linux SPI驱动开发
一,linux内核设备驱动分三类
1,字符设备驱动:按字节来访问设备,字符驱动负责驱动字符设备,这样的驱动通常实现open,close,read,write系统调用。
特点:操作的硬件,按照字节流形式访问
例子:键盘(键值),LCD显示屏(显存),鼠标(相对坐标),UART接口(BT,GPS,GPRS),各种传感器,摄像头触摸屏(绝对坐标),EEPROM等
2, 块设备驱动:在unix下,块设备只能按照512字节或者1024,1536,2048等(以此类推)来访问,但在linux系统下,可以随意字节访问,也就是说,字符驱动和块设备驱动在linux系统下的差别仅仅在于驱动和内核接口的不同。
特点:操作的硬件,按照数据块访问,一次访问512B,4KB
例子:硬盘,U盘,SD卡,TF卡,Nand,NorFlash
3,网络设备驱动:任何网络事物都是通过一个网络接口来实行,这里有两个接口,大家平常见的也应该比较多,eth0,物理接口;lo(回环网络,就是自发自收的意思,这是一个软件接口)。
特点:操作的硬件就是网卡(有线和无线)需要配合网络协议栈,一般都是由网卡芯片厂家写好
二,SPI驱动体系架构:
| 组成部分 | SPI主机控制器驱动 | SPI 核心 | SPI设备驱动 |
| 主要作用 | 注册平台总线驱动、初始化SPI控制器 | 注册SPI总线以及匹配总线与设备 | 注册SPI设备以及构造file_operation |
三,SPI驱动
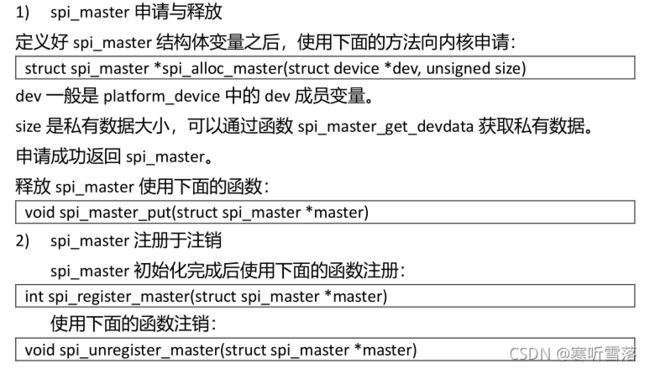
1,SPI 控制器驱动
2,SPI 设备驱动
(1)spi_driver:linux 内核中使用 spi_driver 结构体来表示 spi 设备驱动。spi_driver 结构体定义在文件include/linux/spi/spi.h
struct spi_driver
{
const struct spi_device_id *id_table;
int (*probe)(struct spi_device *spi);
int (*remove)(struct spi_device *spi);
void (*shutdown)(struct spi_device *spi);
struct device_driver driver;
};spi_driver 初始化完成后,使用下面的函数向内核注册:
int spi_register_driver(struct spi_driver *sdrv)
使用下面的函数注销spi_driver:
void spi_unregister_driver(struct spi_driver *sdrv)
(2)id_table用作匹配spi设备,匹配成功就会执行probe函数。设备删除时执 remov 函数。
(3)编写spi 讴备驱动,需要我们去实现其中 probe和remove 两个函数
3,SPI设备:内核中用spi_device结构体表示spi设备,引入设备树后,spi_device就不咋用了,设备树的描述spi 设备方法。
1. qspi: spi@e000d000 {
2. clock-names = "ref_clk", "pclk";
3. clocks = <&clkc 10>, <&clkc 43>;
4. compatible = "xlnx,zynq-qspi-1.0";
5. status = "disabled";
6. interrupt-parent = <&intc>;
7. interrupts = <0 19 4>;
8. reg = <0xe000d000 0x1000>;
9. #address-cells = <1>;
10. #size-cells = <0>;
11.
12. flash: w25q256@0
13. {
14. #address-cells = <1>;
15. #size-cells = <1>;
16. compatible = "w25q256";
17. reg = <0>;
18. spi-max-frequency = <40000000>;
19. m25p,fast-read;
20. };
21. }; 3,驱动和设备的匹配:spi 总线定义结构体 spi_bus_type,在文件 drivers/spi/spi.c 文件中
3,驱动和设备的匹配:spi 总线定义结构体 spi_bus_type,在文件 drivers/spi/spi.c 文件中
struct bus_type spi_bus_type =
{
.name = "spi",
.dev_groups = spi_dev_groups,
.match = spi_match_device,
.uevent = spi_uevent,
};match 函数就是匹配函数,内核中 match 凼数的实现为函数 spi_match_device()
static int spi_match_device(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
const struct spi_device *spi = to_spi_device(dev);
const struct spi_driver *sdrv = to_spi_driver(drv);
/* Attempt an OF style match */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try ACPI */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
if (sdrv->id_table)
return !!spi_match_id(sdrv->id_table, spi);
return strcmp(spi->modalias, drv->name) == 0;
}4, SPI 设备驱动中数据收发处理
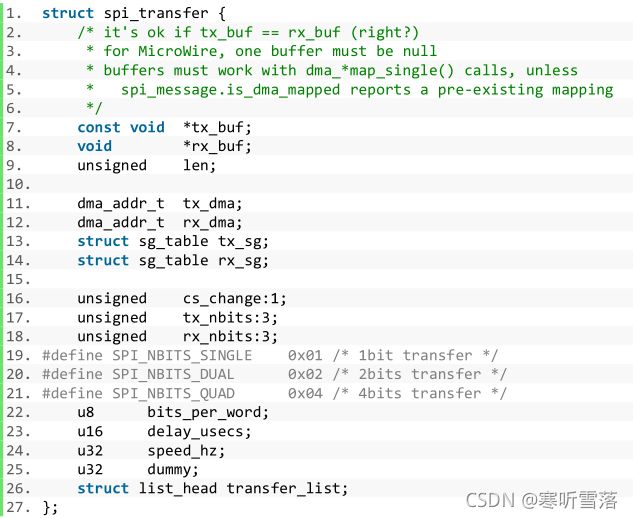
(1)spi_transfer用于描述 spi 的传输信息:
tx_buf、rx_buf 分别是保存发送和接收数据。len 是数据长度,spi 是全双工通讯,在单次通讯中收収数据长度是一样的,所以叧要一个len 就行了。
(2)spi_message是spi_transfer的发送队列,spi_transfer需要添加到spi_message中发送
(3)spi_message 需要使用函数 spi_message_init()来初始化
(4)spi_message初始化完成后使用 spi_message_add_tail()函数把 spi_transfer 添加到
spi_message 中
函数原型:void spi_message_add_tail(struct spi_transfer *t, struct spi_message *m)
(5)spi_sync()函数使用同步阻塞的方式传输 spi_message
函数原型:int spi_sync(struct spi_device *spi, struct spi_message *message)
(6)spi_async()函数使用异步非阻塞的方式传输 spi_message
函数原型:int spi_async(struct spi_device *spi, struct spi_message *message)
四,SPI驱动代码相关
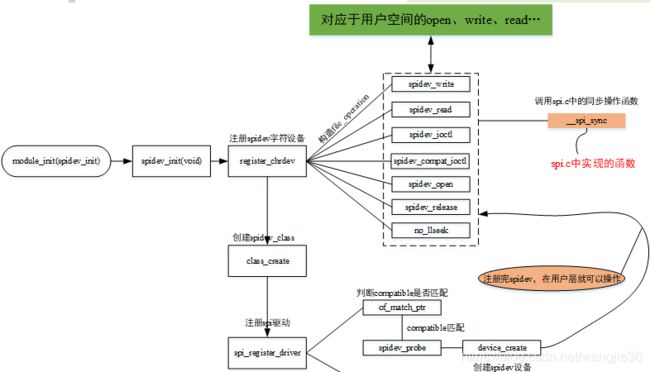
SPI主机控制器是具有特定属性的,这个主要看处理器上搭载的是哪个公司生产的SPI控制器,zynq中可以在其datasheet中找到其SPI控制器是cadence公司的,那么在内核中必然存在cadence控制器的驱动程序。在linux内核源码里,SPI核心驱动是由\drivers\spi\spi.c来实现的,主机控制器程序是由\drivers\spi\spi-cadence.c来实现的,字符设备spidev由\drivers\spi\spidev.c实现。spidev.c、spi.c、spi-cadence.c这三个驱动文件来分析SPI的总线驱动模型。
1,spidev.c文件:它是一个字符设备,满足字符设备的框架(注册设备、构造file_operation结构体、提供给虚拟文件系统的open、read、write函数接口)。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define SPIDEV_MAJOR 153 /* assigned */
#define N_SPI_MINORS 32 /* ... up to 256 */
static DECLARE_BITMAP(minors, N_SPI_MINORS);
#define SPI_MODE_MASK (SPI_CPHA | SPI_CPOL | SPI_CS_HIGH \
| SPI_LSB_FIRST | SPI_3WIRE | SPI_LOOP \
| SPI_NO_CS | SPI_READY | SPI_TX_DUAL \
| SPI_TX_QUAD | SPI_RX_DUAL | SPI_RX_QUAD)
struct spidev_data { //spidev的结构体
dev_t devt;
spinlock_t spi_lock;
struct spi_device *spi;
struct list_head device_entry;
struct mutex buf_lock;
unsigned users;
u8 *tx_buffer;
u8 *rx_buffer;
u32 speed_hz;
};
static LIST_HEAD(device_list);
static DEFINE_MUTEX(device_list_lock);
