如何理解残差网络(resnet)结构和代码实现(Pytorch)笔记分享
在深度学习的网络中,个人认为最基础的还是残差网络,今天分享的并不是残差网络的理论部分,大家只要记住一点,残差网络的思想是贯穿后面很多网络结构之中,看懂了残差网络结构,那么后面的一些先进的网络的结构也很容易看懂。
一、残差块结构
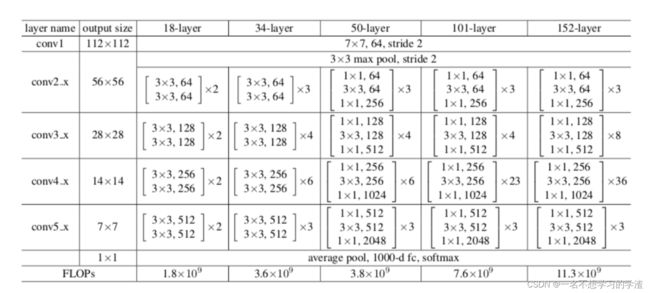
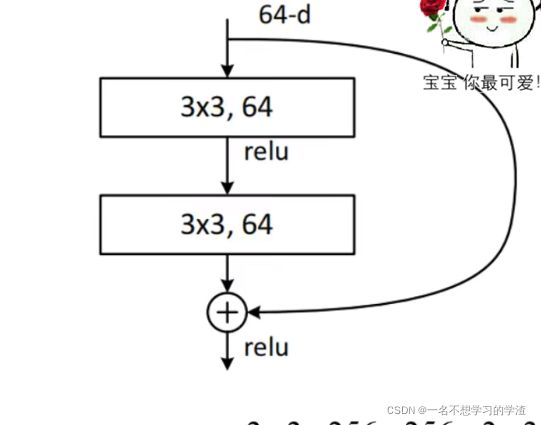
前50层所对应的残差块结构(不包含第50层)代码如下:
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None, **kwargs):#downsample=None表示虚线的残差结构
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
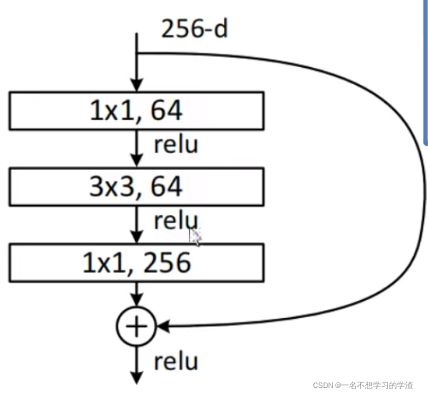
return out后50层所对应的残差块结构(包含第50层)代码如下:
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
"""
注意:原论文中,在虚线残差结构的主分支上,第一个1x1卷积层的步距是2,第二个3x3卷积层步距是1。
但在pytorch官方实现过程中是第一个1x1卷积层的步距是1,第二个3x3卷积层步距是2,
这么做的好处是能够在top1上提升大概0.5%的准确率。
可参考Resnet v1.5 https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch
"""
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None,
groups=1, width_per_group=64):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
width = int(out_channel * (width_per_group / 64.)) * groups
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=width,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=width, groups=groups,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
看到上面的两个残差块,初学者兴许会觉得疑惑,或者看到代码会疑惑,为什么有两种残差块呢?①、其实这两种残差块是针对不同网络层数的,第一个残差结构是针对浅层的残差网络的,比如resnet18,resnet34,而第二个残差结构是针对深层的残差结构的,比如resnet50,resnet101,resnet152。
②、在代码中会分别实现这两种残差块,为的就是方便更改网络的层数。对于残差块结构,一般的网络总是命名成Block。所以看代码使,要对着图来看。
其次需要注意的是,3x3卷积核一般用于降低特征图大小的,1x1卷积一般用于降低或者增加通道数的。
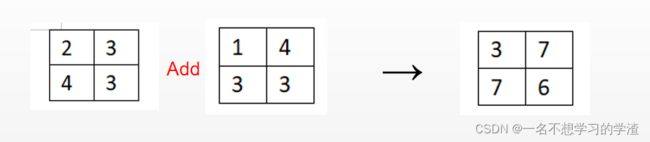
二、concat和add的区别
对于初学者,看到这两个单词还是比较迷的,又或者没法理解。所以这点要注意一下,
concat操作:一般需要特征图的大小相同,才能在对应的通道维度上拼接,比如说下图所示:
add操作:一般需要特征图大小和通道数相同,比如下图左边两个图都是特征大小为2x2,通道数为1的,所以二者能够在对应位置相加。
三、为什么残差边需要进行下采样
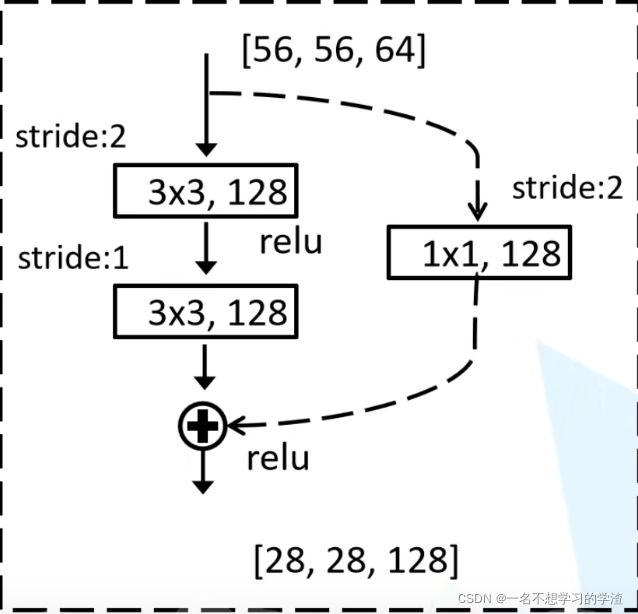
如下图。 你会发现上面的两个残差块的其中一天残差边并没有下图的1x1,128的样式,只能告诉你,这是作者默认你已经入门深度学习了,所以才没有写,我们仔细分析下面的图,首先[56,56,64]经过3x3,128,步长为2的卷积核,会变成[28,28,128],再经过3x3,128,步长为1的卷积核,会变成[28,28,128],但是却和输入的[56,56,64]大小和通道数不一致,所以[56,56,64]在残差边上进行一次3x3,128,步长为2的卷积核,从而也能得到[28,28,128],最后两个[28,28,128]进行相加。
代码如下:
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None, **kwargs):#downsample=None表示虚线的残差结构
