基于SpringBoot实现使用restTemplate实现文件和普通参数的同时上传和接收
在IDEA中,基于SpringBoot实现使用restTemplate实现文件和普通参数的同时上传和接收
-
- 1 准备环境
-
-
- 1.1 开发环境
- 1.2 主要需要的依赖
- 1.3 调用服务端(B) 与 服务被调用端(S) 地址
-
- 2 业务需求
- 3 数据传递
-
-
- 3.1 自定义的用于封装 返回文件和字符串的一个 自定义的类MagicFile(用于作restTemplate期待返回的类型,本质是一个ResultVO类 :Value Object)
- 3.2 调用服务端 -> 服务被调用端 (B -> S 发送数据)
-
-
- 3.2.1 调用服务端(B)发送数据主要流程
- 3.2.2 提供服务被调用端(S)接收发送数据主要流程
- 3.2.3 整个 B->S 流程图示
-
- 3.3 服务被调用端 -> 调用服务端 (S -> B 返回数据)
-
-
- 3.3.1 提供服务被调用端(S)返回数据主要流程
- 3.3.2 调用服务端(B)接收 返回数据主要流程
- 3.3.3 整个主要流程图示
-
- 3.4 实现代码
-
-
- 3.4.1 调用服务端(B)代码 (controller层) 包括 发送数据 和 接收返回的数据
- 3.4.2 提供服务被调用端(S)代码 (controller层) 包括 接收 和 返回 数据
-
- 3.5 注意事项
-
1 准备环境
1.1 开发环境
IDEA-2018.3
1.2 主要需要的依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
commons-io
commons-io
2.8.0
compile
1.3 调用服务端(B) 与 服务被调用端(S) 地址
都为本机地址 localhost
2 业务需求
调用服务端(客户端)发送一个文件(示例为 11.jpg图片文件)和一个字符串普通参数 给 提供服务的被调用端(服务端); 之后 提供服务的被调用端(服务端) 再返回一个文件和字符串普通参数给 调用服务端(客户端)。 具体如下所示:
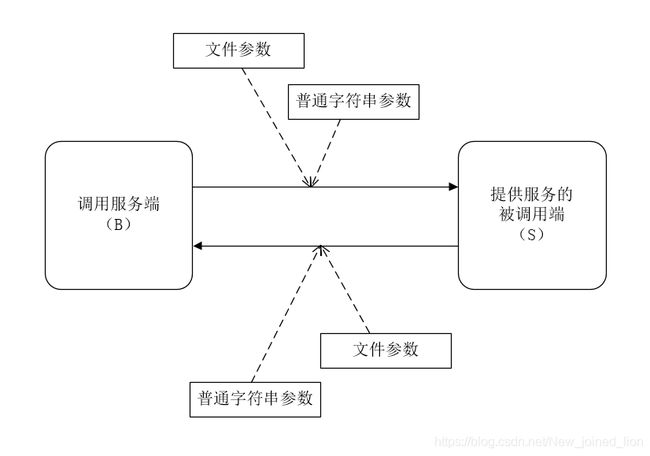
3 数据传递
3.1 自定义的用于封装 返回文件和字符串的一个 自定义的类MagicFile(用于作restTemplate期待返回的类型,本质是一个ResultVO类 :Value Object)
/**
* 用于在HTTP传输时,同时传输文件和相应参数的自定义类
*/
public class MagicFile {
public String fileName = null;
public byte[] fileBytesArray = null;
public MagicFile(){}
public MagicFile(String fileName, byte[] fileBytesArray){
this.fileName = fileName;
this.fileBytesArray = fileBytesArray;
}
public String getFileName() {
return fileName;
}
public void setFileName(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
}
public byte[] getFileBytesArray() {
return fileBytesArray;
}
public void setFileBytesArray(byte[] fileBytesArray) {
this.fileBytesArray = fileBytesArray;
}
}
3.2 调用服务端 -> 服务被调用端 (B -> S 发送数据)
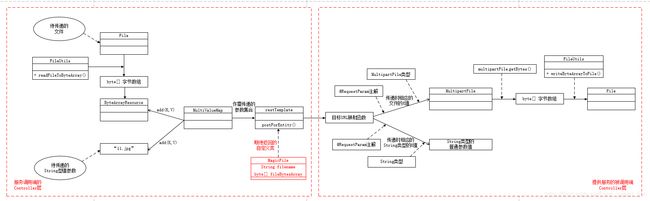
3.2.1 调用服务端(B)发送数据主要流程
① 将准备发送的文件 使用 FileUtils工具 转换成字节数组,再包装成字节数组资源(ByteArrayResource) ----文件参数已准备好
② 准备需要发生的String型参数 ---- 字符串普通参数已准备好
③ 通过 MultiValueMap 映射类型将 文件参数和字符串普通参数再次封装 ---- 整体参数已准备好
④ 调用restTemplate的postForEntity方法,将准备好的整体多值参数(MultiValueMap)作postForEntity方法的数据参数 发送给 被调用端,同时期待返回自定义的MagicFile类(其中封装了文件字节数组和普通的字符串参数)
3.2.2 提供服务被调用端(S)接收发送数据主要流程
① 被调用端借助@RequestParam注解,按键名取值的方式把字节数组形式的文件和普通参数获取到
② 使用MultipartFile类来作接收文件的类型
③ 使用String类来作接收字符串数组的类型 ---- 字符串参数获取已完成
④ 将MultipartFile类的文件转换为字节数组形式
⑤ 将字节数组形式的文件 通过 FileUtils工具 转换为 File文件 ---- 文件参数获取已完成
3.2.3 整个 B->S 流程图示
3.3 服务被调用端 -> 调用服务端 (S -> B 返回数据)
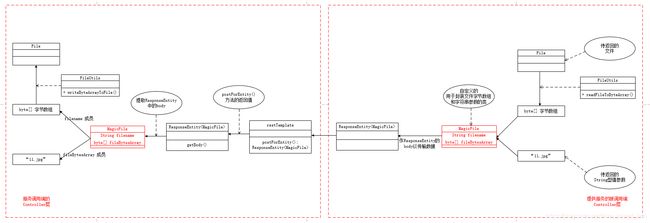
3.3.1 提供服务被调用端(S)返回数据主要流程
① 将待返回的文件使用 FileUtils工具 转换为 字节数组 ---- 文件参数已准备好
② 设置待返回的字符串参数 ---- 字符串普通参数已准备好
③ 借助 自定义的MagicFile类 封装 字节数组形式的文件和字符串参数 ---- 整体参数已准备好
④ 使用 ResponseEntity< MagicFile > ,将 整体参数放入 ResponseEntity的 body 后返回
3.3.2 调用服务端(B)接收 返回数据主要流程
① 调用端由于先前使用了postForEntity方法,其返回值为 ResponseEntity< MagicFile>,此时获得了ResponseEntity
② 通过ResponseEntity 的 getBody()方法,获取 自定义的MagicFile对象 ---- 整个返回的参数已获得
③ 通过MagicFile对象的成员fileBytesArray,获取返回的字节数组形式的文件参数
④ 通过MagicFile对象的成员filename,获取返回的字符串普通参数 ---- 返回的字符串参数已获得
⑤ 再次使用 FileUtils工具 将字节数组形式的文件转换为本地文件 ---- 返回的文件参数已获得
3.3.3 整个主要流程图示
3.4 实现代码
3.4.1 调用服务端(B)代码 (controller层) 包括 发送数据 和 接收返回的数据
@Resource
RestTemplate restTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public String getUpload(Model model){
String url = "http://localhost:8001/restUpload2";
// 将 本地文件 --> 字节数组 --> 字节数组资源
File file = new File("D:/11.jpg");
byte[] bytesFile = null;
try{
bytesFile = FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(file);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ByteArrayResource byteArrayResource = new ByteArrayResource(bytesFile) {