static unsigned bufsiz = 4096;
module_param(bufsiz, uint, S_IRUGO);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(bufsiz, "data bytes in biggest supported SPI message");
/*------------------------spidev的同步操作-----------------------------*/
static ssize_t spidev_sync(struct spidev_data *spidev, struct spi_message *message)
{
DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done);
int status;
struct spi_device *spi;
spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
spi = spidev->spi;
spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
if (spi == NULL)
status = -ESHUTDOWN;
else
status = spi_sync(spi, message); /*调用spi.c中的函数,进行同步操作*/
if (status == 0)
status = message->actual_length;
return status;
}
/*------------------------spidev同步写操作-----------------------------*/
static inline ssize_t
spidev_sync_write(struct spidev_data *spidev, size_t len)
{
struct spi_transfer t = {
.tx_buf = spidev->tx_buffer,
.len = len,
.speed_hz = spidev->speed_hz,
};
struct spi_message m;
spi_message_init(&m);
spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);
return spidev_sync(spidev, &m);
}
/*------------------------spidev同步读操作-----------------------------*/
static inline ssize_t
spidev_sync_read(struct spidev_data *spidev, size_t len)
{
struct spi_transfer t = {
.rx_buf = spidev->rx_buffer,
.len = len,
.speed_hz = spidev->speed_hz,
};
struct spi_message m;
spi_message_init(&m);
spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m);
return spidev_sync(spidev, &m);
}
/*------------------------spidev只读-----------------------------*/
/* Read-only message with current device setup */
static ssize_t
spidev_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
/*spidev读操作(只读模式),,对应于用户空间的read函数*/
{
struct spidev_data *spidev;
ssize_t status = 0;
/* chipselect only toggles at start or end of operation */
if (count > bufsiz)
return -EMSGSIZE;
spidev = filp->private_data;
mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);
status = spidev_sync_read(spidev, count); /*spidev同步读操作*/
if (status > 0) {
unsigned long missing;
missing = copy_to_user(buf, spidev->rx_buffer, status); /*将读回来的数返回给用户空间*/
if (missing == status)
status = -EFAULT;
else
status = status - missing;
}
mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);
return status;
}
/*------------------------spidev只写-----------------------------*/
/* Write-only message with current device setup */
static ssize_t
spidev_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
/*spidev写操作(只写模式),对应于用户空间的write函数*/
size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
struct spidev_data *spidev;
ssize_t status = 0;
unsigned long missing;
/* chipselect only toggles at start or end of operation */
if (count > bufsiz)
return -EMSGSIZE;
spidev = filp->private_data;
mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);
missing = copy_from_user(spidev->tx_buffer, buf, count); /*将用户空间中写入spidev的数据拷贝到内核空间*/
if (missing == 0)
status = spidev_sync_write(spidev, count); /*进行同步写操作*/
else
status = -EFAULT;
mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);
return status;
}
/*------------------------spidev读写操作-----------------------------*/
static int spidev_message(struct spidev_data *spidev, /*启动spidev的数据传输,相当于写一次读一次*/
struct spi_ioc_transfer *u_xfers, unsigned n_xfers)
{
struct spi_message msg;
struct spi_transfer *k_xfers;
struct spi_transfer *k_tmp;
struct spi_ioc_transfer *u_tmp;
unsigned n, total, tx_total, rx_total;
u8 *tx_buf, *rx_buf;
int status = -EFAULT;
spi_message_init(&msg);
k_xfers = kcalloc(n_xfers, sizeof(*k_tmp), GFP_KERNEL);
if (k_xfers == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
/* Construct spi_message, copying any tx data to bounce buffer.
* We walk the array of user-provided transfers, using each one
* to initialize a kernel version of the same transfer.
*/
tx_buf = spidev->tx_buffer;
rx_buf = spidev->rx_buffer;
total = 0;
tx_total = 0;
rx_total = 0;
for (n = n_xfers, k_tmp = k_xfers, u_tmp = u_xfers;
n;
n--, k_tmp++, u_tmp++) {
k_tmp->len = u_tmp->len;
total += k_tmp->len;
/* Since the function returns the total length of transfers
* on success, restrict the total to positive int values to
* avoid the return value looking like an error. Also check
* each transfer length to avoid arithmetic overflow.
