【slam十四讲第二版】【课本例题代码向】【第七讲~视觉里程计Ⅱ】【使用LK光流(cv)】【高斯牛顿法实现单层光流和多层光流】【实现单层直接法和多层直接法】
【slam十四讲第二版】【课本例题代码向】【第七讲~视觉里程计Ⅱ】【使用LK光流(cv)】【高斯牛顿法实现单层光流和多层光流】【实现单层直接法和多层直接法】
- 0 前言
- 1 使用LK光流(cv)
-
- 1.1 前言
- 1.2 useLK.cpp
- 1.3 CMakeLists.txt
- 1.4 输出数据为
- 1.5 感悟
- 2 高斯牛顿法实现单层光流和多层光流
-
- 2.1 前言
- 2.2 optical_flow.cpp
- 2.3 CMakeLists.txt
- 2.4 输出结果为
- 2.5 感悟
- 3 直接法
-
- 3.1 前言
- 3.2 direct_method.cpp
- 3.3 CMakeLists.txt
- 3.4 输出结果
- 3.5 感悟
【slam十四讲第二版】【课本例题代码向】【第三~四讲刚体运动、李群和李代数】【eigen3.3.4和pangolin安装,Sophus及fim的安装使用】【绘制轨迹】【计算轨迹误差】
【slam十四讲第二版】【课本例题代码向】【第五讲~相机与图像】【OpenCV、图像去畸变、双目和RGB-D、遍历图像像素14种】
【slam十四讲第二版】【课本例题代码向】【第六讲~非线性优化】【安装对应版本ceres2.0.0和g2o教程】【手写高斯牛顿、ceres2.0.0、g2o拟合曲线及报错解决方案】
【slam十四讲第二版】【课本例题代码向】【第七讲~视觉里程计Ⅰ】【1OpenCV的ORB特征】【2手写ORB特征】【3对极约束求解相机运动】【4三角测量】【5求解PnP】【3D-3D:ICP】
0 前言
- 这一章节东西不多,希望快点学完
- 该章节所使用的数据集自取:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1daebAx4DNHOtKrX8Up4lew 提取码: dcf5
1 使用LK光流(cv)
1.1 前言
- 这个部分仅仅涉及了如何配置cv中的LK函数的参数问题
- 其中所需要的数据集,以及我的工程包自取:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1mlBdAiSiy2-jc23fYRyImg
提取码:20dv
1.2 useLK.cpp
#include
#include 1.3 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(useLK)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
find_package(OpenCV 3 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES})
add_executable(useLK src/useLK.cpp)
target_link_libraries(useLK ${OpenCV_LIBRARIES})
1.4 输出数据为
/home/bupo/shenlan/zuoye/cap8/useLK/cmake-build-release/useLK /home/bupo/shenlan/zuoye/cap8/useLK/data
LK Flow use time:0.0401681 seconds.
tracked keypoints: 1749
LK Flow use time:0.0229127 seconds.
tracked keypoints: 1742
LK Flow use time:0.0223572 seconds.
tracked keypoints: 1703
LK Flow use time:0.0220847 seconds.
tracked keypoints: 1676
LK Flow use time:0.0232433 seconds.
tracked keypoints: 1664
LK Flow use time:0.0211483 seconds.
tracked keypoints: 1656
LK Flow use time:0.0216098 seconds.
tracked keypoints: 1641
LK Flow use time:0.0220525 seconds.
