【OpenCV-Python】教程:3-2 几何变换(仿射变换,透视变换)
OpenCV Python 几何变换
【目标】
- 学习平移、旋转、缩放、仿射变换、透视变换
- cv.getPerspectiveTransform
仿射变换是平面内的,是多次线性变换的结果,保留了平行性,用3个点就可得到对应的变换矩阵。
透视变换 2D-3D,必须用4个点才能得到变换矩阵;
- 平移
[ 1 0 T x 0 1 T y 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ x y 1 ] = [ x + T x y + T y 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & T_x \\ 0 & 1 & T_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \centerdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x + T_x\\ y+T_y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡100010TxTy1⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤=⎣⎡x+Txy+Ty1⎦⎤
- 缩放
[ S x 0 0 0 S y 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ x y 1 ] = [ x ∗ S x y ∗ S y 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} S_x & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & S_y & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \centerdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x * S_x\\ y * S_y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡Sx000Sy0001⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤=⎣⎡x∗Sxy∗Sy1⎦⎤
- 旋转
[ cos θ − sin θ 0 sin θ cos θ 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ x 0 y 0 1 ] = [ x 1 y 1 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} \cos\theta & -\sin\theta & 0 \\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \centerdot \begin{bmatrix} x_0 \\ y_0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x_1 \\ y_1 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡cosθsinθ0−sinθcosθ0001⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡x0y01⎦⎤=⎣⎡x1y11⎦⎤
- 错切
[ 1 tan ϕ 0 tan ψ 1 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ x y 1 ] = [ x + y tan ϕ y + x tan ψ 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \tan\phi & 0 \\ \tan\psi & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \centerdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x + y\tan\phi \\ y + x\tan\psi \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡1tanψ0tanϕ10001⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤=⎣⎡x+ytanϕy+xtanψ1⎦⎤
- 仿射变换
[ 1 0 T x 0 1 T y 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ S x 0 0 0 S y 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ cos θ − sin θ 0 sin θ cos θ 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ 1 tan ϕ 0 tan ψ 1 0 0 0 1 ] [ 1 0 − T x 0 1 − T y 0 0 1 ] = [ a 0 a 1 b 1 a 2 a 3 b 2 0 0 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & T_x \\ 0 & 1 & T_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \centerdot \begin{bmatrix} S_x & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & S_y & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \centerdot \begin{bmatrix} \cos\theta & -\sin\theta & 0 \\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \centerdot \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \tan\phi & 0 \\ \tan\psi & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & -T_x \\ 0 & 1 & -T_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} a_0 & a_1 & b_1 \\ a_2 & a_3 & b_2 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡100010TxTy1⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡Sx000Sy0001⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡cosθsinθ0−sinθcosθ0001⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡1tanψ0tanϕ10001⎦⎤⎣⎡100010−Tx−Ty1⎦⎤=⎣⎡a0a20a1a30b1b21⎦⎤
- 透视变换
[ a 11 a 12 a 13 a 21 a 22 a 23 a 31 a 32 a 33 ] ⋅ [ x y 1 ] = [ X Y Z ] \begin{bmatrix} a_{11} & a_{12} & a_{13} \\ a_{21} & a_{22} & a_{23} \\ a_{31} & a_{32} & a_{33} \end{bmatrix} \centerdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} X \\ Y \\ Z \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡a11a21a31a12a22a32a13a23a33⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤=⎣⎡XYZ⎦⎤
其中,假定 a 33 = 1 , X ′ = X / Z , Y ′ = Y / Z a_{33}=1, \quad X'=X / Z, \quad Y'=Y/Z a33=1,X′=X/Z,Y′=Y/Z
{ a 11 ⋅ x + a 12 ⋅ y + a 13 − a 31 ⋅ x ⋅ X ′ − a 32 ⋅ y ⋅ X ′ = X ′ a 21 ⋅ x + a 22 ⋅ y + a 23 − a 31 ⋅ x ⋅ Y ′ − a 32 ⋅ y ⋅ Y ′ = Y ′ \begin{cases} a_{11}\cdot x + a_{12}\cdot y + a_{13} - a_{31}\cdot x \cdot X' - a_{32} \cdot y \cdot X' =X' \\ a_{21}\cdot x + a_{22}\cdot y + a_{23} - a_{31}\cdot x \cdot Y' - a_{32} \cdot y \cdot Y' =Y' \end{cases} {a11⋅x+a12⋅y+a13−a31⋅x⋅X′−a32⋅y⋅X′=X′a21⋅x+a22⋅y+a23−a31⋅x⋅Y′−a32⋅y⋅Y′=Y′
从上述公式可以看出,需要4个点
【代码】
- OpenCV Python 图像缩放
import numpy as np
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('messi5.jpg')
res = cv2.resize(img, None, fx=2, fy=2, interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
# #OR
# height, width = img.shape[:2]
# res = cv2.resize(img,(2*width, 2*height), interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
cv2.imshow("img", img)
cv2.imshow("res", res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- OpenCV Python 图像平移
import numpy as np
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('messi5.jpg', 0)
rows,cols = img.shape
M = np.float32([[1,0,100],[0,1,50]])
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (cols,rows))
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.imshow('dst',dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- OpenCV Python 图像旋转
import numpy as np
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('messi5.jpg',0)
