YOLOv5 使用笔记
友情参与:@绵棉
文章目录
- 一、安装 & 配置环境
- 二、获取数据
- 三、标注数据集
- 四、train
-
- 4.1 训练前的准备工作
- 4.2 划分数据集
- 4.3 开始训练
- 4.4 模型继续训练
- 五、detect
- 六、碎碎念
YOLO 为一种目标检测方法,该方法的特点是实现快速检测的同时还达到较高的准确率。作者将目标检测任务看作目标区域预测和类别预测的回归问题。该方法采用单个神经网络直接预测物品边界和类别概率,实现端到端的物品检测。同时,该方法检测速非常快,基础版可以达到45帧/s的实时检测;FastYOLO可以达到155帧/s。与当前最好系统相比,YOLO目标区域定位误差更大,但是背景预测的假阳性优于当前最好的方法。
学识有限,再次不深入探讨 YOLO 的网络结构和原理,仅记录如何使用它。
目标:对视频中的人物进行检测
一、安装 & 配置环境
YOLOv5 下载
我使用的 anaconda 进行环境配置
conda create --name Yolov5 python=3.8
创建好新环境后,在 YOLOv5 的安装路径下有一个 requirements.txt 文件,里面列出了所有 YOLOv5 需要的 package,打开 cmd,输入
pip install -r requirements.txt
即可自动安装完成,中途可能会安装失败,大概率是网络问题,重新安装即可。
由于它自动下载的 pytorch 是 cpu 版,我们需要先删除已经下载的 pytorch
pip uninstall torch
然后去官方网站手动下载 gpu 版本的 pytorch。在测试可以使用 gpu 之后,环境的配置就算是完成了。
torch.cuda.is_available()
二、获取数据
这里我要从视频中抽出若干帧作为数据,进行标注。抽帧代码如下,为了方便以后使用,我直接封装成 class 了:
需要的 package:cv2,os。应该不需要单独安装,在配置 YOLOv5 的时候就安装好了的
class Video2Frame:
def __init__(self, videoPath, savePath, timeInterval=1):
'''
初始化,获取 videoPath 下的所有视频
PARAMETERS:
@ videoPath: 视频的存放路径
@ framesSavePath: 视频切分成帧之后图片的保存路径
@ timeInterval: 保存间隔
'''
self.videoPath = videoPath
self.savePath = savePath
self.timeInterval = timeInterval
self.videos = os.listdir(videoPath)
def getVideoList(self):
return self.videos
def getFrameFromVideos(self, start=0, end=None):
'''
对每个视频创建文件夹,保存 frame
PARAMETER:
@ start: 从第几个视频开始
@ end: 到第几个结束 (不包括end)
'''
length = len(self.videos)
if end == None:
end = length - 1
start = start % length
end = end % length + 1
for i in range(start, end):
self.getFrameFromVideo(i)
def getFrameFromVideo(self, i=0):
'''
对某个视频创建文件夹,保存 frame
PARAMETER:
@ i: 第i个视频
'''
video = self.videos[i]
folderName = video[:-4]
os.chdir(self.savePath)
if not os.path.exists(folderName):
os.mkdir(folderName)
vidCap = cv2.VideoCapture(self.videoPath + "\\" + video)
success, image = vidCap.read()
cnt = 0
while success:
success, image = vidCap.read()
cnt += 1
if cnt % self.timeInterval == 0:
cv2.imencode('.jpg', image)[1].tofile(self.savePath + "\\" + folderName + r"\frame%d.jpg" % cnt)
# if cnt == 200:
# break
print(folderName + ": ", cnt // self.timeInterval, "images")
if __name__ == "__main__":
videos_path = r'.\video'
frames_save_path = r'.\data'
time_interval = 30
v2f = Video2Frame(videos_path, frames_save_path, time_interval)
v2f.getFrameFromVideos(-2)
三、标注数据集
标注数据集需要用到一个工具 labelImg(下载链接)。下载解压之后,首先要做的是删除 labelImg-master\data\predefined_classes.txt 文件中的内容,不然标记的时候会自动添加一些预设的类别。
然后安装 pyqt5(注意要在 YOLOv5 环境下)
pip install pyqt5
如果安装过程中报错,则需要先安装 SIP
pip install SIP
安装完之后在 labelImg 的安装目录下运行 cmd,切换到 YOLOv5 环境,输入
python labelImg.py
即可打开 labelImg,之后可对选定图片进行标注。
四、train
准备好数据之后,就可以开始训练模型了。不过在开始训练之前,我们需要做一些准备工作,也就是配置数据集,关于这里,我写了代码方便数据集的配置,详情可参考 generateDataset
4.1 训练前的准备工作
我们首先需要建立如下的文件夹:
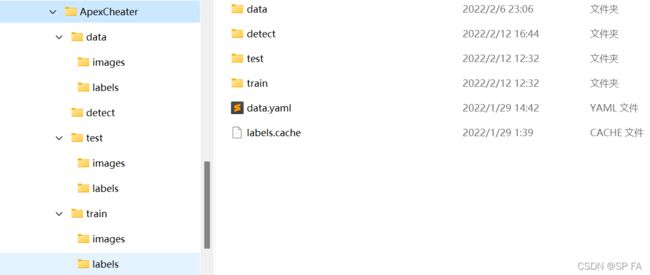
其中 data 文件夹、detect 文件夹 和 labels.cache 是可以没有的。我来一一说明这些个文件的作用。
