Spring: IOC 注解开发,管理第三方bean(IOC/DI配置/注解管理第三方bean、完成Spring与Mybatis及Junit的整合开发)
6,IOC/DI配置管理第三方bean
管理第三方jar包中的类,该如何管理?
6.1 案例:数据源对象管理: 导入包依赖+配置bean
通过一个案例来学习下对于第三方bean该如何进行配置管理。
本次案例将使用数据源Druid(德鲁伊)和C3P0来配置学习下。
6.1.1 案例环境准备
-
创建一个Maven项目
-
pom.xml添加依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId> <artifactId>spring-contextartifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASEversion> dependency> dependencies> -
resources下添加spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> beans> -
编写一个运行类App
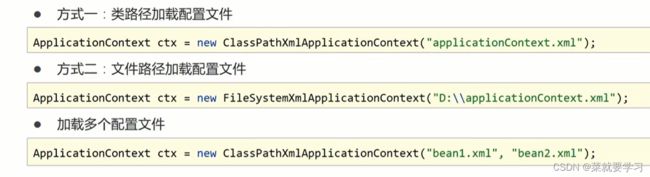
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); } }
6.1.2 实现Druid管理
在上述环境下,我们来对数据源进行配置管理,先来分析下思路:
需求:使用Spring的IOC容器来管理Druid连接池对象
1.使用第三方的技术,需要在pom.xml添加依赖
2.在配置文件中将【第三方的类】制作成一个bean,让IOC容器进行管理
3.数据库连接需要基础的四要素
驱动、连接、用户名和密码,【如何注入】到对应的bean中4.从IOC容器中获取对应的bean对象
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource");,将其打印到控制台查看结果
-
第三方的类指的是什么?
DruidDataSource -
如何注入数据库连接四要素?
setter注入 -
对于新的技术,不知道具体的坐标该如何查找?
- 直接百度搜索
- 从mvn的仓库
https://mvnrepository.com/中进行搜索
6.1.4 实现C3P0管理
管理C3P0数据源,具体的实现步骤是什么呢?
需求:使用Spring的IOC容器来管理C3P0连接池对象
实现方案和上面基本一致,重点要关注管理的是哪个bean对象`?
步骤1:导入C3P0的依赖
pom.xml中添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2version>
dependency>
步骤2:配置第三方bean
在applicationContext.xml配置文件中添加配置
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db"/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="1000"/>
bean>
注意:
- ComboPooledDataSource的属性是通过setter方式进行注入
- 想注入属性就需要在ComboPooledDataSource类或其上层类中有提供属性对应的setter方法
- C3P0的四个属性和Druid的四个属性是不一样的
6.2 加载properties文件
上节中我们已经完成两个数据源druid和C3P0的配置,但是其中包含了一些问题,我们来分析下:
-
问题:
- 在Spring的配置文件中,bean配置时固定的常量如数据库连接四要素,不利于后期维护
-
解决:
- 将这些值提取到一个外部的properties配置文件中
- Spring框架从配置文件中读取属性值来配置
问题提出来后,具体该如何实现?
6.2.1 第三方bean属性优化:通过外部的properties配置
1.2.1.1 实现思路
需求:将数据库连接四要素提取到properties配置文件,spring来加载配置信息并使用这些信息来完成属性注入。
