Python--Numpy简单了解
文章目录
- Python--Numpy简单了解
-
- 1. Numpy优势
-
- 1.1 Numpy介绍 - 数值计算库
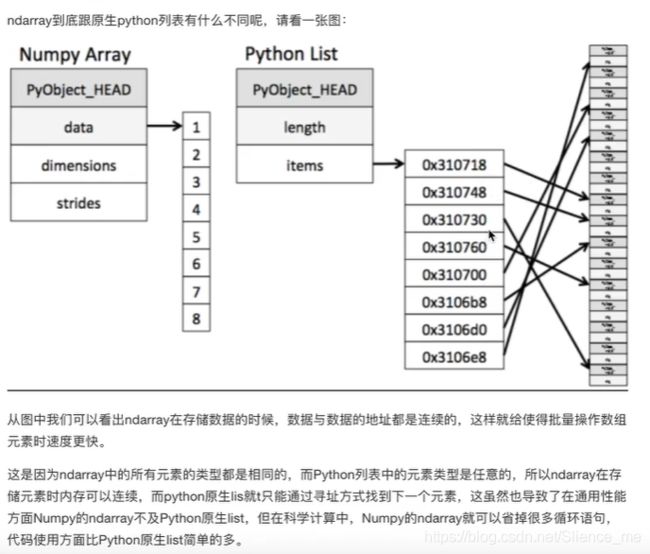
- 1.2 ndarray介绍
- 1.3 ndarray与Python原生list运算效率对比
- 1.4 ndarray的优势
- 2. 认识N维数组-ndarray属性
-
- 2.1 ndarray的属性
- 2.2 ndarray的形状
- 2.3 ndarray的类型
- 3. 基本操作
-
- 3.1 生成数组的方法
-
- 3.1.1 生成0和1
- 3.1.2 从现有数组中生成
- 3.1.3 生成固定范围的数组
- 3.1.4 生成随机数组
- 3.2 数组的索引、切片
- 3.3 形状修改
- 3.4 类型修改
- 3.5 数组的去重
- 4. ndarray运算
-
- 4.1 逻辑运算
- 4.2 统计运算
- 5. 数组间运算
-
- 5.1 场景
- 5.2 数组与数的运算
- 5.3 数组与数组的运算
- 5.4 广播机制
- 5.5 矩阵运算
- 6. 合并、分割
-
- 6.1 合并
- 6.2 分割
- 7. IO操作与数据处理
-
- 7.1 Numpy读取
- 7.2 如何处理缺失值
Python–Numpy简单了解
Numpy高效的运算工具Numpy的优势ndarray属性- 基本操作
ndarray.方法()numpy.函数名()
ndarray运算- 逻辑运算
- 统计运算
- 数组间运算
- 合并、分割、IO操作、数据处理
1. Numpy优势
1.1 Numpy介绍 - 数值计算库
num- numerical 数值化的py- pythonndarrayn- 任意个d- dimension 维度array- 数组
1.2 ndarray介绍
import numpy as np
score = np.array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],
[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],
[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],
[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],
[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],
[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],
[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],
[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
1.3 ndarray与Python原生list运算效率对比
import random
import time
# 生成一个大数组
python_list = []
for i in range(100000000):
python_list.append(random.random())
ndarray_list = np.array(python_list)
# 原生pythonlist求和
t1 = time.time()
a = sum(python_list)
t2 = time.time()
d1 = t2 - t1
# ndarray求和
t3 = time.time()
b = np.sum(ndarray_list)
t4 = time.time()
d2 = t4 - t3
d1= 0.7309620380401611
d2= 0.12980318069458008
1.4 ndarray的优势
2. 认识N维数组-ndarray属性
2.1 ndarray的属性
shapendim:看看维度size:看看大小
dtypeitemsize:一个元素所占大小
- 在创建
ndarray的时候,如果没有指定类型 - 默认
- 整数
int64 - 浮点数
float64
- 整数
array([[80, 89, 86, 67, 79],
[78, 97, 89, 67, 81],
[90, 94, 78, 67, 74],
[91, 91, 90, 67, 69],
[76, 87, 75, 67, 86],
[70, 79, 84, 67, 84],
[94, 92, 93, 67, 64],
[86, 85, 83, 67, 80]])
score.shape # (8, 5)
score.ndim # 2
score.size # 40
score.dtype # dtype('int64')
score.itemsize # 8
2.2 ndarray的形状
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
b = np.array([1,2,3,4])
c = np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]])