tracked keypoints: 1634
进程已结束,退出代码0
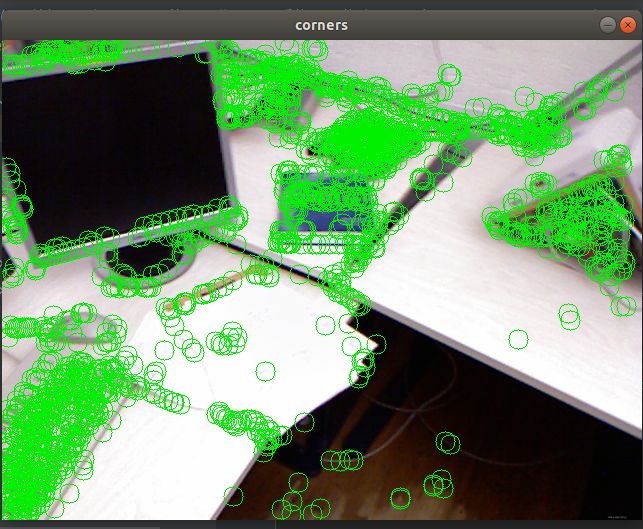
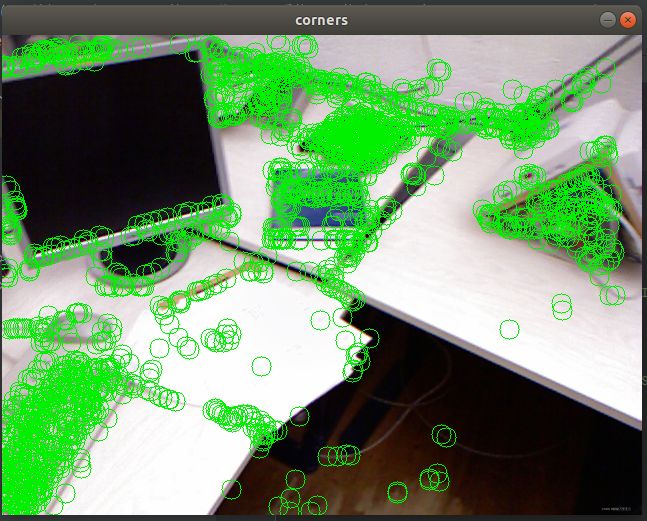
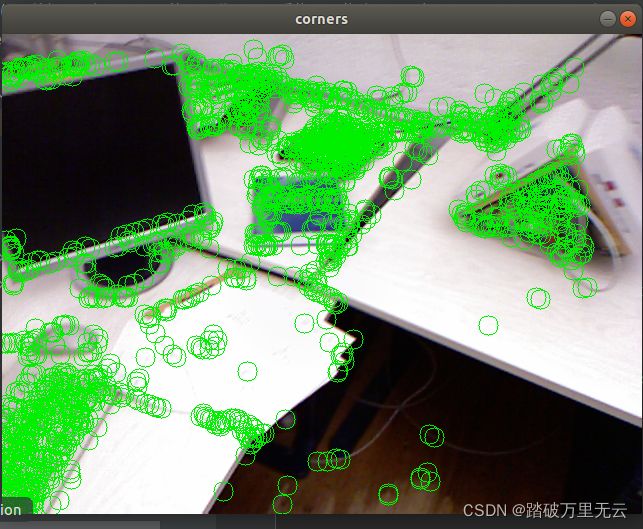
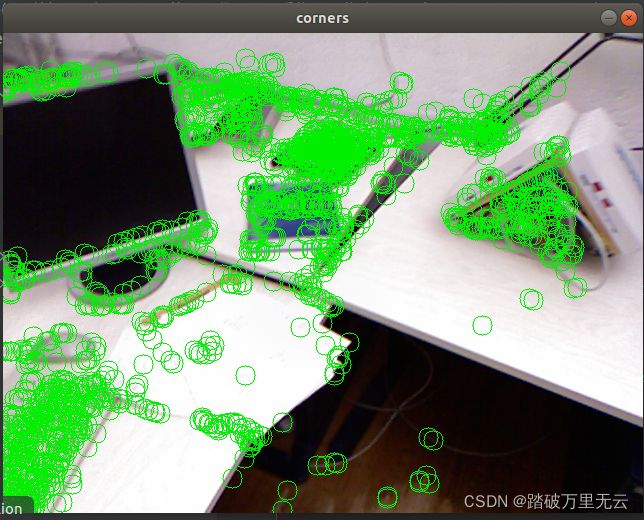
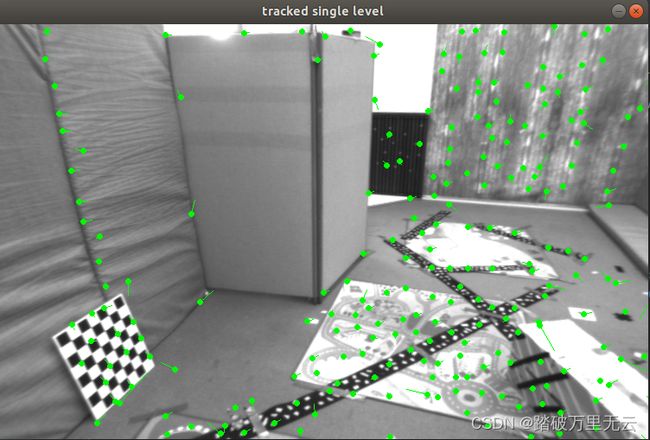
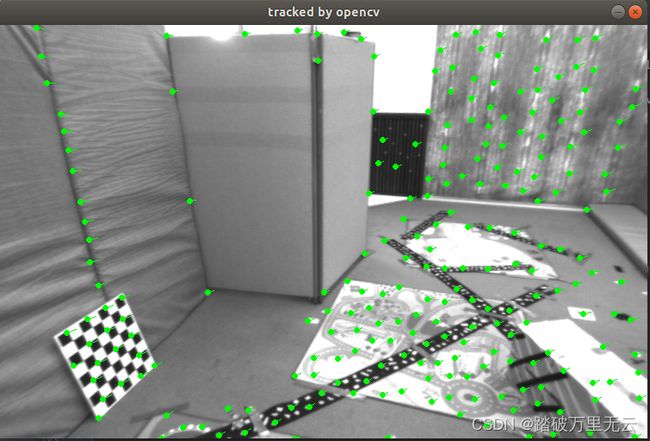
- 图片单张看并直观,最好亲身实践对比更为直观
1.5 感悟
- 暂无
2 高斯牛顿法实现单层光流和多层光流
2.1 前言
- 工程所必须的图片,以及我的实现工程自取:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1CCNdyz1ozrX47z4s49CE5A
提取码:gpjc
2.2 optical_flow.cpp
//
// Created by czy on 2022/4/10.
//
#include 2.3 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(optical_flow)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
#add_definitions("-DENABLE_SSE")
#set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 ${SSE_FLAGS} -g -O3 -march=native")
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
find_package(OpenCV 3 REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/include/eigen3/"
)
add_executable(optical_flow src/optical_flow.cpp)
target_link_libraries(optical_flow ${OpenCV_LIBS})
2.4 输出结果为
/home/bupo/shenlan/zuoye/cap8/optical_flow/cmake-build-release/optical_flow
build pyramid time: 0.000120757
track pyr 3 cost time: 0.00112688
track pyr 2 cost time: 0.000585512
track pyr 1 cost time: 0.000655574
track pyr 0 cost time: 0.00117114
optical flow by gauss-newton: 0.0200876
optical flow by opencv: 0.00293408
进程已结束,退出代码0
2.5 感悟
- 计算时间上没法作比较,但是这样看,多层光流法的耗时和OpenCV大致相当
- 从结果上看,多层光流与OpenCV的效果相当,单层光流要明显弱于多层光流
- 光流对图像的连续性和光照稳定性要求更高一些
- 如果角点提的位置不好,光流也容易跟丢或给出错误的结果,需要后续算法拥有一定的异常值去除机制。
- 光流法可以加速基于特征点的视觉里程计算法,避免计算和匹配描述子的过程,但要求相机运动较平滑(或采样频率较高)
3 直接法
3.1 前言
- 此工程所必需的图片,以及我的工程实现自取:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1kHG3Ukcw3MxgXVCN3GkzIA
提取码:v1vj
3.2 direct_method.cpp
#include 3.3 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(direct_method)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
add_definitions("-DENABLE_SSE")
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14 )
find_package(OpenCV 3 REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
find_package(Pangolin REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/include/eigen3/"
${Pangolin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
add_executable(direct_method src/direct_method.cpp)
