python实现的博弈论简单智能体
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 智能体类
class Gamer:
# 构造方法
def __init__(self, name, choice, benefit, max_, min_):
self.name = name # 智能体名字
self.choice = choice # 博弈选项
self.benefit = benefit # 博弈得益
self.k = len(choice) # 决策数目
self.chance = [self.k] * self.k # 决策概率/期望
self.max_ = max_ # 得益最大值
self.min_ = min_ # 得益最小值
def __str__(self): # 输出方法
return '智能体名称:' + self.name + '\n策略:' + str(self.choice) + \
'概率:' + str(self.chance) + '\n得益:' + str(self.benefit)
def decision(self,e = 0, t=0.0): # 做出决定 e = 1 贪心选择 t 增加不确定性
x = random.uniform(0, sum(self.chance)) # 随机做决定
if random.random() < t: # 有t的概率随意选择
return random.choice(self.choice)
if e :
return self.choice[self.chance.index(max(self.chance))]
for i in range(self.k):
x = x - self.chance[i] # 减去概率,若取到的值小于等于0说明命中
if x <= 0:
return self.choice[i] # 返回命中的决定
return self.choice[-1]
# 按智能体决定给出得益
def give_benefit(self, c_1, c_2): # c_1自己的决定,c_2对方的决定
return self.benefit[c_1][c_2]
# 对概率进行约束处理,防止浮点计算误差
def bind(self):
s = sum(self.chance)
self.chance = [i / s for i in self.chance]
# 以智能体的选择来更新决策概率
def renew(self, c_1, b, lr, e=0, t = 0.0): # c_1自己的决定, b得益值,lr学习率
m = self.choice.index(c_1)
# self.chance[m] += lr * b * self.chance[m]
if e:
self.chance = [(1-t*2) * i for i in self.chance]
self.chance[m] = lr * (b - self.min_) / (self.max_ - self.min_)+(1-lr)*self.chance[m]
else:
self.chance[m] += lr * (b - self.min_) / (self.max_ - self.min_)
self.bind()
# 博弈一下,不更改参数
def play(g1, g2):
cg1 = g1.decision()
cg2 = g2.decision()
return g1.give_benefit(cg1, cg2), g2.give_benefit(cg2, cg1)
# 训练 loop 循环次数,lr 学习率。plot=1时绘图 e为 按期望运算 t为不确定性
def train(g1, g2, loop, lr=0.03, plot=0, e=0,t=0.0):
if plot:
y = [[], []] # 记录概率,绘图用
if e: # 按期望运算时,初始期望大一点
g1.chance = [i + 1000 for i in g1.chance]
g2.chance = [i + 1000 for i in g2.chance]
for epoch in range(loop):
if plot:
y[0].append(g1.chance[0] / sum(g1.chance))
y[1].append(g2.chance[0] / sum(g2.chance))
c_1 = g1.decision(t=t) # 左参与人按概率做出的选择
c_2 = g2.decision(t=t) # 上参与人按概率做出的选择
# c_1 = random.choice(g1.choice) # 左参与人随机做出的选择
# c_2 = random.choice(g2.choice) # 上参与人随机做出的选择
b_1 = g1.give_benefit(c_1, c_2) # 左参与人的得益
b_2 = g2.give_benefit(c_2, c_1) # 上参与人的得益
g1.renew(c_1, b_1, lr, e,t=t) # 左参与人更新
g2.renew(c_2, b_2, lr, e,t=t) # 上参与人更新
if e:
print(g1.chance,g2.chance)
g1.bind(), g2.bind()
if plot:
# 下面这里用于正确显示中文
font = {'family': 'SimHei', # 黑体
'weight': 'bold', # 粗体
'size': '16'} # 大小 16
plt.rc('font', **font)
plt.rc('axes', unicode_minus=False)
x = list(range(len(y[0])))
plt.figure(1) # 开个窗口,准备绘图
plt.plot(x, y[0], label=g1.name+'选择' + str(g1.choice[0]) + '的概率')
plt.plot(x, y[1], label=g2.name+'选择' + str(g2.choice[0]) + '的概率')
plt.legend(loc='lower right') # 显示上面的label
plt.xlabel('训练次数') # x_label
plt.ylabel('概率') # y_label
plt.title('训练次数和选项的概率') # 标题
plt.show()
@staticmethod # 静态方法