1.在resources下创建一个jdbc.properties(文件的名称可以任意)
2.将数据库连接四要素配置到配置文件中
3.在Spring的配置文件中加载properties文件
4.使用加载到的值实现属性注入
其中第3,4步骤是需要大家重点关注,具体是如何实现。
1.2.1.2 实现步骤
步骤1:准备properties配置文件
resources下创建一个jdbc.properties文件,并添加对应的属性键值对
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/spring_db
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
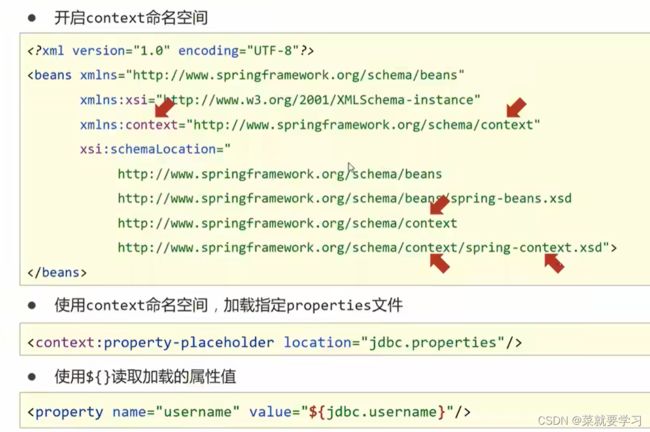
步骤2:开启context命名空间
在applicationContext.xml中开context命名空间
步骤3: 使用context空间加载properties配置文件
在配置文件中使用context命名空间下的标签+属性location来加载properties配置文件
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>
步骤4:${key}完成属性注入
在${key}来读取properties配置文件中的内容并完成属性注入
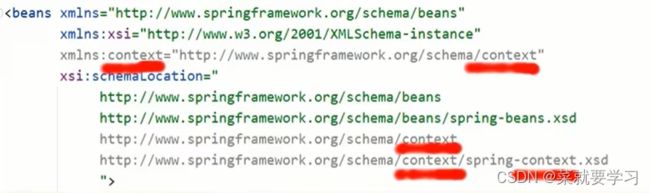
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
bean>
beans>
至此,读取外部properties配置文件中的内容就已经完成。
6.2.2 读取单个属性的实现思路
对于上面的案例,效果不是很明显,我们可以换个案例来演示下:
需求:从properties配置文件中读取key为name的值,并将其注入到BookDao中并在save方法中进行打印。
1.在项目中添加BookDao和BookDaoImpl类
2.为BookDaoImpl添加一个name属性并提供setter方法
3.在jdbc.properties中添加数据注入到bookDao中打印方便查询结果
4.在applicationContext.xml添加配置完成配置文件加载、属性注入(${key})
6.2.3 注意事项
至此,读取properties配置文件中的内容就已经完成,但是在使用的时候,有些注意事项:
问题一:键值对的key为username引发的问题
问题:
解决方案1:
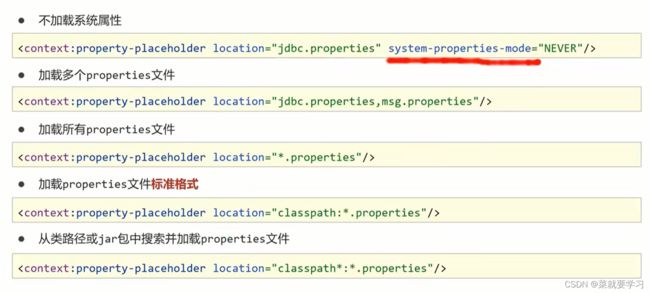
system-properties-mode:设置为NEVER,表示不加载系统属性,就可以解决上述问题。
解决方案2:就是避免使用username作为属性的key。
问题二: 当有多个properties配置文件需要被加载,该如何配置?
说明:
- 方式一:可以实现,如果配置文件多的话,每个都需要配置
- 方式二:
*.properties代表所有以properties结尾的文件都会被加载,可以解决方式一的问题,但是不标准 - 方式三:标准的写法,
classpath:代表的是从根路径下开始查找,但是只能查询当前项目的根路径 - 方式四:不仅可以加载当前项目还可以加载当前项目所依赖的所有项目的根路径下的properties配置文件
7,核心容器
前面已经完成bean与依赖注入的相关知识学习,接下来我们主要学习的是IOC容器中的核心容器。
这里所说的核心容器,大家可以把它简单的理解为ApplicationContext,前面虽然已经用到过,但是并没有系统的学习,接下来咱们从以下几个问题入手来学习下容器的相关知识:
- 如何创建容器?
-
-
容器创建的两种方式
-
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext[掌握]
-
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext[知道即可]
-
-
创建好容器后,如何从容器中获取bean对象?