target_link_libraries(direct_method
${OpenCV_LIBS}
${Pangolin_LIBRARIES}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES} fmt
)
3.4 输出结果
iteration: 0, cost: 396047
iteration: 1, cost: 170343
iteration: 2, cost: 67689.3
iteration: 3, cost: 41756.8
iteration: 4, cost: 41334.7
cost increased: 41340.7, 41334.7
T21 =
0.999992 0.00236441 0.00334249 0.00504878
-0.00237328 0.999994 0.00265186 0.00118042
-0.00333619 -0.00265977 0.999991 -0.733965
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.014914
iteration: 0, cost: 51023
iteration: 1, cost: 49681
cost increased: 49726.2, 49681
T21 =
0.999989 0.00303736 0.00345483 0.00149286
-0.0030451 0.999993 0.00223785 0.00662606
-0.00344801 -0.00224834 0.999992 -0.729061
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00205969
iteration: 0, cost: 70562.6
iteration: 1, cost: 65330.6
T21 =
0.999991 0.0025155 0.00346069 -0.00257406
-0.00252359 0.999994 0.00233607 0.00238353
-0.0034548 -0.00234479 0.999991 -0.734646
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00266652
iteration: 0, cost: 94610.3
T21 =
0.999991 0.00248065 0.00343352 -0.00373127
-0.0024882 0.999994 0.00219463 0.00304309
-0.00342806 -0.00220315 0.999992 -0.732334
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00196489
iteration: 0, cost: 343266
iteration: 1, cost: 227570
iteration: 2, cost: 143200
iteration: 3, cost: 92257.3
iteration: 4, cost: 65107.9
iteration: 5, cost: 57510.2
cost increased: 57801.7, 57510.2
T21 =
0.999972 0.000930072 0.00740586 0.0130114
-0.000964031 0.999989 0.00458318 0.00227666
-0.00740151 -0.0045902 0.999962 -1.45984
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00456659
iteration: 0, cost: 84146.3
iteration: 1, cost: 82026.1
cost increased: 82319.1, 82026.1
T21 =
0.999971 0.00111773 0.00759593 0.00445965
-0.00114863 0.999991 0.00406483 0.00340717
-0.00759132 -0.00407343 0.999963 -1.47139
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00226185
iteration: 0, cost: 131483
iteration: 1, cost: 128277
cost increased: 130601, 128277
T21 =
0.99997 0.000717595 0.00767486 -0.00126053
-0.000747681 0.999992 0.00391796 0.00298949
-0.00767198 -0.00392358 0.999963 -1.48212
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0051404
iteration: 0, cost: 116201
