鲍鱼数据集 岭回归解析解
要求:首先数据集进行一定的预处理,之后计算岭回归的解析解,并采用合适的指标对结果进行评估。
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')#忽略匹配警告
data=pd.read_csv(r'C:/Users/86139/Desktop/大二下/机器学习/机器学习实践/abalone_dataset.csv')
data.head()
| sex | length | diameter | height | whole weight | shucked weight | viscera weight | shell weight | rings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | M | 0.455 | 0.365 | 0.095 | 0.5140 | 0.2245 | 0.1010 | 0.150 | 15 |
| 1 | M | 0.350 | 0.265 | 0.090 | 0.2255 | 0.0995 | 0.0485 | 0.070 | 7 |
| 2 | F | 0.530 | 0.420 | 0.135 | 0.6770 | 0.2565 | 0.1415 | 0.210 | 9 |
| 3 | M | 0.440 | 0.365 | 0.125 | 0.5160 | 0.2155 | 0.1140 | 0.155 | 10 |
| 4 | I | 0.330 | 0.255 | 0.080 | 0.2050 | 0.0895 | 0.0395 | 0.055 | 7 |
一、预处理
#2.1对sex特征进行onehot编码,便于后续模型纳入哑变量
sex_onehot=pd.get_dummies(data['sex'],prefix="sex")
data[sex_onehot.columns]=sex_onehot
data.head()
| sex | length | diameter | height | whole weight | shucked weight | viscera weight | shell weight | rings | sex_F | sex_I | sex_M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | M | 0.455 | 0.365 | 0.095 | 0.5140 | 0.2245 | 0.1010 | 0.150 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | M | 0.350 | 0.265 | 0.090 | 0.2255 | 0.0995 | 0.0485 | 0.070 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | F | 0.530 | 0.420 | 0.135 | 0.6770 | 0.2565 | 0.1415 | 0.210 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | M | 0.440 | 0.365 | 0.125 | 0.5160 | 0.2155 | 0.1140 | 0.155 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | I | 0.330 | 0.255 | 0.080 | 0.2050 | 0.0895 | 0.0395 | 0.055 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
#2.2添加取值为1的特征
data["ones"]=1
data.head()
| sex | length | diameter | height | whole weight | shucked weight | viscera weight | shell weight | rings | sex_F | sex_I | sex_M | ones | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | M | 0.455 | 0.365 | 0.095 | 0.5140 | 0.2245 | 0.1010 | 0.150 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | M | 0.350 | 0.265 | 0.090 | 0.2255 | 0.0995 | 0.0485 | 0.070 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | F | 0.530 | 0.420 | 0.135 | 0.6770 | 0.2565 | 0.1415 | 0.210 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | M | 0.440 | 0.365 | 0.125 | 0.5160 | 0.2155 | 0.1140 | 0.155 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | I | 0.330 | 0.255 | 0.080 | 0.2050 | 0.0895 | 0.0395 | 0.055 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
#2.3根据鲍鱼环计算年龄。
#一般每过一年,鲍鱼就会在其壳上留下一道深深的印记,这叫生长纹,就相当于树木的年轮。在本数据集中,我们要预测的是鲍鱼的年龄,可以通过环数rings 加上1.5得到。
data['age']=data['rings']+1.5
data.head()
| sex | length | diameter | height | whole weight | shucked weight | viscera weight | shell weight | rings | sex_F | sex_I | sex_M | ones | age | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | M | 0.455 | 0.365 | 0.095 | 0.5140 | 0.2245 | 0.1010 | 0.150 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 16.5 |
| 1 | M | 0.350 | 0.265 | 0.090 | 0.2255 | 0.0995 | 0.0485 | 0.070 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 8.5 |
| 2 | F | 0.530 | 0.420 | 0.135 | 0.6770 | 0.2565 | 0.1415 | 0.210 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10.5 |