a # array([[1, 2, 3],
b # array([1, 2, 3, 4])
c # array([[[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]],[[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6]]])
a.shape # (2, 3)
b.shape # (4,)
c.shape # (2, 2, 3)
2.3 ndarray的类型
type(score.dtype)
<type 'numpy.dtype'>
# 指定类型
# 创建数组的时候指定类型
np.array([1.1, 2.2, 3.3], dtype="float32")
dtype是numpy是numpy.dtype类型,先看看对数组来说都有哪些类型
| 名称 | 描述 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|
| np.bool | 用一个字节存储的布尔类型(True或False) | ‘b’ |
| np.int8 | 一个字节大小,-128~127 | ‘i’ |
| np.int16 | 整数,-32768至32767 | ‘i2’ |
| np.int32 | 整数,-231至232 -1 | ‘i4’ |
| np.int64 | 整数,-263至263 -1 | ‘i8’ |
| np.uint8 | 无符号整数,0~255 | ‘u’ |
| np.uint16 | 无符号整数,0~65535 | ‘u2’ |
| np.uint32 | 无符号整数,0~2 ** 32 -1 | ‘u4’ |
| np.uint64 | 无符号整数,0~2 ** 64 -1 | ‘u8’ |
| np.float16 | 半精度浮点数:16位, 正负号1位, 指数5位, 精度10位 | ‘f2’ |
| np.float32 | 单精度浮点数:32位, 正负号1位, 指数8位, 精度23位 | ‘f4’ |
| np.float64 | 双度浮点数:64位, 正负号1位, 指数11位, 精度52位 | ‘f8’ |
| np.complex64 | 复数,分别用两个32位浮点数表示实部和虚部 | ‘c8’ |
| np.complex128 | 复数,分别用两个64位浮点数表示实部和虚部 | ‘c16’ |
| np.object_ | python对象 | ‘O’ |
| np.string | 字符串 | ‘S’ |
| np.unicode | unicode类型 | ‘U’ |
3. 基本操作
adarray.方法()np.函数名()np.array()
3.1 生成数组的方法
3.1.1 生成0和1
np.zeros(shape)np.ones(shape)
# 1 生成0和1的数组
np.zeros(shape=(3, 4), dtype="float32")
-----------------------------------------
array([[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)
np.ones(shape=[2, 3], dtype=np.int32)
-----------------------------------------
array([[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1]], dtype=int32)
3.1.2 从现有数组中生成
np.array() np.copy()深拷贝np.asarray()浅拷贝
data1 = np.array(score)
data2 = np.asarray(score)
data3 = np.copy(score)
score[3, 1] = 10000
修改source,data2改变,data1,data3不改变
3.1.3 生成固定范围的数组
-
np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
- [0, 10] 等距离 生成个数
-
np.arange(a, b, c)
- range(a, b, c)
- [a, b) c是步长
- range(a, b, c)
np.linspace(0, 10, 5)
# array([ 0. , 2.5, 5. , 7.5, 10. ])
np.arange(0, 11, 5)
# array([ 0, 5, 10])
3.1.4 生成随机数组
分布状况 - 直方图
- 均匀分布
每组的可能性相等 - 正态分布
σ 幅度、波动程度、集中程度、稳定性、离散程度
- 均匀分布
uniformlow:float类型,此概率的均值(对应着整个分布的中心centre)scale:float类型,此概率分布的标准差(对应于分布的宽度,scale越大越矮胖,越小越瘦高)size:int or tuple of ints 输出的shape,默认位None,只输出一个值
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
data1 = np.random.uniform(low=-1, high=1, size=1000000)
