seq, 1),seq=20
# 我们的目的是用前20天的数据预测今天的股价,所以我们只需要每个数据序列中第20天的标签即可
# 因为前面用了使用DataFrame中shift方法,所以第20天的标签,实际上就是第21天的股价
pred_value = y_train_pred.detach().numpy()[:,-1,0]
true_value = trainY.detach().numpy()[:,-1,0]
plt.plot(pred_value, label="Preds") # 预测值
plt.plot(true_value, label="Data") # 真实值
plt.legend()
plt.show()
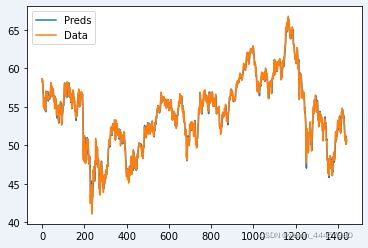
# 纵坐标还有负的,因为前面进行缩放,现在让数据还原成原来的大小
# invert predictions
pred_value = scaler.inverse_transform(pred_value.reshape(-1, 1))
true_value = scaler.inverse_transform(true_value.reshape(-1, 1))
plt.plot(pred_value, label="Preds") # 预测值
plt.plot(true_value, label="Data") # 真实值
plt.legend()
plt.show()
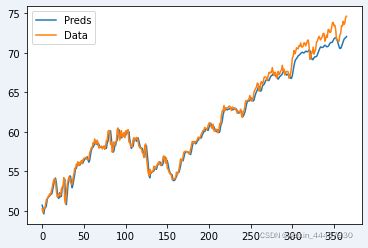
"测试集效果图"
pred_value = y_test_pred.detach().numpy()[:,-1,0]
true_value = testY.detach().numpy()[:,-1,0]
pred_value = scaler.inverse_transform(pred_value.reshape(-1, 1))
true_value = scaler.inverse_transform(true_value.reshape(-1, 1))
plt.plot(pred_value, label="Preds") # 预测值
plt.plot(true_value, label="Data") # 真实值
plt.legend()
plt.show()
前面还拟合的比较好,但是到了后面的时期就不太准确了,可能与前面模型出现过拟合有关系