*/
if (total > INT_MAX || k_tmp->len > INT_MAX) {
status = -EMSGSIZE;
goto done;
}
if (u_tmp->rx_buf) {
/* this transfer needs space in RX bounce buffer */
rx_total += k_tmp->len;
if (rx_total > bufsiz) {
status = -EMSGSIZE;
goto done;
}
k_tmp->rx_buf = rx_buf;
if (!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, (u8 __user *)
(uintptr_t) u_tmp->rx_buf,
u_tmp->len))
goto done;
rx_buf += k_tmp->len;
}
if (u_tmp->tx_buf) {
/* this transfer needs space in TX bounce buffer */
tx_total += k_tmp->len;
if (tx_total > bufsiz) {
status = -EMSGSIZE;
goto done;
}
k_tmp->tx_buf = tx_buf;
if (copy_from_user(tx_buf, (const u8 __user *)
(uintptr_t) u_tmp->tx_buf,
u_tmp->len))
goto done;
tx_buf += k_tmp->len;
}
k_tmp->cs_change = !!u_tmp->cs_change;
k_tmp->tx_nbits = u_tmp->tx_nbits;
k_tmp->rx_nbits = u_tmp->rx_nbits;
k_tmp->bits_per_word = u_tmp->bits_per_word;
k_tmp->delay_usecs = u_tmp->delay_usecs;
k_tmp->speed_hz = u_tmp->speed_hz;
if (!k_tmp->speed_hz)
k_tmp->speed_hz = spidev->speed_hz;
#ifdef VERBOSE
dev_dbg(&spidev->spi->dev,
" xfer len %u %s%s%s%dbits %u usec %uHz\n",
u_tmp->len,
u_tmp->rx_buf ? "rx " : "",
u_tmp->tx_buf ? "tx " : "",
u_tmp->cs_change ? "cs " : "",
u_tmp->bits_per_word ? : spidev->spi->bits_per_word,
u_tmp->delay_usecs,
u_tmp->speed_hz ? : spidev->spi->max_speed_hz);
#endif
spi_message_add_tail(k_tmp, &msg);
}
status = spidev_sync(spidev, &msg);
if (status < 0)
goto done;
/* copy any rx data out of bounce buffer */
rx_buf = spidev->rx_buffer;
for (n = n_xfers, u_tmp = u_xfers; n; n--, u_tmp++) {
if (u_tmp->rx_buf) {
if (__copy_to_user((u8 __user *)
(uintptr_t) u_tmp->rx_buf, rx_buf,
u_tmp->len)) {
status = -EFAULT;
goto done;
}
rx_buf += u_tmp->len;
}
}
status = total;
done:
kfree(k_xfers);
return status;
}
/*------------------------获取用户空间的ioc消息体-----------------------------*/
static struct spi_ioc_transfer *
spidev_get_ioc_message(unsigned int cmd, struct spi_ioc_transfer __user *u_ioc,
unsigned *n_ioc)
{
struct spi_ioc_transfer *ioc;
u32 tmp;
/* Check type, command number and direction */
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != SPI_IOC_MAGIC
|| _IOC_NR(cmd) != _IOC_NR(SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(0))
|| _IOC_DIR(cmd) != _IOC_WRITE)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOTTY);
tmp = _IOC_SIZE(cmd);
if ((tmp % sizeof(struct spi_ioc_transfer)) != 0)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
*n_ioc = tmp / sizeof(struct spi_ioc_transfer);
if (*n_ioc == 0)
return NULL;
/* copy into scratch area */
ioc = kmalloc(tmp, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ioc)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
if (__copy_from_user(ioc, u_ioc, tmp)) {
kfree(ioc);
return ERR_PTR(-EFAULT);
}
return ioc;
}
/*------------------------spi_ioctl函数,对应于用户空间的ioctl函数-----------------------------*/
static long
spidev_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int err = 0;
int retval = 0;
struct spidev_data *spidev;
struct spi_device *spi;
u32 tmp;
unsigned n_ioc;
struct spi_ioc_transfer *ioc;
/* Check type and command number */
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != SPI_IOC_MAGIC)
return -ENOTTY;
/* Check access direction once here; don't repeat below.
* IOC_DIR is from the user perspective, while access_ok is
* from the kernel perspective; so they look reversed.
*/
if (_IOC_DIR(cmd) & _IOC_READ)
err = !access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE,
(void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd));
if (err == 0 && _IOC_DIR(cmd) & _IOC_WRITE)
err = !access_ok(VERIFY_READ,
(void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd));
if (err)
return -EFAULT;
/* guard against device removal before, or while,
* we issue this ioctl.
*/
spidev = filp->private_data;
spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
spi = spi_dev_get(spidev->spi);
spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
if (spi == NULL)
return -ESHUTDOWN;
/* use the buffer lock here for triple duty:
* - prevent I/O (from us) so calling spi_setup() is safe;
* - prevent concurrent SPI_IOC_WR_* from morphing
* data fields while SPI_IOC_RD_* reads them;
* - SPI_IOC_MESSAGE needs the buffer locked "normally".
*/
mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);
switch (cmd) { /*判断ioctl传入的命令*/
/* read requests */
case SPI_IOC_RD_MODE:
retval = __put_user(spi->mode & SPI_MODE_MASK,
(__u8 __user *)arg);
break;
case SPI_IOC_RD_MODE32:
retval = __put_user(spi->mode & SPI_MODE_MASK,
(__u32 __user *)arg);
break;
case SPI_IOC_RD_LSB_FIRST:
retval = __put_user((spi->mode & SPI_LSB_FIRST) ? 1 : 0,
(__u8 __user *)arg);
break;
case SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD:
retval = __put_user(spi->bits_per_word, (__u8 __user *)arg);
break;
case SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ:
retval = __put_user(spidev->speed_hz, (__u32 __user *)arg);
break;
/* write requests */
case SPI_IOC_WR_MODE:
case SPI_IOC_WR_MODE32:
if (cmd == SPI_IOC_WR_MODE)
retval = __get_user(tmp, (u8 __user *)arg);
else
retval = __get_user(tmp, (u32 __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0) {
u32 save = spi->mode;
if (tmp & ~SPI_MODE_MASK) {
retval = -EINVAL;
break;
}
tmp |= spi->mode & ~SPI_MODE_MASK;
spi->mode = (u16)tmp;
retval = spi_setup(spi);
if (retval < 0)
spi->mode = save;
else
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "spi mode %x\n", tmp);
}
break;
case SPI_IOC_WR_LSB_FIRST:
retval = __get_user(tmp, (__u8 __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0) {
u32 save = spi->mode;
if (tmp)
spi->mode |= SPI_LSB_FIRST;
else
spi->mode &= ~SPI_LSB_FIRST;
retval = spi_setup(spi);
if (retval < 0)
spi->mode = save;
else
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%csb first\n",
tmp ? 'l' : 'm');
}
break;
case SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD:
retval = __get_user(tmp, (__u8 __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0) {
u8 save = spi->bits_per_word;
spi->bits_per_word = tmp;
retval = spi_setup(spi);
if (retval < 0)
spi->bits_per_word = save;
else
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%d bits per word\n", tmp);
}
break;
case SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ:
retval = __get_user(tmp, (__u32 __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0) {
u32 save = spi->max_speed_hz;
spi->max_speed_hz = tmp;
retval = spi_setup(spi);
if (retval >= 0)
spidev->speed_hz = tmp;
else
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%d Hz (max)\n", tmp);
spi->max_speed_hz = save;
}
break;
default: /*执行一次发送*/
/* segmented and/or full-duplex I/O request */
/* Check message and copy into scratch area */
ioc = spidev_get_ioc_message(cmd,
(struct spi_ioc_transfer __user *)arg, &n_ioc);
if (IS_ERR(ioc)) {
retval = PTR_ERR(ioc);
break;
}
if (!ioc)
break; /* n_ioc is also 0 */
/* translate to spi_message, execute */
retval = spidev_message(spidev, ioc, n_ioc);
kfree(ioc);
break;
}
mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);
spi_dev_put(spi);
return retval;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
static long
spidev_compat_ioc_message(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
struct spi_ioc_transfer __user *u_ioc;
int retval = 0;
struct spidev_data *spidev;
struct spi_device *spi;
unsigned n_ioc, n;
struct spi_ioc_transfer *ioc;
u_ioc = (struct spi_ioc_transfer __user *) compat_ptr(arg);
if (!access_ok(VERIFY_READ, u_ioc, _IOC_SIZE(cmd)))
return -EFAULT;
/* guard against device removal before, or while,
* we issue this ioctl.
*/
spidev = filp->private_data;
spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
spi = spi_dev_get(spidev->spi);
spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
if (spi == NULL)
return -ESHUTDOWN;
/* SPI_IOC_MESSAGE needs the buffer locked "normally" */
mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);
/* Check message and copy into scratch area */
ioc = spidev_get_ioc_message(cmd, u_ioc, &n_ioc);
if (IS_ERR(ioc)) {
retval = PTR_ERR(ioc);
goto done;
}
if (!ioc)
goto done; /* n_ioc is also 0 */
/* Convert buffer pointers */
for (n = 0; n < n_ioc; n++) {
ioc[n].rx_buf = (uintptr_t) compat_ptr(ioc[n].rx_buf);
ioc[n].tx_buf = (uintptr_t) compat_ptr(ioc[n].tx_buf);
}
/* translate to spi_message, execute */
retval = spidev_message(spidev, ioc, n_ioc);
kfree(ioc);
done:
mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);
spi_dev_put(spi);
return retval;
}
static long
spidev_compat_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) == SPI_IOC_MAGIC
&& _IOC_NR(cmd) == _IOC_NR(SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(0))
&& _IOC_DIR(cmd) == _IOC_WRITE)
return spidev_compat_ioc_message(filp, cmd, arg);
return spidev_ioctl(filp, cmd, (unsigned long)compat_ptr(arg));
}
#else
#define spidev_compat_ioctl NULL
#endif /* CONFIG_COMPAT */
/*------------------------打开spidev设备-----------------------------*/
static int spidev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
struct spidev_data *spidev;
int status = -ENXIO;
mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry(spidev, &device_list, device_entry) {
if (spidev->devt == inode->i_rdev) {
status = 0;
break;
}
}
if (status) {
pr_debug("spidev: nothing for minor %d\n", iminor(inode));
goto err_find_dev;
}
if (!spidev->tx_buffer) {
spidev->tx_buffer = kmalloc(bufsiz, GFP_KERNEL);/*从内核中分配一块内存给tx_buffer*/
if (!spidev->tx_buffer) {
dev_dbg(&spidev->spi->dev, "open/ENOMEM\n");
status = -ENOMEM;
goto err_find_dev;
}
}
if (!spidev->rx_buffer) {
spidev->rx_buffer = kmalloc(bufsiz, GFP_KERNEL);/*从内核中分配一块内存给rx_buffer*/
if (!spidev->rx_buffer) {
dev_dbg(&spidev->spi->dev, "open/ENOMEM\n");
status = -ENOMEM;
goto err_alloc_rx_buf;
}
}
spidev->users++;
filp->private_data = spidev;
nonseekable_open(inode, filp); /*不需要可搜索文件描述符的子系统使用它*/
mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);
return 0;
err_alloc_rx_buf:
kfree(spidev->tx_buffer);
spidev->tx_buffer = NULL;
err_find_dev:
mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);
return status;
}
/*------------------------释放spidev设备-----------------------------*/
static int spidev_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
struct spidev_data *spidev;
mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);
spidev = filp->private_data;
filp->private_data = NULL;
/* last close? */
spidev->users--;
if (!spidev->users) {
int dofree;
kfree(spidev->tx_buffer);
spidev->tx_buffer = NULL;
kfree(spidev->rx_buffer);
spidev->rx_buffer = NULL;
spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
if (spidev->spi)
spidev->speed_hz = spidev->spi->max_speed_hz;
/* ... after we unbound from the underlying device? */
dofree = (spidev->spi == NULL);
spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
if (dofree)
kfree(spidev);
}
mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);
return 0;
}
/*-------------------------------------构造file_operation结构体------------------------------------*/
static const struct file_operations spidev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
/* REVISIT switch to aio primitives, so that userspace
* gets more complete API coverage. It'll simplify things
* too, except for the locking.
*/
.write = spidev_write,
.read = spidev_read,
.unlocked_ioctl = spidev_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = spidev_compat_ioctl,
.open = spidev_open,
.release = spidev_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
};
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* The main reason to have this class is to make mdev/udev create the
* /dev/spidevB.C character device nodes exposing our userspace API.
* It also simplifies memory management.
*/
static struct class *spidev_class;
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
static const struct of_device_id spidev_dt_ids[] = { //驱动程序的可匹配的设备列表
{ .compatible = "rohm,dh2228fv" },
{ .compatible = "lineartechnology,ltc2488" },
{ .compatible = "foocorp,modem" },
{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, spidev_dt_ids);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ACPI
/* Dummy SPI devices not to be used in production systems */
#define SPIDEV_ACPI_DUMMY 1
static const struct acpi_device_id spidev_acpi_ids[] = {
/*
* The ACPI SPT000* devices are only meant for development and
* testing. Systems used in production should have a proper ACPI
* description of the connected peripheral and they should also use
* a proper driver instead of poking directly to the SPI bus.
*/
{ "SPT0001", SPIDEV_ACPI_DUMMY },
{ "SPT0002", SPIDEV_ACPI_DUMMY },
{ "SPT0003", SPIDEV_ACPI_DUMMY },
{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(acpi, spidev_acpi_ids);
static void spidev_probe_acpi(struct spi_device *spi)
{
const struct acpi_device_id *id;
if (!has_acpi_companion(&spi->dev))
return;
id = acpi_match_device(spidev_acpi_ids, &spi->dev);
if (WARN_ON(!id))
return;
if (id->driver_data == SPIDEV_ACPI_DUMMY)
dev_warn(&spi->dev, "do not use this driver in production systems!\n");
}
#else
static inline void spidev_probe_acpi(struct spi_device *spi) {}
#endif
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static int spidev_probe(struct spi_device *spi) /*spidev初始化函数*/
{
struct spidev_data *spidev;
int status;
unsigned long minor;
/*
* spidev should never be referenced in DT without a specific
* compatible string, it is a Linux implementation thing
* rather than a description of the hardware.
*/
if (spi->dev.of_node && !of_match_device(spidev_dt_ids, &spi->dev)) { /*判断设备树中有没有匹配的字符串*/
dev_err(&spi->dev, "buggy DT: spidev listed directly in DT\n");
WARN_ON(spi->dev.of_node &&
!of_match_device(spidev_dt_ids, &spi->dev));
}
spidev_probe_acpi(spi); /*高级配置和电源管理接口*/
/* Allocate driver data */
spidev = kzalloc(sizeof(*spidev), GFP_KERNEL); /*从内核中分配一个spidev_data结构体*/
if (!spidev)
return -ENOMEM;
/* Initialize the driver data */
spidev->spi = spi;
spin_lock_init(&spidev->spi_lock);
mutex_init(&spidev->buf_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&spidev->device_entry);
/* If we can allocate a minor number, hook up this device.
* Reusing minors is fine so long as udev or mdev is working.