def give_parameter(x): # 以得益矩阵生成两个智能体的参数
c1 = [] # 左参与者的决策
c2 = x[0] # 上参与者的决策
b1 = {} # 左参与者的得益
b2 = {} # 上参与者的得益
for i in c2: # 给上参与者决策加键值
b2[i] = {}
k1 = len(x) - 1 # 左参与者的决策数
k2 = len(c2) # 上参与者的决策数
a1 = a2 = -float("inf")
i1 = i2 = float("inf")
for i in range(1, k1 + 1): # 行遍历
c1.append(x[i][0])
b1[x[i][0]] = {} # 对于左参与者的这个决策
for j in range(1, k2 + 1): # 列遍历
b1[x[i][0]][c2[j - 1]] = x[i][j][0]
b2[c2[j - 1]][c1[i - 1]] = x[i][j][1]
if x[i][j][0] > a1:
a1 = x[i][j][0]
elif x[i][j][0] < i1:
i1 = x[i][j][0]
if x[i][j][1] > a2:
a2 = x[i][j][1]
elif x[i][j][1] < i2:
i2 = x[i][j][1]
return c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2
# 智猪博弈参数
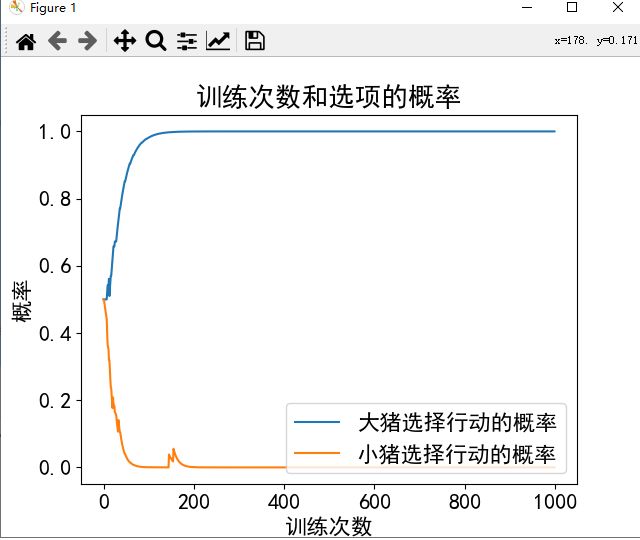
def boxed_pigs():
n1 = '大猪' # 智能体1的名字 左
n2 = '小猪' # 智能体2的名字 上
# 博弈矩阵
b = [['行动', '等待'],
['行动', [5, 1], [4, 4]],
['等待', [9, -1], [0, 0]]]
c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Gamer.give_parameter(b)
return n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2
# 囚徒困境参数
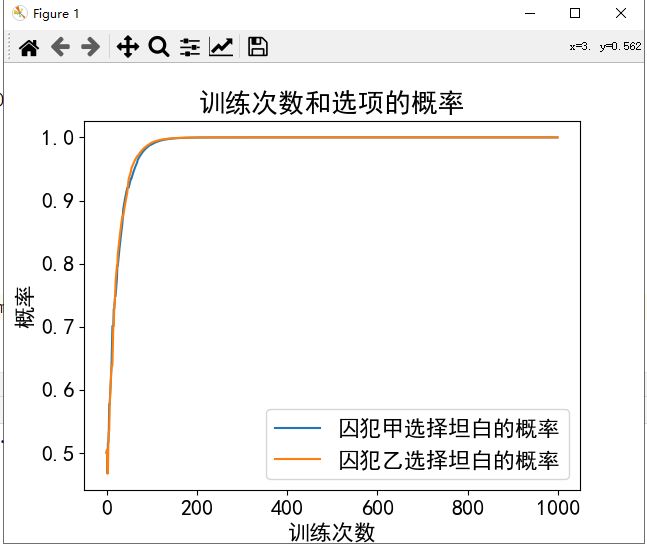
def Prisoner_Dilemma():
n1 = '囚犯甲' # 智能体1的名字 左
n2 = '囚犯乙' # 智能体2的名字 上
# 博弈矩阵
b = [['坦白', '抵赖'],
['坦白', [-3, -3], [0, -5]],
['抵赖', [-5, 0], [-1, -1]]]
c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Gamer.give_parameter(b)
return n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2
# 猎鹿博弈
def Stag_hunt():
n1 = '猎人甲' # 智能体1的名字 左
n2 = '猎人乙' # 智能体2的名字 上
# 博弈矩阵
b = [['猎鹿', '猎兔'],
['猎鹿', [5, 5], [0, 4]],
['猎兔', [4, 0], [4, 4]]]
c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Gamer.give_parameter(b)
return n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2
# 抽查
def Spot_check():
n1 = '职员' # 智能体1的名字 左
n2 = '经理' # 智能体2的名字 上
# 博弈矩阵
b = [['检查', '不检查'],
['勤奋', [10, 8], [8, 10]],
['偷懒', [6, 9], [10, 6]]]
c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Gamer.give_parameter(b)
return n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2
# 点球大战
def Penalty_shootout():
n1 = '格罗索' # 智能体1的名字 左
n2 = '巴特斯' # 智能体2的名字 上
# 博弈矩阵
b = [['左', '中', '右'],
['左', [0.65, 0.35], [0.95, 0.05], [0.95, 0.05]],
['中', [0.95, 0.05], [0.0, 1.0], [0.95, 0.05]],
['右', [0.95, 0.05], [0.95, 0.05], [0.65, 0.35]]]
c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Gamer.give_parameter(b)
return n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2
# main函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = boxed_pigs()
# n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Prisoner_Dilemma()
# n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Stag_hunt()
# n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Spot_check() # +t
# n1, n2, c1, c2, b1, b2, a1, a2, i1, i2 = Penalty_shootout()
gamer_1 = Gamer(n1, c1, b1, a1, i1)
gamer_2 = Gamer(n2, c2, b2, a2, i2)
gamer_1.train(gamer_2,1000,0.1,plot=1,t = 0.01)
# gamer_1.train(gamer_2, 500, 0.3, plot=1, e=1,t=0.03) # 另外一种方法
print(gamer_1)
print(gamer_2)
简单结果示例: