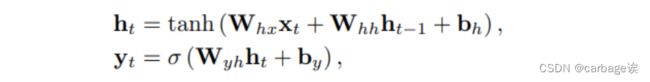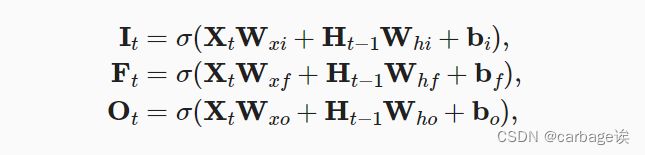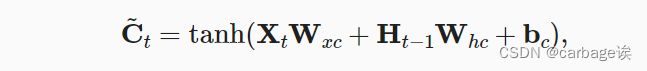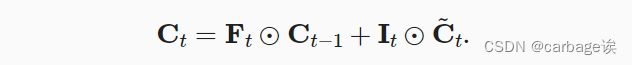DKT学习(一)
DKT实现Pytorch
- DKT
-
- DKT模型
-
- RNN
- LSTM
- 数据集介绍
- 数据集的处理
- 模型
- 隐藏状态处理
- 训练与测试
- 运行
DKT
DKT是Deep Knowledge Tracing的缩写,即深度知识追踪,论文中采用了两种模型,一种是带有sigmoid单位的普通RNN模型,另一种是长-短期记忆(LSTM)模型。
DKT模型
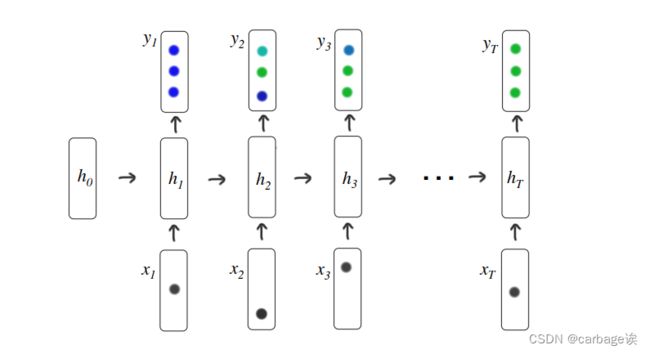
RNN
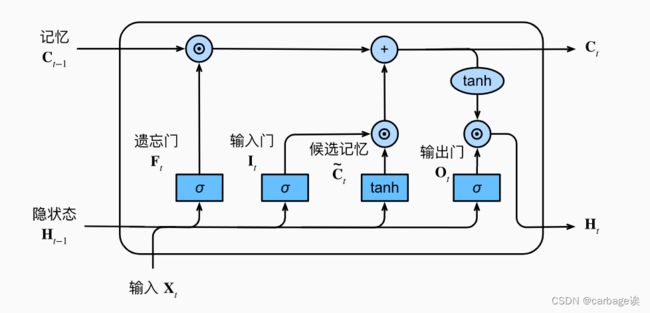
LSTM
数据集介绍
数据集的处理
data.py
# tuple_rows的每一行是tup:[[题目个数], [题目序列], [答对情况]],
# max_num_problems最长题目序列
# max_skill_num是知识点(题目)个数 (即最大题目编号+1)
def load_data(fileName):
rows = []
max_skill_num = 0
max_num_problems = 0
with open(fileName, "r") as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile, delimiter=',')
for row in reader:
rows.append(row) #rows为二维数组
index = 0
print("the number of rows is " + str(len(rows)))
tuple_rows = []
#turn list to tuple
while(index < len(rows)-1):
problems_num = int(rows[index][0])
tmp_max_skill = max(map(int, rows[index+1])) #map不改变原list,而是返回一个新list
if(tmp_max_skill > max_skill_num):
max_skill_num = tmp_max_skill
if(problems_num <= 2): #去除题目个数小于2的数据
index += 3
else:
if problems_num > max_num_problems:
max_num_problems = problems_num
tup = (rows[index], rows[index+1], rows[index+2])
tuple_rows.append(tup)
index += 3
#shuffle the tuple
random.shuffle(tuple_rows)
print("The number of students is ", len(tuple_rows))
print("Finish reading data")
return tuple_rows, max_num_problems, max_skill_num+1 #skill序号从0开始所以最长题目序列为max_skill_num+1
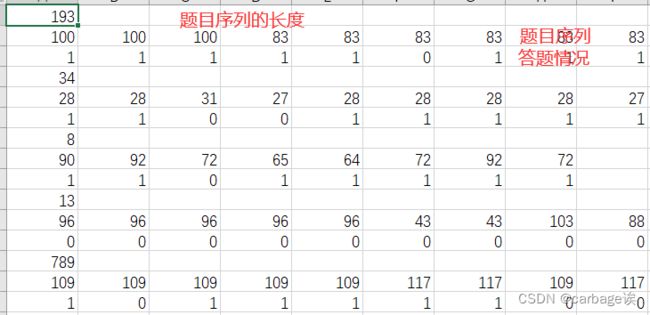
测试data.py
train_data_path='data/0910_b_train.csv'
tuple_rows, max_num_problems, max_skill_num = load_data(train_data_path)
print(max_num_problems)
print(max_skill_num)
print(tuple_rows)
运行结果如下

对模型输入数据的处理部分在run_epoch中
模型
model.py
class DeepKnowledgeTracing(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, rnn_type, input_size, hidden_size, num_skills, dropout=0.6):
super(DeepKnowledgeTracing,self).__init__()
if rnn_type == 'LSTM':
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, dropout=dropout)
else:
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, dropout=dropout)
# nn.Linear是一个全连接层,hidden_size是输入层维数,num_skills是输出层维数
#decoder是隐藏层(self.rnn)到输出层的网络
self.decoder = nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_skills)
self.nhid = hidden_size
self.rnn_type = rnn_type
def forward(self, input, hidden):
#input(时间步数,批量大小,隐层维度)
output, hidden = self.rnn(input, hidden)
#将output的形状改为(时间步数 * 批量大小, 隐藏单元数)
decoded = self.decoder(output.contiguous().view(output.size(0) * output.size(1), output.size(2)))
return decoded, hidden
def init_hidden(self, bsz): #初始化h0 维度为(隐层数,批量大小,隐藏单元数)
weight = next(self.parameters())
if self.rnn_type == 'LSTM':
return (weight.new_zeros(self.nlayers, bsz, self.nhid),
weight.new_zeros(self.nlayers, bsz, self.nhid))
else:
return weight.new_zeros(self.nlayers, bsz, self.nhid)
隐藏状态处理
def repackage_hidden(h):
"""Wraps hidden states in new Tensors, to detach them from their history."""
if isinstance(h, torch.Tensor):
return h.detach()
else:
return tuple(repackage_hidden(v) for v in h)
训练与测试
torch.nn.RNN接收的参数input形状是[时间步数, 批量大小, 特征维数]
def run_epoch(m, optimizer, students, batch_size, num_steps, num_skills, training=True, epoch=1):