-
-
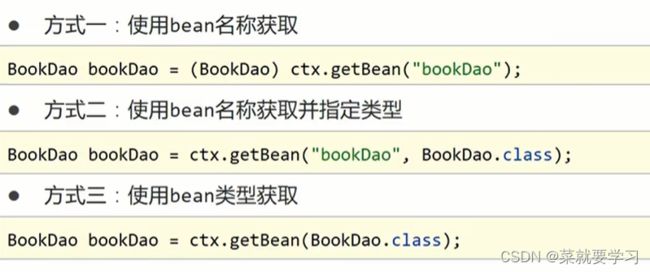
获取Bean的三种方式
-
getBean(“名称”):需要类型转换
-
getBean(“名称”,类型.class):多了一个参数
-
getBean(类型.class):容器中不能有多个该类的bean对象
上述三种方式,各有各的优缺点,用哪个都可以。
-
-
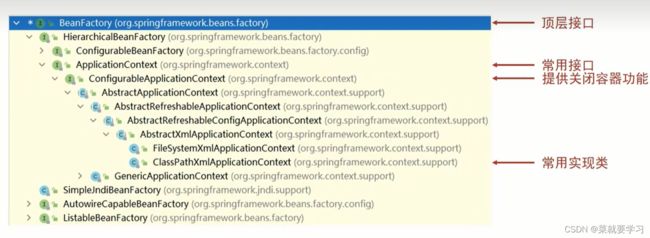
BeanFactory是什么?(所有容器类的顶层j接口)了解

-
BeanFactory是延迟加载,只有在获取bean对象的时候才会去创建
-
ApplicationContext是立即加载,容器加载的时候就会创建bean对象
-
ApplicationContext要想成为延迟加载,只需要按照如下方式进行配置
lazy-init
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="bookDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl" lazy-init="true"/> beans> -
8,IOC/DI注解开发
Spring的IOC/DI对应的配置开发就已经讲解完成,但是使用起来相对来说还是比较复杂的,复杂的地方在配置文件。
要想真正简化开发,就需要用到Spring的注解开发,Spring对注解支持的版本历程:注解开发定义bean和纯注解开发。
小结:
这一节重点掌握的是使用注解完成Spring的bean管理,需要掌握的内容为:
- 记住@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository这四个注解
- applicationContext.xml中
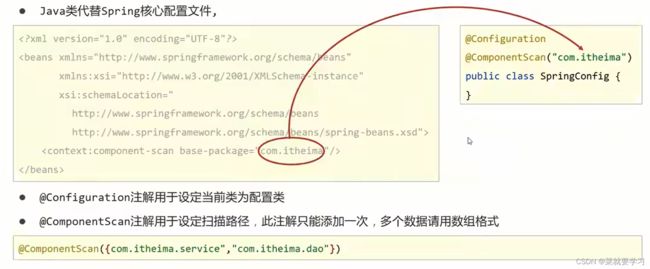
- @Configuration标识该类为配置类,使用类替换applicationContext.xml文件
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是加载XML配置文件
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是加载配置类
8.1 注解开发定义bean
在上述环境的基础上,我们来学一学Spring是如何通过注解实现bean的定义开发?
| 名称 | @Component/@Controller/@Service/@Repository |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置该类为spring管理的bean |
| 属性 | value(默认):定义bean的id |
- @Component注解不可以添加在接口上,因为接口是无法创建对象的。
- @Component注解如果不起名称,会有一个默认值就是
当前类名首字母小写,也可以在App中是按照类型来获取bean对象
衍生注解:作用:方便理解

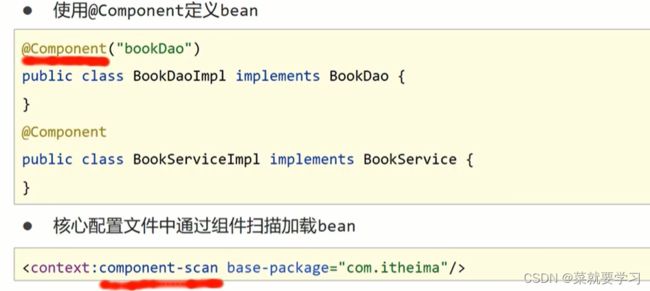
步骤1:删除原XML配置,将配置文件中的
步骤2:Dao上添加注解,在加载类上添加@Component注解
步骤3:配置Spring的注解包扫描:
步骤5:Service上添加注解,在BookServiceImpl类上也添加@Component交给Spring框架管理
8.2 纯注解开发模式(Spring3.0开启)
实现思路为:
- 将配置文件applicationContext.xml删除掉,使用类来替换。
- 纯注解开发的方式的主要内容包括:
| 名称 | @Configuration |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置该类为spring配置类 |
| 属性 | value(默认):定义bean的id |
| 名称 | @ComponentScan |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置spring配置类扫描路径,用于加载使用注解格式定义的bean |
| 属性 | value(默认):扫描路径,此路径可以逐层向下扫描 |
8.3 注解开发 bean作用范围与生命周期管理
使用注解已经完成了bean的管理,接下来按照前面所学习的内容,将通过配置实现的内容都换成对应的注解实现,包含两部分内容:bean作用范围和bean生命周期:
8.3.1 Bean的作用范围: @Scope
@Repository
//@Scope设置bean的作用范围
@Scope("prototype")
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
}
| 名称 | @Scope |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置该类创建对象的作用范围 可用于设置创建出的bean是否为单例对象 |
| 属性 | value(默认):定义bean作用范围, 默认值singleton(单例),可选值prototype(非单例) |
8.3.2 Bean的生命周期:@PostConstruct @PreDestroy
(1)在BookDaoImpl中添加两个方法,init和destroy,方法名可以任意,对方法进行标识,哪个是初始化方法,哪个是销毁方法?
