流畅的python笔记(六)使用一等函数实现设计模式
目录
一、重构策略模式
经典策略模式
使用作为对象的函数实现策略模式
自动选择最佳策略
找出模块中的全部策略
globals()
使用单独模块专门保存所有策略
二、命令模式
总结
一、重构策略模式
经典策略模式
策略模式的定义是:定义 一系列算法(策略),把它们一一封装起来,并且使它们可以相互替换。策略模式使得算法可以独立于使用它的客户而变换,即不同的客户都可以使用某个算法或其它算法。
下面是一个电商领域使用策略模式的例子。
策略模式设计的内容如下:
上下文:即上图中的order,用于把一些计算委托给可互换的不同算法,根据不同算法计算折扣,即用于选择具体策略。
策略:实现不同算法组件的共同接口。即上图中名为Promotion的抽象类。
具体策略:策略的具体子类。fidelityProme、BulkPromo和LargeOrderPromo即这里实现的三个具体策略。
具体策略由上下文类的客户选择,实例化订单之前,系统以某种方式确定选择哪一种策略,然后用这种选择来初始化Order。具体选择哪一种策略,不在当前设计模式的职责范围内。
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from collections import namedtuple
Customer = namedtuple('Customer', 'name fidelity') # 姓名和积分
class LineItem:
def __init__(self, product, quantity, price):
self.product = product
self.quantity = quantity
self.price = price
def total(self) -> '总价格 = 单价 * 数量':
return self.price * self.quantity
class Order: # 上下文
def __init__(self, customer, cart : '购买的所有商品种类', promotion : '用于选择策略, 实参类型就是三个具体策略对象'=None):
self.customer = customer
self.cart = list(cart)
self.promotion = promotion
def total(self):
if not hasattr(self, '__total'):
self.__total = sum(item.total() for item in self.cart)
return self.__total
def due(self) -> "计算账单":
if self.promotion is None:
discount = 0;
else:
discount = self.promotion.discount(self) # 选择策略
return self.total() - discount
def __repr__(self):
fmt = ''
return fmt.format(self.total(), self.due())
class Promotion(ABC): # 策略:抽象基类
@abstractmethod
def discount(self, order):
"""返回折扣金额"""
class FidelityPromo(Promotion): # 第一个具体策略
'''积分1000以上顾客5%折扣'''
def discount(self, order):
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0
class BulkItemPromo(Promotion): # 第二个具体策略
'''单个商品20个以上折扣10%'''
def discount(self, order):
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount
calss LargeOrderPromo(Promotion): # 第三个具体策略
'''不同商品种类达到10个以上折扣7%'''
def discount(self, order):
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_item) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0
如下使用实例中,对于某种策略的选择是由我们手动选定的,即策略模式只是提供了策略的选择方案,但是具体选择哪一种不在策略模式的考虑范围内。
使用作为对象的函数实现策略模式
当函数可以作为对象传参的时候,用类来实现具体策略就不必了。
自动选择最佳策略
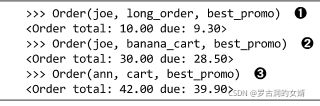
只需要再定义一个函数计算最佳策略即可,注意下边best_promo函数的返回值是函数,max用于选出promo(order)最大的那个promo。
以上方法有个缺陷,每次有了新的策略,都要手动放大promos列表中。
找出模块中的全部策略
在python中,模块(.py文件)也是一等对象,内置函数globals就可以处理模块。
globals()
返回一个字典,表示当前的全局符号表。这个符号表始终针对当前模块,对函数或方法来说,是指定义它们的模块,而不是调用它们的模块。下边例子自动找到了本模块中的所有策略函数。
使用单独模块专门保存所有策略
promotions模块是专门用来保存策略函数的.py文件,inspect是常用的提供高阶内省函数的模块。
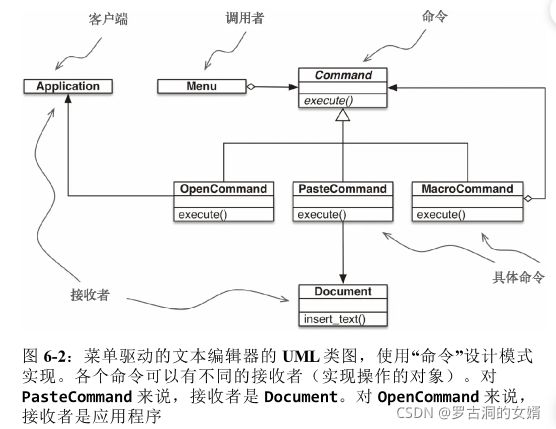
二、命令模式
命令模式也可以通过把函数作为参数传递而简化。
命令模式的目的是解耦调用者(调用操作(函数)的对象)和接收者(提供实现的对象)。比如调用者是图形应用程序中的菜单项,接收者是被编辑的文档或者应用程序自身。即调用者调用了某个操作,但是接收者可以是自身也可以不是自身。
总结
使用一等函数实现设计模式的方法就是,把实现单方法接口的类的实例替换程可调用对象(函数)。