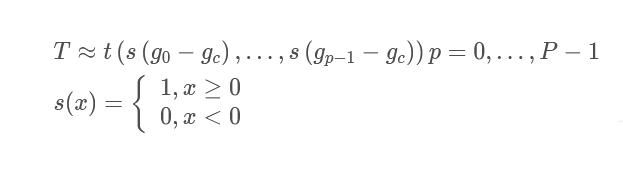2.2 获取图像感兴趣区域_图像之LBP特征描述算子-人脸检测
2.1 简介
LBP指局部二值模式(Local Binary Pattern),是一种用来描述图像局部特征的算子,具有灰度不变性和旋转不变性等显著优点。LBP常应用于人脸识别和目标检测中,在OpenCV中有使用LBP特征进行人脸识别的接口,也有用LBP特征训练目标检测分类器的方法,OpenCV实现了LBP特征的计算,但没有提供一个单独的计算LBP特征的接口。也就是说OpenCV中使用了LBP算法,但是没有提供函数接口。
2.2 算法理论介绍
预备数学:圆的参数方程
代表某个对应圆上某点的半径到x轴的夹角, 和 是圆上某点的坐标。
2.2.1 LBP原理介绍 LBP特征用图像的局部领域的联合分布 来描述图像的纹理特征,如果假设局部邻域中像素个数为,那么纹理特征的联合分布 可以表述成:
其中, 表示相应局部邻域的中心像素的灰度值, 表示以中心像素圆心,以R为半径的圆上的像素的灰度值。
假设中心像素和局部邻域像素相互独立,那么这里可以将上面定义式写成如下形式:
其中决定了局部区域的整体亮度,对于纹理特征,可以忽略这一项,最终得到:
上式说明,将纹理特征定义为邻域像素和中心像素的差的联合分布函数,因为是基本不受亮度均值影响的,所以从上式可以看出,此时统计量T 是一个跟亮度均值,即灰度级无关的值。
最后定义特征函数如下:
定义灰度级不变LBP为:
即二进制编码公式。
通俗解释:
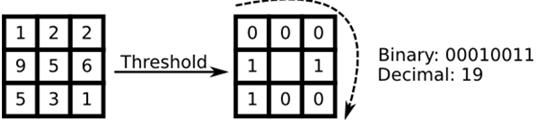
原始的LBP算子定义在像素的邻域内,以邻域中心像素为阈值,相邻的8个像素的灰度值与邻域中心的像素值进行比较,若周围像素大于中心像素值,则该像素点的位置被标记为1,否则为0。这样,邻域内的8个点经过比较可产生8为二进制数,将这8位二进制数依次排列形成一个二进制数字,这个二进制数字就是中心像素的LBP值,LBP值共有种可能,因此LBP值有256种可能。中心像素的LBP值反映了该像素周围区域的纹理信息。
注意:计算LBP特征的图像必须是灰度图,如果是彩色图,需要先转换成灰度图
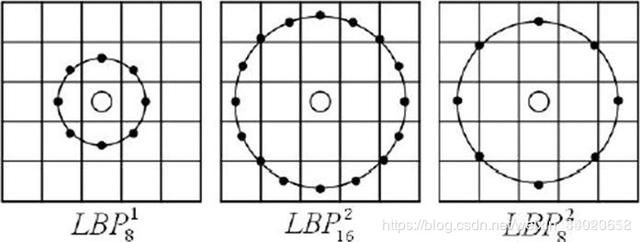
2.2.2 圆形LBP算子
基本的 LBP算子的最大缺陷在于它只覆盖了一个固定半径范围内的小区域,这显然不能满足不同尺寸和频率纹理的需要。为了适应不同尺度的纹理特征,并达到灰度级和旋转不变性的要求,Ojala等对 LBP算子进行了改进,将 3×3邻域扩展到任意邻域,并用圆形邻域代替了正方形邻域,改进后的 LBP算子允许在半径为 R的圆形邻域内有任意多个像素点。从而得到了诸如半径为R的圆形区域内含有P个采样点的LBP算子,表示为;
对于给定中心点,其邻域像素位置为,,其采样点用如下公式计算:
R是采样半径,p是第p个采样点,P是采样数目。如果近邻点不在整数位置上,就需要进行插值运算,可以参考这篇博客 OpenCV框架下的插值算法
3.2.3 LBP旋转不变性及等价模式 LPB特征是灰度不变,但不是旋转不变的,同一幅图像,进行旋转以后,其特征将会有很大的差别,影响匹配的精度。Ojala在LBP算法上,进行改进,实现了具有旋转不变性的LPB的特征。
实现方法:不断旋转圆形邻域得到一系列初始定义的LPB值,取最小值作为该邻域的值。
其中表示具有旋转不变性的LBP特征。为旋转函数,表示将右循环位。
1、举个例子,你是否困惑,一个图像的每一个像素点邻域内的像素点的值都是固定的,得到的采样点经过处理得到的值不是1就是0就已经确定下来了。那是如何实现圆形领域的旋转呢?