"""Runs the model on the given data."""
# lr = lr # learning rate
total_loss = 0
input_size = num_skills * 2
start_time = time.time()
index = 0
actual_labels = []
pred_labels = []
# hidden = torch.zeros((1, batch_size, hidden_size))
hidden = m.init_hidden(batch_size)
count = 0
batch_num = len(students) // batch_size
while(index+batch_size < len(students)):
x = np.zeros((num_steps,batch_size))
# x = np.zeros((batch_size,num_steps))
target_id: List[int] = []
target_correctness = []
for i in range(batch_size):
student = students[index+i]
problem_ids = student[1] #题目序列
correctness = student[2] #答题结果
for j in range(len(problem_ids)-1): #x是答题序列的前n-1个(答题序列的前n-1个作为模型的输入)
problem_id = int(problem_ids[j])
label_index = 0
#答对就是知识点(题目)个数+题号, 答错就是题号, 方便后面转化成one_hot
if(int(correctness[j]) == 0):
label_index = problem_id
else:
label_index = problem_id + num_skills
x[j, i] = label_index
# 1个batch训练结束后用于判断准确率的题号 shape:( (num_steps-1)* batch_size)
target_id.append(j * batch_size * num_skills + i * num_skills + int(problem_ids[j + 1]))
# target_id.append(i*num_steps*num_skills+j*num_skills+int(problem_ids[j+1])) #需要预测的是答题序列的后n-1个(t时刻需要预测t+1时刻)
target_correctness.append(int(correctness[j+1])) #与target_id一一对应,表示是否答对
actual_labels.append(int(correctness[j+1]))
index += batch_size
count += 1
target_id = torch.tensor(target_id, dtype=torch.int64)
target_correctness = torch.tensor(target_correctness, dtype=torch.float)
target_id = target_id.to(device)
target_correctness = target_correctness.to(device)
# One Hot encoding input data [batch_size, num_steps, input_size]
x = torch.tensor(x, dtype=torch.int64) #x(batch_size, num_steps)
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 2) #x(batch_size, num_steps, 1) #unsqueeze()函数起升维的作用,参数dim表示在哪个地方加一个维度
# input_data:(num_steps, batch_size, input_size)
input_data = torch.FloatTensor(num_steps, batch_size, input_size)
# input_data = torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, num_steps, input_size)
input_data.zero_()
# scatter_用于生成one_hot向量,并且会将所有答题序列长度统一为num_steps
input_data.scatter_(2, x, 1) #将1,按照dim=2的方向,根据x所指示的位置,放入input_data中。
print(input_data.shape) #input_data(num_steps, batch_size, input_size)
input_data = input_data.to(device)
if training:
m.train()
if isinstance(hidden, tuple):
hidden = m.init_hidden(batch_size)
for s in hidden:
s.detach_()
s = s.to(device)
else:
hidden = m.init_hidden(batch_size)
hidden = hidden.to(device)
# hidden = m.init_hidden(batch_size)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# m.zero_grad()
# 前向计算, output:(num_steps, batch_size, num_skills)
output, hidden = m(input_data, hidden)
output = output.to(device)
# Get prediction results from output [batch_size, num_steps, num_skills]
# 将输出层转化为一维张量
output = output.contiguous().view(-1)
# tf.gather用一个一维的索引数组,将张量中对应索引的向量提取出来 (源张量,维度轴dim,索引张量)
logits = torch.gather(output, 0, target_id)
# preds
preds = torch.sigmoid(logits)
for p in preds:
pred_labels.append(p.item())
# criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
#计算误差,相当于nn.functional.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits()
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
criterion.to(device)
loss = criterion(logits, target_correctness)
loss.backward()