*/
mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);
minor = find_first_zero_bit(minors, N_SPI_MINORS); /*查找一个可用的次设备号*/
if (minor < N_SPI_MINORS) {
struct device *dev;
spidev->devt = MKDEV(SPIDEV_MAJOR, minor);
dev = device_create(spidev_class, &spi->dev, spidev->devt, /*创建spidev设备*/
spidev, "spidev%d.%d",
spi->master->bus_num, spi->chip_select);
status = PTR_ERR_OR_ZERO(dev);
} else {
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "no minor number available!\n");
status = -ENODEV;
}
if (status == 0) {
set_bit(minor, minors);
list_add(&spidev->device_entry, &device_list);
}
mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);
spidev->speed_hz = spi->max_speed_hz;
if (status == 0)
spi_set_drvdata(spi, spidev);
else
kfree(spidev);
return status;
}
static int spidev_remove(struct spi_device *spi) /*spidev移除函数*/
{
struct spidev_data *spidev = spi_get_drvdata(spi);
/* make sure ops on existing fds can abort cleanly */
spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
spidev->spi = NULL;
spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
/* prevent new opens */
mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);
list_del(&spidev->device_entry);
device_destroy(spidev_class, spidev->devt); /*从spidev_class删除spidev*/
clear_bit(MINOR(spidev->devt), minors); /*清除当前spidev的次设备号*/
if (spidev->users == 0)
kfree(spidev);
mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);
return 0;
}
static struct spi_driver spidev_spi_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "spidev",
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(spidev_dt_ids),
.acpi_match_table = ACPI_PTR(spidev_acpi_ids),
},
.probe = spidev_probe,
.remove = spidev_remove,
/* NOTE: suspend/resume methods are not necessary here.
* We don't do anything except pass the requests to/from
* the underlying controller. The refrigerator handles
* most issues; the controller driver handles the rest.
*/
};
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
static int __init spidev_init(void)
{
int status;
/* Claim our 256 reserved device numbers. Then register a class
* that will key udev/mdev to add/remove /dev nodes. Last, register
* the driver which manages those device numbers.
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON(N_SPI_MINORS > 256);
status = register_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, "spi", &spidev_fops);/*注册spidev字符设备*/
if (status < 0)
return status;
spidev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "spidev"); /*创建spidev_class,并将spidev注册到内核中*/
if (IS_ERR(spidev_class)) {
unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name);
return PTR_ERR(spidev_class);
}
status = spi_register_driver(&spidev_spi_driver); /*注册spi驱动*/
if (status < 0) {
class_destroy(spidev_class);
unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name);
}
return status;
}
module_init(spidev_init); //作为模块加载进内核
static void __exit spidev_exit(void)
{
spi_unregister_driver(&spidev_spi_driver);
class_destroy(spidev_class);
unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name);
}
module_exit(spidev_exit); //从内核卸载该模块
MODULE_AUTHOR("Andrea Paterniani, ");//模块声明
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("User mode SPI device interface");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_ALIAS("spi:spidev"); 2,spi-cadence.c主要作用就是配置SPI主机控制器的。
其中module_platform_driver(cdns_spi_driver),能清楚看到这两个文件并没有直接调用或者交互的关系,但都跟spi.c有调用关系,spi.c的作用就是让spidev和spi-cadence能够关联起来。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* Name of this driver */
#define CDNS_SPI_NAME "cdns-spi"
/* Register offset definitions */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR 0x00 /* Configuration Register, RW */
#define CDNS_SPI_ISR 0x04 /* Interrupt Status Register, RO */
#define CDNS_SPI_IER 0x08 /* Interrupt Enable Register, WO */
#define CDNS_SPI_IDR 0x0c /* Interrupt Disable Register, WO */
#define CDNS_SPI_IMR 0x10 /* Interrupt Enabled Mask Register, RO */
#define CDNS_SPI_ER 0x14 /* Enable/Disable Register, RW */
#define CDNS_SPI_DR 0x18 /* Delay Register, RW */
#define CDNS_SPI_TXD 0x1C /* Data Transmit Register, WO */
#define CDNS_SPI_RXD 0x20 /* Data Receive Register, RO */
#define CDNS_SPI_SICR 0x24 /* Slave Idle Count Register, RW */
#define CDNS_SPI_THLD 0x28 /* Transmit FIFO Watermark Register,RW */
#define SPI_AUTOSUSPEND_TIMEOUT 3000
/*
* SPI Configuration Register bit Masks This register contains various control
bits that affect the operationof the SPI controller
*/
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_MANSTRT 0x00010000 /* Manual TX Start */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_CPHA 0x00000004 /* Clock Phase Control */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_CPOL 0x00000002 /* Clock Polarity Control */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_SSCTRL 0x00003C00 /* Slave Select Mask */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_PERI_SEL 0x00000200 /* Peripheral Select Decode */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_BAUD_DIV 0x00000038 /* Baud Rate Divisor Mask */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_MSTREN 0x00000001 /* Master Enable Mask */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_MANSTRTEN 0x00008000 /* Manual TX Enable Mask */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_SSFORCE 0x00004000 /* Manual SS Enable Mask */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_BAUD_DIV_4 0x00000008 /* Default Baud Div Mask */
#define CDNS_SPI_CR_DEFAULT (CDNS_SPI_CR_MSTREN | \
CDNS_SPI_CR_SSCTRL | \
CDNS_SPI_CR_BAUD_DIV_4)
// CDNS_SPI_CR_SSFORCE | \
/*
* SPI Configuration Register - Baud rate and slave select
* These are the values used in the calculation of baud rate divisor and
* setting the slave select.
*/
#define CDNS_SPI_BAUD_DIV_MAX 7 /* Baud rate divisor maximum */
#define CDNS_SPI_BAUD_DIV_MIN 1 /* Baud rate divisor minimum */
#define CDNS_SPI_BAUD_DIV_SHIFT 3 /* Baud rate divisor shift in CR */
#define CDNS_SPI_SS_SHIFT 10 /* Slave Select field shift in CR */
#define CDNS_SPI_SS0 0x1 /* Slave Select zero */
/*SPI Interrupt Registers bit Masks
* All the four interrupt registers (Status/Mask/Enable/Disable) have the same
* bit definitions.
*/
#define CDNS_SPI_IXR_TXOW 0x00000004 /* SPI TX FIFO Overwater */
#define CDNS_SPI_IXR_MODF 0x00000002 /* SPI Mode Fault */
#define CDNS_SPI_IXR_RXNEMTY 0x00000010 /* SPI RX FIFO Not Empty */
#define CDNS_SPI_IXR_DEFAULT (CDNS_SPI_IXR_TXOW | \ CDNS_SPI_IXR_MODF)
#define CDNS_SPI_IXR_TXFULL 0x00000008 /* SPI TX Full */
#define CDNS_SPI_IXR_ALL 0x0000007F /* SPI all interrupts */
/*
* SPI Enable Register bit Masks
* This register is used to enable or disable the SPI controller
*/
#define CDNS_SPI_ER_ENABLE 0x00000001 /* SPI Enable Bit Mask */
#define CDNS_SPI_ER_DISABLE 0x0 /* SPI Disable Bit Mask */
/* SPI FIFO depth in bytes */
#define CDNS_SPI_FIFO_DEPTH 128
/* Default number of chip select lines */
#define CDNS_SPI_DEFAULT_NUM_CS 4
/**
* struct cdns_spi - This definition defines spi driver instance
* @regs: Virtual address of the SPI controller registers
* @ref_clk: Pointer to the peripheral clock
* @pclk: Pointer to the APB clock
* @speed_hz: Current SPI bus clock speed in Hz
* @txbuf: Pointer to the TX buffer
* @rxbuf: Pointer to the RX buffer
* @tx_bytes: Number of bytes left to transfer
* @rx_bytes: Number of bytes requested
* @dev_busy: Device busy flag
* @is_decoded_cs: Flag for decoder property set or not
*/
struct cdns_spi
{/*定义cadence_spi驱动结构体,一个结构体就是一个对象*/
void __iomem *regs;
struct clk *ref_clk;
struct clk *pclk;
u32 speed_hz;
const u8 *txbuf;
u8 *rxbuf;
int tx_bytes;
int rx_bytes;
u8 dev_busy;
u32 is_decoded_cs;
};
/* Macros for the SPI controller read/write */
static inline u32 cdns_spi_read(struct cdns_spi *xspi,u32 offset)//cadence_spi读寄存器
{
return readl_relaxed(xspi->regs + offset);
}
static inline void cdns_spi_write(struct cdns_spi*xspi, u32 offset,u32 val)/*cadence_spi写寄存器*/
{
writel_relaxed(val, xspi->regs + offset);
}
/**
* cdns_spi_init_hw - Initialize the hardware and configure the SPI controller
* @xspi: Pointer to the cdns_spi structure
* On reset the SPI controller is configured to be in master mode, baud rate
* divisor is set to 4, threshold value for TX FIFO not full interrupt is set
* to 1 and size of the word to be transferred as 8 bit.
