【使用 BERT 的问答系统】第 6 章 :BERT 模型应用:其他任务
大家好,我是Sonhhxg_柒,希望你看完之后,能对你有所帮助,不足请指正!共同学习交流
个人主页-Sonhhxg_柒的博客_CSDN博客
欢迎各位→点赞 + 收藏⭐️ + 留言
系列专栏 - 机器学习【ML】 自然语言处理【NLP】 深度学习【DL】
foreword
✔说明⇢本人讲解主要包括Python、机器学习(ML)、深度学习(DL)、自然语言处理(NLP)等内容。
如果你对这个系列感兴趣的话,可以关注订阅哟
文章目录
情绪分析
命名实体识别
文本分类
文本摘要
结论
在上一章中,我们了解了 BERT 及其在问答系统设计中的应用。本章讨论如何使用 BERT 实现其他 NLP 任务,例如文本分类、命名实体识别、语言翻译等。
BERT 在各种 NLP 任务的许多基准数据集中表现良好,例如 SQuAD(问答数据集)、Natural Questions(事实和非事实问题的问答数据集)、IMDB 电影评论数据集(分类数据)等。现在,我们将看到如何将在这些基准数据集上训练的基于 BERT 的模型用作以下 NLP 任务的预训练模型。
-
情绪分析
-
命名实体识别
-
文本分类
-
文本摘要
我们介绍这些主题,然后看看它们的实现。
情绪分析
情感分析是 NLP 的一个子领域,它识别博客、评论、新闻等给定文本的观点或情感。它可以告知企业对其产品的接受程度和消费者对其的看法。识别社交媒体上的仇恨言论和其他问题也很有用,可以识别人们对特定讨论主题的情绪。情绪分析甚至可以帮助公司根据消费者对特定人口区域特定主题的意见来规划产品发布。
对于本书,我们使用了一个使用 BERT 训练的情感分析模型,它使用.csv格式的数据集,其中每个数据点是一对句子及其观点(即,不是侮辱,侮辱)。对于推理,系统处理用户的查询并提供相同的情绪。
! pip install deeppavlov! python -m deeppavlov install insults_kaggle_bert笔记请使用 '!' 如果您使用的是 Colab Notebook,请在安装命令前添加符号,如刚才所示。
from deeppavlov import build_model, configs4.然后我们将使用 deeppavlov 库的build_model类得到一个情感分析模型。它需要两个参数:
-
配置 文件路径:定义配置文件的名称,其中包含要使用的相关 NLP 模型的详细信息。对于这种情况,我们将使用insults_kaggle_bert。这包含使用情感模型所需的配置。
-
download :如果需要下载模型,则为True ,否则为False。因为我们是第一次这样做,所以这个参数的值将为True。sentiment_model = build_model(configs.classifiers.insults_kaggle_bert,下载=真)
test_input = ['This movie is good', 'You are so dumb!']
results = sentiment_model(test_ input)from deeppavlov import build_model, configs
def build_sentiment_model ():
model = build_model(configs.classifiers.insults_kaggle_bert, download=True)
return model
test_input = ['This movie is good', 'You are so dumb!']
if __name__ == "__main__" :
sentiment_model = build_sentiment_model()
results = sentiment_model(test_ input)
print(results)['Not Insult', 'Insult']现在我们已经了解了如何将基于 BERT 的情绪分析系统用于研究目的,让我们考虑一个场景,您需要在对话系统中启用情绪分析,以便它可以根据查询或请求识别用户的情绪。用户给出的响应。这将有助于对话系统根据用户的情绪做出响应。按照此处给出的步骤将情绪分析系统的功能作为 REST API 发布。
from flask import Flask, request
import json
from SentimentAnalysis.SentimentAnalysis import build_sentiment_model
app=Flask(__name__)
@app.route ("/sentimentAnalysis", methods=['POST'])
def sentimentAnalysis():
try:
json_data = request.get_json(force=True)
questions = json_data['questions']
sentiment_model = build_sentiment_model()
questions_list =[]
for ques in questions:
questions_list.append(ques)
model_output = sentiment_model(questions_list)
index = 0
result = []
for ans in model_output:
sentiment_qa =dict()
sentiment_qa['qustion'] = questions_list[index]
sentiment_qa['answer'] = ans
result.append(sentiment_qa)
result={'results':result}
result = json.dumps(result)
return result
except Exception as e:
return {"Error": str(e)}
if __name__ == "__main__" :
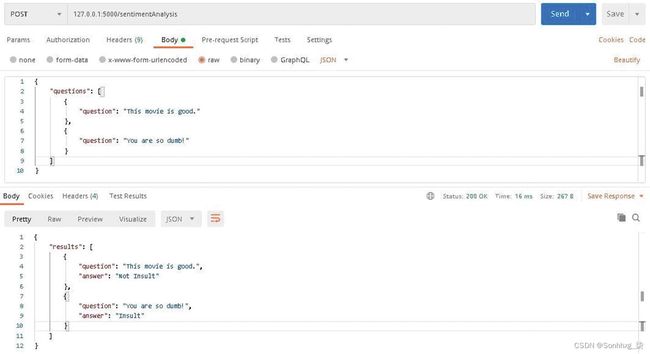
app.run(port="5000")网址: http: //127.0.0.1 :5000/sentimentAnalysis
{
"questions": [
{
"question": "This movie is good."
