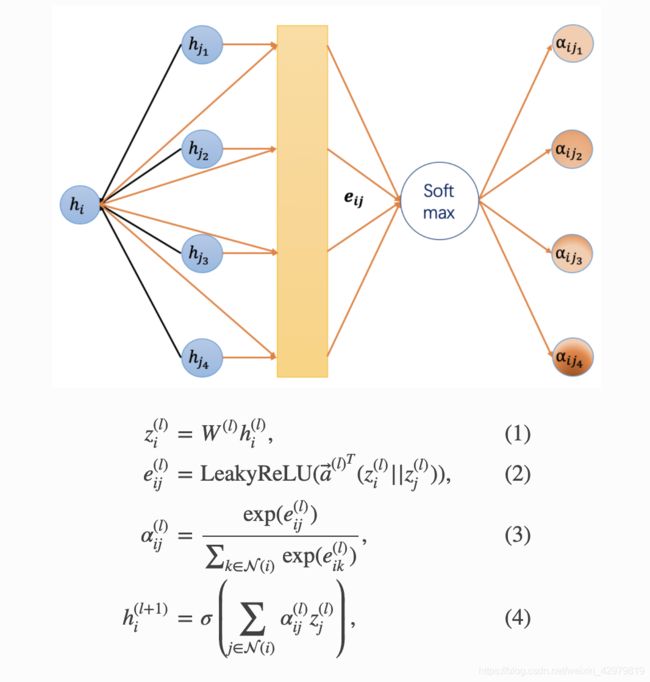
GAT源码剖析
题解:
layer.py
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GraphAttentionLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Simple GAT layer, similar to https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10903
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, dropout, alpha, concat=True):
super(GraphAttentionLayer, self).__init__()
self.dropout = dropout #dropout 参数
self.in_features = in_features # 输入的特征
self.out_features = out_features # 输出特征
self.alpha = alpha
self.concat = concat
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(size=(in_features, out_features)))
'''
先torch.empty创建的是一个size 大小的 torch.Tensor类型 这个类型是不可训练的
然后使用Parameter命令对 原来的Parameter类型进行绑定并且转化为Parameter 类型
Parameter 是一个可训练的类型
'''
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.W.data, gain=1.414) # gain 是两种方法计算的中 a 和 std 计算的重要参数
'''
Xavier 是一种初始化的方式 pytroch 提供了uniform 和 normal 两种方式:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(tensor, gain =1) 是均匀分布 (-a,a)
nn.init.xavier_normal_(tensor, gain=1) 正态分布~N ( 0 ,std )
https://blog.csdn.net/dss_dssssd/article/details/83959474 讲解博客地址
'''
self.a = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(size=(2*out_features, 1)))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.a.data, gain=1.414)
'''
论文中有一个公式whi||whj
|| 是连接符号 通过这个连接,我们把两个1 X F 的矩阵变成了 一个 1 X 2F 的矩阵
然后论文中乘以了一个a 2F X 1 的矩阵 那么就得到了一个数
这个a就是论文中的那个a
而我们的得到的那个数就是我们的attention系数
'''
self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(self.alpha)
'''
因为原式是 aij= softmax(sigmod(a (whi||whj)))
sigmod 是激活函数 这里用的是leaky ReLU 函数
'''
'''
forward 和 _prepare_attentional_mechanism_input 对应的论文 2.1环节
'''
def forward(self, h, adj): # 正向传播
Wh = torch.mm(h, self.W) # h.shape: (N, in_features), Wh.shape: (N, out_features)
# 这里是做一个乘法
a_input = self._prepare_attentional_mechanism_input(Wh)
e = self.leakyrelu(torch.matmul(a_input, self.a).squeeze(2))
zero_vec = -9e15*torch.ones_like(e)
attention = torch.where(adj > 0, e, zero_vec)
attention = F.softmax(attention, dim=1)
attention = F.dropout(attention, self.dropout, training=self.training)
h_prime = torch.matmul(attention, Wh)
if self.concat:
return F.elu(h_prime)
else:
return h_prime
def _prepare_attentional_mechanism_input(self, Wh):
N = Wh.size()[0] # number of nodes
'''
Wh size = [2708,8] 8 是标签数目
size()[0] size顾名思义是大小的意思 [] 的应用是在维度上
这里[0]代表的是在0维度
例如我们创建一个torch.rand([2, 1, 3, 3])
那么 size()[1] 就等于 1
'''
# 下面,创建了两个矩阵,它们在行中的嵌入顺序不同
# (e stands for embedding) e 是 embedding 的基础
# 这些是第一个矩阵的行 (Wh_repeated_in_chunks):
# e1, e1, ..., e1, e2, e2, ..., e2, ..., eN, eN, ..., eN
# '-------------' -> N times '-------------' -> N times '-------------' -> N times
#
# 这些是第二个矩阵的行 (Wh_repeated_alternating):
# e1, e2, ..., eN, e1, e2, ..., eN, ..., e1, e2, ..., eN
# '----------------------------------------------------' -> N times
#
Wh_repeated_in_chunks = Wh.repeat_interleave(N, dim=0)
'''
repeat_interleave(self: Tensor, repeats: _int, dim: Optional[_int]=None) 是复制函数
参数说明:
self: 传入 的数据为 tensor
repeats : 复制到几份
dim : 要复制的维度 可以设定为 0、1、2
Examples:
此处定义了一个4维tensor,要对第2个维度复制,由原来的1变为3,即将设定dim=1。
data1 = torch.rand([2, 1, 3, 3])
