语义分割loss汇总
语义分割的那些loss(甚至还有ssim)
今天我们看下关于语义分割的常规 l o s s loss loss设计,其中还有多个 l o s s loss loss联合一起用的,其中就如 B A S N e t BASNet BASNet这种显著性检测的工作,我们也分析了它的 l o s s loss loss设计。希望各位做分割的,可以在 l o s s loss loss层面,有所启发~
交叉熵损失 Cross Entropy Loss Function
用于图像语义分割任务的最常用损失函数是像素级别的交叉熵损失,这种损失会逐个检查每个像素,将对每个像素类别的预测结果(概率分布向量)与我们的独热编码标签向量( o n e − h o t one-hot one−hot形式)进行比较。
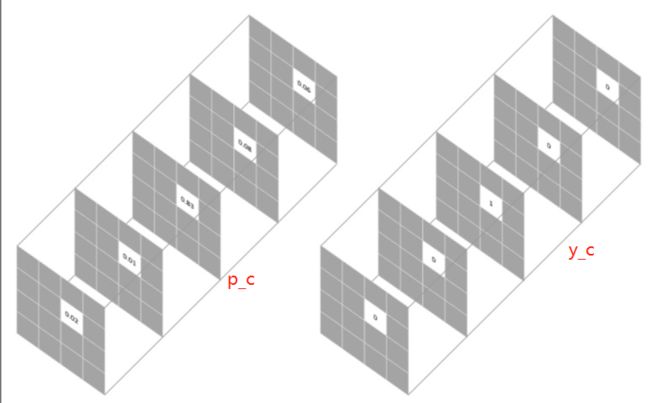
每个像素对应的损失函数为
L = − ∑ c = 1 M y c l o g ( p c ) L = -\sum_{c=1}^{M}y_c log(p_c) L=−c=1∑Myclog(pc)
其中, M M M代表类别数, y c y_c yc是one-hot向量,元素只有 0 0 0 和 1 1 1 两种取值,至于 p c p_c pc表示预测样本属于 c c c 类别的概率。假设我们需要对每个像素的预测类别有5个,则预测的概率分布向量长度为5:
整个图像的损失就是对每个像素的损失求平均值。
特别注意的是,binary entropy loss 是针对类别只有两个的情况,简称 bce loss,损失函数公式为:
b c e l o s s = − y t r u e l o g ( y p r e d ) − ( 1 − y t r u e ) l o g ( 1 − y p r e d ) bce \ loss = -y_{true}log(y_{pred}) - (1-y_{true})log(1-y_{pred}) bce loss=−ytruelog(ypred)−(1−ytrue)log(1−ypred)
交叉熵 L o s s Loss Loss可以用在大多数语义分割场景中,但它有一个明显的缺点,那就是对于只用分割前景和背景的时候,当前景像素的数量远远小于背景像素的数量时,即 y = 0 y=0 y=0 的数量远大于 y = 1 y=1 y=1 的数量,损失函数中 y = 0 y=0 y=0的成分就会占据主导,使得模型严重偏向背景,导致效果不好。
#二值交叉熵,这里输入要经过sigmoid处理
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
nn.BCELoss(F.sigmoid(input), target)
#多分类交叉熵, 用这个 loss 前面不需要加 Softmax 层
nn.CrossEntropyLoss(input, target)
weighted loss
由于交叉熵损失会分别评估每个像素的类别预测,然后对所有像素的损失进行平均,因此我们实质上是在对图像中的每个像素进行平等地学习。如果多个类在图像中的分布不均衡,那么这可能导致训练过程由像素数量多的类所主导,即模型会主要学习数量多的类别样本的特征,并且学习出来的模型会更偏向将像素预测为该类别。
比如对于二分类,正负样本比例为1: 99,此时模型将所有样本都预测为负样本,那么准确率仍有99%这么高,但其实该模型没有任何使用价值。
为了平衡这个差距,就对正样本和负样本的损失赋予不同的权重,带权重的二分类损失函数公式如下:
l o s s = − p o s _ w e i g h t × y t r u e l o g ( y p r e d ) − ( 1 − y t r u e ) l o g ( 1 − y p r e d ) loss = -pos\_weight \times y_{true}log(y_{pred}) - (1-y_{true})log(1-y_{pred}) loss=−pos_weight×ytruelog(ypred)−(1−ytrue)log(1−ypred)
p o s _ w e i g h t = n u m _ n e g n u m _ p o s pos\_weight = \frac{num\_neg}{num\_pos} pos_weight=num_posnum_neg
要减少假阴性样本的数量,设置 p o s _ w e i g h t > 1 pos\_weight>1 pos_weight>1;要减少假阳性样本的数量,设置 p o s _ w e i g h t < 1 pos\_weight<1 pos_weight<1。
Focal loss
何凯明团队在RetinaNet论文中引入了Focal Loss来解决难易样本数量不平衡,我们来回顾一下。 我们知道,One-Stage的目标检测器通常会产生10k数量级的框,但只有极少数是正样本,正负样本数量非常不平衡。为了解决正负样本不均衡的问题,经常在交叉熵损失前加入一个参数 α \alpha α
