YOLOv5-seg数据集制作、模型训练以及TensorRT部署
YOLOv5-seg数据集制作、模型训练以及TensorRT部署
- 版本声明
- 一、数据集制作:图像 Json转txt
- 二、分割模型训练
- 三 tensorRT部署
-
- 1 模型导出
- 2 onnx转trtmodel
- 3 推理部分
版本声明
yolov5-seg:官方地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/v6.2
TensorRT:8.x.x
语言:C++
系统:ubuntu18.04
一、数据集制作:图像 Json转txt
前言:由于yolo仓中提供了标准coco的json文件转txt代码,因此需要将labelme的json文件转为coco json.
- labelme JSON 转COCO JSON
使用labelme的CreatePolygons按钮开始绘制多边形,然后保存为json格式。

https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme/tree/master/examples/instance_segmentation.
在该链接中有个labelme2coco.py脚本,将该脚本下载下来后,执行以下指令即可。其中data_annotated是刚刚标注保存的json标签文件夹,data_dataset_coco是生成MS COCO数据类型的目录。
python labelme2coco.py data_annotated data_dataset_coco --labels label.txt
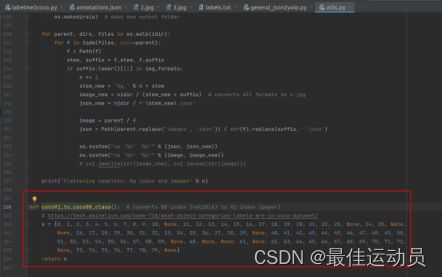
注意:由于自定义的数据集里面标签从0开始 不包括背景 直接转换会报错。修改72行。
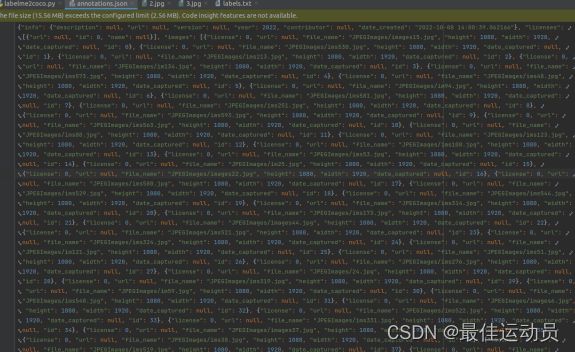
生成三个文件JPEGImages、 Visualization 、annotations.json

JPEGImages中为原图,annotations.json里面是coco格式的文件:
Visualization中的图如下:
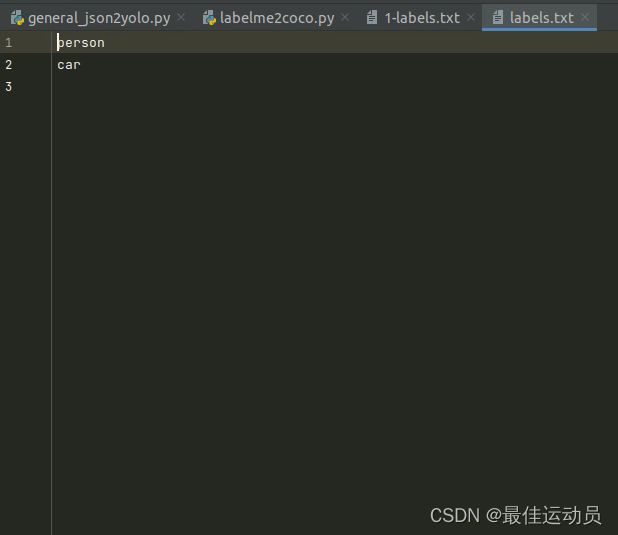
转换前需要自定义label.txt
- COCO JSON转txt
coco128-seg提供了标准的训练格式,我们下载下来看看。[label]+[points]
下载链接link:https://github.com/ultralytics/JSON2YOLO
找到general_json2yolo.py文件,修改路径后直接运行会报错:
No such file or directory xxx/xxxxx/xxx.txt
排查过后发现是我们生成的annotations.json和标准的coco json有出入:(多了JPEGImages/),修改代码313行:
标准的:
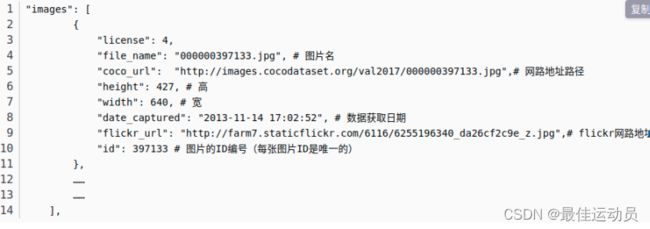
我们的: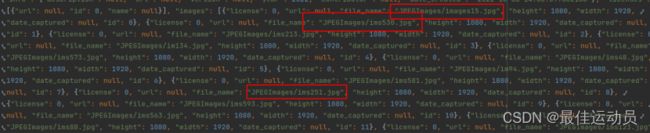
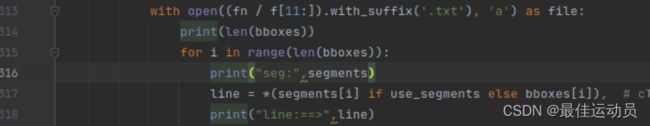 再次运行,报下一个错误:
再次运行,报下一个错误:
TypeError: must be real number, not NoneType
错误指向:

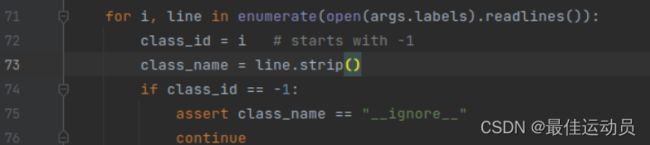
观察文件夹中,已经生成一个xxx.txt且有部分数据,打印line之后发现数据里有[None,point…point]这样的数据。 大体知道了:应该是生成了背景类且没有标签。修改代码跳过这些标签:
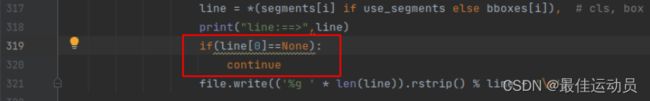
再次运行报错消失,执行完毕没有报错。以为成功了打开txt一个最大的标签仅仅为13,应该是到15(我的数据集一共十六类),中间有几类被消除了,排查错误。应该是这个地方把91–>80类的函数的问题。修改一番,两个地方。(若只修改第二处 会出现-1标签,最高到14)
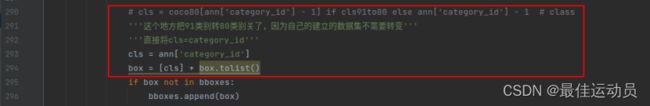
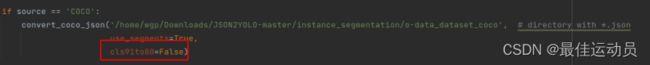 也可以只修改第二处:再修改代码:
