【第一周】数据分析之表示
numpy
Python数据分析与展示_北京理工大学_中国大学MOOC(慕课)
NumPy(Numerical Python) 是 Python 语言的一个扩展程序库,支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算,此外也针对数组运算提供大量的数学函数库。
NumPy 是一个运行速度非常快的数学库,主要用于数组计算,包含:
-
一个强大的N维数组对象 ndarray
-
广播功能函数
-
整合 C/C++/Fortran 代码的工具
-
线性代数、傅里叶变换、随机数生成等功能
创建数组
np.empty()的用法
import numpy as np empty(shape[, dtype, order])
依给定的shape, 和数据类型 dtype, 返回一个一维或者多维数组,数组的元素不为空,为随机产生的数据。
import numpy as np arr4 = np.empty((3, 4), dtype=int) print(arr4)
[[-395521520 577 -395521616 577] [-396143056 577 7733349 7077989] [ 7340143 7471205 7602271 7274607]]
np.arange()
左闭右开
import numpy as np
arr5 = np.arange(10, 20)
print(arr5)
arr6 = np.arange(6)
print(arr6)
arr7 = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)
print('arr7 =\n', arr7)
[10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19] [0 1 2 3 4 5]
arr7 = [[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11]]
arr7 = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 5)
ValueError: cannot reshape array of size 12 into shape (3,5)
np.linspace()
np.linspace主要用来创建等差数列。
用于在线性空间中以均匀步长生成数字序列
默认情况下为闭区间
start:返回样本数据开始点
stop:返回样本数据结束点
num:生成的样本数据量,默认为50
endpoint:True则包含stop;False则不包含stop
retstep:If True, return (samples, step), where step is the spacing between samples.(即如果为True则结果会给出数据间隔)
dtype:输出数组类型
axis:0(默认)或-1
arr8 = np.linspace(1, 10, 20, dtype=float, retstep=True)
print('length:', len(arr8))
print(arr8)
length: 2 (array([ 1. , 1.47368421, 1.94736842, 2.42105263, 2.89473684, 3.36842105, 3.84210526, 4.31578947, 4.78947368, 5.26315789, 5.73684211, 6.21052632, 6.68421053, 7.15789474, 7.63157895, 8.10526316, 8.57894737, 9.05263158, 9.52631579, 10. ]), 0.47368421052631576)
N维数组对象ndarray
由两部分组成:
-
实际的数据
-
描述这些数据的元数据(数据维度、数据类型等)
ndarray数组一般要求所有元素类型相同(同质),数组下标从0开始。
ndarray数组的创建方法
从Python中的列表、元组等类型创建ndarray数组
arr = np.array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [9, 8, 7, 6, 5]])
使用NumPy中函数创建ndarray数组
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| np.arange(n) | 返回ndarray类型,元素从0到n-1 |
| np.ones(shape) | 根据shape生成一个全1数组,shape是元组类型 |
| np.zeros(shape) | 根据shape生成一个全0数组,shape是元组类型 |
| np.full(shape,val) | 根据shape生成一个数组,每个元素值都是val |
| np.eye(n) | 创建一个正方n*n的单位矩阵,对角线是1,其余为0 |
| np.ones_like(a) | 根据a的形状生成一个全1数组 |
| np.zeros_like(a) | 根据a的形状生成一个全0数组 |
| np.full_like(a,val) | 根据a的形状生成一个数组,每个元素值都是val |
| np.linspace() | 根据起止数据等间距地填充数据 |
| np.concatenate() | 将两个或者多个数组合并成一个新的数组 |
从字节流(raw bytes)中创建ndarray数组
从文件中读取特定格式,创建ndarray
ndarray数组的维度变化
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| reshape(shape) | 不改变数组元素,返回一个shape形状数组,原数组不变 |
| resize(shape) | 与reshape()功能一致,但修改原数组 |
| swapaxes(ax1,ax2) | 将数组n个维度中两个维度进行调换 |
| flatten() | 对数组进行降维,返回折叠后的一维数组,原数组不变 |
ndarray数组的类型变化
new_a = a.astype(new_type)
d = np.ones((3,3,4),dtype=np.int) e = d.astype(np.float)
array([[[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]], [[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]], [[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]]])
astype()方法一定会创建新的数组(原始数据的一个拷贝),即使两个类型一致
ndarray数组向列表的转换
ls=a.tolist()
a = np.full((2,3,4),25,dtype=np.int32) a.tolist()
[[[25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25]], [[25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25]]]
ndarray数组的操作
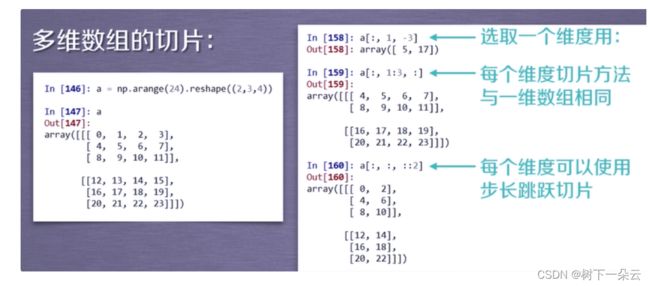
索引与切片
起始编号:终止编号(不含):步长
多维数组的索引
多维数组的切片
NumPy一元函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| np.abs(x) np.fabs(x) | 绝对值 |