C E = { − α l o g ( p ) i f y = 1 − ( 1 − α ) l o g ( 1 − p ) o t h e r CE = \left\{\begin{matrix} -\alpha log(p) & if \ y =1\\ -(1-\alpha)log(1-p) & other \end{matrix}\right. CE={−αlog(p)−(1−α)log(1−p)if y=1other
虽然 α \alpha α 平衡了正负样本数量,但实际上,目标检测中大量的候选目标都是易分样本,这些样本会使损失很低,因此模型应关注那些难分样本,将高置信度的样本损失函数降低一些,就有了Focal loss
F L = { − α ( 1 − p ) γ l o g ( p ) i f y = 1 − ( 1 − α ) p γ l o g ( 1 − p ) i f y = 0 FL = \left\{\begin{matrix} -\alpha(1-p)^{\gamma} log(p) & if \ y =1\\ -(1-\alpha)p^{\gamma} log(1-p) & if \ y =0 \end{matrix}\right. FL={−α(1−p)γlog(p)−(1−α)pγlog(1−p)if y=1if y=0
举个例子,当 γ = 2 \gamma=2 γ=2,如果 p = 0.968 p=0.968 p=0.968, ( 1 − p ) 2 = 0.001 (1-p)^2=0.001 (1−p)2=0.001,这时损失衰减了1000倍。 FL Loss对于简单样本(p比较大)回应较小的loss,标准的CE然后有较大的loss,这样就是对简单样本的一种decay。
论文的实验结果显示,当 γ = 2 , α = 0.25 \gamma=2,\alpha=0.25 γ=2,α=0.25,效果最好,这样损失函数在训练的过程中关注的样本优先级就是正难> 负样本难例 > 正易 > 负易了。
### From https://www.kaggle.com/c/tgs-salt-identification-challenge/discussion/65938
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, alpha=1, gamma=2, logits=False, reduce=True):
super(FocalLoss, self).__init__()
self.alpha = alpha
self.gamma = gamma
self.logits = logits
self.reduce = reduce
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
if self.logits:
BCE_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(inputs, targets, reduce=False)
else:
BCE_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(inputs, targets, reduce=False)
pt = torch.exp(-BCE_loss)
F_loss = self.alpha * (1-pt)**self.gamma * BCE_loss
if self.reduce:
return torch.mean(F_loss)
else:
return F_loss
学习链接推荐
Dice Loss
dice loss 是在医疗图像分割模型VNet中提出的,感兴趣的解剖结构仅占据扫描的非常小的区域,从而使学习过程陷入损失函数的局部最小值。所以要加大前景区域的权重。
Dice系数是一种集合相似度度量的函数,可以理解为是两个轮廓区域的相似程度,用A、B表示两个轮廓区域所包含的点集,公式为:
D i c e ( A , B ) = 2 ∣ A ⋂ B ∣ ∣ A ∣ + ∣ B ∣ Dice(A,B)=2 \frac{|A⋂B|}{|A|+|B|} Dice(A,B)=2∣A∣+∣B∣∣A⋂B∣
其次Dice也可以表示为:
D i c e ( A , B ) = 2 T P 2 T P + F N + F P Dice(A, B) = \frac{2TP}{2TP+FN+FP} Dice(A,B)=2TP+FN+FP2TP
其中TP,FP,FN分别是真阳性、假阳性、假阴性的个数。
d i c e l o s s = 1 − D i c e dice \ loss = 1- Dice dice loss=1−Dice
- dice loss会使训练曲线有时不可信,很难看出收敛,而且dice loss好的模型并不一定在其他的评价标准上效果更好.
