matlab标记圆形,标识圆形目标 - MATLAB & Simulink Example - MathWorks 中国
步骤 1:读取图像
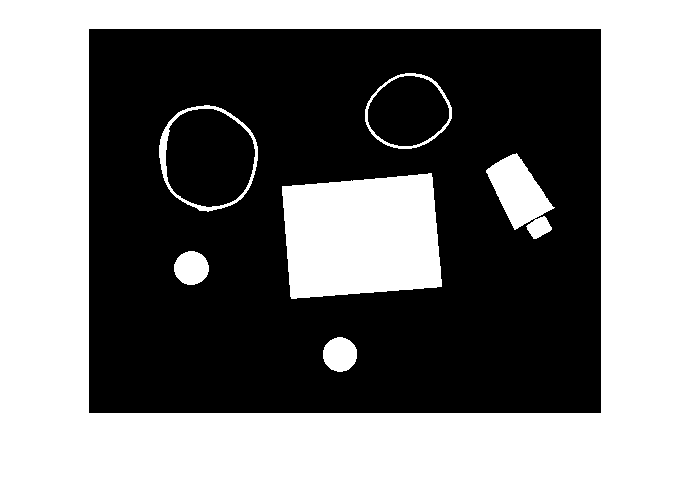
在 pills_etc.png 中进行读取。
RGB = imread('pillsetc.png');
imshow(RGB)
步骤 2:阈值化图像
将图像转换为黑白,以便使用 bwboundaries 为边界跟踪做准备。
I = rgb2gray(RGB);
bw = imbinarize(I);
imshow(bw)
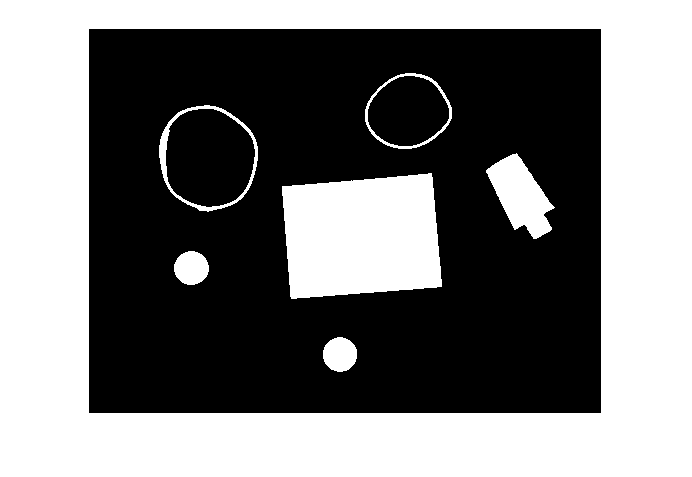
步骤 3:去除噪声
使用形态学函数,删除不属于关注对象的像素。
删除包含少于 30 个像素的所有对象。
bw = bwareaopen(bw,30);
imshow(bw)
填充笔帽中的间隙。
se = strel('disk',2);
bw = imclose(bw,se);
imshow(bw)
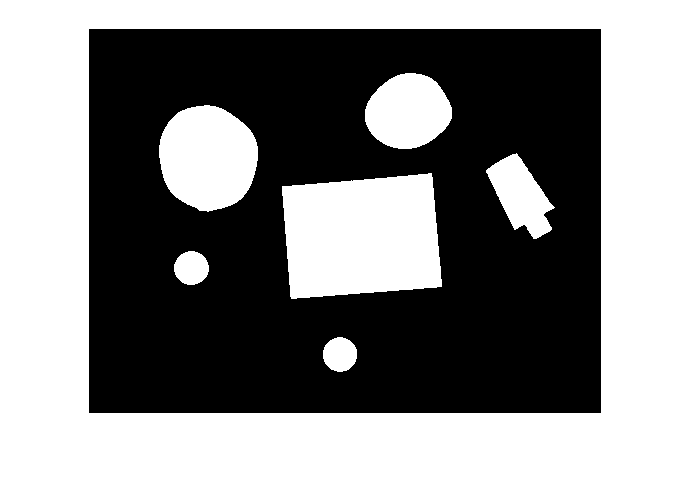
填充任何孔洞,以便可以使用 regionprops 来估计每个边界所包围的面积
bw = imfill(bw,'holes');
imshow(bw)
步骤 4:找到边界
只关注外边界。选项 'noholes' 将通过阻止 bwboundaries 搜索内部轮廓来加快处理速度。
[B,L] = bwboundaries(bw,'noholes');
显示标签矩阵并绘制每个边界。
imshow(label2rgb(L,@jet,[.5 .5 .5]))
hold on
for k = 1:length(B)
boundary = B{k};
plot(boundary(:,2),boundary(:,1),'w','LineWidth',2)
end
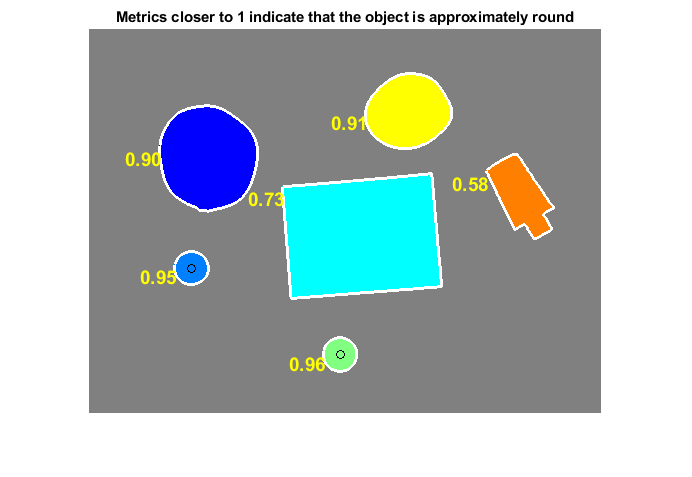
步骤 5:确定哪些对象为圆形
估计每个对象的面积和周长。使用这些结果形成简单的度量来表示对象的圆度:
metric=4π*areaperimeter2
只有对于圆,该度量值等于 1;而对于任何其他形状,该度量值都小于 1。可以通过设置适当的阈值来控制判别过程。此示例中使用 0.94 的阈值,以便只将药丸分类为圆形。
使用 regionprops 获得所有对象的面积估计值。请注意,bwboundaries 返回的标签矩阵可以被 regionprops 重用。
stats = regionprops(L,'Area','Centroid');
threshold = 0.94;
% loop over the boundaries
for k = 1:length(B)
% obtain (X,Y) boundary coordinates corresponding to label 'k'
boundary = B{k};
% compute a simple estimate of the object's perimeter
delta_sq = diff(boundary).^2;
perimeter = sum(sqrt(sum(delta_sq,2)));
% obtain the area calculation corresponding to label 'k'
area = stats(k).Area;
% compute the roundness metric
metric = 4*pi*area/perimeter^2;
% display the results
metric_string = sprintf('%2.2f',metric);
% mark objects above the threshold with a black circle
if metric > threshold
centroid = stats(k).Centroid;
plot(centroid(1),centroid(2),'ko');
end
text(boundary(1,2)-35,boundary(1,1)+13,metric_string,'Color','y',...
'FontSize',14,'FontWeight','bold')
end
title(['Metrics closer to 1 indicate that ',...
'the object is approximately round'])