data2 = torch.repeat_interleave(data1, repeats=3, dim=1)
'''
Wh_repeated_alternating = Wh.repeat(N, 1)
'''
repeat 函数:
第一个参数是复制的份数
第二个参数是复制的维度是那个维度
Examples1:
data1 = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
data1.repeat(2,0)
array([[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[4, 5, 6]])
Examples2:
data1 = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
data1.repeat(2,1)
array([[1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6]])
'''
# Wh_repeated_in_chunks.shape == Wh_repeated_alternating.shape == (N * N, out_features)
# The all_combination_matrix, created below, will look like this (|| denotes concatenation):
# e1 || e1
# e1 || e2
# e1 || e3
# ...
# e1 || eN
# e2 || e1
# e2 || e2
# e2 || e3
# ...
# e2 || eN
# ...
# eN || e1
# eN || e2
# eN || e3
# ...
# eN || eN
all_combinations_matrix = torch.cat([Wh_repeated_in_chunks, Wh_repeated_alternating], dim=1)
'''
上述的eij 就是论文中的eij 相当于制造一个全连接的状态 这样将两个矩阵cat并且指定dim=1之后
就得到了一个 size(N * N, 2 * out_features) 的矩阵
'''
# all_combinations_matrix.shape == (N * N, 2 * out_features)
return all_combinations_matrix.view(N, N, 2 * self.out_features)
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' + str(self.out_features) + ')'
class SpecialSpmmFunction(torch.autograd.Function):
"""仅对稀疏区域反向传播层具有特殊功能。"""
'''
@staticmethod
静态实例方法
也就是说我们可以使用SpecialSpmmFunction.forward()来调用我们这个函数
'''
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, indices, values, shape, b):
''' (猜测)
Args:
ctx: 暂时村东西的
indices: 点对的x,y 下标 COO矩阵
values: x,y下标对应的值
shape: 大小
b:
Returns:
'''
assert indices.requires_grad == False
a = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indices, values, shape)
ctx.save_for_backward(a, b) #save_for_backward把后面backward要用的东西下先存起来
ctx.N = shape[0]
return torch.matmul(a, b)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
a, b = ctx.saved_tensors
grad_values = grad_b = None # 消除梯度 (固定步骤)
if ctx.needs_input_grad[1]:
grad_a_dense = grad_output.matmul(b.t())
edge_idx = a._indices()[0, :] * ctx.N + a._indices()[1, :]
grad_values = grad_a_dense.view(-1)[edge_idx]
if ctx.needs_input_grad[3]:
grad_b = a.t().matmul(grad_output)
return None, grad_values, None, grad_b
class SpecialSpmm(nn.Module):
def forward(self, indices, values, shape, b):
return SpecialSpmmFunction.apply(indices, values, shape, b)
class SpGraphAttentionLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Sparse version GAT layer, similar to https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10903
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, dropout, alpha, concat=True):
super(SpGraphAttentionLayer, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.alpha = alpha
self.concat = concat
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(in_features, out_features)))
nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.W.data, gain=1.414)
self.a = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(1, 2*out_features)))
nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.a.data, gain=1.414)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(self.alpha)
self.special_spmm = SpecialSpmm()
def forward(self, input, adj):
dv = 'cuda' if input.is_cuda else 'cpu'