只需要在对应的方法上添加@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解即可。
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println("book dao save ...");
}
@PostConstruct //在构造方法之后执行,替换 init-method
public void init() {
System.out.println("init ...");
}
@PreDestroy //在销毁方法之前执行,替换 destroy-method
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy ...");
}
}
| 名称 | @PostConstruct |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 方法上 |
| 作用 | 设置该方法为初始化方法 |
| 属性 | 无 |
| 名称 | @PreDestroy |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 方法上 |
| 作用 | 设置该方法为销毁方法 |
| 属性 | 无 |
(2)容器关闭: ctx.close(); //关闭容器
注意:@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解如果找不到,需要导入下面的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
8.4 注解开发依赖注入
Spring为了使用注解简化开发,并没有提供构造函数注入、setter注入对应的注解,只提供了自动装配的注解实现。属性上添加@Autowired注解

知识点1:@Autowired
| 名称 | @Autowired |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 属性注解 或 方法注解(了解) 或 方法形参注解(了解) |
| 位置 | 属性定义上方 或 标准set方法上方 或 类set方法上方 或 方法形参前面 |
| 作用 | 为引用类型属性设置值 |
| 属性 | required:true/false,定义该属性是否允许为null |
知识点2:@Qualifier
| 名称 | @Qualifier |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 属性注解 或 方法注解(了解) |
| 位置 | 属性定义上方 或 标准set方法上方 或 类set方法上方 |
| 作用 | 为引用类型属性指定注入的beanId |
| 属性 | value(默认):设置注入的beanId |
知识点3:@Value
| 名称 | @Value |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 属性注解 或 方法注解(了解) |
| 位置 | 属性定义上方 或 标准set方法上方 或 类set方法上方 |
| 作用 | 为 基本数据类型 或 字符串类型 属性设置值 |
| 属性 | value(默认):要注入的属性值 |
知识点4:@PropertySource
| 名称 | @PropertySource |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 加载properties文件中的属性值 |
| 属性 | value(默认):设置加载的properties文件对应的文件名或文件名组成的数组 |
8.4.2 注解实现按照类型注入:@Autowired
对于这个问题使用注解该如何解决?
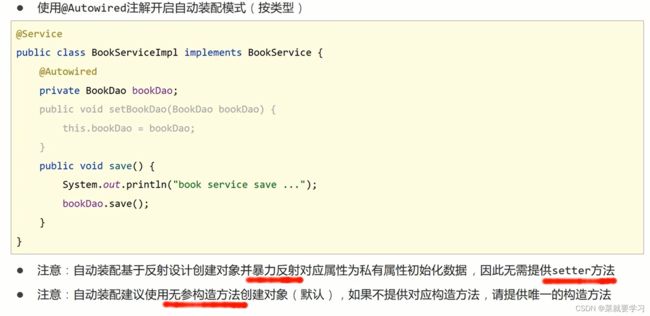
(1) 在BookServiceImpl类的bookDao属性上添加@Autowired注解
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
// public void setBookDao(BookDao bookDao) {
// this.bookDao = bookDao;
// }
public void save() {
System.out.println("book service save ...");
bookDao.save();
}
}
注意:
- @Autowired可以写在属性上,也可也写在setter方法上,最简单的处理方式是
写在属性上并将setter方法删除掉 - 为什么setter方法可以删除呢?
