Pytorch手写数字数据集MNIST图像分类,自写全链接模型实现
文章目录
- 一、MNIST数据集的下载和使用
- 二、认识手写数据集MNIST
-
- 前十张数据的标签
- 三、MNIST数据集全连接模型训练
-
- 1.创建模型
- 2.定义损失函数和优化器
- 3 .编写fit训练函数
- 4.调用fit训练函数,进行训练
- 总结(本文全部代码)
一、MNIST数据集的下载和使用
torchvision内置了常用数据集和最常见的模型
我们通过torchvision导入MNIST数据集
如果之前没有,则此处会联网进行下载
示例代码如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.data
transformation = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(), # 1.转换成Tensor 2.转换到0-1之间 3.会将channel放到第一维度
])
train_ds = datasets.MNIST(
'F:/MnistData/', # 数据存放的路径
train=True,
transform=transformation,
download=True # 如果没有就下载
)
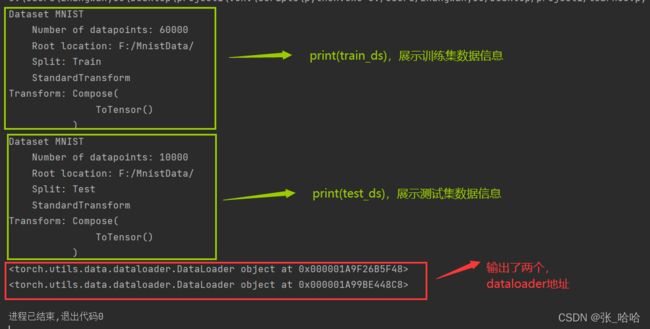
print(train_ds)
test_ds = datasets.MNIST(
'F:/MnistData/',
train=False, # 注意此处为False
transform=transformation,
download=True
)
print(test_ds)
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=256) # 测试集计算量比较少,批次一次可以大点
print(train_dl)
print(test_dl)
二、认识手写数据集MNIST
展示手写数据集中的数据
注意:在Pytorch里图片的表示形式:【batch, channel, hight, width】
示例代码如下:
# 展示一个批次的数据,注意在pytorch里面图片的表示形式
# 在pytorch里图片的表示形式:[batch, channel, hight, width]
imgs, labels = next(iter(train_dl))
print(imgs.shape)
img = imgs[0] # 取出一张图片
print(img.shape)
img = img.numpy()
img = np.squeeze(img)
print(img.shape)
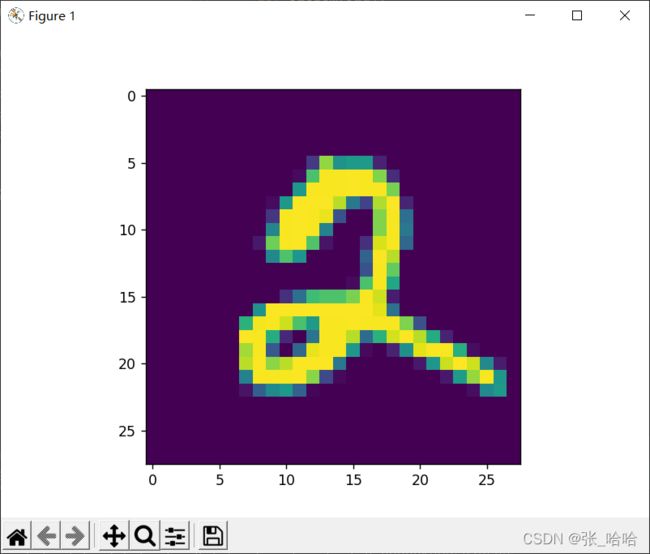
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
# 一次显示多张图片
def imshow(img):
npimg = img.numpy()
npimg = np.squeeze(npimg)
plt.imshow(npimg)
# 一次十张,调用上述方法
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 1))
for i, img in enumerate(imgs[:10]):
plt.subplot(1, 10, i+1)
imshow(img)
plt.show()
# 查看前十张图片标签
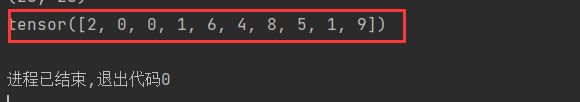
print(labels[:10])
运行结果见下图:
展示数据集中单张照片数据
三、MNIST数据集全连接模型训练
将数据做展平处理,去掉模型中的空间维度
1.创建模型
示例代码如下:
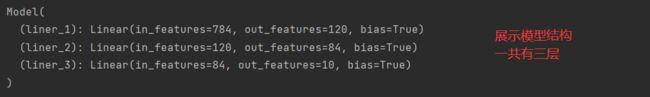
# 创建模型
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.liner_1 = nn.Linear(28*28, 120) # 输入特征维度28*28
self.liner_2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.liner_3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) # 十分类故输出应为十
def forward(self, input):
x = input.view(-1, 28*28)
x = F.relu(self.liner_1(x))
x = F.relu(self.liner_2(x))
x = self.liner_3(x)
return x
model = Model()
print(model)
2.定义损失函数和优化器
示例代码如下:
# 定义损失函数
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 编写优化器
optim = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
3 .编写fit训练函数
示例代码如下
# 编写fit函数,输入模型、输入数据(train_dl, test_dl),对数据输入在模型上训练,并且返回loss和acc
def fit(epoch, model, trainloader, testloader):
correct = 0
total = 0
running_loss = 0
for x, y in trainloader:
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optim.step()
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
total += y.size(0)
running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc = correct / total
epoch_loss = running_loss/len(train_dl.dataset)
test_correct = 0
test_total = 0
test_running_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in testloader:
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
test_correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
test_total += y.size(0)
test_running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_test_acc = correct / total
epoch_test_loss = test_running_loss / len(test_dl.dataset)
print('epoch:', epoch,
'loss:', round(epoch_loss, 3),
'accuracy:', round(epoch_acc, 3),
'test_loss:', round(epoch_test_loss, 3),
'test_accuracy:', round(epoch_test_acc, 3)
)
return epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
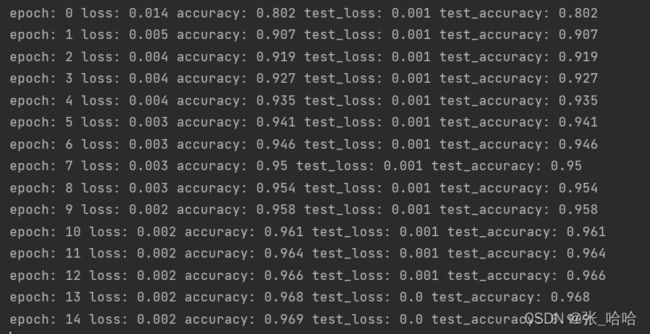
4.调用fit训练函数,进行训练
示例代码如下
# 运行训练过程代码
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
epochs = 15
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc = fit(epoch, model, train_dl, test_dl)