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel,out_channels=out_channel,kernel_size=1,stride=2)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity =self.relu(self.bn3(self.downsample(x)))
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
a=torch.randn((1,64,56,56))
model=BasicBlock(in_channel=64,out_channel=128,stride=2,downsample=True)
out=model(a)
print(out.shape)完整resnet网络代码如下:
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
#下面的类是3x3 3x3的残差结构
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None, **kwargs):#downsample=None表示虚线的残差结构
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
#这个表示后面50层的残差结构
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
"""
注意:原论文中,在虚线残差结构的主分支上,第一个1x1卷积层的步距是2,第二个3x3卷积层步距是1。
但在pytorch官方实现过程中是第一个1x1卷积层的步距是1,第二个3x3卷积层步距是2,
这么做的好处是能够在top1上提升大概0.5%的准确率。
可参考Resnet v1.5 https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch
"""
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None,
groups=1, width_per_group=64):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
width = int(out_channel * (width_per_group / 64.)) * groups
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=width,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=width, groups=groups,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
block,
blocks_num, #对于34层 3,4,6,3
num_classes=1000,
include_top=True,#为了能够搭建更加复杂的网络
groups=1,
width_per_group=64):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
self.groups = groups
self.width_per_group = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2)
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
downsample=downsample,
stride=stride,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet50(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnext50_32x4d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 4
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
def resnext101_32x8d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 8
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
if __name__ == '__main__':
net=resnet34()
print(net)至此网络结构说明完成!希望大家有所收获,有什么疑问的地方,欢迎大家评论!