N = input.size()[0]
edge = adj.nonzero().t()
h = torch.mm(input, self.W)
# h: N x out
assert not torch.isnan(h).any()
# Self-attention on the nodes - Shared attention mechanism
edge_h = torch.cat((h[edge[0, :], :], h[edge[1, :], :]), dim=1).t()
# edge: 2*D x E
edge_e = torch.exp(-self.leakyrelu(self.a.mm(edge_h).squeeze()))
assert not torch.isnan(edge_e).any()
# edge_e: E
e_rowsum = self.special_spmm(edge, edge_e, torch.Size([N, N]), torch.ones(size=(N,1), device=dv))
# e_rowsum: N x 1
edge_e = self.dropout(edge_e)
# edge_e: E
h_prime = self.special_spmm(edge, edge_e, torch.Size([N, N]), h)
assert not torch.isnan(h_prime).any()
# h_prime: N x out
h_prime = h_prime.div(e_rowsum)
# h_prime: N x out
assert not torch.isnan(h_prime).any()
if self.concat:
# if this layer is not last layer,
return F.elu(h_prime)
else:
# if this layer is last layer,
return h_prime
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' + str(self.out_features) + ')'
utils.py
这部分代码和GCN源码中基本一样,详细可以看GCN
import numpy as np
import scipy.sparse as sp
import torch
def encode_onehot(labels):
# 必须在编码之前对类进行排序,以启用静态类编码。
# 换句话说,请确保第一类始终映射到索引0
classes = sorted(list(set(labels)))
classes_dict = {c: np.identity(len(classes))[i, :] for i, c in enumerate(classes)}
# 和GCN一样一行向量代表一个特征, 所以 字典hash的时候直接行hash
labels_onehot = np.array(list(map(classes_dict.get, labels)), dtype=np.int32)
'''
class_dict.get 先得到字典的值
然后使用map 函数 进行映射
'''
return labels_onehot
def load_data(path="./data/cora/", dataset="cora"):
"""Load citation network dataset (cora only for now)"""
print('Loading {} dataset...'.format(dataset))
'''
一下引用的cora数据集
cora数据集介绍可以看https://blog.csdn.net/yeziand01/article/details/93374216
'''
idx_features_labels = np.genfromtxt("{}{}.content".format(path, dataset), dtype=np.dtype(str))
features = sp.csr_matrix(idx_features_labels[:, 1:-1], dtype=np.float32)
labels = encode_onehot(idx_features_labels[:, -1]) #最后一列是标签
# build graph
idx = np.array(idx_features_labels[:, 0], dtype=np.int32)
idx_map = {j: i for i, j in enumerate(idx)}
edges_unordered = np.genfromtxt("{}{}.cites".format(path, dataset), dtype=np.int32)
edges = np.array(list(map(idx_map.get, edges_unordered.flatten())), dtype=np.int32).reshape(edges_unordered.shape)
adj = sp.coo_matrix((np.ones(edges.shape[0]), (edges[:, 0], edges[:, 1])), shape=(labels.shape[0], labels.shape[0]), dtype=np.float32)
# build symmetric adjacency matrix
adj = adj + adj.T.multiply(adj.T > adj) - adj.multiply(adj.T > adj)
features = normalize_features(features)
adj = normalize_adj(adj + sp.eye(adj.shape[0]))
'''
划分数据集
'''
idx_train = range(140)
idx_val = range(200, 500)
idx_test = range(500, 1500)
adj = torch.FloatTensor(np.array(adj.todense()))
features = torch.FloatTensor(np.array(features.todense()))
labels = torch.LongTensor(np.where(labels)[1]) # labels 再 dim=1 这个维度的索引,这里就是列
idx_train = torch.LongTensor(idx_train)
idx_val = torch.LongTensor(idx_val)
idx_test = torch.LongTensor(idx_test)
return adj, features, labels, idx_train, idx_val, idx_test
# 返回数据集
def normalize_adj(mx):
"""Row-normalize sparse matrix"""
rowsum = np.array(mx.sum(1))
r_inv_sqrt = np.power(rowsum, -0.5).flatten()
r_inv_sqrt[np.isinf(r_inv_sqrt)] = 0.