* This function initializes the SPI controller to disable and clear all the
* interrupts, enable manual slave select and manual start, deselect all the
* chip select lines, and enable the SPI controller.
*/
static void cdns_spi_init_hw(struct cdns_spi *xspi)/*初始化cadence spi控制器*/
{
u32 ctrl_reg = CDNS_SPI_CR_DEFAULT;
/*控制寄存器默认为:主机模式使能、无外设被片选、手动片选使能、4分频*/
if (xspi->is_decoded_cs)
ctrl_reg |= CDNS_SPI_CR_PERI_SEL;/*外设片选3-8译码*/
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ER, CDNS_SPI_ER_DISABLE); /*SPI模块去使能*/
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_IDR, CDNS_SPI_IXR_ALL); /*去使能中断寄存器*/
/* Clear the RX FIFO 等待中断状态寄存器和rx_fifo被清空*/
while (cdns_spi_read(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ISR) & CDNS_SPI_IXR_RXNEMTY)
cdns_spi_read(xspi, CDNS_SPI_RXD);
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ISR, CDNS_SPI_IXR_ALL); /*清空spi中断控制器的状态*/
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_CR, ctrl_reg); /*配置控制寄存器*/
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ER, CDNS_SPI_ER_ENABLE); /*使能SPI*/
}
/**
* cdns_spi_chipselect - Select or deselect the chip select line
* @spi: Pointer to the spi_device structure
* @is_high: Select(0) or deselect (1) the chip select line
*/
static void cdns_spi_chipselect(struct spi_device *spi, bool is_high)/*片选操作*/
{
struct cdns_spi*xspi=spi_master_get_devdata(spi->master);//获取spi->master相关信息
u32 ctrl_reg;
ctrl_reg = cdns_spi_read(xspi, CDNS_SPI_CR); /*读spi控制寄存器的值*/
if (is_high)
{
/* Deselect the slave */
ctrl_reg |= CDNS_SPI_CR_SSCTRL;/*不选择该从机*/
} else {
/* Select the slave */
ctrl_reg &= ~CDNS_SPI_CR_SSCTRL;
if (!(xspi->is_decoded_cs)) /*是否用3-8译码器来片选*/
ctrl_reg |= ((~(CDNS_SPI_SS0 << spi->chip_select)) <<
CDNS_SPI_SS_SHIFT) & CDNS_SPI_CR_SSCTRL;
else
ctrl_reg |= (spi->chip_select << CDNS_SPI_SS_SHIFT) &
CDNS_SPI_CR_SSCTRL;
}
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_CR, ctrl_reg);/*重新写控制寄存器的片选位*/
}
/**
* cdns_spi_config_clock_mode - Sets clock polarity and phase
* @spi: Pointer to the spi_device structure
* Sets the requested clock polarity and phase.
*/
static void cdns_spi_config_clock_mode(struct spi_device *spi)/*配置时钟相位和极性*/
{
struct cdns_spi*xspi=spi_master_get_devdata(spi->master);//获取spi->master的相关信息
u32 ctrl_reg, new_ctrl_reg;
new_ctrl_reg = cdns_spi_read(xspi, CDNS_SPI_CR);
ctrl_reg = new_ctrl_reg;
/* Set the SPI clock phase and clock polarity */
new_ctrl_reg &= ~(CDNS_SPI_CR_CPHA | CDNS_SPI_CR_CPOL);
if (spi->mode & SPI_CPHA)
new_ctrl_reg |= CDNS_SPI_CR_CPHA;
if (spi->mode & SPI_CPOL)
new_ctrl_reg |= CDNS_SPI_CR_CPOL;
if (new_ctrl_reg != ctrl_reg)
{
/*
* Just writing the CR register does not seem to apply the clock
* setting changes. This is problematic when changing the clock
* polarity as it will cause the SPI slave to see spurious clock
* transitions. To workaround the issue toggle the ER register.
*/
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ER, CDNS_SPI_ER_DISABLE);
cdns_spi_write(xspi,CDNS_SPI_CR, new_ctrl_reg);/*重新写控制寄存器的时钟模式*/
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ER, CDNS_SPI_ER_ENABLE);
}
}
/**
* cdns_spi_config_clock_freq - Sets clock frequency
* @spi: Pointer to the spi_device structure
* @transfer: Pointer to the spi_transfer structure which provides
* information about next transfer setup parameters
*
* Sets the requested clock frequency.
* Note: If the requested frequency is not an exact match with what can be
* obtained using the prescalar value the driver sets the clock frequency which
* is lower than the requested frequency (maximum lower) for the transfer. If
* the requested frequency is higher or lower than that is supported by the SPI
* controller the driver will set the highest or lowest frequency supported by
* controller.
*/
static void cdns_spi_config_clock_freq(struct spi_device *spi,/*设置SPI时钟频率*/
struct spi_transfer *transfer)
{
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(spi->master);
u32 ctrl_reg, baud_rate_val;
unsigned long frequency;
frequency = clk_get_rate(xspi->ref_clk);
ctrl_reg = cdns_spi_read(xspi, CDNS_SPI_CR);
/* Set the clock frequency */
if (xspi->speed_hz != transfer->speed_hz)
{
/* first valid value is 1 */
baud_rate_val = CDNS_SPI_BAUD_DIV_MIN;
while ((baud_rate_val < CDNS_SPI_BAUD_DIV_MAX) &&
(frequency / (2 << baud_rate_val)) > transfer->speed_hz)
baud_rate_val++;
ctrl_reg &= ~CDNS_SPI_CR_BAUD_DIV;
ctrl_reg |= baud_rate_val << CDNS_SPI_BAUD_DIV_SHIFT;
xspi->speed_hz = frequency / (2 << baud_rate_val);
}
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_CR, ctrl_reg);
}
/**
* cdns_spi_setup_transfer - Configure SPI controller for specified transfer
* @spi: Pointer to the spi_device structure
* @transfer: Pointer to the spi_transfer structure which provides
* information about next transfer setup parameters
*
* Sets the operational mode of SPI controller for the next SPI transfer and
* sets the requested clock frequency.