也可以只修改第二处:再修改代码:
下面展示一些 内联代码片。
cls = coco80[ann['category_id'] - 1] if cls91to80 else ann['category_id'] - 1 # class
cls = coco80[ann['category_id']] if cls91to80 else ann['category_id'] - 1 # class
coco91_to_coco80_class()函数:
二、分割模型训练
训练的步骤和目标检测模型一致,下载模型 yolov5s-seg.pt,划分数据集 、修改配置文件、不再详述了。

三 tensorRT部署
1 模型导出
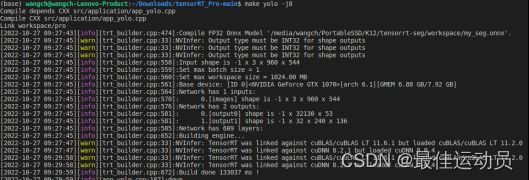
使用官方的export.py文件直接导出时,netron可视化之后如下:
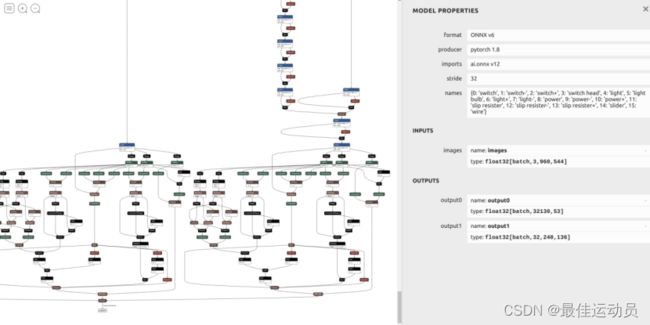
onnx比较混乱,需要进一步修改,所有的修改如下,参考杜老的仓link:https://github.com/shouxieai/learning-cuda-trt/tree/main:
# line 55 forward function in yolov5/models/yolo.py
# bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
# x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
# modified into:
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
bs = -1
ny = int(ny)
nx = int(nx)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
# line 70 in yolov5/models/yolo.py
# z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
# modified into:
z.append(y.view(bs, self.na * ny * nx, self.no))
############# for yolov5-6.0 #####################
# line 65 in yolov5/models/yolo.py
# if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4] or self.onnx_dynamic:
# self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
# modified into:
if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4] or self.onnx_dynamic:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
# disconnect for pytorch trace
anchor_grid = (self.anchors[i].clone() * self.stride[i]).view(1, -1, 1, 1, 2)
# line 70 in yolov5/models/yolo.py
# y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
# modified into:
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * anchor_grid # wh
# line 73 in yolov5/models/yolo.py
# wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
# modified into:
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * anchor_grid # wh
############# for yolov5-6.0 #####################