data 文件夹用来放所有的数据。detect 文件夹用来放预测用的文件,我在这里面放的是视频,也可以是图片。train 文件夹下是两个子文件夹 images 和 labels,分别放了训练用的图片和标签。test 文件夹结构和 train 相同,用来放测试数据。data.yaml 是配置文件,我们需要在文件内写入以下代码:
train: ../ApexCheater/train/images
val: ../ApexCheater/test/images
nc: 2
names: ['body', 'head']
train 和 val 是相对于 YOLOv5 安装路径的,nc 表示分类的数量,names 表示各类别的名称,注意顺序不要乱。
4.2 划分数据集
由于数据规模较小,我按照 7:3 的比例进行划分,代码如下:
需要的package:os,shutil,random
class separateData:
def __init__(self, lst, dataPath):
'''
Initialise the class and print the size of train, test, detect set
PARAMETERS:
@ lst: Represents the proportion of train, test, detect set
@ dataPath: The path of the data set
'''
# Get the total size of the data set
self.tot = len(os.listdir(dataPath + r"\images"))
self.dataPath = dataPath
# Get train size, test size and print them
self.trainSize = int(self.tot * lst[0])
self.testSize = int(self.tot * lst[1])
print("train size: ", self.trainSize)
print("test size: ", self.testSize)
# If you need to separate data into detect set
if len(lst) == 3:
self.detectSize = int(self.tot * lst[2])
print("detect size: ", self.detectSize)
def getRandomList(self, num, selected=[]):
'''
This function is used to choose some data randomly.
PARAMETERS:
@ num: The number of the elements of list.
@ selected: A list represents previously selected data. Default value selected=[]
RETURN:
Return a list represents the serial number of the data, randomly.
'''
lst = []
for i in range(0, num):
# Loops until r is not in lst and selected. That means r
# was never chosen in this for loop or previous program.
while True:
r = random.randint(0, self.tot - 1)
if not((r in lst) or (r in selected)):
lst.append(r)
break
return lst
def copyData(self, i, path):
'''
There must be two folders under the given path, 'images' and 'labels'
and this function will copy the images and labels into given folders respectively.
PARAMETERS:
@ i: The serial number of the data.
@ path: Where the data will be copied to.
'''
JPG = self.dataPath + r"\images\apexCheater(" + str(i) + ").jpg"
TXT = self.dataPath + r"\labels\apexCheater(" + str(i) + ").txt"
shutil.copy(JPG, path + r"\images")
shutil.copy(TXT, path + r"\labels")
def deleteData(self, path):
'''
Delete the data under the given path.
There must be two folders under the given path, 'images' and 'labels'.
PARAMETER:
@ path: The path you want to delete data under it.
'''
if path == "":
return
jpgPath = path + r"\images"
txtPath = path + r"\labels"
os.chdir(jpgPath)
for data in os.listdir(jpgPath):
os.remove(data)
os.chdir(txtPath)
for data in os.listdir(txtPath):
os.remove(data)
def separateTrainTestDetect(self, trainPath, testPath, detectPath="", isDataDelete=False):
'''
Separate data set into train, test, detect set, or just train and test set.
PARAMETERS:
@ trainPath: The path of train set.
@ testPath: The path of test set.
@ detectPath: The path of detect set. Default value detectPath="".
@ isDataDelete: Whether to delete original data. Default value isDataDelete=False.