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
static int cdns_spi_setup_transfer(struct spi_device *spi,/*为指定的发送配置SPI控制器*/
struct spi_transfer *transfer)
{
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(spi->master);
cdns_spi_config_clock_freq(spi, transfer);
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%s, mode %d, %u bits/w, %u clock speed\n",
__func__, spi->mode, spi->bits_per_word,
xspi->speed_hz);
return 0;
}
/**
* cdns_spi_fill_tx_fifo - Fills the TX FIFO with as many bytes as possible
* @xspi: Pointer to the cdns_spi structure
*/
static void cdns_spi_fill_tx_fifo(struct cdns_spi *xspi)/*向tx_buf中填充数据*/
{
unsigned long trans_cnt = 0;
while ((trans_cnt < CDNS_SPI_FIFO_DEPTH) && (xspi->tx_bytes > 0))
{
if (xspi->txbuf)
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_TXD, *xspi->txbuf++);
else
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_TXD, 0);
xspi->tx_bytes--;
trans_cnt++;
}
}
/**
* cdns_spi_irq - Interrupt service routine of the SPI controller
* @irq: IRQ number
* @dev_id: Pointer to the xspi structure
*
* This function handles TX empty and Mode Fault interrupts only.
* On TX empty interrupt this function reads the received data from RX FIFO and
* fills the TX FIFO if there is any data remaining to be transferred.
* On Mode Fault interrupt this function indicates that transfer is completed,
* the SPI subsystem will identify the error as the remaining bytes to be
* transferred is non-zero.
*
* Return: IRQ_HANDLED when handled; IRQ_NONE otherwise.
*/
static irqreturn_t cdns_spi_irq(int irq, void *dev_id)/*SPI控制器中断服务*/
{
struct spi_master *master = dev_id;
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
u32 intr_status, status;
status = IRQ_NONE;
intr_status = cdns_spi_read(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ISR);
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ISR, intr_status);
if (intr_status & CDNS_SPI_IXR_MODF)
{
/* Indicate that transfer is completed, the SPI subsystem will
* identify the error as the remaining bytes to be
* transferred is non-zero
*/
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_IDR, CDNS_SPI_IXR_DEFAULT);
spi_finalize_current_transfer(master);
status = IRQ_HANDLED;
}
else if (intr_status & CDNS_SPI_IXR_TXOW)
{
unsigned long trans_cnt;
trans_cnt = xspi->rx_bytes - xspi->tx_bytes;
/* Read out the data from the RX FIFO */
while (trans_cnt)
{
u8 data;
data = cdns_spi_read(xspi, CDNS_SPI_RXD);
if (xspi->rxbuf)
*xspi->rxbuf++ = data;
xspi->rx_bytes--;
trans_cnt--;
}
if (xspi->tx_bytes)
{
/* There is more data to send */
cdns_spi_fill_tx_fifo(xspi);
}
else
{
/* Transfer is completed */
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_IDR,
CDNS_SPI_IXR_DEFAULT);
spi_finalize_current_transfer(master);
}
status = IRQ_HANDLED;
}
return status;
}
static int cdns_prepare_message(struct spi_master *master,/*准备发送*/
struct spi_message *msg)
{
cdns_spi_config_clock_mode(msg->spi);
return 0;
}
/**
* cdns_transfer_one - Initiates the SPI transfer
* @master: Pointer to spi_master structure
* @spi: Pointer to the spi_device structure
* @transfer: Pointer to the spi_transfer structure which provides
* information about next transfer parameters
*
* This function fills the TX FIFO, starts the SPI transfer and
* returns a positive transfer count so that core will wait for completion.
*
* Return: Number of bytes transferred in the last transfer
*/
static int cdns_transfer_one(struct spi_master *master,/*初始化SPI发送*/
struct spi_device *spi,
struct spi_transfer *transfer)
{
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
xspi->txbuf = transfer->tx_buf;
xspi->rxbuf = transfer->rx_buf;
xspi->tx_bytes = transfer->len;
xspi->rx_bytes = transfer->len;
cdns_spi_setup_transfer(spi, transfer);/*设置SPI时钟频率*/
cdns_spi_fill_tx_fifo(xspi);/*向tx_buf中填充数据*/
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_IER, CDNS_SPI_IXR_DEFAULT);
return transfer->len;
}
/**
* cdns_prepare_transfer_hardware - Prepares hardware for transfer.
* @master: Pointer to the spi_master structure which provides
* information about the controller.
*
* This function enables SPI master controller.
*
* Return: 0 always
*/
static int cdns_prepare_transfer_hardware(struct spi_master *master)/*准备硬件去发送*/
{
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ER, CDNS_SPI_ER_ENABLE);
return 0;
}
/**
* cdns_unprepare_transfer_hardware - Relaxes hardware after transfer
* @master: Pointer to the spi_master structure which provides
* information about the controller.
*
* This function disables the SPI master controller.
*
* Return: 0 always
*/
static int cdns_unprepare_transfer_hardware(struct spi_master *master)/*发送完成后释放硬件*/
{
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ER, CDNS_SPI_ER_DISABLE);
return 0;
}
/**
* cdns_spi_probe - Probe method for the SPI driver
* @pdev: Pointer to the platform_device structure
*
* This function initializes the driver data structures and the hardware.
*
* Return: 0 on success and error value on error
*/
static int cdns_spi_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)/*cadence_spi驱动探针函数*/
{
int ret = 0, irq;
struct spi_master *master;
struct cdns_spi *xspi;
struct resource *res;
u32 num_cs;
master = spi_alloc_master(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*xspi));//分配一个SPI主机控制器
if (!master)
return -ENOMEM;
xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
master->dev.of_node = pdev->dev.of_node;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, master);
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); //获取设备树中SPI的IO资源
xspi->regs = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, res); //对寄存器进行映射
if (IS_ERR(xspi->regs)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(xspi->regs);
goto remove_master;
}
xspi->pclk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "pclk"); //获取ARB时钟,用作配置寄存器
if (IS_ERR(xspi->pclk)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "pclk clock not found.\n");
ret = PTR_ERR(xspi->pclk);
goto remove_master;
}
xspi->ref_clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "ref_clk"); //获取参考时钟,用作波特率
if (IS_ERR(xspi->ref_clk)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "ref_clk clock not found.\n");
ret = PTR_ERR(xspi->ref_clk);
goto remove_master;
}
ret = clk_prepare_enable(xspi->pclk); //使能APB时钟
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Unable to enable APB clock.\n");
goto remove_master;
}
ret = clk_prepare_enable(xspi->ref_clk); //使能参考时钟
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Unable to enable device clock.\n");
goto clk_dis_apb;
}
pm_runtime_use_autosuspend(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_set_autosuspend_delay(&pdev->dev, SPI_AUTOSUSPEND_TIMEOUT);
pm_runtime_set_active(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_enable(&pdev->dev);
ret = of_property_read_u32(pdev->dev.of_node, "num-cs", &num_cs);//获取设备树中num-cs资源
if (ret < 0)
master->num_chipselect = CDNS_SPI_DEFAULT_NUM_CS;
else
master->num_chipselect = num_cs;
ret = of_property_read_u32(pdev->dev.of_node, "is-decoded-cs",//获取设备树中is-decoded-cs资源
&xspi->is_decoded_cs);
if (ret < 0)
xspi->is_decoded_cs = 0;
/* SPI controller initializations */
cdns_spi_init_hw(xspi);
pm_runtime_mark_last_busy(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_put_autosuspend(&pdev->dev);
irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);//获取设备树中中断资源
if (irq <= 0) {
ret = -ENXIO;
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "irq number is invalid\n");
goto clk_dis_all;
}
ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, irq, cdns_spi_irq,//向系统申请中断
0, pdev->name, master);
if (ret != 0) {
ret = -ENXIO;
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "request_irq failed\n");
goto clk_dis_all;
}
master->prepare_transfer_hardware = cdns_prepare_transfer_hardware; //使能SPI寄存器
master->prepare_message = cdns_prepare_message; //设置SPI的时钟和相位
master->transfer_one = cdns_transfer_one; //设置波特率
master->unprepare_transfer_hardware = cdns_unprepare_transfer_hardware; //关闭SPI寄存器
master->set_cs = cdns_spi_chipselect; //片选
master->auto_runtime_pm = true;
master->mode_bits = SPI_CPOL | SPI_CPHA;
/* Set to default valid value */
master->max_speed_hz = clk_get_rate(xspi->ref_clk) / 4; // 设置波特率、字长默认值
xspi->speed_hz = master->max_speed_hz;
master->bits_per_word_mask = SPI_BPW_MASK(8);
ret = spi_register_master(master); //向系统注册SPI主机控制器
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "spi_register_master failed\n");
goto clk_dis_all;
}
return ret;
clk_dis_all:
pm_runtime_set_suspended(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_disable(&pdev->dev);
clk_disable_unprepare(xspi->ref_clk);
clk_dis_apb:
clk_disable_unprepare(xspi->pclk);
remove_master:
spi_master_put(master);
return ret;
}
/**
* cdns_spi_remove - Remove method for the SPI driver
* @pdev: Pointer to the platform_device structure
*
* This function is called if a device is physically removed from the system or
* if the driver module is being unloaded. It frees all resources allocated to
* the device.
