图像处理(四):边缘检测(二):sobel和canny
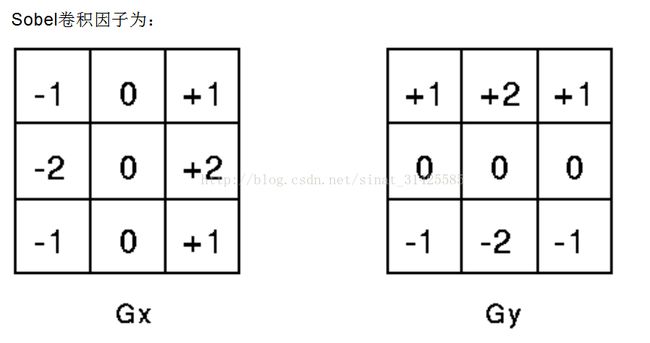
具体原理,参考博客点击打开链接,最常用的边缘检测算子有:sobel、canny、prewitt、Roberts等,sobel算子模板为:
sobel算子考虑了邻域信息,相当于对图像先做加权平均,然后再做微分运算。
Canny算子:
1、使用Gassian滤波器平滑处理;
2、使用sobel算子分别计算x,y方向梯度分量及梯度方向;
3、对梯度进行非极大值抑制;
4、使用双阈值对边缘进一步检测和增强;
实现代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
// define sobel kernel
const int sobel_kernel_y[9] = { -1, -2, -1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 1 };
const int sobel_kernel_x[9] = { -1, 0, 1, -2, 0, 2, -1, 0, 1 };
// 3x3 位置
const int locations[9][2] = { { -1, -1 }, { -1, 0 }, { -1, 1 },
{ 0, -1 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 1 },
{ 1, -1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, 1 } };
// 8领域
const int neighbors[8][2] = { { -1, -1 }, { -1, 0 }, { -1, 1 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 }, { 1, -1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, 1 } };
int main()
{
Mat src = imread("lena.jpg");
Mat image = src.clone();
GaussianBlur(src, image, Size(3, 3), 1.5);
Mat gray;
cvtColor(image, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
Mat sobel_x = Mat::zeros(gray.rows, gray.cols, CV_8UC1);
Mat sobel_y = Mat::zeros(gray.rows, gray.cols, CV_8UC1);
Mat sobel_xy = Mat::zeros(gray.rows, gray.cols, CV_64FC1);
int i, j, k;
// compute sobel_x, sobel_y
for (i = 1; i < gray.rows - 1; i++)
for (j = 1; j < gray.cols - 1; j++)
{
int temp_x = 0, temp_y = 0;
for (k = 0; k < 9; k++)
{
temp_x += sobel_kernel_x[k] * gray.at(i + locations[k][0], j + locations[k][1]);
temp_y += sobel_kernel_y[k] * gray.at(i + locations[k][0], j + locations[k][1]);
}
sobel_x.at(i, j) = temp_x;
sobel_y.at(i, j) = temp_y;
//sobel_xy.at(i, j) = sqrt(temp_x * temp_x + temp_y * temp_y);
sobel_xy.at(i, j) = abs(temp_x) + abs(temp_y);
}
Mat directions = Mat::zeros(gray.rows, gray.cols, CV_64FC1);
// compute direction
for (i = 1; i < gray.rows - 1; i++)
for (j = 1; j < gray.cols - 1; j++)
{
// atan2的取值范围为[-pi,pi]
float t = atan2(sobel_y.at(i, j), sobel_x.at(i, j));
if (t < 0)
{
t += CV_PI;
}
directions.at(i, j) = t;
}
float t = 0;
// 非极大值抑制
for (i = 1; i < gray.rows - 1; i++)
for (j = 1; j < gray.cols - 1; j++)
{
t = directions.at(i, j);
// 0 - 22.5,
if (((t >= 0) && (t < CV_PI / 8.0)) || ((t >= 7.0 * CV_PI / 8.0) && (t < CV_PI)))
{
if ((sobel_xy.at(i, j) < sobel_xy.at(i, j + 1)) ||
(sobel_xy.at(i, j) < sobel_xy.at(i, j - 1)))
{
sobel_xy.at(i, j) = 0;
}
}
// 22.5 - 67.5
else if ((t >= CV_PI / 8.0) && (t < 3.0 * CV_PI / 8.0))
{
if ((sobel_xy.at(i, j) < sobel_xy.at(i - 1, j + 1)) ||
(sobel_xy.at(i, j) < sobel_xy.at(i + 1, j - 1)))
{
sobel_xy.at(i, j) = 0;
}
}
// 67.5 - 112.5
else if ((t >= 3.0 * CV_PI / 8.0) && (t < 5.0 * CV_PI / 8.0))
{
if ((sobel_xy.at(i, j) < sobel_xy.at(i - 1, j)) ||
(sobel_xy.at(i, j) < sobel_xy.at(i + 1, j)))
{
sobel_xy.at(i, j) = 0;
}
}
// 112.5 - 157.5
else if ((t >= 5.0 * CV_PI / 8.0) && (t < 7.0 * CV_PI / 8.0))
{
if ((sobel_xy.at(i, j) < sobel_xy.at(i - 1, j - 1)) ||
(sobel_xy.at(i, j) < sobel_xy.at(i + 1, j + 1)))
{
sobel_xy.at(i, j) = 0;
}
}
}
// 双阈值滤波
float lower_t = 30;
float upper_t = 100;
Mat My_canny = Mat::zeros(sobel_xy.rows, sobel_xy.cols, CV_8UC1);
Mat sobel_xy_mask = Mat::zeros(sobel_xy.rows, sobel_xy.cols, CV_32FC1);
sobel_xy.copyTo(sobel_xy_mask);
// 将两个阈值能够判断的进行判断
for (i = 1; i < sobel_xy_mask.rows - 1; i++)
for (j = 1; j < sobel_xy_mask.cols - 1; j++)
{
if (sobel_xy_mask.at(i, j) > upper_t)
{
My_canny.at(i, j) = 255;
sobel_xy_mask.at (i, j) = 0; // 用完就置0,方便后面的检测
}
if (sobel_xy_mask.at(i, j) < lower_t)
{
sobel_xy.at(i, j) = 0;
}
}
// 对两个阈值中间的部分进行增强
for (i = 1; i < sobel_xy_mask.rows - 1; i++)
for (j = 1; j < sobel_xy_mask.cols - 1; j++)
{
if (sobel_xy_mask.at(i, j ) >= lower_t)
{
// 遍历八领域 ,看八邻域是否有255
for (k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
if (My_canny.at(i + neighbors[k][0], j + neighbors[k][1]) == 255)
{
My_canny.at(i, j) = 255;
sobel_xy_mask.at(i, j) = 0;
break;
}
}
}
}
Mat canny_sys;
Canny(gray, canny_sys, 30, 100);
namedWindow("gray", 0);
resizeWindow("sobel_x", 300, 300);
namedWindow("sobel_x", 0);
resizeWindow("sobel_y", 300, 300);
namedWindow("sobel_y", 0);
resizeWindow("sobel_xy", 300, 300);
namedWindow("sobel_xy", 0);
resizeWindow("sobel_xy", 300, 300);
namedWindow("My_canny", 0);
resizeWindow("My_canny", 300, 300);
namedWindow("canny_sys", 0);
resizeWindow("canny_sys", 300, 300);
imshow("gray", gray);
imshow("sobel_x", sobel_x);
imshow("sobel_y", sobel_y);
imshow("sobel_xy", sobel_xy);
imshow("My_canny", My_canny);
imshow("canny_sys", canny_sys);
waitKey();
return 0;
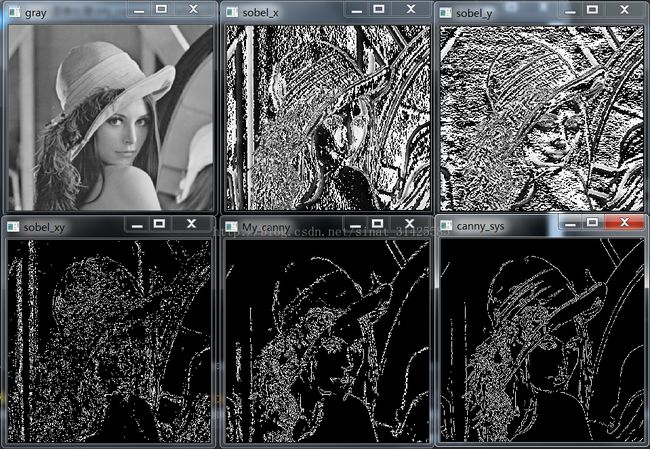
} 效果如下:
跟opencv自带的canny效果好像存在一定偏差,具体原因等过段时间研究一下源代码~