array([-0.49795073, -0.28524454, 0.56473937, ..., 0.6141957 ,
0.4149972 , 0.89473129])
# 1、创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)
# 2、绘制直方图
plt.hist(data1, 1000)
# 3、显示图像
plt.show()
- 正态分布
normallow:此概率的均值(对应着整个分布的中心centre)scale:float此概率分布的标准差(对应于分布的宽度,scale越大越矮胖,越小越瘦高)size:int or tuple of ints 输出的shape,默认位None,只输出一个值
# 正态分布
data2 = np.random.normal(loc=1.75, scale=0.1, size=1000000)
# 1、创建画布
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)
# 2、绘制直方图
plt.hist(data2, 1000)
# 3、显示图像
plt.show()
3.2 数组的索引、切片
stock_change = np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=(8, 10))
# 返回结果
array([[-0.03469926, 1.68760014, 0.05915316, 2.4473136 , -0.61776756, -0.56253866, -1.24738637, 0.48320978, 1.01227938, -1.44509723],[-1.8391253 , -1.10142576, 0.09582268, 1.01589092, -1.20262068, 0.76134643, -0.76782097, -1.11192773, 0.81609586, 0.07659056],[-0.74293074, -0.7836588 , 1.32639574, -0.52735663, 1.4167841 , 2.10286726, -0.21687665, -0.33073563, -0.46648617, 0.07926839],[ 0.45914676, -0.78330377, -1.10763289, 0.10612596, -0.63375855,-1.88121415, 0.6523779 , -1.27459184, -0.1828502 , -0.76587891],[-0.50413407, -1.35848099, -2.21633535, -1.39300681, 0.13159471, 0.65429138, 0.32207255, 1.41792558, 1.12357799, -0.68599018],[ 0.3627785 , 1.00279706, -0.68137875, -2.14800075, -2.82895231,-1.69360338, 1.43816168, -2.02116677, 1.30746801, 1.41979011],[-2.93762047, 0.22199761, 0.98788788, 0.37899235, 0.28281886,-1.75837237, -0.09262863, -0.92354076, 1.11467277, 0.76034531],[-0.39473551, 0.28402164, -0.15729195, -0.59342945, -1.0311294 ,-1.07651428, 0.18618331, 1.5780439 , 1.31285558, 0.10777784]])
# 获取第一个股票的前3个交易日的涨跌幅数据
stock_change[0, :3]
# 返回结果
array([-0.03469926, 1.68760014, 0.05915316])
一维、二维、三维的数组如何索引?
# 三维,一维
a1 = np.array([ [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]], [[12,3,34],[5,6,7]]])
# 返回结果
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[12, 3, 34],
[ 5, 6, 7]]])
# 索引、切片
a1.shape # (2, 2, 3)
a1[1, 0, 2] # 34
# 修改
a1[1, 0, 2] = 100000
# 返回结果
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[ 12, 3, 100000],
[ 5, 6, 7]]])
3.3 形状修改
ndarray.reshape(shape)返回新的ndarray,原始数据没有改变ndarray.resize(shape)没有返回值,对原始的ndarray进行了修改ndarray.T转置 行变成列,列变成行
ndarray.reshape(shape)返回新的ndarray,原始数据没有改变
# 需求:让刚才的股票行、日期列反过来,变成日期行,股票列
stock_change
# 返回结果
array(