iteration: 1, cost: 107584
T21 =
0.999971 0.000699842 0.0075908 -0.00251934
-0.000728114 0.999993 0.0037224 0.00402137
-0.00758814 -0.00372782 0.999964 -1.4814
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00574368
iteration: 0, cost: 343049
iteration: 1, cost: 278665
iteration: 2, cost: 228254
cost increased: 259728, 228254
T21 =
0.999936 0.00162163 0.0111886 -0.0311607
-0.00171416 0.999964 0.00826583 -0.060339
-0.0111748 -0.00828448 0.999903 -2.02919
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00641602
iteration: 0, cost: 365842
iteration: 1, cost: 161026
iteration: 2, cost: 144814
cost increased: 178462, 144814
T21 =
0.999932 0.00143823 0.0115848 -0.0100368
-0.0015029 0.999983 0.00557577 -0.00555529
-0.0115765 -0.0055928 0.999917 -2.16362
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00550733
iteration: 0, cost: 178501
cost increased: 208142, 178501
T21 =
0.999935 0.00136293 0.0113536 0.00549402
-0.00142462 0.999984 0.00542701 -0.00318685
-0.011346 -0.00544282 0.999921 -2.20097
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00316008
iteration: 0, cost: 199364
iteration: 1, cost: 197451
iteration: 2, cost: 186346
cost increased: 187693, 186346
T21 =
0.999935 0.00135574 0.0113347 0.00437121
-0.00141595 0.999985 0.00530537 -0.00269083
-0.0113274 -0.00532107 0.999922 -2.23656
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00400765
iteration: 0, cost: 374461
iteration: 1, cost: 338582
iteration: 2, cost: 272162
iteration: 3, cost: 239430
iteration: 4, cost: 199236
iteration: 5, cost: 172497
iteration: 6, cost: 149510
iteration: 7, cost: 138870
iteration: 8, cost: 134446
iteration: 9, cost: 133814
T21 =
0.999872 -0.000298538 0.0160126 0.0253576
0.000182741 0.999974 0.00723266 -0.00504601
-0.0160143 -0.0072288 0.999846 -2.96692
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00723083
iteration: 0, cost: 160214
iteration: 1, cost: 153883
iteration: 2, cost: 153388
cost increased: 154647, 153388
T21 =
0.999865 -0.000321718 0.0163994 0.0131472
0.000212646 0.999978 0.00665231 -0.00453241
-0.0164012 -0.00664793 0.999843 -3.00764
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00315668
iteration: 0, cost: 228034
iteration: 1, cost: 219766
iteration: 2, cost: 217807