// 必须重写该方法,否则服务器MultipartRequest.getFile获取文件为空,
// 但是return的变量名 作SubmittedFileName(可自定义),并非做接收端按键取值时的文件的键名
// 即上传的文件具有两个名字: 键名 和 提交的文件名SubmittedFileName
@Override
public String getFilename() {
return "xxxxx";
}
};
// httpRequest body
MultiValueMap paramsMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
paramsMap.add("file", byteArrayResource);
paramsMap.add("fileName", "11.jpg");
// httpRequest header
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
httpHeaders.set("Content-Type", "multipart/form-data");
HttpEntity> request =
new HttpEntity>(paramsMap , httpHeaders);
ResponseEntity response = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, paramsMap, MagicFile.class);
// ResponseEntity response = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, request, String.class);
// 接收 被调用端(S) 返回的 带有 文件和普通字符串 自定义MagicFile类型的参数
MagicFile magicFile = response.getBody();
byte[] returnBytesFile = null;
String mes = null;
try{
returnBytesFile = magicFile.getFileBytesArray();
if(returnBytesFile == null){
throw new RuntimeException("接收二进制文件流为空!");
}
mes = magicFile.getFileName();
if(mes == null){
throw new RuntimeException("接收二进制文件流 的 信息 为空!");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
String downloadPath = "E:/download/";
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
String downloadFileName = downloadPath + uuid+".nc";
File downloadFile = new File(downloadFileName);
try{
FileUtils.writeByteArrayToFile(downloadFile, returnBytesFile);
System.err.println("返回的文件已保存完毕!!!");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 往返回的前端index页面 添加参数
model.addAttribute("message", mes);
// 返回 index 页面
return "index";
}
3.4.2 提供服务被调用端(S)代码 (controller层) 包括 接收 和 返回 数据
/**
* 以注解的形式获取请求中携带的参数
* @param file
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/restUpload2")
public ResponseEntity restUpload(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file,
@RequestParam("fileName")String fileName){
// 获取传递的参数
byte[] bytesFile = null;
try{
if(file == null){
throw new RuntimeException("接收的文件为空!");
}
if (fileName == null){
throw new RuntimeException("接收的文件名为空!");
}
bytesFile = file.getBytes();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 字节数组 --> 本地文件
String downLoadUrl = "E:/upload/";
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
String filePath = downLoadUrl + uuid + ".jpg";
File receiveFile = new File(filePath);
try {
FileUtils.writeByteArrayToFile(receiveFile, bytesFile);
System.err.println("创建本地文件成功 -- 方式2");
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//准备 返回的 文件参数和 普通字符串参数
File returnFile = new File("D:/test.nc");
byte[] returnBytesFile = null;
try{
returnBytesFile = FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(returnFile);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
MagicFile magicFile = new MagicFile(fileName, returnBytesFile);
return new ResponseEntity(magicFile, HttpStatus.OK);
}
3.5 注意事项
在 B -> S 模拟发送文件时,使用的示例是11.jpg,被调用端(S)接收该文件时,需要预先知道传输文件的后缀名 .jpg,才可以正确接收。
即有如下代码:
String downLoadUrl = "E:/upload/";
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
String filePath = downLoadUrl + uuid + ".jpg";
File receiveFile = new File(filePath);
同样,在S -> B 返回文件时,使用的示例是test.nc文件,故调用端(B)接收该文件时,也需要预先知道传输文件的后缀名 .nc,才可以正确接收。
即有如下代码:
String downloadPath = "E:/download/";
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
String downloadFileName = downloadPath + uuid+".nc";
File downloadFile = new File(downloadFileName);