飞桨领航团AI达人创造营4-在Jetson Nano上基于python部署Paddle Inference(硬件部署)
在Jetson Nano上基于python部署Paddle Inference(硬件部署)
一、准备好一块新鲜出炉的Jetson nano,并配好基础的开发环境

1.基础配置方法
直接参考我多年来总结的保姆式基础配置方案,只花2小时就能实现开机自连wifi,远程桌面随时访问,废话不多说,直接上车!
Jetson系列——Ubuntu18.04版本基础配置(换源、远程桌面、开机自连WIFi)
二、安装PaddlePaddle环境
1.直接下载官方编译好的Jetson nano预测库
下载地址:PaddlePaddle官方Linux预测库whl包下载
(一般来说,大家需要到官网上自行下载最新版本),不过这里为了方便起见,我已经准备好2.1.1版本的预测库,如果有最新版的,建议去官网下载。
2.直接将左边的paddlepaddle_gpu-2.1.1-cp36-cp36m-linux_aarch64.7z下载解压后将whl文件并传到Jetson nano上即可。
In [4]
# 安装whl
pip3 install paddlepaddle_gpu-2.1.1-cp36-cp36m-linux_aarch64.whl
In [5]
# 打开python3测试
import paddle
paddle.fluid.install_check.run_check()
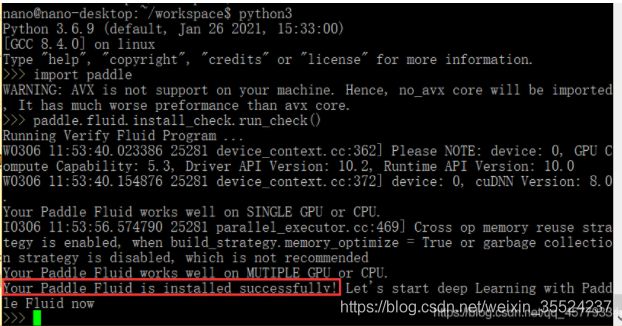
三、测试Paddle Inference
(1)拉取Paddle-Inference-Demo:
在gitee上下载
!git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Inference-Demo.git
!unzip -oq /home/aistudio/Paddle-Inference-Demo-master.zip
2)测试跑通GPU预测模型
需要注意的是,需要将所有子文件夹中的run.sh最后的python修改为python3:
cd Paddle-Inference-Demo/python
chmod +x run_demo.sh
./run_demo.sh
四、报错解决
也可以选择运行单个模型的run.sh。如果过程中有报错,请继续往下看。
(1)运行demo过程中卡住

解决方法:
扩大运行内存 (亲测:建议至少给8G,反正6G不行)
sudo fallocate -l 8G /var/swapfile8G
sudo chmod 600 /var/swapfile8G
sudo mkswap /var/swapfile8G
sudo swapon /var/swapfile8G
sudo bash -c ‘echo “/var/swapfile8G swap swap defaults 0 0” >> /etc/fstab’
扩大虚拟内存后,运行正常:
(2)core dumped
原因是因为JetPack4.4自带的numpy版本不对,numpy版本应为1.18.3。

解决方法:
pip3 uninstall numpy
python3 -m pip install numpy==1.18.3 -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
五、部署自己的目标检测模型
新建目录mywork:
mkdir /home/mywor
把需要部署的文件拷贝到/home/mywork中
在mywork目录中新建a.py文件
import cv2
import numpy as np
from paddle.inference import Config
from paddle.inference import PrecisionType
from paddle.inference import create_predictor
import yaml
import time
# ————图像预处理函数—————— #
def resize(img, target_size):
“”“resize to target size”""
if not isinstance(img, np.ndarray):
raise TypeError(‘image type is not numpy.’)
im_shape = img.shape
im_size_min = np.min(im_shape[0:2])
im_size_max = np.max(im_shape[0:2])
im_scale_x = float(target_size) / float(im_shape[1])
im_scale_y = float(target_size) / float(im_shape[0])
img = cv2.resize(img, None, None, fx=im_scale_x, fy=im_scale_y)
return img
def normalize(img, mean, std):
img = img / 255.0
mean = np.array(mean)[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :]
std = np.array(std)[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :]
img -= mean
img /= std
return img
def preprocess(img, img_size):
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
img = resize(img, img_size)
img = img[:, :, ::-1].astype(‘float32’) # bgr -> rgb
img = normalize(img, mean, std)
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # hwc -> chw
return img[np.newaxis, :]
# ——————模型配置、预测相关函数————————— #
def predict_config(model_file, params_file):
‘’’
函数功能:初始化预测模型predictor
函数输入:模型结构文件,模型参数文件
函数输出:预测器predictor
‘’’
# 根据预测部署的实际情况,设置Config
config = Config()
# 读取模型文件
config.set_prog_file(model_file)
config.set_params_file(params_file)
# Config默认是使用CPU预测,若要使用GPU预测,需要手动开启,设置运行的GPU卡号和分配的初始显存。
config.enable_use_gpu(500, 0)
# 可以设置开启IR优化、开启内存优化。
config.switch_ir_optim()
config.enable_memory_optim()
config.enable_tensorrt_engine(workspace_size=1 << 30, precision_mode=PrecisionType.Float32,max_batch_size=1, min_subgraph_size=5, use_static=False, use_calib_mode=False)
predictor = create_predictor(config)
return predictor
def predict(predictor, img):
'''
函数功能:初始化预测模型predictor
函数输入:模型结构文件,模型参数文件
函数输出:预测器predictor
'''
input_names = predictor.get_input_names()
for i, name in enumerate(input_names):
input_tensor = predictor.get_input_handle(name)
input_tensor.reshape(img[i].shape)
input_tensor.copy_from_cpu(img[i].copy())
# 执行Predictor
predictor.run()
# 获取输出
results = []
# 获取输出
output_names = predictor.get_output_names()
for i, name in enumerate(output_names):
output_tensor = predictor.get_output_handle(name)
output_data = output_tensor.copy_to_cpu()
results.append(output_data)
return results
# ————后处理函数 #
def draw_bbox_image(frame, result, label_list, threshold=0.5):
for res in result:
cat_id, score, bbox = res[0], res[1], res[2:]
if score < threshold:
continue
for i in bbox:
int(i)
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = bbox
cv2.rectangle(frame, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), (255,0,255), 2)
print('category id is {}, bbox is {}'.format(cat_id, bbox))
try:
label_id = label_list[int(cat_id)]
# #cv2.putText(图像, 文字, (x, y), 字体, 大小, (b, g, r), 宽度)
cv2.putText(frame, label_id, (int(xmin), int(ymin-2)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255,0,0), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, str(round(score,2)), (int(xmin-35), int(ymin-2)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0,255,0), 2)
except KeyError:
pass
if name == ‘main’:
# 从infer_cfg.yml中读出label
infer_cfg = open('yolov3_r50vd_dcn_270e_coco/infer_cfg.yml')
data = infer_cfg.read()
yaml_reader = yaml.load(data)
label_list = yaml_reader['label_list']
print(label_list)
# 配置模型参数
model_file = "./yolov3_r50vd_dcn_270e_coco/model.pdmodel"
params_file = "./yolov3_r50vd_dcn_270e_coco/model.pdiparams"
# 初始化预测模型
predictor = predict_config(model_file, params_file)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 图像尺寸相关参数初始化
ret, img = cap.read()
im_size = 224
scale_factor = np.array([im_size * 1. / img.shape[0], im_size * 1. / img.shape[1]]).reshape((1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
im_shape = np.array([im_size, im_size]).reshape((1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
# 预处理
data = preprocess(frame, im_size)
time_start=time.time()
# 预测
result = predict(predictor, [im_shape, data, scale_factor])
print('Time Cost:{}'.format(time.time()-time_start) , "s")
draw_bbox_image(frame, result[0], label_list, threshold=0.1)
cv2.imshow("frame", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
效果展示
采用模型为yolov3_r50vd_dcn_270e:

