自己制作目标检测数据集
自己制作目标检测数据集
这里介绍2个制作目标检测数据集的工具:labelImg和labelme。用pip list查看自己电脑是否已安装这两个库,没有的话分别用pip install labelImg和 pip install labelme安装。
![]()
用labelImg默认生成的标签是.xml格式的,用labelme生成的标签是.json格式。labelImg可以修改标签格式,labelImg点击Save下面的Pascal VOC可以换成YOLO格式。
使用方法
两者使用方法一样,界面都差不多。直接cmd窗口输入labelImg或者labelme即可打开工具。
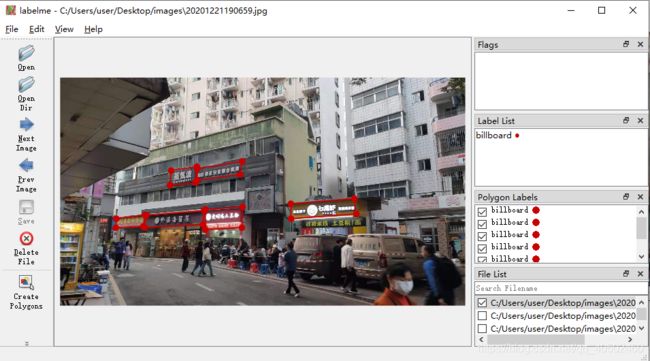
首先点击Open Dir打开我们存放图片的文件夹,labelImg点击Create RectBox即可在图片上画框,如果为检测困难物体,在右上角difficult那里打勾,画框介绍点Save或者Next Image就会在存放图片的文件夹下生产对应的.xml文件,一般直接用Next Image。labelImg点击Edit->Create Rectangle即可在图上画框,labelme还可以用Create Polygons在图片上画多边形,保存后在存放图片的文件夹下生产对应的.json文件,同样也是一张图片对应一个json文件,如果要将所有json文件合并成一个,可以用下面的代码实现:
import os
import argparse
import json
from labelme import utils
import numpy as np
import glob
import PIL.Image
#from PIL import Image
class labelme2coco(object):
def __init__(self, labelme_json, save_json_path="./val.json"):
self.labelme_json = labelme_json
self.save_json_path = save_json_path
self.images = []
self.categories = []
self.annotations = []
self.label = []
self.annID = 1
self.height = 0
self.width = 0
self.save_json()
def data_transfer(self):
for num, json_file in enumerate(self.labelme_json):
with open(json_file, "r") as fp:
print(json_file)
data = json.load(fp)
for key in data:
print(key)
print(data["shapes"])
self.images.append(self.image(data, num))
for shapes in data["shapes"]:
label = shapes["label"].split("_")
if label not in self.label:
self.label.append(label)
points = shapes["points"]
self.annotations.append(self.annotation(points, label, num))
self.annID += 1
# Sort all text labels so they are in the same order across data splits.
self.label.sort()
for label in self.label:
self.categories.append(self.category(label))
for annotation in self.annotations:
annotation["category_id"] = self.getcatid(annotation["category_id"])
def image(self, data, num):
image = {}
img = utils.img_b64_to_arr(data["imageData"])
height, width = img.shape[:2]
img = None
image["height"] = height
image["width"] = width
image["id"] = num
image["file_name"] = data["imagePath"].split("/")[-1]
self.height = height
self.width = width
return image
def category(self, label):
category = {}
category["supercategory"] = label[0]
category["id"] = len(self.categories)
category["name"] = label[0]
return category
def annotation(self, points, label, num):
annotation = {}
contour = np.array(points)
x = contour[:, 0]
y = contour[:, 1]
area = 0.5 * np.abs(np.dot(x, np.roll(y, 1)) - np.dot(y, np.roll(x, 1)))
annotation["segmentation"] = [list(np.asarray(points).flatten())]
annotation["iscrowd"] = 0
annotation["area"] = area
annotation["image_id"] = num
annotation["bbox"] = list(map(float, self.getbbox(points)))
annotation["category_id"] = label[0] # self.getcatid(label)
annotation["id"] = self.annID
return annotation
def getcatid(self, label):
for category in self.categories:
if label == category["name"]:
return category["id"]
print("label: {} not in categories: {}.".format(label, self.categories))
exit()
return -1
def getbbox(self, points):
polygons = points
mask = self.polygons_to_mask([self.height, self.width], polygons)
return self.mask2box(mask)
def mask2box(self, mask):
index = np.argwhere(mask == 1)
rows = index[:, 0]
clos = index[:, 1]
left_top_r = np.min(rows) # y
left_top_c = np.min(clos) # x
right_bottom_r = np.max(rows)
right_bottom_c = np.max(clos)
return [
left_top_c,
left_top_r,
right_bottom_c - left_top_c,
right_bottom_r - left_top_r,
]
def polygons_to_mask(self, img_shape, polygons):
mask = np.zeros(img_shape, dtype=np.uint8)
mask = PIL.Image.fromarray(mask)
xy = list(map(tuple, polygons))
PIL.ImageDraw.Draw(mask).polygon(xy=xy, outline=1, fill=1)
mask = np.array(mask, dtype=bool)
return mask
def data2coco(self):
data_coco = {}
data_coco["images"] = self.images
data_coco["categories"] = self.categories
data_coco["annotations"] = self.annotations
return data_coco
def save_json(self):
print("save coco json")
self.data_transfer()
self.data_coco = self.data2coco()
print(self.save_json_path)
os.makedirs(
os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(self.save_json_path)), exist_ok=True
)
json.dump(self.data_coco, open(self.save_json_path, "w"), indent=4)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import argparse
#parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
# description="labelme annotation to coco data json file."
#)
#parser.add_argument(
# "labelme_images",
# help="Directory to labelme images and annotation json files.",
# type=str,
#)
#parser.add_argument(
# "--output", help="Output json file path.", default="trainval.json"
#)
#args = parser.parse_args()
#labelme_json = glob.glob(os.path.join(args.labelme_images, "*.json"))
filename = os.path.join("C:/Users/user/Desktop/images", "*.json")
#print(filename, "first")
labelme_json = glob.glob(filename)
#print("labelme_json",labelme_json)
output = "C:/Users/user/Desktop/images/train.json"
labelme2coco(labelme_json, output)