事实上,应该换个角度,并且是通过示例的方式来理解。
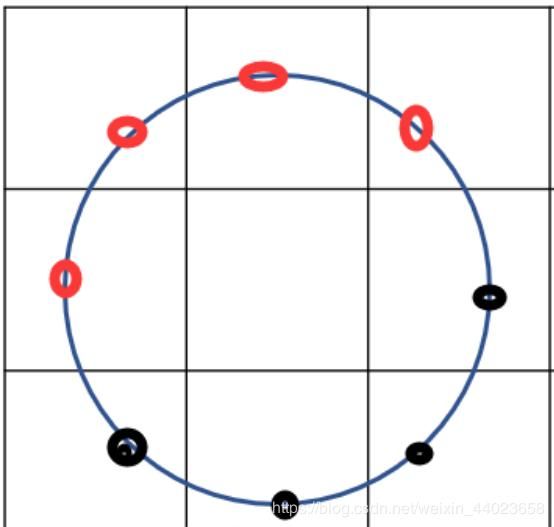
假设,我规定一个图像全部使用半径为1且采样点为8的邻域且这个领域中已经确定有四个点的为0,另外四个点为1,而组合顺序不定。比如其中的一种情况如下图:
那么我们可以想一下,会有多少种序列的排列情况。应该是 种
- 事实上, 如果仅告知要使用半径为1采样点为8的邻域, 对于任意一个区域, 圆形LBP值会产生 256种不同的输出
- 注意邻域是由半径和采样点共同决定,并且是对图像所有像素点均使用相同种类的邻域
2、为了能将这个问题解释得稍微简单,我们再简化一个场景
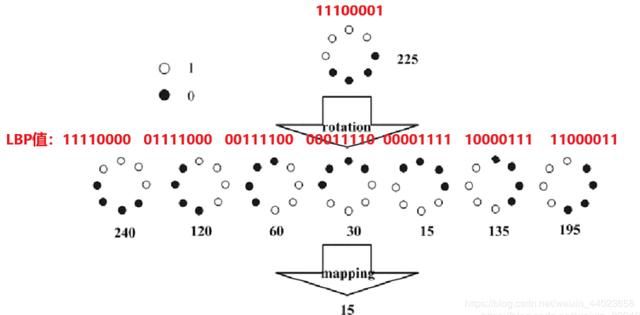
假设某个像素点计算得到的二进制模式为:11100001,求解其旋转不变性处理后的LBP值(十进制)。
第一,由11100001可知,该像素点在进行LBP算子计算时的邻域设定为采样点为8。并且,该中心点所在邻域的8个像素点中存在4个位置的像素点的数值大于中心像素。1110001的LBP值是225。 第二,计算8个采样点且四个值为1的二进制模式,并且跟“11100001”类似的是这四个1的点要紧挨着进行旋转的二进制模式,如下图所示,除了11100001,还有另外7种模式。经过计算可知,加上11100001总共8种模式对应的LBP值中15是最小,所以11100001经过旋转处理后的LBP值就不再是225,而是15了。
同理,当某个像素点的二进制模式为以下7种(11110000、01111000、00111100、00011110、00001111、10000111、11000011)的任意一种,其旋转不变性的LBP值都是15!