# line 77 in yolov5/models/yolo.py
# return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
# modified into:
return x if self.training else torch.cat(z, 1)
# line 52 in yolov5/export.py
# torch.onnx.export(dynamic_axes={'images': {0: 'batch', 2: 'height', 3: 'width'}, # shape(1,3,640,640)
# 'output': {0: 'batch', 1: 'anchors'} # shape(1,25200,85) 修改为
# modified into:
torch.onnx.export(dynamic_axes={'images': {0: 'batch'}, # shape(1,3,640,640)
'output': {0: 'batch'} # shape(1,25200,85)
由于版本不同修改的地方也稍有改变
修改后:
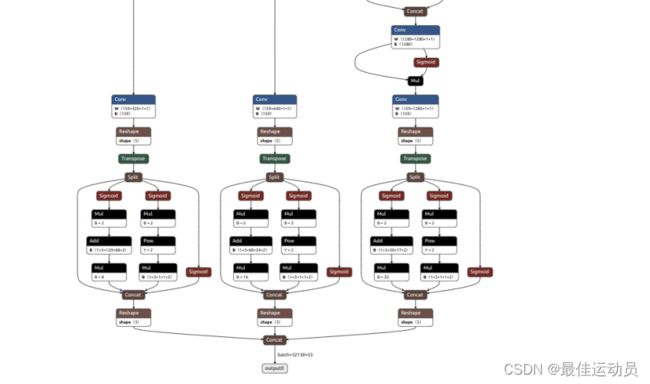
导出指令:python export.py --weights runs/train-seg/exp3/weights/best.pt --include onnx --dynamic
2 onnx转trtmodel
TRT::compile(
mode, // FP32、FP16、INT8
test_batch_size, // max batch size
onnx_file, // source
model_file, // save to
{},
int8process,
"inference"
);
3 推理部分
static void inference(Type type, TRT::Mode mode, const string& model_file){
auto engine = TRT::load_infer(model_file);
if(engine == nullptr){
INFOE("Engine is nullptr");
return;
}
auto image = cv::imread("xxx.jpg");
//绘制结果
int col=image.cols; //1920
int row=image.rows; //1080
Mat mask_seg=image.clone();
Mat mask_box=image.clone();//3 channel
Mat cut_img=image.clone();
auto input = engine->tensor("images"); // engine->input(0);
auto output = engine->tensor("output0"); // engine->output(1);//[batch , 32130 , 53]
auto output1 = engine->tensor("output1"); // (batch, 32, 136, 240) ==>(16,32,136,240)
int num_bboxes = output->size(1);//32130
int num_classes = output->size(2) - 5 ;
float confidence_threshold = 0.5;
float nms_threshold = 0.45;
int MAX_IMAGE_BBOX = 1000;
int NUM_BOX_ELEMENT = 39; // left, top, right, bottom, confidence, class, keepflag ,32 mask
int netWidth = 640;
int netHeigh = 640;
int segWidth = 160;
int segHeight = 160;
float mask_thresh = 0.2;
TRT::Tensor output_array_device(TRT::DataType::Float);
// use max = 1 batch to inference.