- 属于直接在评价标准上进行优化。
- 不均衡的场景下的确好使。
### From https://www.kaggle.com/bigironsphere/loss-function-library-keras-pytorch
class DiceLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, weight=None, size_average=True):
super(DiceLoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, inputs, targets, smooth=1):
#comment out if your model contains a sigmoid or equivalent activation layer
inputs = F.sigmoid(inputs)
#flatten label and prediction tensors
inputs = inputs.view(-1)
targets = targets.view(-1)
intersection = (inputs * targets).sum()
dice = (2.*intersection + smooth)/(inputs.sum() + targets.sum() + smooth)
return 1 - dice
class DiceBCELoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, weight=None, size_average=True):
super(DiceBCELoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, inputs, targets, smooth=1):
#comment out if your model contains a sigmoid or equivalent activation layer
inputs = F.sigmoid(inputs)
#flatten label and prediction tensors
inputs = inputs.view(-1)
targets = targets.view(-1)
intersection = (inputs * targets).sum()
dice_loss = 1 - (2.*intersection + smooth)/(inputs.sum() + targets.sum() + smooth)
BCE = F.binary_cross_entropy(inputs, targets, reduction='mean')
Dice_BCE = BCE + dice_loss
return Dice_BCE
IOU Loss
可类比DICE LOSS,也是直接针对评价标准进行优化,公式如下:
I O U = 1 − A ⋂ B A ⋃ B IOU = 1 - \frac{A \bigcap B}{A \bigcup B} IOU=1−A⋃BA⋂B
它和Dice Loss一样仍然存在训练过程不稳定的问题,IOU Loss在分割任务中不常用。
### From https://www.kaggle.com/bigironsphere/loss-function-library-keras-pytorch
class IoULoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, weight=None, size_average=True):
super(IoULoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, inputs, targets, smooth=1):
#comment out if your model contains a sigmoid or equivalent activation layer
inputs = F.sigmoid(inputs)
#flatten label and prediction tensors
inputs = inputs.view(-1)
targets = targets.view(-1)
#intersection is equivalent to True Positive count
#union is the mutually inclusive area of all labels & predictions
intersection = (inputs * targets).sum()
total = (inputs + targets).sum()
union = total - intersection
IoU = (intersection + smooth)/(union + smooth)
return 1 - IoU
几种多loss搭配方案
BCE + Dice Loss
即将BCE Loss和Dice Loss进行组合,在数据较为均衡的情况下有所改善,但是在数据极度不均衡的情况下交叉熵Loss会在迭代几个Epoch之后远远小于Dice Loss,这个组合Loss会退化为Dice Loss。
Focal Loss + Dice Loss
这个Loss的组合应该最早见于腾讯医疗AI实验室2018年在《Medical Physics》上发表的这篇论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1808.05238.pdf。论文提出了使用Focal Loss和Dice Loss来处理小器官的分割问题。同时也解决数据不平衡和难易样本的问题
Lovasz-Softmax Loss
Kaggle神器。这篇论文是CVPR 2018的,原地址为:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.08790.pdf。对原理感兴趣可以去看一下论文,这个损失是对Jaccard(IOU) Loss进行Lovaze扩展,表现更好。
"""
Lovasz-Softmax and Jaccard hinge loss in PyTorch
Maxim Berman 2018 ESAT-PSI KU Leuven (MIT License)