- 自动装配基于反射设计创建对象并通过暴力反射为私有属性进行设值
- 普通反射只能获取public修饰的内容
- 暴力反射除了获取public修饰的内容还可以获取private修改的内容
- 所以此处无需提供setter方法
(2)@Autowired是按照类型注入,那么对应BookDao接口如果有多个实现类,按照类型注入就无法区分到底注入哪个对象,解决方案:按照名称注入
-
先给两个Dao类分别起个名称 @Repository(“beanid”)
@Repository("bookDao") public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { public void save() { System.out.println("book dao save ..." ); } } @Repository("bookDao2") public class BookDaoImpl2 implements BookDao { public void save() { System.out.println("book dao save ...2" ); } }- @Autowired默认按照类型自动装配,如果IOC容器中同类的Bean找到多个,就按照变量名和Bean的名称匹配。如果变量名叫
bookDao而容器中也有一个booDao,所以可以成功注入。
- @Autowired默认按照类型自动装配,如果IOC容器中同类的Bean找到多个,就按照变量名和Bean的名称匹配。如果变量名叫
8.4.3 注解实现按照名称注入:@Qualifier
当根据类型在容器中找到多个bean,注入参数的属性名又和容器中bean的名称不一致,就需要使用到@Qualifier来指定注入哪个名称的bean对象。
给容器中bean起别名 @Repository(“beanId”)
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("bookDao1")
private BookDao bookDao;
public void save() {
System.out.println("book service save ...");
bookDao.save();
}
}
@Qualifier注解后的值就是需要注入的bean的名称。
注意:@Qualifier不能独立使用,必须和@Autowired一起使用
8.4.5 注解读取properties配置文件 @Value(“${ }”)@Repository()
@Value一般会被用在从properties配置文件中读取内容进行使用
@Value(“${name}”):读取配置文件中对应属性的内容
@Repository(“bookDao”): 加载配置文件
@Repository("bookDao")
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
public void save() {
System.out.println("book dao save ..." + name);
}
}
注意:
-
如果读取的properties配置文件有多个,可以使用
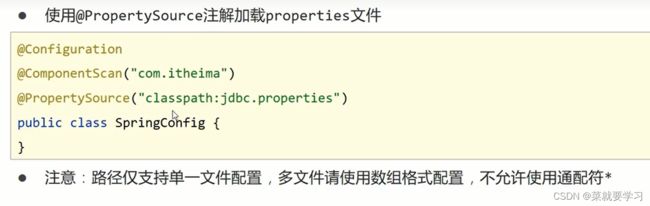
@PropertySource的属性来指定多个@PropertySource({"jdbc.properties","xxx.properties"}) -
@PropertySource注解属性中不支持使用通配符*,运行会报错 -
@PropertySource注解属性中可以把classpath:加上,代表从当前项目的根路径找文件@PropertySource({"classpath:jdbc.properties"})
9,IOC/DI注解开发管理第三方bean
定义bean
自己开发的类:注解进行管理,
jar包中第三方的类,无法在类原始代码上面添加注解,使用注解==@Bean==。
9.1 注解开发管理第三方bean
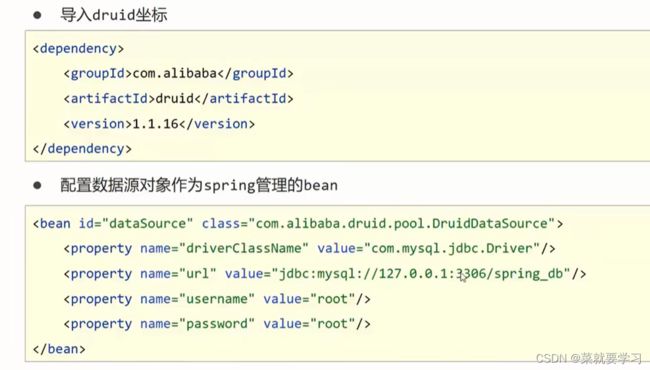
在上述环境中完成对Druid数据源的管理,具体的实现步骤为:
步骤1:导入对应的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.16version>
dependency>
步骤2:在配置类中添加一个方法
定义一个方法获得要管理的对象,注意该方法的返回值就是要创建的Bean对象类型,方法名为BeanId
步骤3:在方法上添加@Bean注解
@Bean注解的作用是将方法的返回值制作为Spring管理的一个bean对象
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
注意:不能使用DataSource ds = new DruidDataSource()
因为DataSource接口中没有对应的setter方法来设置属性。
步骤4:从IOC容器中获取对象并操作
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
DataSource dataSource = ctx.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource);
}
}
至此使用@Bean来管理第三方bean的案例就已经完成。
如果有多个bean要被Spring管理,直接在配置类中多些几个方法,方法上添加@Bean注解即可。
知识点1:@Bean
| 名称 | @Bean |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置该方法的返回值作为spring管理的bean |
| 属性 | value(默认):定义bean的id |
9.2 引入外部配置类+被Spring配置类加载
如果把所有的第三方bean都配置到Spring的配置类SpringConfig中,虽然可以,但是不利于代码阅读和分类管理,
解决:按照类别将这些bean配置到不同的配置类中
对于数据源的bean,我们新建一个JdbcConfig配置类,并把数据源配置到该类下。
public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("root");
return ds;
}
}
现在的问题是,这个配置类如何能被Spring配置类加载到,并创建DataSource对象在IOC容器中?
针对这个问题,有两个解决方案:
方法一:使用包扫描引入在Spring的配置类上添加包扫描(不推荐)
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.config")
public class SpringConfig {
}
不能很快的知晓都引入了哪些配置类,所有这种方式不推荐使用。
方法二: 在Spring配置类中使用@Import注解手动引入需要加载的配置类
@Configuration
@Import({JdbcConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
Import注解在配置类中只能写一次,参数为数组、可以引入多个配置类。
知识点2:@Import
| 名称 | @Import |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 导入配置类 |
| 属性 | value(默认):定义导入的配置类类名, 当配置类有多个时使用数组格式一次性导入多个配置类 |
9.3 注解开发:实现为第三方bean依赖注入
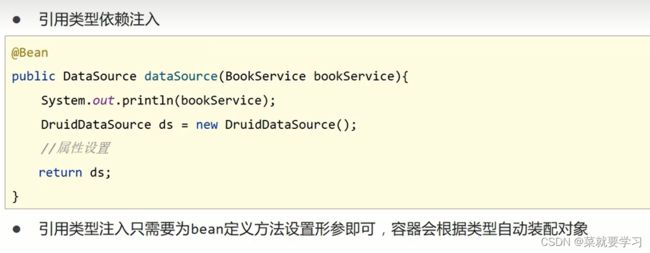
在使用@Bean创建bean对象的时候,如果方法在创建的过程中需要其他资源该怎么办?
这些资源会有两大类,分别是简单数据类型 和引用数据类型。
4.4.1 简单数据类型:成员变量 @Value
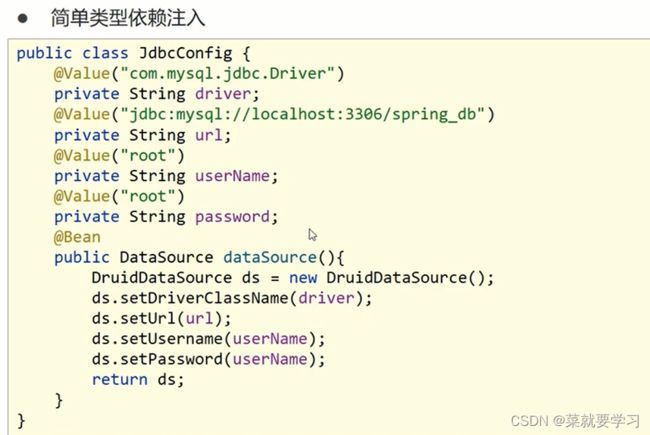
步骤1:resources目录下添加jdbc.properties
步骤2:配置文件中提供四个键值对分别是数据库的四要素
步骤3:使用@PropertySource加载jdbc.properties配置文件
步骤4:类中提供四个属性
步骤5:使用@Value注解引入值,修改@Value注解属性的值,将其修改为${key},key就是键值对中的键的值
4.4.2 引用数据类型:方法形参 自动装配
10,Spring整合
Spring有一个容器,叫做IoC容器,里面保存bean。在进行企业级开发的时候,其实除了让Spring管理自己写的类之外,还要使用和管理第三方的技术。
下面结合IoC和DI,整合2个常用技术,进一步加深对Spring的使用理解。
10.1 Spring整合Mybatis思路分析
10.1.1 环境准备
Mybatis开发的相关内容:
步骤1:准备数据库表
Mybatis是来操作数据库表,所以先创建一个数据库及表
create database spring_db character set utf8;
use spring_db;
create table tbl_account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(35),
money double
);
步骤2:创建项目导入jar包
项目的pom.xml添加相关依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.16version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>3.5.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.47version>
dependency>
dependencies>
步骤3:根据表创建模型类
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double money;
//setter...getter...toString...方法略
}
步骤4:创建Dao接口
public interface AccountDao {
@Insert("insert into tbl_account(name,money)values(#{name},#{money})")
void save(Account account);
@Delete("delete from tbl_account where id = #{id} ")
void delete(Integer id);
@Update("update tbl_account set name = #{name} , money = #{money} where id = #{id} ")
void update(Account account);
@Select("select * from tbl_account")
List<Account> findAll();
@Select("select * from tbl_account where id = #{id} ")
Account findById(Integer id);
}
步骤5:创建Service接口和实现类
public interface AccountService {
void save(Account account);
void delete(Integer id);
void update(Account account);
List<Account> findAll();
Account findById(Integer id);
}
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void save(Account account) {
accountDao.save(account);
}
public void update(Account account){
accountDao.update(account);
}
public void delete(Integer id) {
accountDao.delete(id);
}
public Account findById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.findById(id);
}
public List<Account> findAll() {
return accountDao.findAll();
}
}
步骤6:添加jdbc.properties文件
resources目录下添加,用于配置数据库连接四要素
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db?useSSL=false