int max_batch_size = 1;
input->resize_single_dim(0, max_batch_size).to_gpu();
output_array_device.resize(max_batch_size, 1 + MAX_IMAGE_BBOX * NUM_BOX_ELEMENT).to_gpu();
output_array_device.set_stream(engine->get_stream());
// set batch = 1 image
int ibatch = 0;
image_to_tensor(image, input, type, ibatch);
// do async 异步
engine->forward(false);
float* output_ptr = output1->cpu<float>();
//vector 2 mat
int size[]={32,segHeight,segWidth};
//cout<<"size"<
cv::Mat mask_protos = cv::Mat_<float>(3,size,CV_8UC1);
for(int iii=0;iii<32;iii++)
{
//unchar *data=mask_protos.ptr(iii);
for(int jjj=0;jjj<segHeight;jjj++)
{
//unchar *data2=data.ptr(jjj);
for(int kkk=0;kkk<segWidth;kkk++)
{
//data2[kkk]=output_ptr[iii*136*240+jjj*240+kkk];
mask_protos.at<float>(iii,jjj,kkk)=output_ptr[iii*segHeight*segWidth+jjj*segWidth+kkk];
}
}
}
float* d2i_affine_matrix = static_cast<float*>(input->get_workspace()->gpu());
Yolo::decode_kernel_invoker(
output->gpu<float>(ibatch),
num_bboxes, num_classes,
confidence_threshold,
d2i_affine_matrix, output_array_device.gpu<float>(ibatch),
MAX_IMAGE_BBOX, engine->get_stream()
);
Yolo::nms_kernel_invoker(
output_array_device.gpu<float>(ibatch),
nms_threshold,
MAX_IMAGE_BBOX, engine->get_stream()
);
float* parray = output_array_device.cpu<float>();
int num_box = min(static_cast<int>(*parray), MAX_IMAGE_BBOX);//取最小值
//new a mat and new a vector
Mat mask_proposals;
vector<OutputSeg> f_output;
vector<vector<float>>proposal; //[23,32] output0 =>mask
int num_box1=0;
Rect holeImgRect(0, 0, col, row);
for(int i = 0; i < num_box; ++i){ //遍历所有的框
float* pbox = parray + 1 + i * NUM_BOX_ELEMENT;//+1+i*7 1:表示这个数组的元素数量
int keepflag = pbox[6];
vector<float> temp;
OutputSeg result;
if(keepflag == 1 ){
num_box1+=1;
// left, top, right, bottom, confidence,class, keepflag
// pbox[0], pbox[1], pbox[2], pbox[3], pbox[4], pbox[5], pbox[6]
float left = pbox[0];
float top = pbox[1];
float right = pbox[2];
float bottom = pbox[3];
float confidence = pbox[4];
for(int ii=0;ii<32;ii++)
{
temp.push_back(pbox[ii+7]);
}
proposal.push_back(temp);
result.id=pbox[5];
result.confidence=pbox[4];
cv::Rect rect(left, top, right-left, bottom-top);
result.box=rect & holeImgRect;//; //x,y,w,h
f_output.push_back(result);
int label = static_cast<int>(pbox[5]);
uint8_t b, g, r;
tie(b, g, r) = iLogger::random_color(label);
cv::rectangle(image, cv::Point(left, top), cv::Point(right, bottom), cv::Scalar(b, g, r), 3);
auto name = cocolabels[label];
auto caption = iLogger::format("%s %.2f", name, confidence);
int width = cv::getTextSize(caption, 0, 1, 1, nullptr).width + 10;
cv::rectangle(image, cv::Point(left-3, top-33), cv::Point(left + width, top), cv::Scalar(b, g, r), -1);
cv::putText(image, caption, cv::Point(left, top-5), 0, 1, cv::Scalar::all(0), 2, 16);
}
//对应于python中的process_mask
//vector2mat
for (int i = 0; i < proposal.size(); ++i)
{mask_proposals.push_back(Mat(proposal[i]).t());}
/获取 proto 也就是output1的输出
//逻辑 GetMask
Vec4d params; //根据实际图片输入 和 onnx模型输入输出 计算的,此处直接写死
params[0]=0.5;
params[1]=0.5;
params[2]=0.0;
params[3]=2.0;
Mat protos = mask_protos.reshape(0, {32,136 * 240});
Mat matmulRes = ( mask_proposals * protos).t(); //23,32 * 32,32640 ==> 23,32640
Mat masks = matmulRes.reshape(proposal.size(),{136,240}); //上一步骤作转置的原因://Mat Mat::reshape(int cn,int rows=0) const cn:表示通道数(channels),如果设置为0,则表示通道不变;
vector<Mat> maskChannels; //分离通道
split(masks, maskChannels);
for (int index = 0; index < f_output.size(); ++index) {
Mat dest,mask;
//sigmoid
cv::exp(-maskChannels[index],dest);//e^x
dest= 1.0/(1.0 + dest);
//_netWidth = 960; _netHeight=544; //ONNX图片输入宽度\高度 // const int _segWidth = 240;
Rect roi(int(params[2] / netWidth * segWidth), int(params[3] / netHeigh * segHeight), int(segWidth - params[2] / 2), int(segHeight- 0/2)); //136-params[3]/2最后一个参数改了 mask会有偏移
dest = dest(roi);
resize(dest, mask, cv::Size(col,row), INTER_LINEAR);//srcImgShape (1920,1080)//INTER_NEAREST 最近临插值 PYTHON中用的就是 INTER_LINEAR - 双线性插值
//crop
Rect temp_rect = f_output[index].box;
mask = mask(temp_rect) > mask_thresh; //mask_threshg mask阈值
f_output[index].boxMask =mask;
}
//DrawPred 绘制结果
for (int i=0;i<f_output.size();i++)
{
int lf, tp,wd,hg;
float confidence;
lf=f_output[i].box.x;
tp=f_output[i].box.y;
wd=f_output[i].box.width;
hg=f_output[i].box.height;
confidence=f_output[i].confidence;
int label = static_cast<int>(f_output[i].id);
//生成随机颜色
uint8_t b, g, r;
tie(b, g, r) = iLogger::random_color(label);
cv::rectangle(mask_box, cv::Point(lf, tp), cv::Point(lf+wd, tp+hg), cv::Scalar(b, g, r), 3);//绘制box框
auto name = cocolabels[label];
auto caption = iLogger::format("%s %.2f", name, confidence);
int width = cv::getTextSize(caption, 0, 1, 1, nullptr).width + 10;
cv::rectangle(mask_box, cv::Point(lf-3, tp-33), cv::Point(lf + width, tp), cv::Scalar(b, g, r), -1);//绘制label的框
cv::putText(mask_box, caption, cv::Point(lf, tp-5), 0, 1, cv::Scalar::all(0), 2, 16);
mask_seg(f_output[i].box).setTo(cv::Scalar(b, g, r), f_output[i].boxMask);//绘制mask
}
addWeighted(mask_box, 0.6, mask_seg, 0.4, 0, mask_box); //将mask加在原图上面
}