【OpenCV-Python】教程:3-3 阈值化 threshold,Otsu
OpenCV Python 阈值化
【目标】
- 简单阈值
- 自适应阈值
- Otsu阈值
【代码】
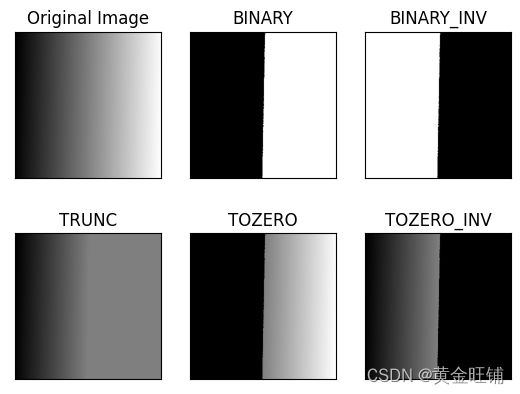
- 简单阈值
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('gradient2.png',0)
ret,thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret,thresh2 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
ret,thresh3 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TRUNC)
ret,thresh4 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO)
ret,thresh5 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV)
titles = ['Original Image','BINARY','BINARY_INV','TRUNC','TOZERO','TOZERO_INV']
images = [img, thresh1, thresh2, thresh3, thresh4, thresh5]
for i in range(6):
plt.subplot(2,3,i+1),plt.imshow(images[i],'gray',vmin=0,vmax=255)
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
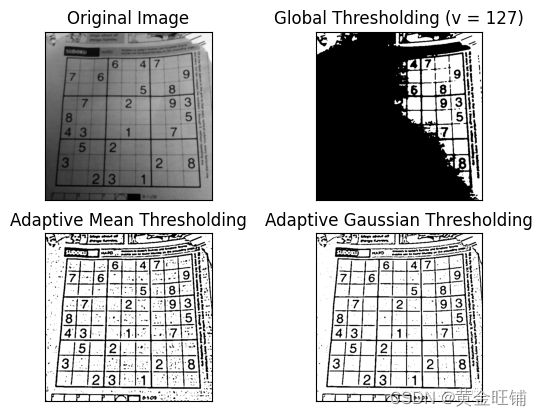
- 自适应阈值
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('sudoku.png', 0)
img = cv2.medianBlur(img, 5)
ret, th1 = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
th2 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 2)
th3 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 2)
titles = ['Original Image', 'Global Thresholding (v = 127)',
'Adaptive Mean Thresholding', 'Adaptive Gaussian Thresholding']
images = [img, th1, th2, th3]
for i in range(4):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1), plt.imshow(images[i], 'gray')
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
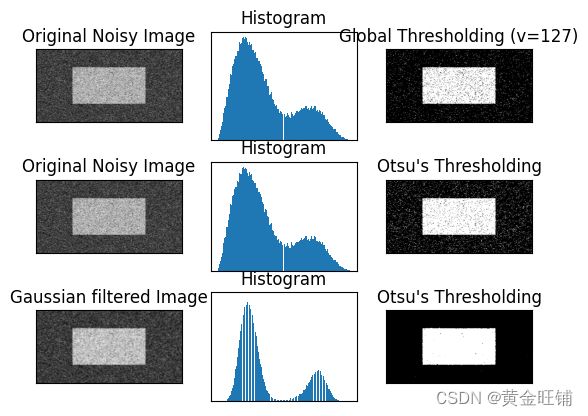
- Otsu 阈值化
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('noisy2.png', 0)
# global thresholding
ret1, th1 = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# Otsu's thresholding
ret2, th2 = cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# Otsu's thresholding after Gaussian filtering
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (5, 5), 0)
ret3, th3 = cv2.threshold(blur, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# plot all the images and their histograms
images = [img, 0, th1,
img, 0, th2,
blur, 0, th3]
titles = ['Original Noisy Image', 'Histogram', 'Global Thresholding (v=127)',
'Original Noisy Image', 'Histogram', "Otsu's Thresholding",
'Gaussian filtered Image', 'Histogram', "Otsu's Thresholding"]
for i in range(3):
plt.subplot(3, 3, i*3+1), plt.imshow(images[i*3], 'gray')
plt.title(titles[i*3]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(3, 3, i*3+2), plt.hist(images[i*3].ravel(), 256)
plt.title(titles[i*3+1]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(3, 3, i*3+3), plt.imshow(images[i*3+2], 'gray')
plt.title(titles[i*3+2]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
【接口】
- threshold()
double cv::threshold ( InputArray src,
OutputArray dst,
double thresh,
double maxval,
int type
);
cv.threshold( src, thresh, maxval, type[, dst] ) -> retval, dst
对图像进行阈值处理
src: 输入图像
dst: 输出图像
thresh: 阈值
maxval: THRESH_BINARY/THRESH_BINARY_INV 这两种类型时使用的最大值
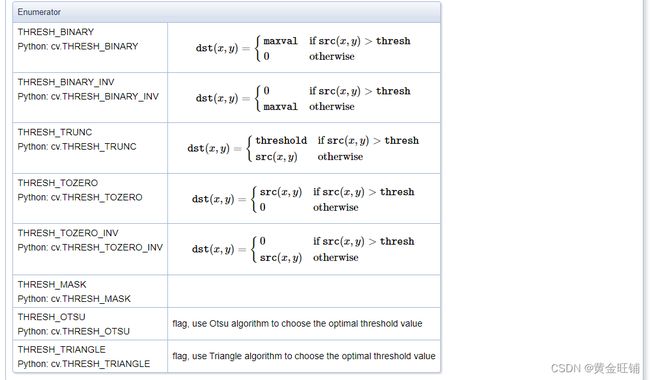
type: 阈值处理类型,见下
retval: 计算的阈值(Otsu或Triangle时)
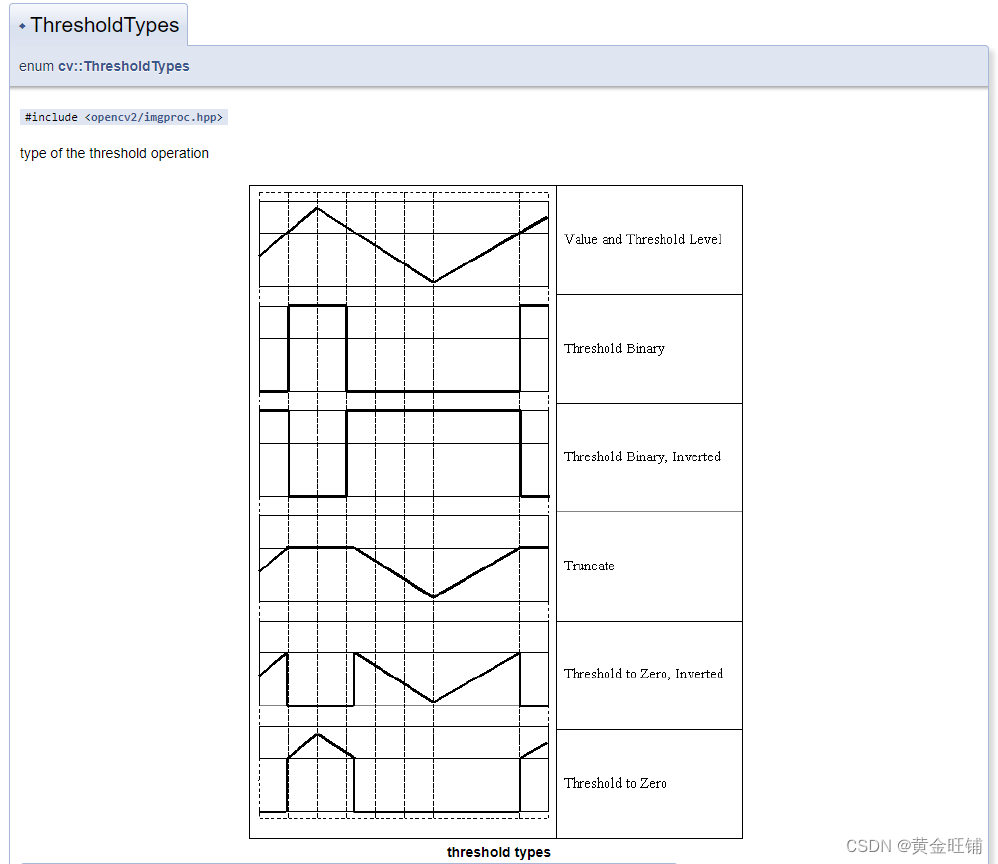
ThresholdTypes
enum cv::ThresholdTypes {
cv::THRESH_BINARY = 0,
cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV = 1,
cv::THRESH_TRUNC = 2,
cv::THRESH_TOZERO = 3,
cv::THRESH_TOZERO_INV = 4,
cv::THRESH_MASK = 7,
cv::THRESH_OTSU = 8,
cv::THRESH_TRIANGLE = 16
}
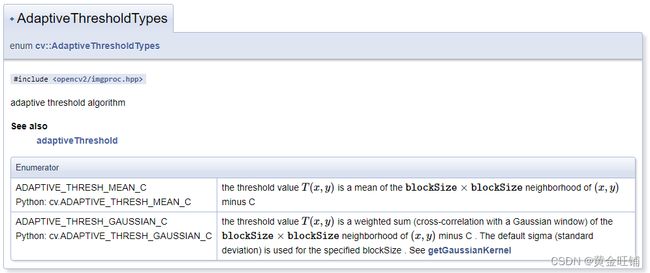
- adaptiveThreshold()
void cv::adaptiveThreshold ( InputArray src,
OutputArray dst,
double maxValue,
int adaptiveMethod,
int thresholdType,
int blockSize,
double C
);
cv.adaptiveThreshold( src, maxValue, adaptiveMethod, thresholdType, blockSize, C[, dst] ) -> dst
自适应阈值
src: 8 位单通道图像
dst: 结果图像,大小和类型与源图像一致
maxValue: 当条件满足时被赋予的值,非零
adaptiveMethod: 自适应方法,见下
thresholdType: 只能是 THRESH_BINARY 或 THRESH_BINARY_INV
blockSize: 块的大小,用于邻域计算使用
C: 平均值或加权值减去的常数,一般为正数,也可以为负数或者0
【参考】
- OpenCV 官方文档