torch.nn.BCELoss用法
1. 定义
数学公式为Loss = -w * [p * log(q) + (1-p) * log(1-q)],其中p、q分别为理论标签、实际预测值,w为权重。这里的log对应数学上的ln。
PyTorch对应函数为:
torch.nn.BCELoss(weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction=‘mean’)
计算目标值和预测值之间的二进制交叉熵损失函数。
有四个可选参数:weight、size_average、reduce、reduction
(1) weight必须和target的shape一致,默认为none。定义BCELoss的时候指定即可。
(2) 默认情况下 nn.BCELoss(),reduce = True,size_average = True。
(3) 如果reduce为False,size_average不起作用,返回向量形式的loss。
(4) 如果reduce为True,size_average为True,返回loss的均值,即loss.mean()。
(5) 如果reduce为True,size_average为False,返回loss的和,即loss.sum()。
(6) 如果reduction = ‘none’,直接返回向量形式的 loss。
(7) 如果reduction = ‘sum’,返回loss之和。
(8) 如果reduction = ''elementwise_mean,返回loss的平均值。
(9) 如果reduction = ''mean,返回loss的平均值
2. 验证代码
1>
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
m = nn.Sigmoid()
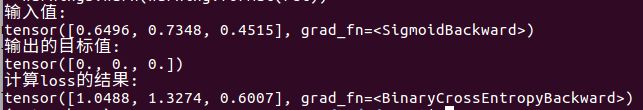
loss = nn.BCELoss(size_average=False, reduce=False)
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
lossinput = m(input)
output = loss(lossinput, target)
print("输入值:")
print(lossinput)
print("输出的目标值:")
print(target)
print("计算loss的结果:")
print(output)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
m = nn.Sigmoid()
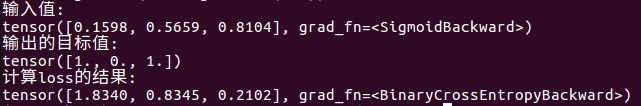
loss = nn.BCELoss(size_average=True, reduce=False)
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
lossinput = m(input)
output = loss(lossinput, target)
print("输入值:")
print(lossinput)
print("输出的目标值:")
print(target)
print("计算loss的结果:")
print(output)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
m = nn.Sigmoid()
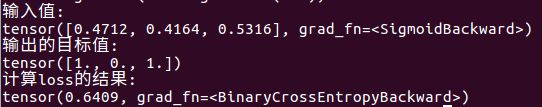
loss = nn.BCELoss(size_average=True, reduce=True)
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
lossinput = m(input)
output = loss(lossinput, target)
print("输入值:")
print(lossinput)
print("输出的目标值:")
print(target)
print("计算loss的结果:")
print(output)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
m = nn.Sigmoid()
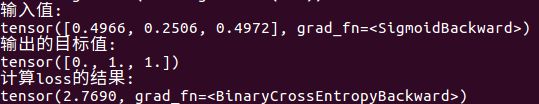
loss = nn.BCELoss(size_average=False, reduce=True)
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
lossinput = m(input)
output = loss(lossinput, target)
print("输入值:")
print(lossinput)
print("输出的目标值:")
print(target)
print("计算loss的结果:")
print(output)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
m = nn.Sigmoid()
loss = nn.BCELoss(reduction = 'none')
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
lossinput = m(input)
output = loss(lossinput, target)
print("输入值:")
print(lossinput)
print("输出的目标值:")
print(target)
print("计算loss的结果:")
print(output)
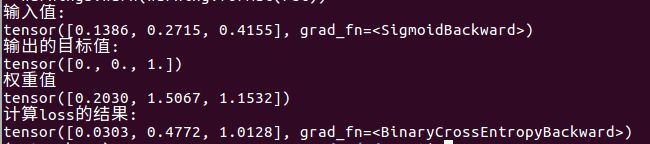
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
m = nn.Sigmoid()
weights=torch.randn(3)
loss = nn.BCELoss(weight=weights,size_average=False, reduce=False)
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
lossinput = m(input)
output = loss(lossinput, target)
print("输入值:")
print(lossinput)
print("输出的目标值:")
print(target)
print("权重值")
print(weights)
print("计算loss的结果:")
print(output)
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/tmk_01/article/details/80844260
https://www.cnblogs.com/wanghui-garcia/p/10862733.html