[[-0.03469926, 1.68760014, 0.05915316, 2.4473136 , -0.61776756,
-0.56253866, -1.24738637, 0.48320978, 1.01227938, -1.44509723],
[-1.8391253 , -1.10142576, 0.09582268, 1.01589092, -1.20262068,
0.76134643, -0.76782097, -1.11192773, 0.81609586, 0.07659056],
[-0.74293074, -0.7836588 , 1.32639574, -0.52735663, 1.4167841 ,
2.10286726, -0.21687665, -0.33073563, -0.46648617, 0.07926839],
[ 0.45914676, -0.78330377, -1.10763289, 0.10612596, -0.63375855,
-1.88121415, 0.6523779 , -1.27459184, -0.1828502 , -0.76587891],
[-0.50413407, -1.35848099, -2.21633535, -1.39300681, 0.13159471,
0.65429138, 0.32207255, 1.41792558, 1.12357799, -0.68599018],
[ 0.3627785 , 1.00279706, -0.68137875, -2.14800075, -2.82895231,
-1.69360338, 1.43816168, -2.02116677, 1.30746801, 1.41979011],
[-2.93762047, 0.22199761, 0.98788788, 0.37899235, 0.28281886,
-1.75837237, -0.09262863, -0.92354076, 1.11467277, 0.76034531],
[-0.39473551, 0.28402164, -0.15729195, -0.59342945, -1.0311294 ,
-1.07651428, 0.18618331, 1.5780439 , 1.31285558, 0.10777784]])
stock_change.reshape((10, 8))
# 返回结果
array(
[[-0.03469926, 1.68760014, 0.05915316, 2.4473136 , -0.61776756,
-0.56253866, -1.24738637, 0.48320978],
[ 1.01227938, -1.44509723, -1.8391253 , -1.10142576, 0.09582268,
1.01589092, -1.20262068, 0.76134643],
[-0.76782097, -1.11192773, 0.81609586, 0.07659056, -0.74293074,
-0.7836588 , 1.32639574, -0.52735663],
[ 1.4167841 , 2.10286726, -0.21687665, -0.33073563, -0.46648617,
0.07926839, 0.45914676, -0.78330377],
[-1.10763289, 0.10612596, -0.63375855, -1.88121415, 0.6523779 ,
-1.27459184, -0.1828502 , -0.76587891],
[-0.50413407, -1.35848099, -2.21633535, -1.39300681, 0.13159471,
0.65429138, 0.32207255, 1.41792558],
[ 1.12357799, -0.68599018, 0.3627785 , 1.00279706, -0.68137875,
-2.14800075, -2.82895231, -1.69360338],
[ 1.43816168, -2.02116677, 1.30746801, 1.41979011, -2.93762047,
0.22199761, 0.98788788, 0.37899235],
[ 0.28281886, -1.75837237, -0.09262863, -0.92354076, 1.11467277,
0.76034531, -0.39473551, 0.28402164],
[-0.15729195, -0.59342945, -1.0311294 , -1.07651428, 0.18618331,
1.5780439 , 1.31285558, 0.10777784]])
ndarray.resize(shape)没有返回值,对原始的ndarray进行了修改
stock_change.shape # (8, 10)
stock_change.resize((10, 8))
stock_change.shape # (10, 8)
ndarray.T转置 行变成列,列变成行
stock_change.T
3.4 类型修改
ndarray.astype(type)ndarray序列化到本地ndarray.tostring()
stock_change.astype("int32")
# 返回结果
array([[ 0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 0, -1, 0, 1, -1],
[-1, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, -1, 0, 0],
[ 0, -1, -2, -1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[ 0, 1, 0, -2, -2, -1, 1, -2, 1, 1],
[-2, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 0]], dtype=int32)
stock_change.tobytes()
b'\x95&\x99\xdd\x19\xc4\xa1\xbfm8\x88\x00i\x00\xfb?\x92\xbc\x81\xa1RI\xae?\xa2\x95x&\x19\x94\x03@\x9f?\xbev\xc0\xc4\xe3\xbf\x87\xf4H\x13Q\x00\xe2\xbf\x9eM\x85hK\xf5\xf3\xbf\x17mZ\xb2\xe8\xec\xde?U\xca\xd4\xdbK2\xf0?G\xc6\xbbD\x1e\x1f\xf7\xbf\x9f-\xb0\xa5\x0em\xfd\xbf\x9b\xd0h\x9dp\x9f\xf1\xbfyH\x8e\xc3\xd5\x87\xb8?\x1d\x89v\xd5\x16A\xf0?\x89Aj-\xef=\xf3\xbf\xbc\x8ea/\xf3\\\xe8?\x94\xb8\xbaJ\xfd\x91\xe8\xbfv\xc0\x92\xbct\xca\xf1\xbf\x82\x82\x19\x11u\x1d\xea?\xf2.\x96Qp\x9b\xb3?g\xed\xef\xb0\x16\xc6\xe7\xbf\xf2\xbf!\x9c\xbb\x13\xe9\xbf\x7fv\x1e\xbd\xea8\xf5?\x1e \x9d\x02\x1b\xe0\xe0\xbf?\x99O\xce%\xab\xf6?\x84;\xb9\x11\xac\xd2\x00@p\xe3\xa07\x9d\xc2\xcb\xbfop\x94\xc4\xc5*\xd5\xbfN\x15)\xca\xe8\xda\xdd\xbf4\xa8\x8b\xf1\xeeJ\xb4?Qd\x8e\x1c\xa9b\xdd?\xc8\x92\xb6\x10\xd3\x10\xe9\xbf\xf1\x80\x87C\xdd\xb8\xf1\xbf\x18\x02B \x12+\xbb?Xv\xb4\x02\xc0G\xe4\xbf\xa6,\x8a\x02t\x19\xfe\xbf\xb4\xc9\xaf\x9cG\xe0\xe4?wCsj\xbad\xf4\xbf\xbc\xb1\xd5\xa9\xa2g\xc7\xbf\xbc\xc6\x8d{\x14\x82\xe8\xbf>\xf7\xae\xc6\xdd!\xe0\xbf\xacB\x9c\x90V\xbc\xf5\xbfb\xae\xfa\x06\x0e\xbb\x01\xc0_B\xe1\x82\xc1I\xf6\xbfw\x9f\xb6m\x18\xd8\xc0?\x93\xcb\x8e{\xf4\xef\xe4?\xfe\xc1\xba,\xd6\x9c\xd4?k\x85)\xbc\xd2\xaf\xf6?{g\x82\xea,\xfa\xf1?s}\xaf\xad\xa1\xf3\xe5\xbfD(cM\xc37\xd7?(\x1a\xff\xect\x0b\xf0?7e\x80\xce\xda\xcd\xe5\xbf"\xd5\xe1\x03\x1b/\x01\xc0\x94\x85?\xbf\xb1\xa1\x06\xc0w\x08\x14\xdc\xff\x18\xfb\xbf\x9f\x1eL\xd2\xb5\x02\xf7?\xb0-5{Y+\x00\xc0;\xf5<\x94c\xeb\xf4?a\x8f\xb1\xd6u\xb7\xf6?%Kr)?\x80\x07\xc0\x9e\x1c%\xedjj\xcc?F\xa0C\t\xc7\x9c\xef?\xf3\xc3\xfd\x1eiA\xd8?\xcc\x9e\x84D\xb4\x19\xd2?\xdd$J\x10K"\xfc\xbf\xe6E\xb3\x95\x82\xb6\xb7\xbf\x0cN\xa4Z\xa5\x8d\xed\xbf\x96\xdd\xee\x1c\xb3\xd5\xf1?\x05\x8c\x12\xb0\xbfT\xe8?/\xa5\x1a\xb9XC\xd9\xbf~Z!\x1ci-\xd2?\x1f\xe4\xe3\x83$"\xc4\xbf_&\xc5\xc0_\xfd\xe2\xbf\xbf\x16\xac\x8b\x81\x7f\xf0\xbf\xf7\xba)\tg9\xf1\xbf\xb7q\x8c\xd7\xda\xd4\xc7?\x98P\xb7\xf4\xaa?\xf9?\x8c\x98P\xdbt\x01\xf5?t\xd8 -T\x97\xbb?'