'''
if isDataDelete:
self.deleteData(trainPath)
self.deleteData(testPath)
self.deleteData(detectPath)
testList = self.getRandomList(self.testSize)
detectList = self.getRandomList(self.detectSize, testList)
for i in detectList:
self.copyData(i, detectPath)
for i in testList:
self.copyData(i, testPath)
for i in range(0, self.tot):
if not((i in testList) or (i in detectList)):
self.copyData(i, trainPath)
if __name__ == "__main__":
rootPath = r".\ApexCheater"
dataPath = rootPath + r"\data"
trainPath = rootPath + r"\train"
testPath = rootPath + r"\test"
detectPath = rootPath + r"\detect"
sd = separateData([0.7, 0.3, 0], dataPath)
sd.separateTrainTestDetect(trainPath, testPath, isDataDelete=True)
print("finished")
4.3 开始训练
我使用的是 pycharm,因为 YOLOv5 提供了使用 jupyter notebook 进行训练的教程,在这里就不展开了,只记一下如何使用 pycharm 进行训练。
首先打开 YOLOv5 项目,然后打开 train.py 文件
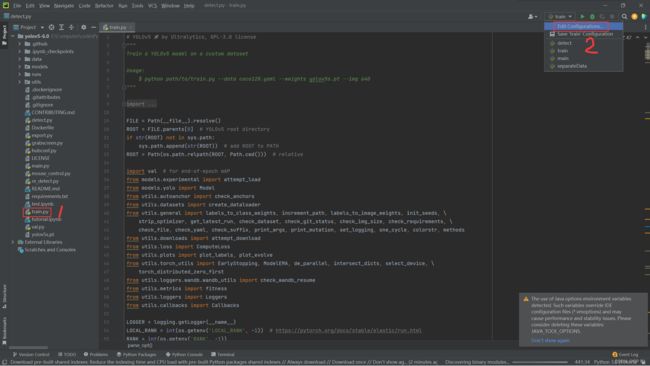
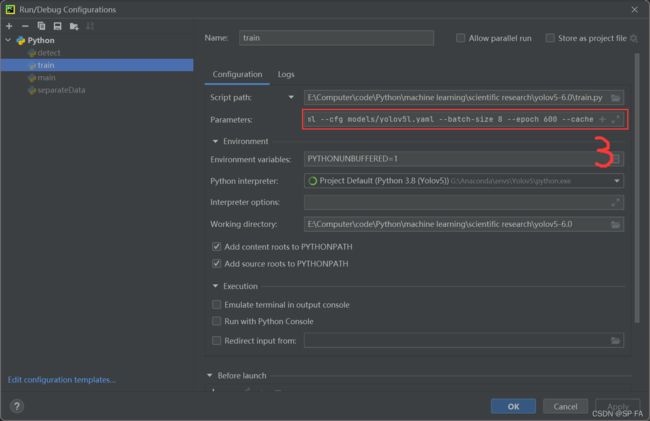
配置如下参数:
--data ../ApexCheater/data.yaml
--cfg models/yolov5s.yaml
--batch-size 8
--epoch 600
--cache
其中 models 文件夹下提供了好多模型,可以根据情况自行选择。配置完成后点击运行即可。
关于报错 “页面文件太小,无法完成操作” 的解决方法:
这个错误的原因是虚拟内存过小导致的,把 C 盘的虚拟内存设置的大一些就好。但是据棉棉所说,应该是扩大 python 安装位置对应盘的虚拟内存。但具体情况是:我的 conda 在 G 盘,占用的是 C 虚拟内存;绵绵的 conda 在 E 盘,而且也是 E 盘的虚拟内存有占用。另外运行相同数据和模型,绵绵的内存占用量几乎是我的 4 倍,我们不知道具体原因,也无从查证。
4.4 模型继续训练
有时候可能会遇到模型训练到一半被迫中断的情况,此时我们可以通过开启 --resume 参数来继续训练我们的模型。
我们只需要在参数中添加如下参数即可。
--resume runs/train/exp/weights/last.pt
对于已经训练完的模型,我们也可以继续进行训练。首先假设当前 epoch 为 2000,且模型已经训练完,我们想让它再额外训练 1000。我们需要在配置完 --resume 后修改 -epoch 为 3000,然后该如下代码:
在 train.py 中的 186 行添加
ckpt['epoch'] = 2000
五、detect
打开 YOLOv5 项目中的 detect.py 文件,配置如下参数:
--weight ./runs/train/exp12/weights/best.pt
--img 640
--conf 0.25
--source ../ApexCheater/detect
然后运行程序即可。注意 --img 的图片大小必须和 train 的时候保持一致。
六、碎碎念
为了跑模型和绵绵一起去换了内存条,换完之后打游戏那叫一个爽啊!
开摆!