train_loss.append(epoch_loss)
train_acc.append(epoch_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
# 绘图
plt.plot(range(1, epochs+1), train_loss, label='train_loss')
plt.plot(range(1, epochs+1), test_loss, label='test_loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
总结(本文全部代码)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.data
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
transformation = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(), # 1.转换成Tensor 2.转换到0-1之间 3.会将channel放到第一维度
])
train_ds = datasets.MNIST(
'F:/MnistData/', # 数据存放的路径
train=True,
transform=transformation,
download=True # 如果没有就下载
)
print(train_ds)
test_ds = datasets.MNIST(
'F:/MnistData/',
train=False, # 注意此处为False
transform=transformation,
download=True
)
print(test_ds)
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=256) # 测试集计算量比较少,批次一次可以大点
print(train_dl)
print(test_dl)
# 展示一个批次的数据,注意在pytorch里面图片的表示形式
# 在pytorch里图片的表示形式:[batch, channel, hight, width]
imgs, labels = next(iter(train_dl))
print(imgs.shape)
img = imgs[0] # 取出一张图片
print(img.shape)
img = img.numpy()
img = np.squeeze(img)
print(img.shape)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
# 一次显示多张图片
def imshow(img):
npimg = img.numpy()
npimg = np.squeeze(npimg)
plt.imshow(npimg)
# 一次十张,调用上述方法
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 1))
for i, img in enumerate(imgs[:10]):
plt.subplot(1, 10, i+1)
imshow(img)
plt.show()
# 查看前十张图片标签
print(labels[:10])
# 创建模型
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.liner_1 = nn.Linear(28*28, 120) # 输入特征维度28*28
self.liner_2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.liner_3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) # 十分类故输出应为十
def forward(self, input):
x = input.view(-1, 28*28)
x = F.relu(self.liner_1(x))
x = F.relu(self.liner_2(x))
x = self.liner_3(x)
return x
model = Model()
print(model)
# 定义损失函数
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 编写优化器
optim = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
# 编写fit函数,输入模型、输入数据(train_dl, test_dl),对数据输入在模型上训练,并且返回loss和acc
def fit(epoch, model, trainloader, testloader):
correct = 0
total = 0
running_loss = 0
for x, y in trainloader:
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optim.step()
with torch.no_grad():
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
total += y.size(0)
running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc = correct / total
epoch_loss = running_loss/len(train_dl.dataset)
test_correct = 0
test_total = 0
test_running_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in testloader:
y_pred = model(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1)
test_correct += (y_pred == y).sum().item()
test_total += y.size(0)
test_running_loss += loss.item()
epoch_test_acc = correct / total
epoch_test_loss = test_running_loss / len(test_dl.dataset)
print('epoch:', epoch,
'loss:', round(epoch_loss, 3),
'accuracy:', round(epoch_acc, 3),
'test_loss:', round(epoch_test_loss, 3),
'test_accuracy:', round(epoch_test_acc, 3)
)
return epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
# 运行训练过程代码
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
epochs = 15
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch_loss, epoch_acc, epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc = fit(epoch, model, train_dl, test_dl)
train_loss.append(epoch_loss)
train_acc.append(epoch_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
# 绘图
plt.plot(range(1, epochs+1), train_loss, label='train_loss')
plt.plot(range(1, epochs+1), test_loss, label='test_loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()