| 3 | M | 0.440 | 0.365 | 0.125 | 0.5160 | 0.2155 | 0.1140 | 0.155 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 11.5 |
| 4 | I | 0.330 | 0.255 | 0.080 | 0.2050 | 0.0895 | 0.0395 | 0.055 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 8.5 |
#2.4筛选特征
#将预测目标设置为 age列,然后构造两组特征,一组包含ones,一组不包含ones。对于 sex相关的列,我们只使用sex_F和sex_M。
y=data['age']#因变量
features_with_ones=[ 'length', 'diameter', 'height', 'whole weight', 'shucked weight',
'viscera weight', 'shell weight', 'sex_F', 'sex_M','ones']
features_without_ones=[ 'length', 'diameter', 'height', 'whole weight', 'shucked weight',
'viscera weight', 'shell weight', 'sex_F', 'sex_M']
X=data[features_with_ones]
#2.5 将鲍鱼数据集划分为训练集和测试集
#将数据集随机划分为训练集和测试集,其中80%样本为训练集,剩余20%样本为测试集。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=111)
二、计算岭回归解析解
(1)使用Numpy实现岭回归(Rigde)
def ridge_regression(X,y,ridge_lambda):
penalty_matrix=np.eye(X.shape[1])
penalty_matrix[X.shape[1]-1][X.shape[1]-1]=0
w=np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)+ridge_lambda*penalty_matrix).dot(X.T).dot(y)
return w
import numpy as np
w2=ridge_regression(X_train,y_train,1.0)
w2
array([ 2.30976528, 6.72038628, 10.23298909, 7.05879189,
-17.16249532, -7.2343118 , 9.3936994 , 0.96869974,
0.9422174 , 4.80583032])
w2=pd.DataFrame(data=w2,index=X.columns,columns=['numpy_ridge_w'])
w2['numpy_ridge_w']=w2
w2.round(decimals=2)
| numpy_ridge_w | |
|---|---|
| length | 2.31 |
| diameter | 6.72 |
| height | 10.23 |
| whole weight | 7.06 |
| shucked weight | -17.16 |
| viscera weight | -7.23 |
| shell weight | 9.39 |
| sex_F | 0.97 |
| sex_M | 0.94 |
| ones | 4.81 |
(2)利用sklearn实现岭回归
#与sklearn中岭回归对比,同样正则化系数设置为 1
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
#模型实例化
ridge=Ridge(alpha=1)
#模型训练
ridge.fit(X_train[features_without_ones],y_train)
w_ridge=[]
w_ridge.extend(ridge.coef_)#coef_权重向量
w_ridge.append(ridge.intercept_)#intercept_决策函数的独立项,即截距b值。如果fit_intercept = False,则设置为0.0。
w2["ridge_sklearn_w"]=w_ridge
w2.round(decimals=2)
| numpy_ridge_w | ridge_sklearn_w | |
|---|---|---|
| length | 2.31 | 2.31 |
| diameter | 6.72 | 6.72 |
| height | 10.23 | 10.23 |
| whole weight | 7.06 | 7.06 |
| shucked weight | -17.16 | -17.16 |
| viscera weight | -7.23 | -7.23 |
| shell weight | 9.39 | 9.39 |
| sex_F | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| sex_M | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| ones | 4.81 | 4.81 |
**
三、结果评估
**
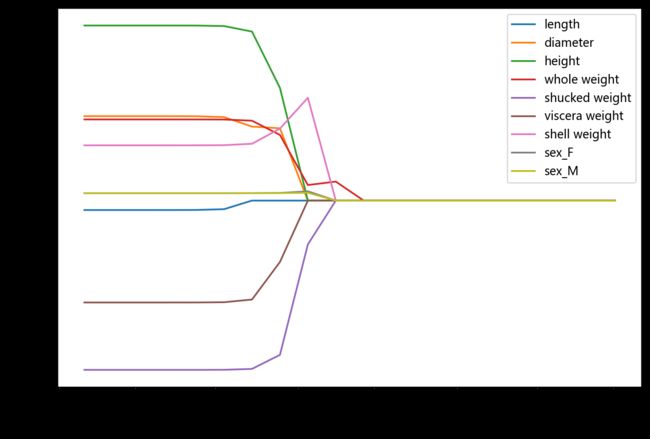
#岭迹分析
alpha=np.logspace(-10,10,20)
coef=pd.DataFrame()
for alpha in alpha:
lasso_clf=Lasso(alpha=alpha)
lasso_clf.fit(X_train[features_without_ones],y_train)
df=pd.DataFrame([lasso_clf.coef_],columns=X_train[features_without_ones].columns)
df['alpha']=alpha
coef=coef.append(df,ignore_index=True)
coef.round(decimals=2)
| length | diameter | height | whole weight | shucked weight | viscera weight | shell weight | sex_F | sex_M | alpha | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.12 | 10.00 | 20.74 | 9.61 | -20.05 | -12.07 | 6.55 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 1 | -1.12 | 10.00 | 20.74 | 9.61 | -20.05 | -12.07 | 6.55 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 2 | -1.12 | 10.00 | 20.74 | 9.61 | -20.05 | -12.07 | 6.55 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 3 | -1.12 | 10.00 | 20.74 | 9.61 | -20.05 | -12.07 | 6.55 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 4 | -1.11 | 9.99 | 20.73 | 9.61 | -20.05 | -12.07 | 6.55 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 5 | -1.02 | 9.89 | 20.67 | 9.60 | -20.04 | -12.04 | 6.56 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 6 | -0.00 | 8.76 | 20.02 | 9.46 | -19.94 | -11.72 | 6.73 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 7 | 0.00 | 8.56 | 13.35 | 7.78 | -18.27 | -7.28 | 8.52 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.84 | -5.19 | 0.00 | 12.18 | 1.10 | 0.93 | 3.000000e-02 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.25 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.000000e-01 |
| 10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.360000e+00 |
| 11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.793000e+01 |
| 12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4.281300e+02 |
| 13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4.832930e+03 |
| 14 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 5.455595e+04 |
| 15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6.158482e+05 |
| 16 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6.951928e+06 |
| 17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 7.847600e+07 |
| 18 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 8.858668e+08 |
| 19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.000000e+10 |
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
#plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei','Times New Roman']
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['Microsoft YaHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi']=200#分辨率
plt.figure(figsize=(9,6))
coef['alpha']=coef['alpha']
for feature in X_train.columns[:-1]:
plt.plot('alpha',feature,data=coef)
ax=plt.gca()
ax.set_xscale('log')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlabel(r'$\alpha$',fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('系数',fontsize=15)
Text(0, 0.5, '系数')
回归模型的评价指标
鲍鱼年龄预测模型效果评价
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
#MAE平均绝对误差
y_test_pred_ridge=ridge.predict(X_test[features_without_ones])
print(round(mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_test_pred_ridge),4))
#MSE 均方误差
y_test_pred_ridge=ridge.predict(X_test[features_without_ones])
print(round(mean_squared_error(y_test,y_test_pred_ridge),4))
#R^2系数
print(round(r2_score(y_test,y_test_pred_ridge),4))
1.5984
4.959
0.5563
残差图
残差图是一种用来诊断回归模型效果的图。在残差图中,如果点随机分布在0附近,则说明回归效果较好。如果在残差图中发现了某种结构,则说明回归效果不佳,需要重新建模。
plt.figure(figsize=(9,6),dpi=600)
y_train_pred_ridge=ridge.predict(X_train[features_without_ones])
plt.scatter(y_train_pred_ridge,y_train_pred_ridge-y_train,c='g',alpha=0.6)
plt.scatter(y_test_pred_ridge,y_test_pred_ridge-y_test,c='r',alpha=0.6)
plt.hlines(y=0,xmin=0,xmax=30,colors="b",alpha=0.6)
plt.ylabel('Residuals')
plt.xlabel('Predict')
Text(0.5, 0, 'Predict')