3.5 数组的去重
set():只能处理一维np.unique()
temp = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4],[3, 4, 5, 6]])
# 返回结果
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[3, 4, 5, 6]])
np.unique(temp)
# 返回结果
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
set(temp.flatten()) # 将多维降维成一维,然后用set去重 只能处理一维
# 返回结果
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
4. ndarray运算
4.1 逻辑运算
- 布尔索引
- 通用判断函数
np.all(布尔值)- 只要有一个
False就返回False,只有全是True才返回True
- 只要有一个
np.any()- 只要有一个
True就返回True,只有全是False才返回False
- 只要有一个
np.where(三元运算符)np.where(布尔值,True的位置的值,False的位置的值)
stock_change = np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=(8, 10))
# 返回结果
array([[ 1.46338968, -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916, 0.46446682,0.83167611, -1.35770374, -0.65001192, 1.38319911, -0.93415832],[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.19314047, 1.34072589,0.09361683, 1.19030379, 1.4371421 , -0.97829363, -0.11962767],[-1.48252741, -0.69347186, 0.91122464, -0.30606473, 0.41598897,0.79542753, -0.01447862, -1.49943117, -0.23285809, 0.42806777],[ 0.39438905, -1.31770556, 1.7344868 , -1.52812773, -0.47703227,-0.3795497 , -0.88422651, 1.37510973, -0.93622775, 0.49257673],[-0.9822216 , -1.09482936, -0.81834523, 0.57335311, 0.97390091,0.05314952, -0.58316743, 0.19264426, 0.02081861, 0.84445247],[ 0.41739964, -0.26826893, -0.70003442, -0.58593912, 0.86546709,-1.30304864, 0.05254567, -1.73976785, -0.43532247, 0.4760526 ],[-0.21739882, 0.52007085, -0.60160491, 0.57108639, 1.03303301,-0.69172579, 1.04716985, -0.22985706, -0.11125069, 0.87722923],[-0.183266 , 0.56273065, 0.29357786, -0.19343363, -1.54547303,-0.31977163, -0.00659025, 0.48160678, 0.88443604, -0.48456825]])
--------------------------------------------------
# 逻辑判断, 如果涨跌幅大于0.5就标记为True 否则为False
stock_change > 0.5
# 返回结果
array([[ True, False, False, False, False, True, False, False, True,False],[False, False, False, True, True, False, True, True, False,False],[False, False, True, False, False, True, False, False, False,False],[False, False, True, False, False, False, False, True, False,False],[False, False, False, True, True, False, False, False, False,True],[False, False, False, False, True, False, False, False, False,False],[False, True, False, True, True, False, True, False, False,True],[False, True, False, False, False, False, False, False, True,False]])
--------------------------------------------------
stock_change[stock_change > 0.5] = 1.1
# 返回结果
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916, 0.46446682,1.1 , -1.35770374, -0.65001192, 1.1 , -0.93415832],[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.1 , 1.1 ,0.09361683, 1.1 , 1.1 , -0.97829363, -0.11962767],[-1.48252741, -0.69347186, 1.1 , -0.30606473, 0.41598897,1.1 , -0.01447862, -1.49943117, -0.23285809, 0.42806777],[ 0.39438905, -1.31770556, 1.1 , -1.52812773, -0.47703227,-0.3795497 , -0.88422651, 1.1 , -0.93622775, 0.49257673],[-0.9822216 , -1.09482936, -0.81834523, 1.1 , 1.1 ,0.05314952, -0.58316743, 0.19264426, 0.02081861, 1.1 ],[ 0.41739964, -0.26826893, -0.70003442, -0.58593912, 1.1 ,-1.30304864, 0.05254567, -1.73976785, -0.43532247, 0.4760526 ],[-0.21739882, 1.1 , -0.60160491, 1.1 , 1.1 ,-0.69172579, 1.1 , -0.22985706, -0.11125069, 1.1 ],[-0.183266 , 1.1 , 0.29357786, -0.19343363, -1.54547303,-0.31977163, -0.00659025, 0.48160678, 1.1 , -0.48456825]])
# 判断stock_change[0:2, 0:5]是否全是上涨的
stock_change[0:2, 0:5] > 0
# 返回结果
array([[ True, False, True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, True, True]])
--------------------------------------------------
np.all(stock_change[0:2, 0:5] > 0)
# 返回结果
False
--------------------------------------------------
# 判断前5只股票这段期间是否有上涨的
np.any(stock_change[:5, :] > 0)
# 返回结果
True
# 判断前四个股票前四天的涨跌幅 大于0的置为1,否则为0
temp = stock_change[:4, :4]
# 返回结果
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916],
[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.1 ],
[-1.48252741, -0.69347186, 1.1 , -0.30606473],
[ 0.39438905, -1.31770556, 1.1 , -1.52812773]])
--------------------------------------------------
np.where(temp > 0, 1, 0)
# 返回结果
array([[1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0]])
--------------------------------------------------
temp > 0
# 返回结果
array([[ True, False, True, True],
[ True, True, True, True],
[False, False, True, False],
[ True, False, True, False]])
--------------------------------------------------
np.where([[ True, False, True, True],
[ True, True, True, True],
[False, False, True, False],
[ True, False, True, False]], 1, 0)
# 返回结果
array([[1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0]])
--------------------------------------------------
# 判断前四个股票前四天的涨跌幅 大于0.5并且小于1的,换为1,否则为0
# 判断前四个股票前四天的涨跌幅 大于0.5或者小于-0.5的,换为1,否则为0
# (temp > 0.5) and (temp < 1)
np.logical_and(temp > 0.5, temp < 1)
# 返回结果
array([[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False]])
--------------------------------------------------
np.where([[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False]], 1, 0)
# 返回结果
array([[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]])
--------------------------------------------------
np.where(np.logical_and(temp > 0.5, temp < 1), 1, 0)
# 返回结果
array([[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]])
--------------------------------------------------
np.logical_or(temp > 0.5, temp < -0.5)
# 返回结果
array([[ True, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, True],
[ True, True, True, False],
[False, True, True, True]])
--------------------------------------------------
np.where(np.logical_or(temp > 0.5, temp < -0.5), 11, 3)
# 返回结果
array([[11, 3, 3, 3],
[ 3, 3, 3, 11],
[11, 11, 11, 3],
[ 3, 11, 11, 11]])
4.2 统计运算
axis轴的取值并不一定,Numpy中不同的API轴的值不一样,
在这里,axis 0代表行,1代表列
- 统计指标函数
min, max, mean, median, var, stdnp.函数名ndarray.方法名
- 返回最大值、最小值所在位置
np.argmax(temp, axis=)np.argmin(temp, axis=)
# 前四只股票前四天的最大涨幅
temp # shape: (4, 4) 0 1
# 返回结果
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916],
[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.1 ],
[-1.48252741, -0.69347186, 1.1 , -0.30606473],
[ 0.39438905, -1.31770556, 1.1 , -1.52812773]])
--------------------------------------------------
temp.max(axis=0)# 按列求最大值
# 返回结果
array([1.1 , 0.24078108, 1.1 , 1.1 ])
--------------------------------------------------
np.max(temp, axis=-1)
# 返回结果
array([1.1, 1.1, 1.1, 1.1])
--------------------------------------------------
np.argmax(temp, axis=-1)
# 返回结果
array([0, 3, 2, 2])
5. 数组间运算
5.1 场景
5.2 数组与数的运算
+-*/
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4], [5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 1]])
arr / 10
# 返回结果
array([[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1, 0.4],
[0.5, 0.6, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.1]])
5.3 数组与数组的运算
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4], [5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 1]])