| np.sqrt(x) | 各元素的平方根 |
| np.square(x) | 各元素的平方 |
| np.log(x) np.log10(x) np.log2(x) | 各元素的自然对数、10底对数和2底对数 |
| np.ceil(x) np.floor(x) | 各元素的ceiling值或floor值 |
| np.rint(x) | 各元素的四舍五入值 |
| np.modf(x) | 各元素的小数和整数部分以两个独立数组形式返回 |
| np.cos(x) np.cosh(x) np.sin(x) np.sinh(x) np.tan(x) np.tanh(x) | 计算各元素的普通型和双曲型三角函数 |
| np.exp(x) | 计算各元素的指数值 |
| np.sign(x) | 计算各元素的符号值,1(+),0,-1(-) |
a = np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4)) a = np.sqrt(a) np.modf(a)
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) array([[[0. , 1. , 1.41421356, 1.73205081], [2. , 2.23606798, 2.44948974, 2.64575131], [2.82842712, 3. , 3.16227766, 3.31662479]], [[3.46410162, 3.60555128, 3.74165739, 3.87298335], [4. , 4.12310563, 4.24264069, 4.35889894], [4.47213595, 4.58257569, 4.69041576, 4.79583152]]])
NumPy二元函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| + - * / ** | 两个数组元素进行对应运算 |
| np.maximum(x,y) np.fmax() np.minimum(x,y) np.fmin() | 元素级的最大值/最小值计算 |
| np.mod(x,y) | 元素级的模运算 |
| np.copysign(x,y) | 将数组y中各元素值得符号赋值给数组x对应元素 |
| > < >= <= == != | 算数比较,产生布尔型数组 |
a = np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4)) a = np.sqrt(a) np.modf(a)
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) array([[[0. , 1. , 1.41421356, 1.73205081], [2. , 2.23606798, 2.44948974, 2.64575131], [2.82842712, 3. , 3.16227766, 3.31662479]], [[3.46410162, 3.60555128, 3.74165739, 3.87298335], [4. , 4.12310563, 4.24264069, 4.35889894], [4.47213595, 4.58257569, 4.69041576, 4.79583152]]]) (array([[[0. , 0. , 0.41421356, 0.73205081], [0. , 0.23606798, 0.44948974, 0.64575131], [0.82842712, 0. , 0.16227766, 0.31662479]], [[0.46410162, 0.60555128, 0.74165739, 0.87298335], [0. , 0.12310563, 0.24264069, 0.35889894], [0.47213595, 0.58257569, 0.69041576, 0.79583152]]]), array([[[0., 1., 1., 1.], [2., 2., 2., 2.], [2., 3., 3., 3.]], [[3., 3., 3., 3.], [4., 4., 4., 4.], [4., 4., 4., 4.]]]))
NumPy数据存取与函数
CSV文件读取
np.savetxt(frame, array, fmt='%.18e', delimiter=None)
frame:文件、字符串或产生器,可以使.gz或.bz2的压缩文件
array:存入文件的数组
fmt:写入文件的格式
delimiter:分割字符串,默认是任何空格
a = np.arange(100).reshape(5, 20)
np.savetxt('a.csv', a, fmt='%.1f', delimiter=',')
np.loadtxt(frame, dtype=np.float, delimiter=None, unpack=False)
farme:文件、字符串或产生器,可以使.gz或.bz2的压缩文件
dtype:数据类型
delimiter:分割字符串,默认是任何空格
unpack:如果True,读入的属性将分别写入不同变量
b = np.loadtxt('a.csv', dtype=np.int32, delimiter=',')
CSV文件局限性
只能存取一维和二维数组
多维数组存储
a.tofile(frame,sep='',format='%s')
frame:文件、字符串
sep:数据分割字符串,如果空串,写入文件为二进制
fromat:写入数据格式
a = np.arange(100).reshape(5, 10, 2)
print(a)
# a.tofile("b.dat", sep=",", format='%d')
a.tofile("b.dat", format='%d') # 为二进制文件
np.fromfile(frame, dtype=float, count=-1, sep='')
frmae:文件、字符串
dtype:读取的数据类型
count:读入元素个数,-1表示读入整个文件
sep:数据分割字符串,如果是空串,写入文件为二进制。
c = np.fromfile("b.dat", dtype=np.int32, sep=",").reshape(5, 10, 2)
NumPy的便捷文件存取
np.save(fname, array)或者np.savez(fname, array)
frame:文件名,以.npy为拓展名,压缩拓展名为.npz
array:数组变量
np.load(fname)
d = np.arange(100).reshape(5, 10, 2)
print(d)
np.save("a.npy", d)
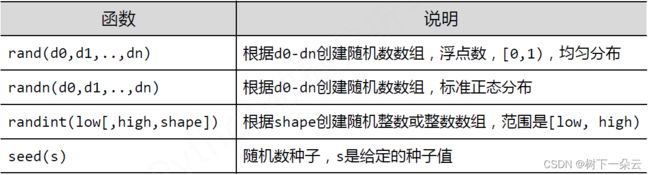
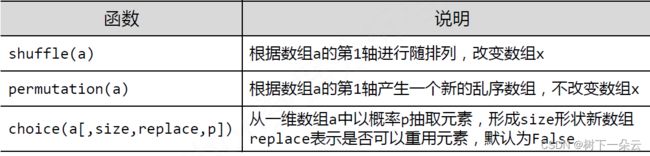
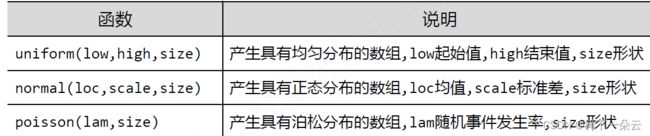
NumPy的随机函数
u = np.random.uniform(0, 10, (3, 4)) print(u) n = np.random.normal(10, 5, (3, 4)) print(n)
NumPy的统计函数
NumPy的梯度函数
a = np.random.randint(0, 20, (5)) print(a) print(np.gradient(a)) c = np.random.randint(0, 50, (3, 5)) print(c) print(np.gradient(c))