*
* Return: 0 on success and error value on error
*/
static int cdns_spi_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)/*cadence_spi驱动移除*/
{
struct spi_master *master = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
cdns_spi_write(xspi, CDNS_SPI_ER, CDNS_SPI_ER_DISABLE);
clk_disable_unprepare(xspi->ref_clk);
clk_disable_unprepare(xspi->pclk);
pm_runtime_set_suspended(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_disable(&pdev->dev);
spi_unregister_master(master);
return 0;
}
/**
* cdns_spi_suspend - Suspend method for the SPI driver
* @dev: Address of the platform_device structure
*
* This function disables the SPI controller and
* changes the driver state to "suspend"
*
* Return: 0 on success and error value on error
*/
static int __maybe_unused cdns_spi_suspend(struct device *dev)/*cadence_spi驱动暂停*/
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct spi_master *master = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
return spi_master_suspend(master);
}
/**
* cdns_spi_resume - Resume method for the SPI driver
* @dev: Address of the platform_device structure
*
* This function changes the driver state to "ready"
*
* Return: 0 on success and error value on error
*/
static int __maybe_unused cdns_spi_resume(struct device *dev)/*cadence_spi驱动恢复*/
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct spi_master *master = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
cdns_spi_init_hw(xspi);
return spi_master_resume(master);
}
/**
* cdns_spi_runtime_resume - Runtime resume method for the SPI driver
* @dev: Address of the platform_device structure
*
* This function enables the clocks
*
* Return: 0 on success and error value on error
*/
static int __maybe_unused cnds_runtime_resume(struct device *dev)/*SPI驱动程序的运行时恢复*/
{
struct spi_master *master = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
int ret;
ret = clk_prepare_enable(xspi->pclk);
if (ret) {
dev_err(dev, "Cannot enable APB clock.\n");
return ret;
}
ret = clk_prepare_enable(xspi->ref_clk);
if (ret) {
dev_err(dev, "Cannot enable device clock.\n");
clk_disable(xspi->pclk);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
/**
* cdns_spi_runtime_suspend - Runtime suspend method for the SPI driver
* @dev: Address of the platform_device structure
*
* This function disables the clocks
*
* Return: Always 0
*/
static int __maybe_unused cnds_runtime_suspend(struct device *dev)/*SPI驱动程序的运行时挂起*/
{
struct spi_master *master = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
struct cdns_spi *xspi = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
clk_disable_unprepare(xspi->ref_clk);
clk_disable_unprepare(xspi->pclk);
return 0;
}
static const struct dev_pm_ops cdns_spi_dev_pm_ops = {
SET_RUNTIME_PM_OPS(cnds_runtime_suspend,
cnds_runtime_resume, NULL)
SET_SYSTEM_SLEEP_PM_OPS(cdns_spi_suspend, cdns_spi_resume)
};
static const struct of_device_id cdns_spi_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "xlnx,zynq-spi-r1p6" },
{ .compatible = "cdns,spi-r1p6" },
{ /* end of table */ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, cdns_spi_of_match);
/* cdns_spi_driver - This structure defines the SPI subsystem platform driver */
static struct platform_driver cdns_spi_driver = {
.probe = cdns_spi_probe,
.remove = cdns_spi_remove,
.driver = {
.name = CDNS_SPI_NAME,
.of_match_table = cdns_spi_of_match,
.pm = &cdns_spi_dev_pm_ops,
},
};
module_platform_driver(cdns_spi_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Xilinx, Inc.");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Cadence SPI driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); 3,spi.c作用就是向内核注册SPI总线,以及向内核注册spi的主机控制器,只有向spi.c中先注册了主机控制器,在spi-cadence.c中才可以向内核申请一个SPI主机控制器,以及向内核注册,spi-cadence.c与spi.c的联系就建立起来了。
static int __init spi_init(void)
{
int status;
buf = kmalloc(SPI_BUFSIZ, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!buf)
{
status = -ENOMEM;
goto err0;
}
status = bus_register(&spi_bus_type); /*注册spi总线*/
if (status < 0)
goto err1;
status = class_register(&spi_master_class);/*将spi_master注册到内核中*/
if (status < 0)
goto err2;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC))
WARN_ON(of_reconfig_notifier_register(&spi_of_notifier));
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ACPI))
WARN_ON(acpi_reconfig_notifier_register(&spi_acpi_notifier));
return 0;
err2:
bus_unregister(&spi_bus_type);
err1:
kfree(buf);
buf = NULL;
err0:
return status;
}
/* board_info is normally registered in arch_initcall(),
* but even essential drivers wait till later
* REVISIT only boardinfo really needs static linking. the rest (device and
* driver registration) _could_ be dynamically linked (modular) ... costs
* include needing to have boardinfo data structures be much more public.
*/
postcore_initcall(spi_init);//在moudule_init之前加载三,总结:
1,应用层和底层调用关系
应用程序open->C库open->软中断->内核的sys_open->驱动open接口
应用程序close->C库close->软中断->内核的sys_close->驱动release接口
应用程序read->C库read->软中断->内核的sys_read->驱动read接口
应用程序write->C库write->软中断->内核的sys_write->驱动write
2,本质:将原先驱动中的硬件和软件撤离分开, 软件一旦写好,将来硬件发生变化,无需改动软件,要改只改硬件部分即可!这样驱动开发者的重心放在硬件部分即可,软件一旦写好需要改动!
3,SPI中断的步骤:linux内核分离思想的实现基于platform机制原理
第一步:向内核注册SPI总线以及SPI主机控制器;
第二步:向内核申请一个SPI主机控制器的空间,注册我们要用的主机控制器;
第三步:向内核注册SPI设备,以及构造file_operation结构体;
重点关注struct platform_device和struct platform_driver这两个结构体。底层连接以后用户空间就可以通过open、write、read、ioctl函数来操作字符设备spidev了。