深度学习01--Mnist手写体识别
纯记录自己在深度学习方面的学习历程--基于b站的人工智能许多up主的教学视频
- 定义一个多层感知机的类
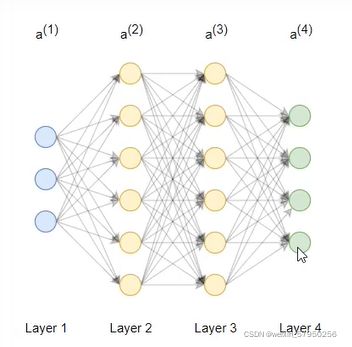
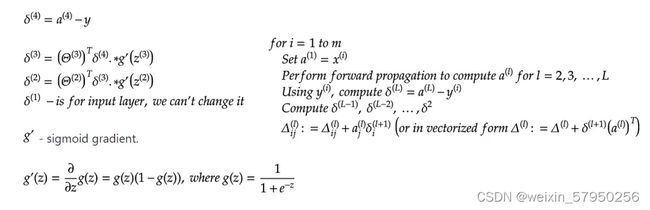
import numpy as np from utils.features import prepare_for_training from utils.hypothesis import sigmoid, sigmoid_gradient # 定义一个类,叫多层感知机--multilayer perceptron class MultilayerPerceptron: # 初始化,data--数据,label--标签,layers--神经网络层数,normalize_data--归一化 def __init__(self, data, labels, layers, normalize_data=False): data_processed = prepare_for_training(data, normalize_data=normalize_data)[0] self.data = data_processed self.labels = labels self.layers = layers # 预计三层 28*28*1=784 25 10 self.normalize_data = normalize_data self.ws = MultilayerPerceptron.w_init(layers) # 对权重参数的初始化 # 训练模块 max--迭代次数,alpha--学习率 def train(self, max=1000, alpha=0.1): unroll_ws = MultilayerPerceptron.unroll(self.ws) (optimized_ws, loss_history) = MultilayerPerceptron.gradient_descent(self.data, self.labels, self.layers, unroll_ws, max, alpha) self.ws = MultilayerPerceptron.roll(optimized_ws, self.layers) return self.ws, loss_history # 测试 def predict(self, data): data_processed = prepare_for_training(data, normalize_data=self.normalize_data)[0] num_examples = data_processed.shape[0] predictions = MultilayerPerceptron.forward(data_processed, self.layers, self.ws) return np.argmax(predictions, axis=1).reshape((num_examples, 1)) # 对权重参数的初始化 def w_init(layers): num_layers = len(layers) ws = {} # 实际循环两次,生成两个w矩阵:25*785 10*26 for index in range(num_layers - 1): income = layers[index] outcome = layers[index + 1] # +1根据权重公式xw+b,考虑到b,例784*25+25=(784+1)*25 ws[index] = np.random.rand(outcome, income + 1) * 0.05 # *0.05是使随机生成的值尽量小 return ws # 将矩阵展开为一维向量 def unroll(matrixs): num_matrixs = len(matrixs) result = np.array([]) for index in range(num_matrixs): result = np.hstack((result, matrixs[index].flatten())) return result # 将一维向量转为矩阵 def roll(matrixs, layers): num_layers = len(layers) result = {} shift = 0 for index in range(num_layers - 1): income = layers[index] outcome = layers[index + 1] matrix_width = income + 1 matrix_heigh = outcome start = shift end = start + matrix_heigh * matrix_width result[index] = matrixs[start:end].reshape(matrix_heigh, matrix_width) shift = shift + matrix_heigh * matrix_width return result # 梯度下降 def gradient_descent(data, labels, layers, unroll_ws, max, alpha): optimized_ws = unroll_ws loss_history = [] for index in range(max): loss = MultilayerPerceptron.loss_function(data, labels, layers, MultilayerPerceptron.roll(optimized_ws, layers)) loss_history.append(loss) gradient_w = MultilayerPerceptron.gradient_step(data, labels, optimized_ws, layers) optimized_ws = optimized_ws - alpha * gradient_w return optimized_ws, loss_history # 损失函数 def loss_function(data, labels, layers, ws): num_examples = data.shape[0] num_labels = layers[-1] # one hot 编码 one_hot_labels = np.zeros((num_examples, num_labels)) for index in range(num_examples): one_hot_labels[index][labels[index][0]] = 1 # 前向传播,得到预测值 predictions = MultilayerPerceptron.forward(data, layers, ws) set1_loss = np.sum(np.log(predictions[one_hot_labels == 1])) set0_loss = np.sum(np.log(1 - predictions[one_hot_labels == 0])) loss = (-1 / num_examples) * (set0_loss + set1_loss) return loss # 前向传播 def forward(data, layers, ws): num_layers = len(layers) num_examples = data.shape[0] income = data for index in range(num_layers - 1): w = ws[index] outcome_activation = sigmoid(np.dot(income, w.T)) # 这里只计算了wx,没有加上b outcome_activation = np.hstack((np.ones((num_examples, 1)), outcome_activation)) # 加了一列1 income = outcome_activation return income[:, 1:] # 最终返回结果不含b # 逐层计算梯度 def gradient_step(data, labels, optimized_ws, layers): ws = MultilayerPerceptron.roll(optimized_ws, layers) w_gradient = MultilayerPerceptron.back(data, labels, ws, layers) w_gradient_unroll = MultilayerPerceptron.unroll(w_gradient) return w_gradient_unroll # 反向传播 def back(data, labels, thetas, layers): num_layers = len(layers) (num_examples, num_features) = data.shape num_label_types = layers[-1] # 存放每一层对结果的影响 deltas = {} for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1): in_count = layers[layer_index] out_count = layers[layer_index + 1] deltas[layer_index] = np.zeros((out_count, in_count + 1)) # 25*785 10*26 for example_index in range(num_examples): # 拿到输入层 layers_inputs = {} layers_activations = {} layers_activation = data[example_index, :].reshape((num_features, 1)) layers_activations[0] = layers_activation # 逐层计算 for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1): layer_theta = thetas[layer_index] layer_input = np.dot(layer_theta, layers_activation) layers_activation = np.vstack((np.array([1]), sigmoid(layer_input))) layers_inputs[layer_index + 1] = layer_input # 后一层结果 layers_activations[layer_index + 1] = layers_activation # 后一层经过激活函数的结果 output_layer_activation = layers_activation[1:, :] # 保持输出结果与真实值之间的差异 delta = {} # 真实结果 bitwise_label = np.zeros((num_label_types, 1)) bitwise_label[labels[example_index][0]] = 1 # 计算 delta[num_layers - 1] = output_layer_activation - bitwise_label # 遍历循环 L L-1 L-2....2 for layer_index in range(num_layers - 2, 0, -1): layer_theta = thetas[layer_index] next_delta = delta[layer_index + 1] layer_input = layers_inputs[layer_index] layer_input = np.vstack((np.array((1)), layer_input)) delta[layer_index] = np.dot(layer_theta.T, next_delta) * sigmoid_gradient(layer_input) delta[layer_index] = delta[layer_index][1:, :] # 微调结果 for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1): layer_delta = np.dot(delta[layer_index + 1], layers_activations[layer_index].T) deltas[layer_index] = deltas[layer_index] + layer_delta for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1): deltas[layer_index] = deltas[layer_index] * (1 / num_examples) return deltas -
在main中调用,并进行可视化的展示(mnist数据集可以自己去下载)
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import math from multilayer_perceptron import MultilayerPerceptron data = pd.read_csv('./data/MNIST_CSV格式/mnist_train.csv') # 展示数据 numbers = 25 num_cell = math.ceil(math.sqrt(numbers)) plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) for plot in range(numbers): picture = data[plot:plot+1].values label = picture[0][0] pixel = picture[0][1:] picture_size = int(math.sqrt(pixel.shape[0])) frame = pixel.reshape((picture_size,picture_size)) plt.subplot(num_cell,num_cell,plot+1) plt.imshow(frame,cmap='Greys') plt.title(label) plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.5,hspace=0.5) plt.show() train_data = data.sample(frac=0.8) test_data = data.drop(train_data.index) train_data = train_data.values test_data = test_data.values num_training_examples = 700 pixel_train = train_data[:num_training_examples,1:] label_train = train_data[:num_training_examples,[0]] pixel_test = test_data[:,1:] label_test = test_data[:,[0]] layers=[784,25,10] normalize_data = True max = 300 alpha = 0.1 multilayerPerceptron = MultilayerPerceptron(pixel_train,label_train,layers,normalize_data) (ws,loss_history) = multilayerPerceptron.train(max,alpha) plt.plot(range(len(loss_history)),loss_history) plt.xlabel('Gradient descent steps') plt.ylabel('loss') plt.show() result_train = multilayerPerceptron.predict(pixel_train) result_test = multilayerPerceptron.predict(pixel_test) train_percent = np.sum(result_train == label_train) / label_train.shape[0] * 100 test_percent = np.sum(result_test == label_test) / label_test.shape[0] * 100 print('训练集准确率',train_percent) print('测试集准确率',test_percent) numbers_to_display = 64 num_cells = math.ceil(math.sqrt(numbers_to_display)) plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15)) for plot_index in range(numbers_to_display): digit_label = label_test[plot_index, 0] digit_pixels = pixel_test[plot_index, :] predicted_label = result_test[plot_index][0] image_size = int(math.sqrt(digit_pixels. shape[0])) frame = digit_pixels.reshape((image_size, image_size)) color_map = 'Greens' if predicted_label == digit_label else 'Reds' plt.subplot(num_cells, num_cells, plot_index + 1) plt.imshow(frame, cmap=color_map) plt.title(predicted_label) plt.tick_params(axis='both',which='both',bottom=False,left=False,labelbottom=False) plt.subplots_adjust (hspace=0.5,wspace=0.5) plt.show( )