"""
from __future__ import print_function, division
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
try:
from itertools import ifilterfalse
except ImportError: # py3k
from itertools import filterfalse as ifilterfalse
def lovasz_grad(gt_sorted):
"""
Computes gradient of the Lovasz extension w.r.t sorted errors
See Alg. 1 in paper
"""
p = len(gt_sorted)
gts = gt_sorted.sum()
intersection = gts - gt_sorted.float().cumsum(0)
union = gts + (1 - gt_sorted).float().cumsum(0)
jaccard = 1. - intersection / union
if p > 1: # cover 1-pixel case
jaccard[1:p] = jaccard[1:p] - jaccard[0:-1]
return jaccard
def iou_binary(preds, labels, EMPTY=1., ignore=None, per_image=True):
"""
IoU for foreground class
binary: 1 foreground, 0 background
"""
if not per_image:
preds, labels = (preds,), (labels,)
ious = []
for pred, label in zip(preds, labels):
intersection = ((label == 1) & (pred == 1)).sum()
union = ((label == 1) | ((pred == 1) & (label != ignore))).sum()
if not union:
iou = EMPTY
else:
iou = float(intersection) / float(union)
ious.append(iou)
iou = mean(ious) # mean accross images if per_image
return 100 * iou
def iou(preds, labels, C, EMPTY=1., ignore=None, per_image=False):
"""
Array of IoU for each (non ignored) class
"""
if not per_image:
preds, labels = (preds,), (labels,)
ious = []
for pred, label in zip(preds, labels):
iou = []
for i in range(C):
if i != ignore: # The ignored label is sometimes among predicted classes (ENet - CityScapes)
intersection = ((label == i) & (pred == i)).sum()
union = ((label == i) | ((pred == i) & (label != ignore))).sum()
if not union:
iou.append(EMPTY)
else:
iou.append(float(intersection) / float(union))
ious.append(iou)
ious = [mean(iou) for iou in zip(*ious)] # mean accross images if per_image
return 100 * np.array(ious)
# --------------------------- BINARY LOSSES ---------------------------
def lovasz_hinge(logits, labels, per_image=True, ignore=None):
"""
Binary Lovasz hinge loss
logits: [B, H, W] Variable, logits at each pixel (between -\infty and +\infty)
labels: [B, H, W] Tensor, binary ground truth masks (0 or 1)
per_image: compute the loss per image instead of per batch
ignore: void class id
"""
if per_image:
loss = mean(lovasz_hinge_flat(*flatten_binary_scores(log.unsqueeze(0), lab.unsqueeze(0), ignore))
for log, lab in zip(logits, labels))
else:
loss = lovasz_hinge_flat(*flatten_binary_scores(logits, labels, ignore))
return loss
def lovasz_hinge_flat(logits, labels):
"""
Binary Lovasz hinge loss
logits: [P] Variable, logits at each prediction (between -\infty and +\infty)
labels: [P] Tensor, binary ground truth labels (0 or 1)
ignore: label to ignore
"""
if len(labels) == 0:
# only void pixels, the gradients should be 0
return logits.sum() * 0.
signs = 2. * labels.float() - 1.