},
{
"question": "You are so dumb!"
}
]
}
{
"results": [
{
" question": "This movie is good.",
"answer": "Not Insult"
},
{
" question": "You are so dumb!",
"answer": "Insult"
}
]
}
可以从 GitHub 下载本练习的代码库,网址为Python_code/Chapter6/SentimentAnalysis at master · bertbook/Python_code · GitHub。
命名实体识别
-
搜索引擎 :这用于为用户提出的查询识别相关文档。例如,让我们使用“什么是 Microsoft Outlook?” 在此查询中,“Microsoft Outlook”是应用程序类型的实体。因此,搜索引擎将更加重视将 Microsoft Outlook 识别为实体的文档。
-
对话系统 :实体在对话系统的设计中起着重要作用。实体被用在对话系统中,以消除用户提出的问题的歧义,如果它与常见问题有关但针对不同的实体。例如,用户输入了查询“我在 Outlook 中遇到问题”。对话系统有两种解决方案:一种用于 Outlook,另一种用于 Gmail。因为 Outlook 和 Gmail 都是不同的实体,所以解决方案也是如此。因此,识别完意图(即Issue)后,接下来识别的就是实体(即Outlook),会话系统据此给出解决方案。
存在许多用于实体识别的注释数据集。不过,对于本书,我们将演示一个实体模型,该模型已经使用 BERT 作为基线在 OntoNotes 数据集上进行了训练。该数据集收集了 1,745,000 条英语、900,000 条中文和 300,000 条阿拉伯文本数据,这些数据来自电话对话、新闻专线、广播新闻、广播对话和博客等各种来源。
在这个数据集中,实体被标注了 18 个类别,例如组织、艺术作品、单词中的数字、数字、数量、人物、位置、地缘政治实体、时间、日期、设施、事件、法律、国籍或宗教或政治团体,语言、货币、百分比和产品等。
! pip install deeppavlov安装后,您将看到类似于图6-5的输出。
! python -m deeppavlov install ner_ontonotes_bert_mult笔记
请使用 '!' 如果您使用的是 Colab Notebook,请在安装命令前添加符号,如刚才所示。
from deeppavlov import build_model, configs4.然后我们将使用 deeppavlov 库的build_model类获得一个实体模型。它需要两个参数:
-
配置 文件路径:定义配置文件的名称,其中包含要使用的相关 NLP 模型的详细信息。对于这种情况,我们将使用ner_ontonotes_bert_mult。该文件包含在 OntoNotes 上训练的实体模型所需的所有配置。
-
下载:如果需要下载模型,则为True ,否则为False。因为我们是第一次这样做,所以这个参数的值将为True。
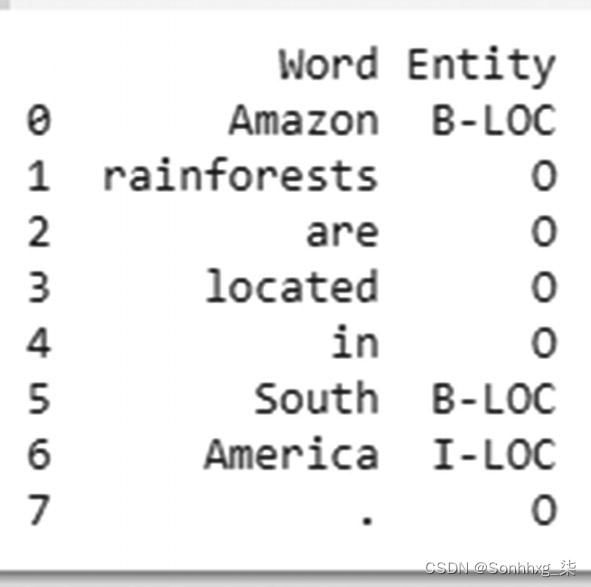
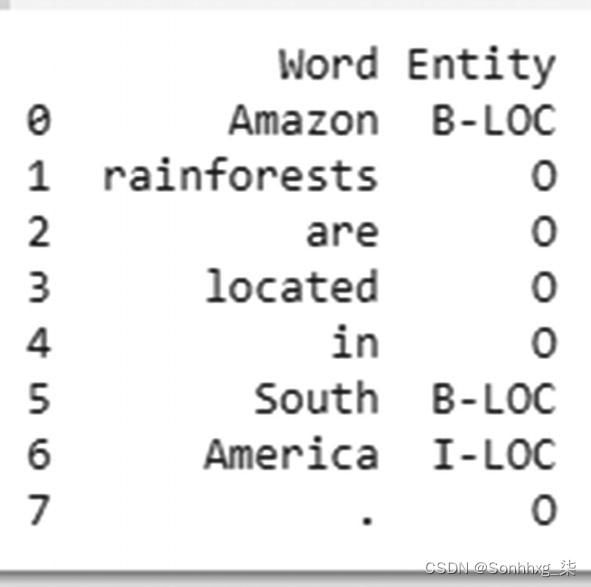
ner_model = build_model(configs. ner.ner_ontonotes_bert_mult, download=True)test_input = ["Amazon rainforests are located in South America."]
results = ner_model(test_ input)from deeppavlov import build_model, configs
import pandas as pd
def build_ner_model ():
model = build_model(configs. ner.ner_ontonotes_bert_mult, download=True)
return model
if __name__=="__main__":
test_input = ["Amazon rainforests are located in South America."]
ner_model = build_ner_model()
results = ner_model(test_ input)
results = pd.DataFrame(zip(results[0][0],results[1][0]), columns=['Word','Entity'])
print(results)现在我们已经了解了如何将基于 BERT 的实体识别系统用于研究目的,接下来我们考虑一个场景,在该场景中我们需要部署此功能以供对话系统使用。对话系统通常使用实体来配置或开发用例。例如,对于用例“面对 Outlook 的问题”,该系统可用于将“Outlook”识别为一个实体。在这种情况下,您需要使用以下步骤将实体识别系统的功能发布或公开为REST API 。
from flask import Flask, request
import json
from NamedEntityRecognition.NamedEntityRecognition import build_ner_model
app=Flask(__name__)
@app.route ("/namedEntity", methods=['POST'])
def namedEntity():
try:
json_data = request.get_json(force=True)
query = json_data['query']
ner_model = build_ner_model()
model_output = ner_model([query])
words= model_output[0][0]
tags = model_output[1][0]
result_json = dict()
result_json['query'] = query
entities = []
index = 0
for word in words:
word_tag_dict=dict()
word_tag_dict['word'] = word
word_tag_dict['tag'] = tags[index]
index = index+1
entities.append(word_tag_dict)
result_json['entities'] = entities
result = json.dumps(result_json)
return result
except Exception as e:
return {"Error": str(e)}
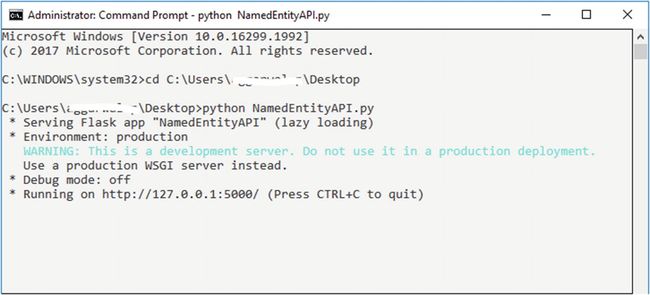
if __name__ == "__main__" :
app.run(port="5000")Python NamedEntiityAPI.py网址: http: //127.0.0.1 :5000/namedEntity
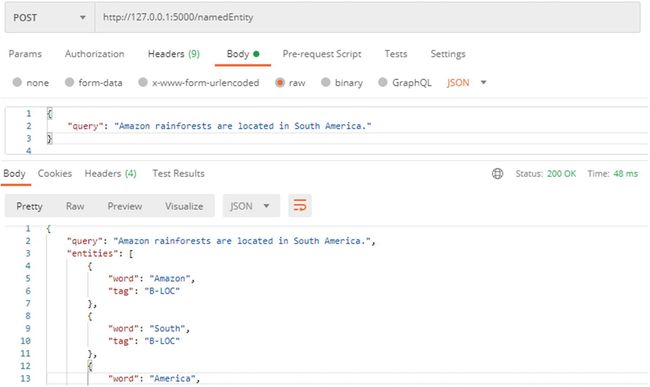
{
"query": "Amazon rainforests are located in South America."