等价模式:
一个LBP算子可以产生不同的二进制模式,对于将会产生种模式。比如邻域内有种模式。如此多的二值模式对于信息的提取和识别都是不利的。
Ojala等认为,在实际图像中,绝大多数LPB模式最多只包含两次从1到0或从0到1的跳变。
等价模式:当某个局部二进制模式所对应的循环二进制数从0到1或从1到0最多有两次跳变时,该局部二进制模式所对应的二进制就称为一个等价模式。
比如:00000000,11111111,11110010,10111111都是等价模式。
检查某种模式是否是等价模式:
将其和其移动一位后的二进制模式按位相减。并绝对值求和。若U 小于等于2,则为等价模式。
混合模式:除了等价模式之外的称为混合模式。
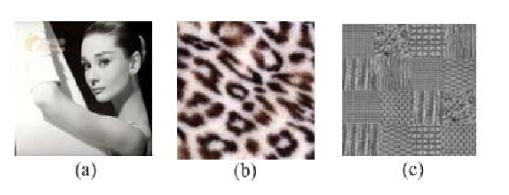
改进后的LPB模式数由2 (p为邻域集内的采集点数 ) 降维为 。维数减少,可以降低高频噪声的影响。Ojala认为等价模式占总模式中的绝大数。下图( a ), ( b ), ( c )等价模式分别占88%,93%和76%。
可以通过低通滤波的方法来增强等价模式所占的比例。图( c )经过高斯滤波后,其等价模式所占比可以增加到90%。
直方图计算 LBP有多少维,直方图就有多少个区间,直方图计算首先统计每一个区间里面的像素个数。一般还会将一副图划分几个子区域
然后统计每个区域的直方图,即每个LBP值出现的频率;然后对该直方图进行归一化处理。最后将得到的每个区域的统计直方图进行连接成为一个特征向量,也就是整幅图的LBP纹理特征向量。最后用分类器进行分类。
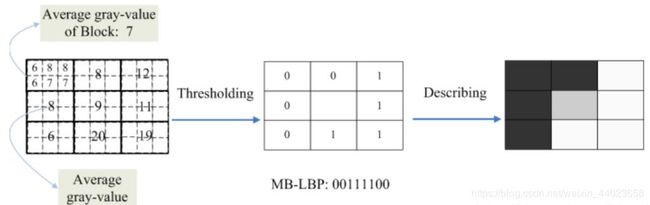
MB-LBP 传统的LBP特征能获取的信息有限,MB-LBP特征将一张图片划分为几个矩形区域,再分别获取矩形区域里面的特征。
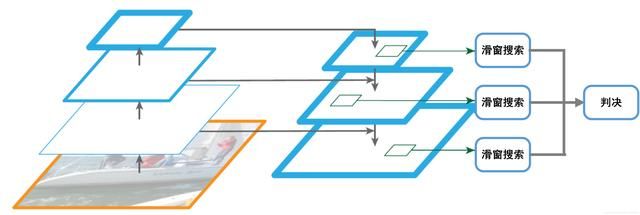
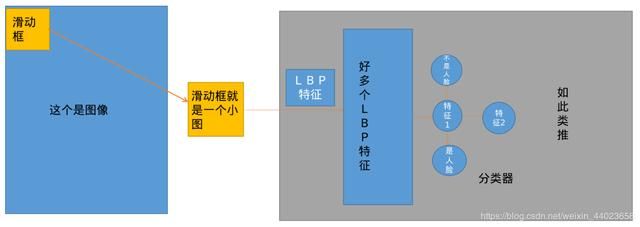
2.3.4 人脸检测流程 人脸检测过程采用多尺度滑窗搜索方式,每个尺度通过一定步长截取大小为20x20的窗口,然后将窗口放到分类器中进行是不是人脸的判决,如果是人脸则该窗口通过所有分类器;反之,会在某一级分类器被排除。
2.3 基于OpenCV的实现
- 使用OpenCV的LBP于预训练模型
- 将haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml下载至本地以方便调用,下载链接:https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/master/data/lbpcascades/lbpcascade_frontalface_improved.xml
python
#coding:utf-8import cv2 as cv# 读取原始图像img= cv.imread('E:/python-project/deep-learning/picture/test2.jpg')#face_detect = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')face_detect = cv.CascadeClassifier("E:/python-project/deep-learning/picture/lbpcascade_frontalface_improved.xml")# 检测人脸# 灰度处理gray = cv.cvtColor(img, code=cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 检查人脸 按照1.1倍放到 周围最小像素为5face_zone = face_detect.detectMultiScale(gray, scaleFactor = 2, minNeighbors = 2) # maxSize = (55,55)print ('识别人脸的信息:',face_zone)# 绘制矩形和圆形检测人脸for x, y, w, h in face_zone: # 绘制矩形人脸区域 cv.rectangle(img, pt1 = (x, y), pt2 = (x+w, y+h), color = [0,0,255], thickness=2) # 绘制圆形人脸区域 radius表示半径 cv.circle(img, center = (x + w//2, y + h//2), radius = w//2, color = [0,255,0], thickness = 2)# 设置图片可以手动调节大小cv.namedWindow("Easmount-CSDN", 0)# 显示图片cv.imshow("Easmount-CSDN", img)# 等待显示 设置任意键退出程序cv.waitKey(0)cv.destroyAllWindows()在这里插入图片描述
c++
uchar GetMinBinary(uchar *binary){ // 计算8个二进制 uchar LBPValue[8] = { 0 }; for (int i = 0; i <= 7; ++i) { LBPValue[0] += binary[i] <= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 128; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 - widthOfExtendedImage] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 64; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 - widthOfExtendedImage + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 32; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 16; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 8; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 4; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage - 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 2; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 - 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 1; colOfLBPImage[0] = LBPValue; } }}// 等价灰度不变LBP(58)void UniformNormalLBPImage(const Mat &srcImage, Mat &LBPImage)// 计算等价模式LBP特征图{ // 参数检查,内存分配 CV_Assert(srcImage.depth() == CV_8U && srcImage.channels() == 1); LBPImage.create(srcImage.size(), srcImage.type()); // 计算LBP图 // 扩充原图像边界,便于边界处理 Mat extendedImage; copyMakeBorder(srcImage, extendedImage, 