Python---OpenCV入门之图像轮廓
目录
前言
一、图像轮廓
1.图像轮廓的概念
2.查找图像轮廓
3.cv2.findContours()函数
4.绘制图像轮廓
二、计算轮廓的面积及长度
1.矩特征
2.计算轮廓的面积
3.计算轮廓的长度
三、Hu特征
四、轮廓拟合
1.矩形包围框
2.最小包围框
3.最小包围圆形
4.最优拟合椭圆
5.最优拟合直线
总结
前言
随着人工智能的不断发展,OpenCV这门技术也越来越重要,很多人都开启了学习OpenCV,本文就介绍了OpenCV的基础的内容
本内容素材来自小傅老师
原图:shape.jpg
一、图像轮廓
1.图像轮廓的概念
2.查找图像轮廓
3.cv2.findContours()函数
4.绘制图像轮廓
二、计算轮廓的面积及长度
1.矩特征
2.计算轮廓的面积
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('shape.jpg') #读取图像
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) #转为灰度值图
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray,220,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY) #转为二值图
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_TREE,\
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) #寻找轮廓
n=len(contours) #轮廓个数
contoursImg=[]
for i in range(n):
area = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
print(f"轮廓{i}的面积:\n{area}")
3.计算轮廓的长度
n=len(contours) #轮廓个数
contoursImg=[]
for i in range(n):
length = cv2.arcLength(contours[i], True) #获取轮廓长度
print(f"轮廓{i}的长度:\n{length}")
三、Hu特征
Hu矩是归一化中心矩的线性组合,Hu矩再图像旋转,缩放,平移等操作后,仍能保持矩的不变性,经常使用 Hu 矩来识别图像的特征。在 OpenCV 中,使用函数 cv2.HuMoments()可以得到 Hu 距。该函数使用 cv2.moments()函数的返回值作为参数,返回 7 个 Hu 矩值。
1.形状匹配
通过Hu 矩可以来判断两个对象的一致性。但是结果比较抽象,OpenCV 提供了 cv2.matchShapes() 对两个对象的Hu矩进行比较。
import cv2
o1 = cv2.imread('m1.png')
o2 = cv2.imread('m2.png')
o3 = cv2.imread('m3.png')
gray1 = cv2.cvtColor(o1,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray2 = cv2.cvtColor(o2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray3 = cv2.cvtColor(o3,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, binary1 = cv2.threshold(gray1,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret, binary2 = cv2.threshold(gray2,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret, binary3 = cv2.threshold(gray3,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours1, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary1,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours2, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary2,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours3, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary3,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnt1 = contours1[0]
cnt2 = contours2[0]
cnt3 = contours3[0]
ret0 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt1,1,0.0)
ret1 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt2,1,0.0)
ret2 = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt3,1,0.0)
print("相同图像的 matchShape=",ret0)
print("相似图像的 matchShape=",ret1)
print("不相似图像的 matchShape=",ret2)
四、轮廓拟合
1.矩形包围框
import cv2
img=cv2.imread('shape.jpg')
cv2.imshow("original",img)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
x,y,w,h=cv2.boundingRect(contours[0])
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,0,0),2)
cv2.imshow("result",img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()结果:
2.最小包围框
import cv2
o=cv2.imread('shape.jpg')
cv2.imshow("original",o)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(o,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contours[1])
print("返回值 rect:\n",rect)
points = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
print("\n 转换后的 points:\n",points)
points = np.int64(points) #取整,np.int64=np.int0
image=cv2.drawContours(o,[points],0,(0,0,0),2)
cv2.imshow("result",o)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()结果
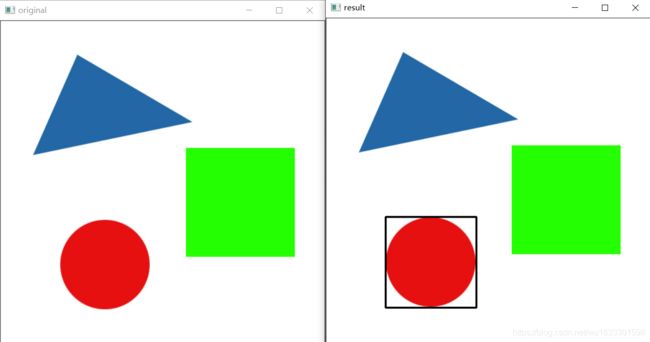
3.最小包围圆形
import cv2
o=cv2.imread('shape.jpg')
cv2.imshow("original",o)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(o,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
(x,y),radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(contours[1])
center = (int(x),int(y))
radius = int(radius)
cv2.circle(o,center,radius,(0,0,0),2) # 跟 matplotlib 类似吧。。
cv2.imshow("result",o)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()4.最优拟合椭圆
import cv2
o=cv2.imread('shape.jpg')
cv2.imshow("original",o)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(o,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(contours[1])
print("ellipse=",ellipse)
cv2.ellipse(o,ellipse,(0,255,0),3)
cv2.imshow("result",o)
cv2.waitKey(0)
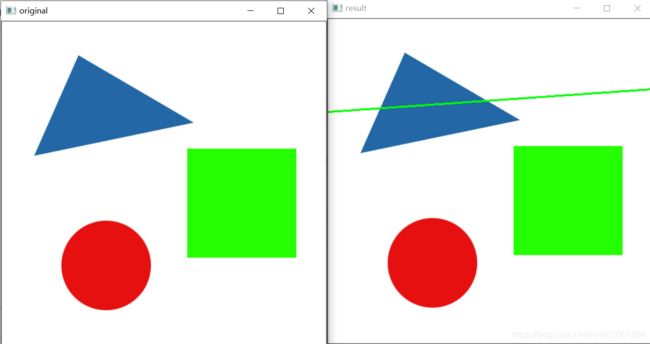
cv2.destroyAllWindows()5.最优拟合直线
import cv2
o=cv2.imread('shape.jpg')
cv2.imshow("original",o)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(o,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
rows,cols = o.shape[:2]
[vx,vy,x,y] = cv2.fitLine(contours[1], cv2.DIST_L2,0,0.01,0.01) # 返回值是共线的归一化向量,和线上一点
lefty = int((-x*vy/vx) + y) # 说白了就是一个方向和一个点,点斜式嘛,还啥vec4f,,讲究
righty = int(((cols-x)*vy/vx)+y) # 计算两个点,代值计算就行
cv2.line(o,(cols-1,righty),(0,lefty),(0,255,0),2)
cv2.imshow("result",o)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容。