yolov5的head修改为decouple head
yolov5的head修改为decouple head
yolox的decoupled head结构
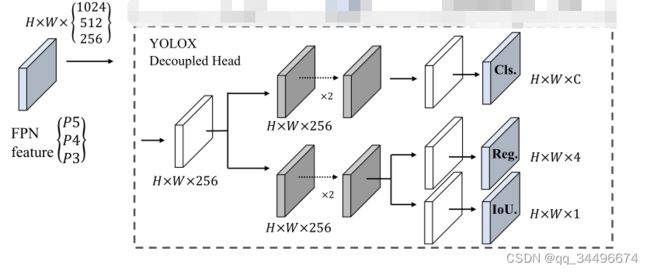
本来想将yolov5的head修改为decoupled head,与yolox的decouple head对齐,但是没注意,该成了如下结构:
1.修改models下的yolo.py文件中的Detect
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2)
# self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.m_box = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, 4 * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.m_conf = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, 1 * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.m_labels = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, self.nc * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.base_conv = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = x, out_channels = 256, ksize = 1, stride = 1) for x in ch)
self.cls_convs = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = 256, out_channels = 256, ksize = 3, stride = 1) for x in ch)
self.reg_convs = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = 256, out_channels = 256, ksize = 3, stride = 1) for x in ch)
# self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, 4 * self.na, 1) for x in ch, nn.Conv2d(x, 1 * self.na, 1) for x in ch,nn.Conv2d(x, self.nc * self.na, 1) for x in ch)
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)self.ch = ch
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
# # x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # convs
# print("&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&", i)
# print(x[i].shape)
# print(self.base_conv[i])
# print("%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
x_feature = self.base_conv[i](x[i])
# x_feature = x[i]
cls_feature = self.cls_convs[i](x_feature)
reg_feature = self.reg_convs[i](x_feature)
# reg_feature = x_feature
m_box = self.m_box[i](reg_feature)
m_conf = self.m_conf[i](reg_feature)
m_labels = self.m_labels[i](cls_feature)
x[i] = torch.cat((m_box,m_conf, m_labels),1)
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
2.在yolo.py中添加
def get_activation(name="silu", inplace=True):
if name == "silu":
module = nn.SiLU(inplace=inplace)
elif name == "relu":
module = nn.ReLU(inplace=inplace)
elif name == "lrelu":
module = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=inplace)
else:
raise AttributeError("Unsupported act type: {}".format(name))
return module
class BaseConv(nn.Module):
"""A Conv2d -> Batchnorm -> silu/leaky relu block"""
def __init__(
self, in_channels, out_channels, ksize, stride, groups=1, bias=False, act="silu"
):
super().__init__()
# same padding
pad = (ksize - 1) // 2
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=ksize,
stride=stride,
padding=pad,
groups=groups,
bias=bias,
)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.act = get_activation(act, inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
# print(self.bn(self.conv(x)).shape)
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
# return self.bn(self.conv(x))
def fuseforward(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
decouple head的特点:
由于训练模型时,应该是channels = 256的地方改成了channels = x(失误),所以在decoupled head的部分参数量比yolox要大一些,以下的结果是在channels= x的情况下得出
比yolov5s参数多,计算量大,在我自己的2.5万的数据量下map提升了3%多
1.模型给出的目标cls较高,需要将conf的阈值设置较大(0.5),不然准确率较低
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.5, help='confidence threshold')
2.对于少样本的检测效果较好,召回率的提升比准确率多
3.在conf设置为0.25时,召回率比yolov5s高,但是准确率低;在conf设置为0.5时,召回率与准确率比yolov5s高
4.比yolov5s参数多,计算量大,在2.5万的数据量下map提升了3%多
对于decouple head的改进

改进:
1.将红色框中的conv去掉,缩小参数量和计算量;
2.channels =256 ,512 ,1024是考虑不增加参数,不进行featuremap的信息压缩
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
特点
1.模型给出的目标cls较高,需要将conf的阈值设置较大(0.4),不然准确率较低
2.对于少样本的检测效果较好,准确率的提升比召回率多
3. 准确率的提升比召回率多,
该改进不如上面的模型提升多,但是参数量小,计算量小少9Gflop,占用显存少
decoupled head指标提升的原因:由于yolov5s原本的head不能完全的提取featuremap中的信息,decoupled head能够较为充分的提取featuremap的信息;
疑问
为什么decoupled head目标的cls会比较高,没想明白
为什么去掉base_conv,召回率要比准确率提升少