iteration: 3, cost: 216831
T21 =
0.999865 -0.000174516 0.0164416 0.00277336
7.12694e-05 0.99998 0.00627998 -0.00533273
-0.0164424 -0.00627796 0.999845 -3.01819
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00339888
iteration: 0, cost: 321505
iteration: 1, cost: 305955
iteration: 2, cost: 301146
iteration: 3, cost: 300392
cost increased: 300465, 300392
T21 =
0.999864 0.000259749 0.0164957 -0.0113293
-0.000356412 0.999983 0.00585725 0.000432521
-0.0164939 -0.00586233 0.999847 -3.0269
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00484743
iteration: 0, cost: 417833
iteration: 1, cost: 380020
iteration: 2, cost: 307367
iteration: 3, cost: 240955
iteration: 4, cost: 199866
iteration: 5, cost: 178705
iteration: 6, cost: 170523
iteration: 7, cost: 167044
iteration: 8, cost: 167006
iteration: 9, cost: 165164
T21 =
0.999797 0.000553496 0.0201461 0.0322426
-0.000698722 0.999974 0.00720231 0.0119608
-0.0201416 -0.00721492 0.999771 -3.7632
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00491216
iteration: 0, cost: 247795
iteration: 1, cost: 235625
iteration: 2, cost: 231769
iteration: 3, cost: 230604
cost increased: 231102, 230604
T21 =
0.999785 0.000734281 0.0207129 0.00793156
-0.000875909 0.999976 0.00682944 0.00753941
-0.0207073 -0.00684612 0.999762 -3.83512
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.0034232
iteration: 0, cost: 340213
iteration: 1, cost: 332062
iteration: 2, cost: 329315
cost increased: 329633, 329315
T21 =
0.999777 0.00109462 0.0210725 -0.00805546
-0.00122663 0.99998 0.00625257 0.011897
-0.0210652 -0.00627702 0.999758 -3.85499
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00298498
iteration: 0, cost: 429783
iteration: 1, cost: 420138
iteration: 2, cost: 416552
cost increased: 418560, 416552
T21 =
0.999785 0.00137068 0.0206667 -0.00333605
-0.00149613 0.999981 0.00605567 0.00868662
-0.020658 -0.00608529 0.999768 -3.86068
0 0 0 1
direct method for single layer: 0.00266961
进程已结束,退出代码0
3.5 感悟
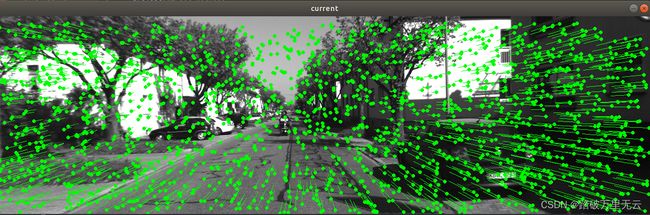
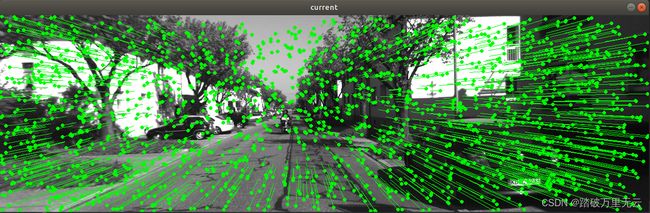
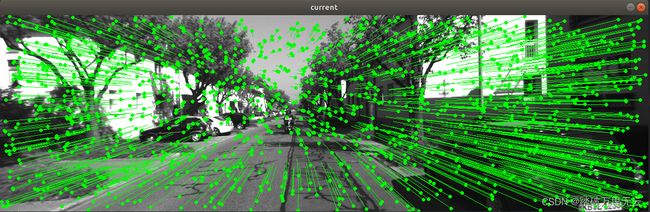
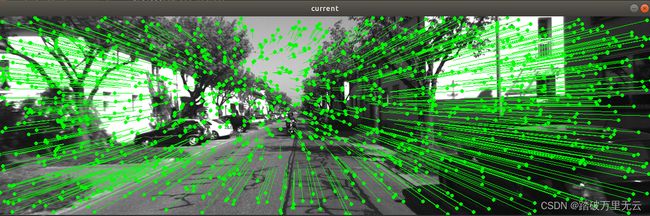
- 书上p230详细介绍了直接法的优缺点
- 上述的结果图中:每个小圆点是此时的点,而每个点都有一个自己的”尾巴“,这个尾巴的末尾就是该点在之前时刻的位置,所以可以看出,摄像头是向前前进的,从而有一种像素扑面而来的可视化