r_mat_inv_sqrt = sp.diags(r_inv_sqrt)
return mx.dot(r_mat_inv_sqrt).transpose().dot(r_mat_inv_sqrt)
def normalize_features(mx):
"""Row-normalize sparse matrix"""
rowsum = np.array(mx.sum(1))
r_inv = np.power(rowsum, -1).flatten()
r_inv[np.isinf(r_inv)] = 0.
r_mat_inv = sp.diags(r_inv)
mx = r_mat_inv.dot(mx)
# 用对角矩阵与原始矩阵的点积起到标准化的作用,原始矩阵中每一行
# 元素都会与对应的r_inv相乘,最终相当于除以了sum
return mx
def accuracy(output, labels):
preds = output.max(1)[1].type_as(labels)
correct = preds.eq(labels).double()
correct = correct.sum()
return correct / len(labels)
modle.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from layers import GraphAttentionLayer, SpGraphAttentionLayer
'''
这里有两个modle 一个是GAT 一个是spGAT
'''
class GAT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nfeat, nhid, nclass, dropout, alpha, nheads):
"""Dense version of GAT."""
super(GAT, self).__init__() # 使用super 继承并且能够改写父类方法
self.dropout = dropout
# dropout 参数
self.attentions = [GraphAttentionLayer(nfeat, nhid, dropout=dropout, alpha=alpha, concat=True) for _ in range(nheads)]
'''
这里有多少个头就要有多少组attentions
论文中是三个头所以有三条线(三个头)这里有nheads个
把这些头 装在list里面
'''
for i, attention in enumerate(self.attentions):
# enumerate 函数 把每个attentions 的值和下标组成tuple 分别给i 和 attention
self.add_module('attention_{}'.format(i), attention)
self.out_att = GraphAttentionLayer(nhid * nheads, nclass, dropout=dropout, alpha=alpha, concat=False)
# multi-head 隐藏层到输出
def forward(self, x, adj):
# 前向传播固定格式 输入层添加dropout防止过拟合
x = F.dropout(x, self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = torch.cat([att(x, adj) for att in self.attentions], dim=1)
# torch.cat 对应论文公式(5)
x = F.dropout(x, self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = F.elu(self.out_att(x, adj))
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
'''
spGAT和GAT一样
'''
class SpGAT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nfeat, nhid, nclass, dropout, alpha, nheads):
"""Sparse version of GAT."""
super(SpGAT, self).__init__()
self.dropout = dropout
self.attentions = [SpGraphAttentionLayer(nfeat,
nhid,
dropout=dropout,
alpha=alpha,
concat=True) for _ in range(nheads)]
for i, attention in enumerate(self.attentions):
self.add_module('attention_{}'.format(i), attention)
self.out_att = SpGraphAttentionLayer(nhid * nheads,
nclass,
dropout=dropout,
alpha=alpha,
concat=False)
def forward(self, x, adj):
x = F.dropout(x, self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = torch.cat([att(x, adj) for att in self.attentions], dim=1)
x = F.dropout(x, self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = F.elu(self.out_att(x, adj))
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
train.py
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import glob
import time
import random
import argparse
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
from utils import load_data, accuracy
from models import GAT, SpGAT
# Training settings
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False, help='Disables CUDA training.')
parser.add_argument('--fastmode', action='store_true', default=False, help='Validate during training pass.')
parser.add_argument('--sparse', action='store_true', default=False, help='GAT with sparse version or not.')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=72, help='Random seed.')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=10000, help='Number of epochs to train.')