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
useSSL:关闭MySQL的SSL连接
步骤7:添加Mybatis核心配置文件
DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbc.properties">properties>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.itheima.domain"/>
typeAliases>
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}">property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}">property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}">property>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<package name="com.itheima.dao">package>
mappers>
configuration>
步骤8:编写应用程序
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 2. 加载SqlMapConfig.xml配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml.bak");
// 3. 创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(inputStream);
// 4. 获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 5. 执行SqlSession对象执行查询,获取结果User
AccountDao accountDao = sqlSession.getMapper(AccountDao.class);
Account ac = accountDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(ac);
// 6. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
}
步骤9:运行程序
10.1.2 整合思路分析
Mybatis的基础环境我们已经准备好了,接下来就得分析下在上述的内容中,哪些对象可以交给Spring来管理?
-
整合Mybatis,就是将Mybatis用到的内容交给Spring管理,分析下mybaits配置文件

说明:
- 第一行读取外部properties配置文件,Spring有提供具体的解决方案
@PropertySource,需要交给Spring - 第二行起别名包扫描,为SqlSessionFactory服务的,需要交给Spring
- 第三行主要用于做连接池,Spring之前我们已经整合了Druid连接池,这块也需要交给Spring
- 前面三行一起都是为了创建SqlSession对象用的,那么用Spring管理SqlSession对象吗?回忆下SqlSession是由SqlSessionFactory创建出来的,所以只需要将SqlSessionFactory交给Spring管理即可。
- 第四行是Mapper接口和映射文件[如果使用注解就没有该映射文件],这个是在获取到SqlSession以后执行具体操作的时候用,所以它和SqlSessionFactory创建的时机都不在同一个时间,可能需要单独管理。
- 第一行读取外部properties配置文件,Spring有提供具体的解决方案
10.2 Spring整合Mybatis:SqlSessionFactoryBean / MapperScannerConfigurer
前面我们已经分析了Spring与Mybatis的整合,大体需要做两件事,
第一件事是:Spring要管理MyBatis中的SqlSessionFactory,类SqlSessionFactoryBean
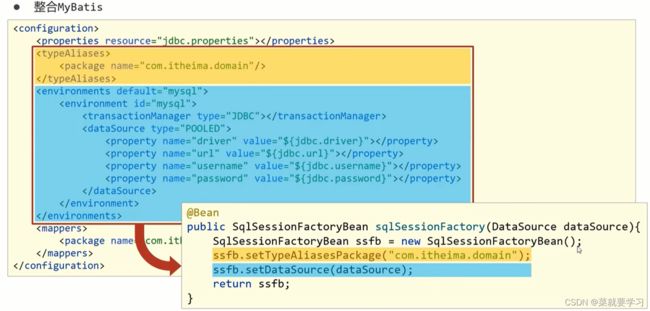
第二件事是:Spring要管理Mapper接口的扫描, 类MapperScannerConfigurer
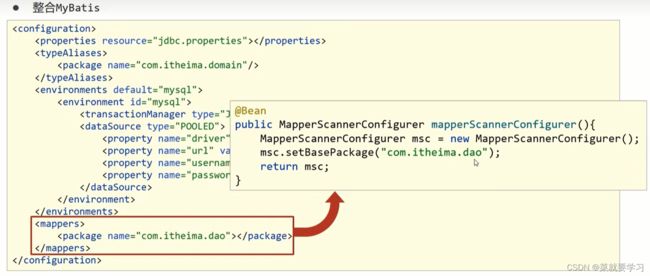 MapperScannerConfigurer对象也是MyBatis提供的专用于整合的jar包中的类,用来处理原始配置文件中的mappers相关配置,加载数据层的Mapper接口类
MapperScannerConfigurer对象也是MyBatis提供的专用于整合的jar包中的类,用来处理原始配置文件中的mappers相关配置,加载数据层的Mapper接口类
- MapperScannerConfigurer有一个核心属性basePackage,就是用来设置所扫描的包路径
具体该如何实现,具体的步骤为:
步骤1:项目中导入整合需要的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-springartifactId>
<version>1.3.0version>
dependency>
步骤2:创建Spring的主配置类
//配置类注解
@Configuration
//包扫描,主要扫描的是项目中的AccountServiceImpl类
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
public class SpringConfig {
}
步骤3:创建数据源的配置类
在配置类中完成数据源的创建
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String userName;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(userName);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
}