errors = (1. - logits * Variable(signs))
errors_sorted, perm = torch.sort(errors, dim=0, descending=True)
perm = perm.data
gt_sorted = labels[perm]
grad = lovasz_grad(gt_sorted)
loss = torch.dot(F.relu(errors_sorted), Variable(grad))
return loss
def flatten_binary_scores(scores, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Flattens predictions in the batch (binary case)
Remove labels equal to 'ignore'
"""
scores = scores.view(-1)
labels = labels.view(-1)
if ignore is None:
return scores, labels
valid = (labels != ignore)
vscores = scores[valid]
vlabels = labels[valid]
return vscores, vlabels
class StableBCELoss(torch.nn.modules.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(StableBCELoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, input, target):
neg_abs = - input.abs()
loss = input.clamp(min=0) - input * target + (1 + neg_abs.exp()).log()
return loss.mean()
def binary_xloss(logits, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Binary Cross entropy loss
logits: [B, H, W] Variable, logits at each pixel (between -\infty and +\infty)
labels: [B, H, W] Tensor, binary ground truth masks (0 or 1)
ignore: void class id
"""
logits, labels = flatten_binary_scores(logits, labels, ignore)
loss = StableBCELoss()(logits, Variable(labels.float()))
return loss
# --------------------------- MULTICLASS LOSSES ---------------------------
def lovasz_softmax(probas, labels, classes='present', per_image=False, ignore=None):
"""
Multi-class Lovasz-Softmax loss
probas: [B, C, H, W] Variable, class probabilities at each prediction (between 0 and 1).
Interpreted as binary (sigmoid) output with outputs of size [B, H, W].
labels: [B, H, W] Tensor, ground truth labels (between 0 and C - 1)
classes: 'all' for all, 'present' for classes present in labels, or a list of classes to average.
per_image: compute the loss per image instead of per batch
ignore: void class labels
"""
if per_image:
loss = mean(lovasz_softmax_flat(*flatten_probas(prob.unsqueeze(0), lab.unsqueeze(0), ignore), classes=classes)
for prob, lab in zip(probas, labels))
else:
loss = lovasz_softmax_flat(*flatten_probas(probas, labels, ignore), classes=classes)
return loss
def lovasz_softmax_flat(probas, labels, classes='present'):
"""
Multi-class Lovasz-Softmax loss
probas: [P, C] Variable, class probabilities at each prediction (between 0 and 1)
labels: [P] Tensor, ground truth labels (between 0 and C - 1)
classes: 'all' for all, 'present' for classes present in labels, or a list of classes to average.
"""
if probas.numel() == 0:
# only void pixels, the gradients should be 0
return probas * 0.
C = probas.size(1)
losses = []
class_to_sum = list(range(C)) if classes in ['all', 'present'] else classes
for c in class_to_sum:
fg = (labels == c).float() # foreground for class c
if (classes is 'present' and fg.sum() == 0):
continue
if C == 1:
if len(classes) > 1:
raise ValueError('Sigmoid output possible only with 1 class')
class_pred = probas[:, 0]
else:
class_pred = probas[:, c]
errors = (Variable(fg) - class_pred).abs()
errors_sorted, perm = torch.sort(errors, 0, descending=True)
perm = perm.data
fg_sorted = fg[perm]
losses.append(torch.dot(errors_sorted, Variable(lovasz_grad(fg_sorted))))
return mean(losses)
def flatten_probas(probas, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Flattens predictions in the batch
"""
if probas.dim() == 3:
# assumes output of a sigmoid layer
B, H, W = probas.size()
probas = probas.view(B, 1, H, W)
B, C, H, W = probas.size()
probas = probas.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(-1, C) # B * H * W, C = P, C
labels = labels.view(-1)
if ignore is None:
return probas, labels
valid = (labels != ignore)
vprobas = probas[valid.nonzero().squeeze()]
vlabels = labels[valid]
return vprobas, vlabels
def xloss(logits, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Cross entropy loss
"""
return F.cross_entropy(logits, Variable(labels), ignore_index=255)
# --------------------------- HELPER FUNCTIONS ---------------------------
def isnan(x):
return x != x
def mean(l, ignore_nan=False, empty=0):
"""
nanmean compatible with generators.
"""
l = iter(l)
if ignore_nan:
l = ifilterfalse(isnan, l)
try:
n = 1
acc = next(l)
except StopIteration:
if empty == 'raise':
raise ValueError('Empty mean')
return empty
for n, v in enumerate(l, 2):
acc += v
if n == 1:
return acc
return acc / n
BASNet
一种专注于边缘以及精细结构分割的网络,同时提出一种混合loss,对这篇论文感兴趣的同学,可以看一下本文的详细总结:https://share.mubu.com/doc/3XISi_xs1he
ℓ k = ℓ b c e k + ℓ s s i m k + ℓ i o u k \ell^{k}=\ell^{k}_{bce}+\ell^{k}_{ssim}+\ell^{k}_{iou} ℓk=ℓbcek+ℓssimk+ℓiouk
二元交叉熵BCE、结构相似性SSIM和IOU损失,分别指导网络学习三级(即像素级、补丁级和图像级)层次结构表示。在边缘结构分割以及精细结构分割方面,表现优秀。
BCE损失是二元分类和分割中使用最广泛的损失,作用:pixel-level
ℓ b c e = − ∑ ( r , c ) [ G ( r , c ) l o g ( S ( r , c ) ) + ( 1 − G ( r , c ) ) l o g ( 1 − S ( r , c ) ) ] \ell_{bce} = -\sum_{(r, c)} [G(r,c)log(S(r,c)) + (1-G(r,c))log(1-S(r,c))] ℓbce=−(r,c)∑[G(r,c)log(S(r,c))+(1−G(r,c))log(1−S(r,c))]
G ( r , c ) ∈ { 0 , 1 } G(r,c)\in \left \{ 0,1 \right \} G(r,c)∈{0,1}是像素 ( r , c ) (r, c) (r,c)的标签; S ( r , c ) S(r, c) S(r,c)是分割对象的预测概率
SSIM最初设计用于图像质量评估。它可以捕获图像中的结构信息。因此,我们将其集成到训练损失中以学习标签的的结构信息。作用:patch-level
x = { x j : j = 1 , . . . , N 2 } x = \left \{ x_j:j=1, ..., N^2 \right \} x={xj:j=1,...,N2}
x x x是预测概率图S中裁剪出来的两个对应的图像块 p a t c h patch patch(大小为 N × N N \times N N×N)的像素值。
y = { y j : j = 1 , . . . , N 2 } y= \left \{ y_j:j=1, ..., N^2 \right \} y={yj:j=1,...,N2}
y y y是二值GT标签掩码 G G G中裁剪出的两个对应的图像path(大小: N × N N \times N N×N)的像素值
ℓ s s i m = 1 − ( 2 μ x μ y + C 1 ) ( 2 σ x y + C 2 ) ( μ x 2 + μ y 2 + C 1 ) ( μ x 2 + μ y 2 + C 2 ) \ell _{ssim} = 1-\frac{(2\mu_x\mu_y + C_1)(2\sigma_{xy} + C_2)}{(\mu^2_x+\mu^2_y +C_1)(\mu^2_x+\mu^2_y+C_2)} ℓssim=1−(μx2+μy2+C1)(μx2+μy2+C2)(2μxμy+C1)(2σxy+C2)
其中 μ x \mu_x μx, μ y \mu_y μy 和 μ x \mu_x μx, μ y \mu_y μy 分别是 x x x 和 y y y 的均值和标准差, σ x y \sigma_{xy} σxy 是协方差,为了避免除以 0,设置 C 1 = 0.0 1 2 C_1 = 0.01^2 C1=0.012 和 C 2 = 0.0 3 2 C_2 = 0.03^2 C2=0.032
IoU 最初被提出用于测量两个集合之间的相似性,并已成为目标检测和分割的标准评估措施。最近,它已被用作训练损失,是一种针对优化目标的损失函数,作用:map-level
为了确保其可区分性,我们采用了 的 IoU 损失:
ℓ i o u = 1 − ∑ r = 1 H ∑ c = 1 W S ( r , c ) G ( r , c ) ∑ r = 1 H ∑ c = 1 W [ S ( r , c ) + G ( r , c ) − S ( r , c ) G ( r , c ) ] \ell_{iou} = 1- \frac{\sum_{r=1}^{H}\sum_{c=1}^{W}S(r,c)G(r,c)}{\sum_{r=1}^H\sum_{c=1}^W[S(r,c)+G(r,c)-S(r,c)G(r,c)]} ℓiou=1−∑r=1H∑c=1W[S(r,c)+G(r,c)−S(r,c)G(r,c)]∑r=1H∑c=1WS(r,c)G(r,c)
其中
G ( r , c ) ∈ { 0 , 1 } G(r, c)\in \left \{ 0,1 \right \} G(r,c)∈{0,1}
是像素的 ( r , c ) (r,c) (r,c)的GT 标签, S ( r , c ) S(r, c) S(r,c) 是分割对象的预测概率。
bce_loss = nn.BCELoss(size_average=True)
ssim_loss = SSIM(window_size=11,size_average=True)
iou_loss = IOU(size_average=True)
def bce_ssim_loss(pred,target):
bce_out = bce_loss(pred,target)
ssim_out = 1 - ssim_loss(pred,target)
iou_out = iou_loss(pred,target)
