pytorch神经网络基本骨架nn.module的使用
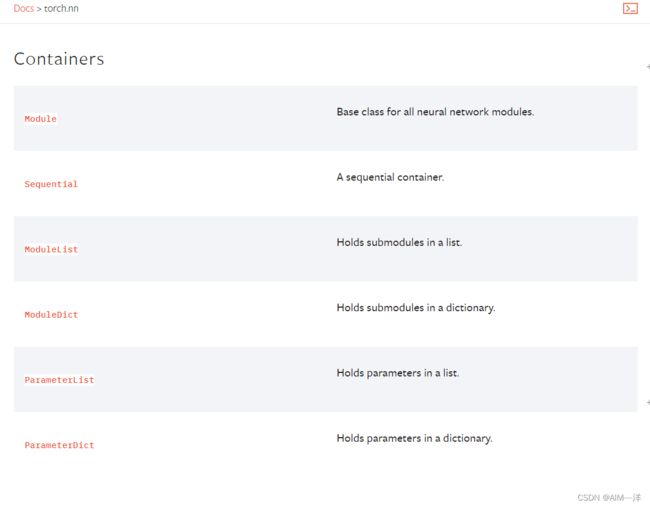
1.Containers
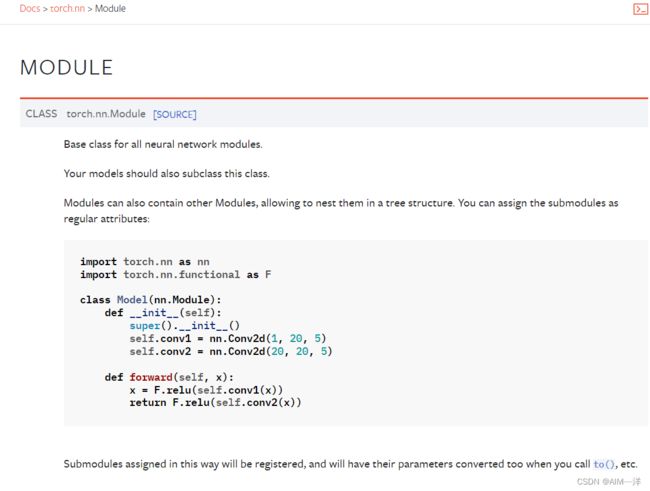
1.1Module
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Module(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Module, self).__init__()
self.conv1=nn.Conv2d(1, 20, 5)
self.conv2=nn.Conv2d(20, 20,5)
def forward(self,x):
x=F.relu(self.conv1(x))
return F.relu(self.conv2(x))
这其中nn.Module的构造函数,一直到super这一行都是一种固定搭配,在下面两行中conv1和conv2是自定义的卷积。

分析最后这个forward(self,x)
输入一个x:
首先是进行了卷积
然后是进行非线性激活函数Relu
再然后又进行了卷积
最后再进行了一次非线性激活函数Relu.
输出。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Module(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Module, self).__init__()
def forward(self,x):
y=x+1
return F.relu(y)
yang=Module()
x=torch.Tensor([1.0])
output=yang(x)
print(output)

我们设置一个简单的程序来使用这个框架,可以看到,在输入张量x后,经过非线性激活函数,最后输出了张量2.0。以一种及其简单的过程走完了框架,更多的内容只需要对其进行填充即可。
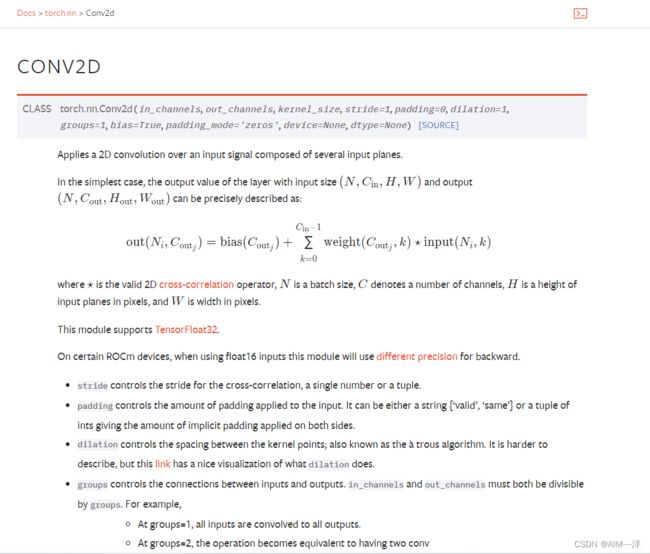
2.Convolution卷积层
2.1.CONV2D
input:在这里为其提供一个输入
weight:权重,也可以叫卷积核
bias:偏置
stride:其中的一个路径,移动步数
padding:
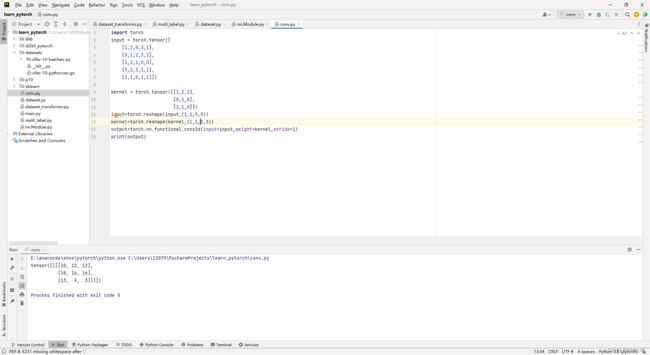
这里设置一个卷积核,和一个5x5的图像数据
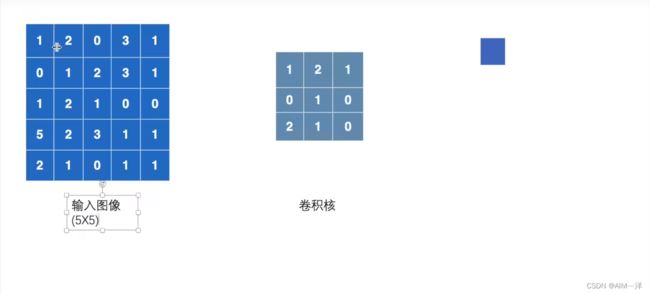
我们将其进行相乘后输出第一个值:10.当Stride为1的时候移动的步数(格子数量)为1.

import torch
input = torch.tensor([
[1,2,0,3,1],
[0,1,2,3,1],
[1,2,1,0,0],
[5,2,3,1,1],
[2,1,0,1,1]])
kernel = torch.tensor([[1,2,1],
[0,1,0],
[2,1,0]])
input=torch.reshape(input,(1,1,5,5))
kernel=torch.reshape(kernel,(1,1,3,3))
output=torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input=input,weight=kernel,stride=1)
print(output)