性能分析:CPU、GPU、GPU+TensorRT预测时间对比
关于如何更改预测模式
所有的模式都在predict_config() 函数中,其中:
GPU预测:config.enable_use_gpu(500, 0) (注释掉该代码即为CPU模式)
开启IR优化、开启内存优化:config.switch_ir_optim() 和config.enable_memory_optim() (一般都开启)
TensorRT加速:config.enable_tensorrt_engine()
def predict_config(model_file, params_file):
‘’’
函数功能:初始化预测模型predictor
函数输入:模型结构文件,模型参数文件
函数输出:预测器predictor
‘’’
# 根据预测部署的实际情况,设置Config
config = Config()
# 读取模型文件
config.set_prog_file(model_file)
config.set_params_file(params_file)
# Config默认是使用CPU预测,若要使用GPU预测,需要手动开启,设置运行的GPU卡号和分配的初始显存。
config.enable_use_gpu(500, 0)
# 可以设置开启IR优化、开启内存优化。
config.switch_ir_optim()
config.enable_memory_optim()
config.enable_tensorrt_engine(workspace_size=1 << 30, precision_mode=PrecisionType.Float32,max_batch_size=1, min_subgraph_size=5, use_static=False, use_calib_mode=False)
predictor = create_predictor(config)
return predictor
测试模型:mobilenet v1
1.图像尺寸为224
(1)使用CPU预测:平均每帧预测时间为0.24s
(2)开启GPU加速:平均每帧预测时间为0.039s
(3)使用TensorRT加速后:平均每帧预测时间为0.027s
测试模型:yolov3_r50vd
1.图像尺寸为:608
(1)使用CPU预测:平均每帧预测时间为12.8s(因为时间太长,没有过多测试,但是前5帧基本都这个速度)
(2)开启GPU加速:平均每帧预测时间为0.81s
(3)使用TensorRT加速后:
Float32模式:平均每帧预测时间为0.54s config.enable_tensorrt_engine(workspace_size=1 << 30, precision_mode=PrecisionType.Float32,max_batch_size=1, min_subgraph_size=5, use_static=False, use_calib_mode=False)
Float16(Half)模式:平均每帧预测时间为0.34s config.enable_tensorrt_engine(workspace_size=1 << 30, precision_mode=PrecisionType.Half,max_batch_size=1, min_subgraph_size=5, use_static=False, use_calib_mode=False)
2.图像尺寸为:224
(1)使用CPU预测:平均每帧预测时间为1.8s
(2)开启GPU加速:平均每帧预测时间为0.18s
(3)使用TensorRT加速后:会报错(因为在模型内部训练时的输入即为608*608,而当前版本TRT不支持动态调整input,所以只能将在模型训练时的尺寸修改后再使用TRT,报错如下所示)
具体关于TRT的资料可以参考:https://paddle-inference.readthedocs.io/en/master/optimize/paddle_trt.html ,这里说的很清楚关于TRT动态shape和静态shape都分别支持哪些模型,同时可以调整TRT的对应参数,从而实现对模型预测速度的进一步提升。
文章同时也开源在CSDN,大家可以直接进行访问:Jetson Nano——基于python API部署Paddle Inference GPU预测库(2.1.1)