# `clip_grad_norm` helps prevent the exploding gradient problem in RNNs / LSTMs.
# 梯度截断,防止在RNNs或者LSTMs中梯度爆炸的问题
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(m.parameters(), max_grad_norm)
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
else:
with torch.no_grad():
m.eval()
if isinstance(hidden, tuple):
hidden = m.init_hidden(batch_size)
for s in hidden:
s.detach_()
s = s.to(device)
else:
hidden = m.init_hidden(batch_size)
hidden = hidden.to(device)
output, hidden = m(input_data, hidden)
output = output.to(device)
output = output.contiguous().view(-1)
logits = torch.gather(output, 0, target_id)
# preds
preds = torch.sigmoid(logits)
for p in preds:
pred_labels.append(p.item())
# criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
criterion.to(device)
loss = criterion(logits, target_correctness)
total_loss += loss.item()
hidden = repackage_hidden(hidden)
# print pred_labels
rmse = sqrt(mean_squared_error(actual_labels, pred_labels))
fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(actual_labels, pred_labels, pos_label=1)
auc = metrics.auc(fpr, tpr)
print("Epoch: {}, Batch {}/{} AUC: {}".format(epoch, count, batch_num, auc))
# calculate r^2
r2 = r2_score(actual_labels, pred_labels)
return rmse, auc, r2
运行遇到的错误
RuntimeError: cudnn RNN backward can only be called in training mode
原因:由于在训练时,设置的是m.train() 切换到预测模式时, 设置为m.eval(), 再回到训练环节,此时的网络依然是eval()模式,因此出现上述bug, 只要在继续训练模型之前加上m.train()即可解决问题
运行
train_data_path = '../input/dktdata/0910_b_train.csv'
test_data_path = '../input/dktdata/0910_b_test.csv'
train_students, train_max_num_problems, train_max_skill_num = load_data(train_data_path)
num_steps = train_max_num_problems
num_skills = train_max_skill_num
test_students, test_max_num_problems, test_max_skill_num = load_data(test_data_path)
input_size = num_skills * 2
batch_size = 32
hidden_size = 256
lr = 0.1
max_grad_norm = 20
evaluation_interval = 5
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
epochs = 100
epochs_list = []
train_auc_list = []
test_auc_list = []
model = DeepKnowledgeTracing('LSTM', input_size, hidden_size, num_skills)
model.to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr, eps=0.1)
for i in range(epochs):
rmse, auc, r2 = run_epoch(model, optimizer, train_students, batch_size, num_steps, num_skills, epoch=i)
print(rmse, auc, r2)
# Testing
if ((i + 1) % evaluation_interval == 0):
epochs_list.append(i+1)
train_auc_list.append(auc)
rmse, auc, r2 = run_epoch(model, optimizer, test_students, batch_size, num_steps, num_skills, training=False)
print('Testing')
print(rmse, auc, r2)
test_auc_list.append(auc)
在自己电脑上用CPU运行太慢,在kaggle上使用GPU运行
每个batch输入32条数据,每次迭代需要输入97个batch;
每迭代5次训练集,就在测试集上面进行一次测试;
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10), dpi=100)
plt.plot(epochs_list, train_auc_list,label="train")
plt.plot(epochs_list, test_auc_list, label="test")
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("AUC")
plt.scatter(epochs_list, train_auc_list)
plt.scatter(epochs_list, test_auc_list)
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
参考文章:DKT学习