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.005, help='Initial learning rate.')
parser.add_argument('--weight_decay', type=float, default=5e-4, help='Weight decay (L2 loss on parameters).')
parser.add_argument('--hidden', type=int, default=2, help='Number of hidden units.')
parser.add_argument('--nb_heads', type=int, default=2, help='Number of head attentions.')
parser.add_argument('--dropout', type=float, default=0.6, help='Dropout rate (1 - keep probability).')
parser.add_argument('--alpha', type=float, default=0.2, help='Alpha for the leaky_relu.')
parser.add_argument('--patience', type=int, default=100, help='Patience')
args = parser.parse_args()
args.cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
random.seed(args.seed)
np.random.seed(args.seed)
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
if args.cuda:
torch.cuda.manual_seed(args.seed)
# Load data
adj, features, labels, idx_train, idx_val, idx_test = load_data()
# Model and optimizer
# 选择GAT或者spGAT 和 优化器(optimizer)
if args.sparse:
model = SpGAT(nfeat=features.shape[1],
nhid=args.hidden,
nclass=int(labels.max()) + 1,
dropout=args.dropout,
nheads=args.nb_heads,
alpha=args.alpha)
else:
model = GAT(nfeat=features.shape[1],
nhid=args.hidden,
nclass=int(labels.max()) + 1,
dropout=args.dropout,
nheads=args.nb_heads,
alpha=args.alpha)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),
lr=args.lr,
weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
# 是否选择cuda 运行
if args.cuda:
model.cuda()
features = features.cuda()
adj = adj.cuda()
labels = labels.cuda()
idx_train = idx_train.cuda()
idx_val = idx_val.cuda()
idx_test = idx_test.cuda()
features, adj, labels = Variable(features), Variable(adj), Variable(labels)
'''
Variable 和 Tensor 是pytorch 两个基本的对象
variable是一种可以不断变化的变量,符合反向传播 而tensor不能反向传播
Variable计算时,会逐步生成计算图,这个图将所有的计算节点都连接起来,最后进行loss反向传播时
一次性将所有Variable里的梯度计算出来,然而tensor没有这个能力
所以我们使用GPU算的时候需要将Tensor 转换成 Variable
'''
def train(epoch):
t = time.time()
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(features, adj)
loss_train = F.nll_loss(output[idx_train], labels[idx_train])
acc_train = accuracy(output[idx_train], labels[idx_train])
loss_train.backward()
optimizer.step()
if not args.fastmode:
# Evaluate validation set performance separately,
# deactivates dropout during validation run.
model.eval()
output = model(features, adj)
loss_val = F.nll_loss(output[idx_val], labels[idx_val])
acc_val = accuracy(output[idx_val], labels[idx_val])
print('Epoch: {:04d}'.format(epoch+1),
'loss_train: {:.4f}'.format(loss_train.data.item()),
'acc_train: {:.4f}'.format(acc_train.data.item()),
'loss_val: {:.4f}'.format(loss_val.data.item()),
'acc_val: {:.4f}'.format(acc_val.data.item()),
'time: {:.4f}s'.format(time.time() - t))
return loss_val.data.item()
def compute_test():
model.eval()
output = model(features, adj)
loss_test = F.nll_loss(output[idx_test], labels[idx_test])
acc_test = accuracy(output[idx_test], labels[idx_test])
print("Test set results:",
"loss= {:.4f}".format(loss_test.item()),
"accuracy= {:.4f}".format(acc_test.item()))
# Train model
t_total = time.time()
loss_values = []
bad_counter = 0
best = args.epochs + 1
best_epoch = 0
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
loss_values.append(train(epoch))
torch.save(model.state_dict(), '{}.pkl'.format(epoch))
if loss_values[-1] < best:
best = loss_values[-1]
best_epoch = epoch
bad_counter = 0
else:
bad_counter += 1
if bad_counter == args.patience:
break
files = glob.glob('*.pkl')
for file in files:
epoch_nb = int(file.split('.')[0])
if epoch_nb < best_epoch:
os.remove(file)
files = glob.glob('*.pkl')
for file in files:
epoch_nb = int(file.split('.')[0])
if epoch_nb > best_epoch:
os.remove(file)
print("Optimization Finished!")
print("Total time elapsed: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - t_total))
# Restore best model
print('Loading {}th epoch'.format(best_epoch))
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('{}.pkl'.format(best_epoch)))
# Testing
compute_test()