A*算法实现全局路径规划——基于python
A*算法简介
一种在已知地图、目标点和起始点的情况下,寻找最短路径的启发式算法。
数学表达式:核心在于计算F值
F = G + H F = G + H F=G+H
其中:
F:为总移动代价
G:起点到当前点的代价(已经发生的代价)
H:当前点到目标点的代价(尚未发生,人为预估的代价)
H值的计算可用欧拉距离或曼哈顿距离等
启发函数的定义需体现出“引导性”,能够“引导”粒子向目标点移动
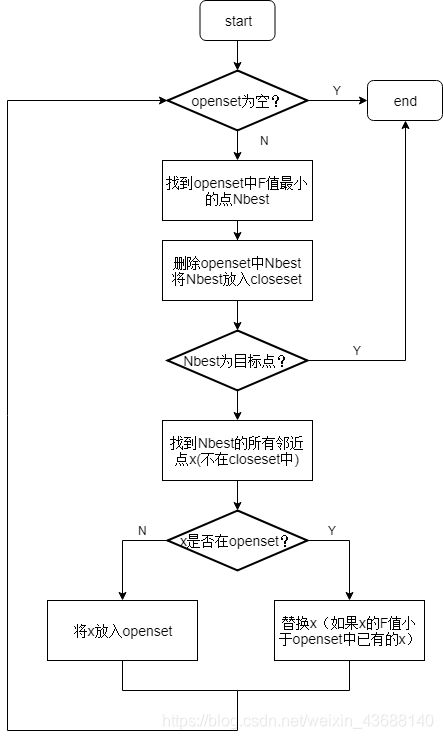
算法实现思路
python代码实现
"""
Author: Tomanlon
Copyright: Tomanlon
Date: 2019-3-9
Description: Simple demo for displaying astar algorithm with path find
MailBox: [email protected]
"""
"""
Author:Zheng Yeping
Data:2021-6-5
Description:Add some details about the code
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
#define node
#定义Node节点类
#坐标、父节点、代价、索引
class Node:
def __init__(self,x,y,parent,cost,index):
self.x = x
self.y = y
#used for tracking path node in closeset
self.parent = parent
self.cost = cost
# node index
self.index = index
# tracking path node
# 计算路径上所有点的坐标
# 父结点的作用:保证封闭列表中,节点的顺序性
def calc_path(goaln,closeset):
rx,ry=[goaln.x],[goaln.y]
print (closeset[-1])
#goal parent node in closeset
parentn = closeset[-1]
while parentn!=None:
rx.append(parentn.x)
ry.append(parentn.y)
parentn = parentn.parent
return rx,ry
# astar algorithm core
def astar_plan(sx,sy,gx,gy):
# 生成地图
# ox,oy为障碍物坐标点
# xwidth,ywidth为地图的长和宽
ox,oy,xwidth,ywidth=map_generation()
# show map
plt.figure('Astar algorithm demo')
plt.plot(ox,oy,'ks')
plt.plot(sx,sy,'bs')
plt.plot(gx,gy,'ro')
#定义每个点的可运动方向(8个)
motion = motion_model()
# 初始化开放列表与封闭列表
openset,closeset=dict(),dict()
sidx = sy*xwidth+sx
gidx = gy*xwidth+gx
# start node and goal node
#Node(x,y,父节点,代价,索引)
starn=Node(sx,sy,None,0,sidx)
goaln=Node(gx,gy,None,0,gidx)
#起点放入开放列表
openset[sidx] = starn
while 1:
# calculate node with min f_cost as current node
# h_cost()是启发函数,评估当前点到目标点的代价
c_id = min(openset,key=lambda o:openset[o].cost + h_cost(openset[o],goaln))
#代价F值最小的点,作为考察节点
curnode = openset[c_id]
# if arrive goal point break else closset add current node and remove current node from openset
if curnode.x == goaln.x and curnode.y == goaln.y:
print ('find goal')
closeset[-1] = curnode
break
else:
closeset[c_id] = curnode
plt.plot(curnode.x,curnode.y,'gx')
if len(openset.keys())%10==0:
plt.pause(0.01)
del openset[c_id]
# check 8 direction point
for j in range(len(motion)):
newnode = Node(curnode.x+motion[j][0],
curnode.y+motion[j][1],
curnode, #新节点的父结点为当前节点
curnode.cost + motion[j][2], # F=G+H,已知代价(已经发生的)加上预估代价
c_id)
# 计算新节点的索引值
n_id = index_calc(newnode,xwidth)
# if node in closeset out of loop once
# 新节点在封闭列表中,则跳过
if n_id in closeset:
continue
# 新节点是障碍物,则跳过
if node_verify(newnode,ox,oy):
continue
# 新节点不在开放列表,则立即加入开放列表
# 新节点在开放列表,则比较该节点的F值;如果新节点的F值更小,则替换
if n_id not in openset:
openset[n_id] = newnode
else:
# id对应唯一的点,但到达该点的方式有很多,不同的方式对应不同的父结点和代价G
# 更新openset已有点,主要是更新点的父结点和已发生代价值G
if openset[n_id].cost >= newnode.cost:
openset[n_id] = newnode
# get path node x ,y
px,py = calc_path(goaln,closeset)
return px,py
#初始化地图
#产生地图数据障碍物坐标点(ox,oy)
def map_generation():
# ox,oy list for obstacles
ox,oy=[],[]
#边界
for i in range(60):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(0)
for i in range(60):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(60)
for i in range(60):
ox.append(0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(60):
ox.append(60)
oy.append(i)
#障碍物坐标
for i in range(25):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(20)
for i in range(40):
ox.append(35)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(40):
ox.append(50)
oy.append(60-i)
minx = min(ox)
miny = min(oy)
maxx = max(ox)
maxy = max(oy)
# map xwidth, ywidth
xwidth = maxx-minx
ywidth = maxy-miny
return ox,oy,xwidth,ywidth
# motion model in 8 direction with 8 g_costs
# 定义运动模型,向每个节点的8个方向运动,并产生运动代价
def motion_model():
motion =[[1,0,1],
[1,1,math.sqrt(2)],
[1,-1,math.sqrt(2)],
[0,1,1],
[0,-1,1],
[-1,1,math.sqrt(2)],
[-1,0,1],
[-1,-1,math.sqrt(2)]]
return motion
#定义评价函数,当前点到目的点的预估代价
#可采用欧氏距离或曼哈顿距离
#曼哈顿距离:两点在坐标系上轴距之和|x1-x0|+|y1-y0|
#欧式距离:直线距离
def h_cost(node,goal):
# Weight
w = 1.0
#h = w*math.sqrt((goal.x-node.x)**2 + (goal.y-node.y)**2)
# Mahattan distance
h = w*(abs(goal.x-node.x) + abs(goal.y-node.y))
return h
# Node index obtain
# 计算节点索引,感觉是将二维转化为一维
def index_calc(node,xwid):
n_id = node.y*xwid + node.x
return n_id
# Verify node is in obstacle or not
#判断节点是否为障碍物
def node_verify(node,ox,oy):
if (node.x,node.y) in zip(ox,oy):
return True
else:
return False
def main():
# Define start point(sx,sy),goal point(gx,gy)
sx,sy=15,15
gx,gy=55,50
# Astar algorithm tracking path node
rx,ry=astar_plan(sx,sy,gx,gy)
print (rx,ry)
# show path
plt.plot(rx,ry,'r-',linewidth=3)
plt.show()
if __name__ =="__main__":
main()
参考文献
[1] 陶满礼. ROS机器人编程与SLAM算法解析指南[M]. 北京:人民邮电出版社