rows,cols = img.shape
# cols-1 and rows-1 are the coordinate limits.
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(((cols-1)/2.0,(rows-1)/2.0),90,1)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(cols, rows))
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('dst', dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- OpenCV Python 仿射变换
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('drawing.png')
rows,cols,ch = img.shape
pts1 = np.float32([[20,20],[110,20],[50,110]])
pts2 = np.float32([[10,50],[120,40],[30,150]])
M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1,pts2)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(cols,rows))
plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img),plt.title('Input')
plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(dst),plt.title('Output')
plt.show()
- OpenCV Python 图像透视变换
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('sudoku.png')
rows, cols, ch = img.shape
pts1 = np.float32([[56, 65], [368, 52], [28, 387], [389, 390]])
pts2 = np.float32([[0, 0], [300, 0], [0, 300], [300, 300]])
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1, pts2)
dst = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, (300, 300))
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(img), plt.title('Input')
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(dst), plt.title('Output')
plt.show()
【接口说明】
- cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (cols,rows))
void cv::warpAffine ( InputArray src,
OutputArray dst,
InputArray M,
Size dsize,
int flags = INTER_LINEAR,
int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT,
const Scalar & borderValue = Scalar()
);
cv.warpAffine( src, M, dsize[, dst[, flags[, borderMode[, borderValue]]]] ) -> dst
对一个图像进行仿射变换
src: 输入图像
dst: 输出图像,像素类型和源图像一致,尺寸可以指定
M: 2x3的变换矩阵
dsize: 输出图像的尺寸
flags: 插值方法,见InterpolationFlags
borderMode: 边缘模式,见下面的BorderTypes
borderValue: 默认为0,当边缘模式为 constant时,填充的值
InterpolationFlags
BorderTypes
- cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(((cols-1)/2.0,(rows-1)/2.0),90,1)
Mat cv::getRotationMatrix2D ( Point2f center,
double angle,
double scale
);
cv.getRotationMatrix2D( center, angle, scale ) -> retval
通过
中心点,旋转角度和尺度来计算仿射变换矩阵
center: 源图像的旋转中心
angle: 旋转角度
scale: 各项同性变化因子
- cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1,pts2)
//
Mat cv::getAffineTransform(const Point2f src[],
const Point2f dst[]
);
Mat cv::getAffineTransform(InputArray src,
InputArray dst
);
cv.getAffineTransform( src, dst ) -> retval
通过变换前的点和变换后的点计算仿射变换矩阵,提供3对点就可以了
src: 源图像的顶点
dst: 仿射变换后的顶点
- cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1, pts2)
Mat cv::getPerspectiveTransform ( InputArray src,
InputArray dst,
int solveMethod = DECOMP_LU
);
Mat cv::getPerspectiveTransform ( const Point2f src[],
const Point2f dst[],
int solveMethod = DECOMP_LU
);
cv.getPerspectiveTransform( src, dst[, solveMethod] ) -> retval
计算透射变换矩阵, 至少4个点
src: 输入点集
dst: 变换后的点集
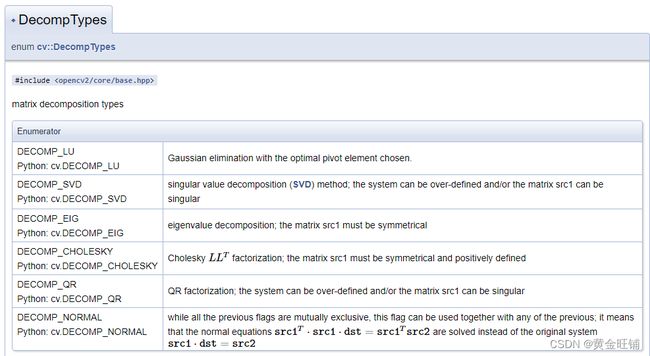
solveMethod: 矩阵分解类型
DecompTypes
- cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, (300, 300))
void cv::warpPerspective ( InputArray src,
OutputArray dst,
InputArray M,
Size dsize,
int flags = INTER_LINEAR,
int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT,
const Scalar & borderValue = Scalar()
);
cv.warpPerspective( src, M, dsize[, dst[, flags[, borderMode[, borderValue]]]] ) -> dst
透视变换
src: 输入图像
dst: 输出图像,像素类型和源图像一致,尺寸可以指定
M: 2x3的变换矩阵
dsize: 输出图像的尺寸
flags: 插值方法,见InterpolationFlags
borderMode: 边缘模式,见下面的BorderTypes
borderValue: 默认为0,当边缘模式为 constant时,填充的值
【参考】
- opencv 官网
- 【opencv实践】仿射变换和透视变换
- 几何变换中的仿射变换和透视变换的原理
- 番外篇: 仿射变换与透视变换