loss = bce_out + ssim_out + iou_out
return loss
SSIM模块
def gaussian(window_size, sigma):
gauss = torch.Tensor([exp(-(x - window_size//2)**2/float(2*sigma**2)) for x in range(window_size)])
return gauss/gauss.sum()
def create_window(window_size, channel):
_1D_window = gaussian(window_size, 1.5).unsqueeze(1)
_2D_window = _1D_window.mm(_1D_window.t()).float().unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
window = Variable(_2D_window.expand(channel, 1, window_size, window_size).contiguous())
return window
def _ssim(img1, img2, window, window_size, channel, size_average = True):
mu1 = F.conv2d(img1, window, padding = window_size//2, groups = channel)
mu2 = F.conv2d(img2, window, padding = window_size//2, groups = channel)
mu1_sq = mu1.pow(2)
mu2_sq = mu2.pow(2)
mu1_mu2 = mu1*mu2
sigma1_sq = F.conv2d(img1*img1, window, padding = window_size//2, groups = channel) - mu1_sq
sigma2_sq = F.conv2d(img2*img2, window, padding = window_size//2, groups = channel) - mu2_sq
sigma12 = F.conv2d(img1*img2, window, padding = window_size//2, groups = channel) - mu1_mu2
C1 = 0.01**2
C2 = 0.03**2
ssim_map = ((2*mu1_mu2 + C1)*(2*sigma12 + C2))/((mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1)*(sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2))
if size_average:
return ssim_map.mean()
else:
return ssim_map.mean(1).mean(1).mean(1)
class SSIM(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, window_size = 11, size_average = True):
super(SSIM, self).__init__()
self.window_size = window_size
self.size_average = size_average
self.channel = 1
self.window = create_window(window_size, self.channel)
def forward(self, img1, img2):
(_, channel, _, _) = img1.size()
if channel == self.channel and self.window.data.type() == img1.data.type():
window = self.window
else:
window = create_window(self.window_size, channel)
if img1.is_cuda:
window = window.cuda(img1.get_device())
window = window.type_as(img1)
self.window = window
self.channel = channel
return _ssim(img1, img2, window, self.window_size, channel, self.size_average)
IOU LOSS
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
def _iou(pred, target, size_average = True):
b = pred.shape[0]
IoU = 0.0
for i in range(0,b):
#compute the IoU of the foreground
Iand1 = torch.sum(target[i,:,:,:]*pred[i,:,:,:])
Ior1 = torch.sum(target[i,:,:,:]) + torch.sum(pred[i,:,:,:])-Iand1
IoU1 = Iand1/Ior1
#IoU loss is (1-IoU1)
IoU = IoU + (1-IoU1)
return IoU/b
class IOU(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, size_average = True):
super(IOU, self).__init__()
self.size_average = size_average
def forward(self, pred, target):
return _iou(pred, target, self.size_average)