机器学习算法--python实现随机森林(分类)
python实现随机森林(分类)
可以把随机森林看成是决策树的集 合。随机森林背后的逻辑是对分别受较大方差影响的多个决策树取平均值, 以建立一个具有更好的泛化性能和不易过拟合的强大模型。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, [2, 3]]
y = iris.target
print('Class labels:', np.unique(y))
# Splitting data into 70% training and 30% test data:
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1, stratify=y)
X_combined = np.vstack((X_train, X_test))
y_combined = np.hstack((y_train, y_test))
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, test_idx=None, resolution=0.02):
# setup marker generator and color map
markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v')
colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
# plot the decision surface
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution),
np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.3, cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0],
y=X[y == cl, 1],
alpha=0.8,
c=colors[idx],
marker=markers[idx],
label=cl,
edgecolor='black')
# highlight test samples
if test_idx:
# plot all samples
X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx]
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0],
X_test[:, 1],
c='y',
edgecolor='black',
alpha=1.0,
linewidth=1,
marker='o',
s=100,
label='test set')
forest = RandomForestClassifier(criterion='gini',
n_estimators=25,
random_state=1,
n_jobs=2)
forest.fit(X_train, y_train)
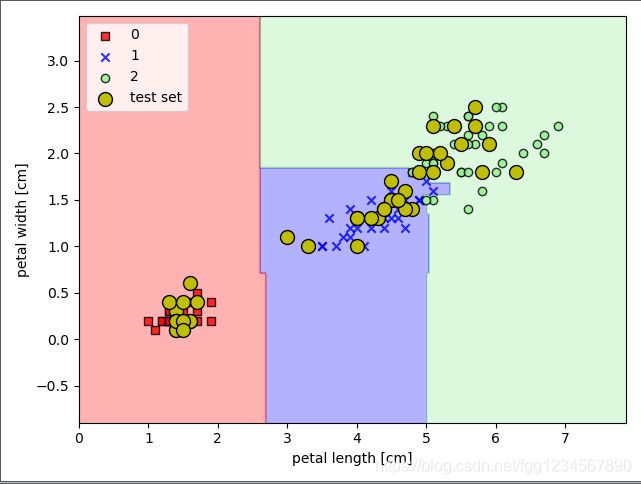
plot_decision_regions(X_combined, y_combined,
classifier=forest, test_idx=range(105, 150))
plt.xlabel('petal length [cm]')
plt.ylabel('petal width [cm]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.tight_layout()
#plt.savefig('images/03_22.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
运行结果:
Class labels: [0 1 2]