步骤4:主配置类中读properties并引入数据源配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@Import(JdbcConfig.class)
public class SpringConfig {
}
步骤5:创建Mybatis配置类并配置SqlSessionFactory
public class MybatisConfig {
//定义bean,SqlSessionFactoryBean,用于产生SqlSessionFactory对象
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
//设置模型类的别名扫描,包根据需要设定
ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.itheima.domain");
//设置数据源
ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
return ssfb;
}
//定义bean,返回MapperScannerConfigurer对象
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer(){
MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
//设置扫描映射的包,包根据需要设定
msc.setBasePackage("com.itheima.dao");
return msc;
}
}
步骤6:主配置类中引入Mybatis配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class,MybatisConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
步骤7:编写运行类
在运行类中,从IOC容器中获取Service对象,调用方法获取结果
public class App2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
AccountService accountService = ctx.getBean(AccountService.class);
Account ac = accountService.findById(1);
System.out.println(ac);
}
}
步骤8:运行程序
支持Spring与Mybatis的整合就已经完成了,其中主要用到的两个类分别是:
- SqlSessionFactoryBean
- MapperScannerConfigurer
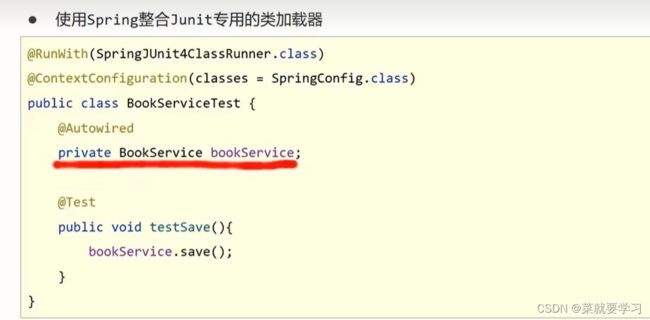
10.3 Spring整合Junit: @RunWith /@ContextConfiguration
Junit是一个搞单元测试用的辅助工具,它不是我们程序的主体,也不会参加最终程序的运行
在上述环境的基础上,我们来对Junit进行整合。
步骤1:引入依赖
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-testartifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
步骤2:编写测试类
在test\java下创建一个AccountServiceTest,这个名字任意
//设置类运行器
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//设置Spring环境对应的配置类
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {SpringConfiguration.class}) //加载配置类
//@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})//加载配置文件
public class AccountServiceTest {
//支持自动装配注入bean
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void testFindById(){
System.out.println(accountService.findById(1));
}
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
System.out.println(accountService.findAll());
}
}
注意:
- 单元测试,如果测试的是注解配置类,则使用
@ContextConfiguration(classes = 配置类.class) - 单元测试,如果测试的是配置文件,则使用
@ContextConfiguration(locations={配置文件名,...}) - Junit运行后是基于Spring环境运行的,所以Spring提供了一个专用的类运行器,这个务必要设置,这个类运行器就在Spring的测试专用包中提供的,导入的坐标就是这个东西
SpringJUnit4ClassRunner - 上面两个配置都是固定格式,当需要测试哪个bean时,使用自动装配加载对应的对象,下面的工作就和以前做Junit单元测试完全一样了
知识点1:@RunWith
| 名称 | @RunWith |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 测试类注解 |
| 位置 | 测试类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置JUnit运行器 |
| 属性 | value(默认):运行所使用的运行期 |
知识点2:@ContextConfiguration
| 名称 | @ContextConfiguration |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 测试类注解 |
| 位置 | 测试类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置JUnit加载的Spring核心配置 |
| 属性 | classes:核心配置类,可以使用数组的格式设定加载多个配置类 locations:配置文件,可以使用数组的格式设定加载多个配置文件名称 |