1, 1, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT); // 构建LBP 等价模式查找表 //int table[256]; //BuildUniformPatternTable(table); // LUT(256种每一种模式对应的等价模式) static const int table[256] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 6, 7, 8, 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 11, 12, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 13, 0, 0, 0, 14, 0, 15, 16, 17, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 18, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 19, 0, 0, 0, 20, 0, 21, 22, 23, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 24, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 25, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 26, 0, 0, 0, 27, 0, 28, 29, 30, 31, 0, 32, 0, 0, 0, 33, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 34, 0, 0, 0, 0 , 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 35, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 36, 37, 38, 0, 39, 0, 0, 0, 40, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 41, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 42 , 43, 44, 0, 45, 0, 0, 0, 46, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 47, 48, 49, 0, 50, 0, 0, 0, 51, 52, 53, 0, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58 }; // 计算LBP int heightOfExtendedImage = extendedImage.rows; int widthOfExtendedImage = extendedImage.cols; int widthOfLBP = LBPImage.cols; uchar *rowOfExtendedImage = extendedImage.data + widthOfExtendedImage + 1; uchar *rowOfLBPImage = LBPImage.data; for (int y = 1; y <= heightOfExtendedImage - 2; ++y, rowOfExtendedImage += widthOfExtendedImage, rowOfLBPImage += widthOfLBP) { // 列 uchar *colOfExtendedImage = rowOfExtendedImage; uchar *colOfLBPImage = rowOfLBPImage; for (int x = 1; x <= widthOfExtendedImage - 2; ++x, ++colOfExtendedImage, ++colOfLBPImage) { // 计算LBP值 int LBPValue = 0; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 - widthOfExtendedImage - 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 128; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 - widthOfExtendedImage] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 64; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 - widthOfExtendedImage + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 32; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 16; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 8; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 4; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage - 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 2; if (colOfExtendedImage[0 - 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0]) LBPValue += 1; colOfLBPImage[0] = table[LBPValue]; } }}// 等价旋转不变LBP(9)void UniformRotInvLBPImage(const Mat &srcImage, Mat &LBPImage){ // 参数检查,内存分配 CV_Assert(srcImage.depth() == CV_8U && srcImage.channels() == 1); LBPImage.create(srcImage.size(), srcImage.type()); // 扩充图像,处理边界情况 Mat extendedImage; copyMakeBorder(srcImage, extendedImage, 1, 1, 1, 1, BORDER_DEFAULT); // 构建LBP 等价模式查找表 //int table[256]; //BuildUniformPatternTable(table); // 通过查找表 static const int table[256] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 6, 7, 8, 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 11, 12, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 13, 0, 0, 0, 14, 0, 15, 16, 17, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 18, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 19, 0, 0, 0, 20, 0, 21, 22, 23, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 24, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 25, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 26, 0, 0, 0, 27, 0, 28, 29, 30, 31, 0, 32, 0, 0, 0, 33, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 34, 0, 0, 0, 0 , 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 35, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 36, 37, 38, 0, 39, 0, 0, 0, 40, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 41, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 42 , 43, 44, 0, 45, 0, 0, 0, 46, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 47, 48, 49, 0, 50, 0, 0, 0, 51, 52, 53, 0, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58 }; uchar binary[8] = { 0 };// 记录每个像素的LBP值 int heigthOfExtendedImage = extendedImage.rows; int widthOfExtendedImage = extendedImage.cols; int widthOfLBPImage = LBPImage.cols; uchar *rowOfExtendedImage = extendedImage.data + widthOfExtendedImage + 1; uchar *rowOfLBPImage = LBPImage.data; for (int y = 1; y <= heigthOfExtendedImage - 2; ++y, rowOfExtendedImage += widthOfExtendedImage, rowOfLBPImage += widthOfLBPImage) { // 列 uchar *colOfExtendedImage = rowOfExtendedImage; uchar *colOfLBPImage = rowOfLBPImage; for (int x = 1; x <= widthOfExtendedImage - 2; ++x, ++colOfExtendedImage, ++colOfLBPImage) { // 计算旋转不变LBP(最小的二进制模式) binary[0] = colOfExtendedImage[0 - widthOfExtendedImage - 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0] ? 1 : 0; binary[1] = colOfExtendedImage[0 - widthOfExtendedImage] >= colOfExtendedImage[0] ? 1 : 0; binary[2] = colOfExtendedImage[0 - widthOfExtendedImage + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0] ? 1 : 0; binary[3] = colOfExtendedImage[0 + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0] ? 1 : 0; binary[4] = colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage + 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0] ? 1 : 0; binary[5] = colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage] >= colOfExtendedImage[0] ? 1 : 0; binary[6] = colOfExtendedImage[0 + widthOfExtendedImage - 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0] ? 1 : 0; binary[7] = colOfExtendedImage[0 - 1] >= colOfExtendedImage[0] ? 1 : 0; int minValue = GetMinBinary(binary); // 计算58种等价模式LBP int value58 = table[minValue]; // 计算9种等价模式 colOfLBPImage[0] = ComputeValue9(value58); } }}//灰度不变常规LBP(256)特征void NormalLBPFeature(const Mat &srcImage, Size cellSize, Mat &featureVector){ // 参数检查,内存分配 CV_Assert(srcImage.depth() == CV_8U && srcImage.channels() == 1); Mat LBPImage; NormalLBPImage(srcImage, LBPImage); // 计算cell个数 int widthOfCell = cellSize.width; int heightOfCell = cellSize.height; int numberOfCell_X = srcImage.cols / widthOfCell;// X方向cell的个数 int numberOfCell_Y = srcImage.rows / heightOfCell; // 特征向量的个数 int numberOfDimension = 256 * numberOfCell_X*numberOfCell_Y; featureVector.create(1, numberOfDimension, CV_32FC1); featureVector.setTo(Scalar(0)); // 计算LBP特征向量 int stepOfCell = srcImage.cols; int pixelCount = cellSize.width*cellSize.height; float *dataOfFeatureVector = (float *)featureVector.data; // cell的特征向量在最终特征向量中的起始位置 int index = -256; for (int y = 0; y <= numberOfCell_Y - 1; ++y) { for (int x = 0; x <= numberOfCell_X - 1; ++x) { index += 256; // 计算每个cell的LBP直方图 Mat cell = LBPImage(Rect(x * widthOfCell, y * heightOfCell, widthOfCell, heightOfCell)); uchar *rowOfCell = cell.data; for (int y_Cell = 0; y_Cell <= cell.rows - 1; ++y_Cell, rowOfCell += stepOfCell) { uchar *colOfCell = rowOfCell; for (int x_Cell = 0; x_Cell <= cell.cols - 1; ++x_Cell, ++colOfCell) { ++dataOfFeatureVector[index + colOfCell[0]]; } } // 一定要归一化!