arr2 = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 4, 5, 6]])
array([[1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4],
[5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 1]])
5.4 广播机制
执行broadcast的前提在于,两个ndarray执行的是element-wise的运算,Broadcast机制的功能是为了方便不同形状的ndarray(numpy库的核心数据结构)进行数学运算
- 维度相等
- shape(其中相对应的一个地方为1)
广播的原则:如果两个数组的后缘维度(trailing dimension,即从末尾开始算起的维度)的轴长度相符,或其中的一方的长度为1,则认为它们是广播兼容的。广播会在缺失和(或)长度为1的维度上进行。
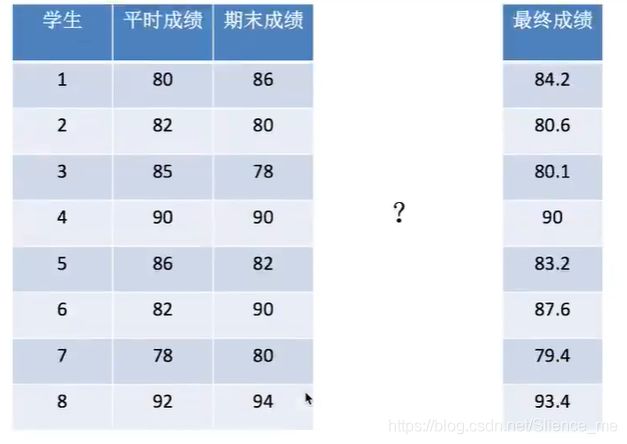
5.5 矩阵运算
1 什么是矩阵
矩阵matrix 二维数组
矩阵 & 二维数组
两种方法存储矩阵
1)ndarray 二维数组
矩阵乘法:
np.matmul
np.dot
2)matrix数据结构
2 矩阵乘法运算
形状
(m, n) * (n, l) = (m, l)
运算规则
A (2, 3) B(3, 2)
A * B = (2, 2)
# ndarray存储矩阵
data = np.array([[80, 86],
[82, 80],
[85, 78],
[90, 90],
[86, 82],
[82, 90],
[78, 80],
[92, 94]])
# matrix存储矩阵
data_mat = np.mat([[80, 86],
[82, 80],
[85, 78],
[90, 90],
[86, 82],
[82, 90],
[78, 80],
[92, 94]])
type(data_mat)
numpy.matrixlib.defmatrix.matrix
data # (8, 2) * (2, 1) = (8, 1)
np.matmul(data, weights)
array([[84.2],
[80.6],
[80.1],
[90. ],
[83.2],
[87.6],
[79.4],
[93.4]])
np.dot(data, weights)
array([[84.2],
[80.6],
[80.1],
[90. ],
[83.2],
[87.6],
[79.4],
[93.4]])
data_mat * weights_mat
matrix([[84.2],
[80.6],
[80.1],
[90. ],
[83.2],
[87.6],
[79.4],
[93.4]])
data @ weights
array([[84.2],
[80.6],
[80.1],
[90. ],
[83.2],
[87.6],
[79.4],
[93.4]])
6. 合并、分割
6.1 合并
a = stock_change[:2, 0:4]
b = stock_change[4:6, 0:4]
a
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916],
[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.1 ]])
a.shape # (2, 4)
a.reshape((-1, 2))
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704],
[ 0.29667843, 0.16606916],
[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108],
[ 0.122042 , 1.1 ]])
b
array([[-0.9822216 , -1.09482936, -0.81834523, 1.1 ],
[ 0.41739964, -0.26826893, -0.70003442, -0.58593912]])
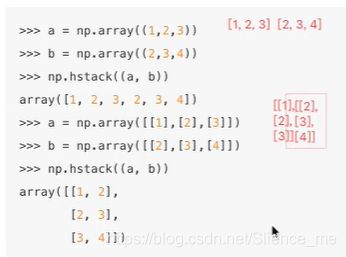
np.hstack((a, b))
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916, -0.9822216 ,
-1.09482936, -0.81834523, 1.1 ],
[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.1 , 0.41739964,
-0.26826893, -0.70003442, -0.58593912]])
np.concatenate((a, b), axis=1)
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916, -0.9822216 ,
-1.09482936, -0.81834523, 1.1 ],
[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.1 , 0.41739964,
-0.26826893, -0.70003442, -0.58593912]])
np.vstack((a, b))
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916],
[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.1 ],
[-0.9822216 , -1.09482936, -0.81834523, 1.1 ],
[ 0.41739964, -0.26826893, -0.70003442, -0.58593912]])
np.concatenate((a, b), axis=0)
array([[ 1.1 , -0.45576704, 0.29667843, 0.16606916],
[ 0.36775845, 0.24078108, 0.122042 , 1.1 ],
[-0.9822216 , -1.09482936, -0.81834523, 1.1 ],
[ 0.41739964, -0.26826893, -0.70003442, -0.58593912]])
6.2 分割
7. IO操作与数据处理
7.1 Numpy读取
data = np.genfromtxt("test.csv", delimiter=",")
array([[ nan, nan, nan, nan],
[ 1. , 123. , 1.4, 23. ],
[ 2. , 110. , nan, 18. ],
def fill_nan_by_column_mean(t):
for i in range(t.shape[1]):
# 计算nan的个数
nan_num = np.count_nonzero(t[:, i][t[:, i] != t[:, i]])
if nan_num > 0:
now_col = t[:, i]
# 求和
now_col_not_nan = now_col[np.isnan(now_col) == False].sum()
# 和/个数
now_col_mean = now_col_not_nan / (t.shape[0] - nan_num)
# 赋值给now_col
now_col[np.isnan(now_col)] = now_col_mean
# 赋值给t,即更新t的当前列
t[:, i] = now_col
return t
7.2 如何处理缺失值
两种思路:
- 直接删除含有缺失值的样本
- 替换/插补
- 按列求平均,用平均值进行填补