否则分类器计算误差很大 for (int i = 0; i <= 255; ++i) dataOfFeatureVector[index + i] /= pixelCount; } }}// 等价灰度不变LBP(58)特征void UniformNormalLBPFeature(const Mat &srcImage, Size cellSize, Mat &featureVector){ // 参数检查,内存分配 CV_Assert(srcImage.depth() == CV_8U && srcImage.channels() == 1); Mat LBPImage; UniformNormalLBPImage(srcImage, LBPImage); // 计算cell个数 int widthOfCell = cellSize.width; int heightOfCell = cellSize.height; int numberOfCell_X = srcImage.cols / widthOfCell;// X方向cell的个数 int numberOfCell_Y = srcImage.rows / heightOfCell; // 特征向量的个数 int numberOfDimension = 58 * numberOfCell_X*numberOfCell_Y; featureVector.create(1, numberOfDimension, CV_32FC1); featureVector.setTo(Scalar(0)); // 计算LBP特征向量 int stepOfCell = srcImage.cols; int index = -58;// cell的特征向量在最终特征向量中的起始位置 float *dataOfFeatureVector = (float *)featureVector.data; for (int y = 0; y <= numberOfCell_Y - 1; ++y) { for (int x = 0; x <= numberOfCell_X - 1; ++x) { index += 58; // 计算每个cell的LBP直方图 Mat cell = LBPImage(Rect(x * widthOfCell, y * heightOfCell, widthOfCell, heightOfCell)); uchar *rowOfCell = cell.data; int sum = 0; // 每个cell的等价模式总数 for (int y_Cell = 0; y_Cell <= cell.rows - 1; ++y_Cell, rowOfCell += stepOfCell) { uchar *colOfCell = rowOfCell; for (int x_Cell = 0; x_Cell <= cell.cols - 1; ++x_Cell, ++colOfCell) { if (colOfCell[0] != 0) { // 在直方图中转化为0~57,所以是colOfCell[0] - 1 ++dataOfFeatureVector[index + colOfCell[0] - 1]; ++sum; } } } // 一定要归一化!否则分类器计算误差很大 for (int i = 0; i <= 57; ++i) dataOfFeatureVector[index + i] /= sum; } }}// 等价旋转不变LBP(9)特征void UniformRotInvLBPFeature(const Mat &srcImage, Size cellSize, Mat &featureVector){ // 参数检查,内存分配 CV_Assert(srcImage.depth() == CV_8U && srcImage.channels() == 1); Mat LBPImage; UniformRotInvLBPImage(srcImage, LBPImage); // 计算cell个数 int widthOfCell = cellSize.width; int heightOfCell = cellSize.height; int numberOfCell_X = srcImage.cols / widthOfCell;// X方向cell的个数 int numberOfCell_Y = srcImage.rows / heightOfCell; // 特征向量的个数 int numberOfDimension = 9 * numberOfCell_X*numberOfCell_Y; featureVector.create(1, numberOfDimension, CV_32FC1); featureVector.setTo(Scalar(0)); // 计算LBP特征向量 int stepOfCell = srcImage.cols; int index = -9;// cell的特征向量在最终特征向量中的起始位置 float *dataOfFeatureVector = (float *)featureVector.data; for (int y = 0; y <= numberOfCell_Y - 1; ++y) { for (int x = 0; x <= numberOfCell_X - 1; ++x) { index += 9; // 计算每个cell的LBP直方图 Mat cell = LBPImage(Rect(x * widthOfCell, y * heightOfCell, widthOfCell, heightOfCell)); uchar *rowOfCell = cell.data; int sum = 0; // 每个cell的等价模式总数 for (int y_Cell = 0; y_Cell <= cell.rows - 1; ++y_Cell, rowOfCell += stepOfCell) { uchar *colOfCell = rowOfCell; for (int x_Cell = 0; x_Cell <= cell.cols - 1; ++x_Cell, ++colOfCell) { if (colOfCell[0] != 0) { // 在直方图中转化为0~8,所以是colOfCell[0] - 1 ++dataOfFeatureVector[index + colOfCell[0] - 1]; ++sum; } } } // 直方图归一化 for (int i = 0; i <= 8; ++i) dataOfFeatureVector[index + i] /= sum; } }}