}
{
"query": "Amazon rainforests are located in South America.",
"entities": [
{
"word": "Amazon",
"tag": "B-LOC"
},
{
"word": "South",
"tag": "B-LOC "
},
{
"word": "America",
"tag": "I-LOC "
}
]
}
可以从 GitHub 下载此练习的代码库,网址为Python_code/Chapter6/NamedEntityRecognition at master · bertbook/Python_code · GitHub。
文本分类
文本分类可以定义为将文本分配或分类到特定类别或类中的问题。文档分类或分类、意图分类、垃圾博客检测等都属于文本分类。在这里,文本可以是任何内容,例如句子、文档、博客等。文本分类利用 NLP 方法进行预处理,例如标记化、停用词删除、短语提取、实体提取等。
在推理过程中,文本分类分析文本(文档、博客或句子)并将其分配给预训练类别。例如,如果文档指的是政治,那么这就属于政治范畴。在某些情况下,一个文档可能属于多个类别(称为多标签分类)。例如,如果文档既谈论政治又谈论体育,那么它将被归类到这两个类别中;即政治和体育。
-
alt.atheism
-
soc.religion.christian
-
comp.graphics
-
sci.med
! pip3 install -q tensorflow_gpu==2.1.0
! pip3 install -q ktrainfrom sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
import ktrainclasses = ['alt.atheism', 'soc.religion.christian','comp.graphics', 'sci.med']
train_data = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train', categories=classes, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
test_data = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='test', categories=classes, shuffle=True, random_state=42)-
Model name:这表示要使用的BERT模型的名称。在这种情况下,我们使用了 distillBERT 而不是 BERT base。
-
Length of article:设置文章的最大长度。这里,最大长度只能是512。如果指定任何长度大于512的文章,它会被自动截断。
-
Classes:这是需要考虑进行培训的课程列表。
MODEL_NAME = 'distilbert-base-uncased'
trans = text.Transformer(MODEL_NAME, maxlen=500, classes=train_classes)
train_preprocess = trans.preprocess_train(train_features, train_labels)
val_preprocess = trans.preprocess_test(test_features, test_labels)
model_data = trans.get_classifier()
classification_model = ktrain.get_learner(model_data, train_data=train_preprocess, val_data=val_preprocess, batch_size=6)
classification_model.fit_onecycle(5e-5, 4)predictor = ktrain.get_predictor(classification_model.model, preproc=trans)
input_text = 'Babies with down syndrome have an extra chromosome.'
results = predictor.predict(input_text)from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
import ktrain
from ktrain import text
def preprocess_dataset():
classes = ['alt.atheism', 'soc.religion.christian','comp.graphics', 'sci.med']
train_data = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train', categories=classess, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
test_data = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='test', categories=classes, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
return train_data.data,train_data.target, test_data.data,test_data.target,classes
def create_text_classification_model():
MODEL_NAME = 'distilbert-base-uncased'
train_features, train_labels, test_features, test_labels, train_classes =preprocess_dataset()
trans = text.Transformer(MODEL_NAME, maxlen=500, classes=train_classes)
train_preprocess = trans.preprocess_train(train_features, train_labels)
val_preprocess = trans.preprocess_test(test_features, test_labels)
model_data = trans.get_classifier()
classification_model = ktrain.get_learner(model_data, train_data=train_preprocess, val_data=val_preprocess, batch_size=6)
classification_model.fit_onecycle(5e-5, 4)
return classification_model, trans
def predict_category(classification_model, trans, input_text):
predictor = ktrain.get_predictor(classification_model.model, preproc=trans)
results = predictor.predict(input_text)
return results
if __name__ == "__main__" :
classification_model, trans = create_text_classification_model()
input_text = 'Babies with down syndrome have an extra chromosome.'
print(predict_category(classification_model, trans, input_text))sci.med现在,我们已经了解了如何将基于 BERT 的文本分类系统用于研究目的。接下来,考虑您需要部署此功能以供对话系统使用的场景。对话系统可以利用它作为意图分类或识别系统来配置或开发用例。例如,对于“面临 Outlook 问题”的用例,该系统可用于将意图识别为“问题”。在这种情况下,您需要按照以下步骤将意图分类系统的功能发布或公开为REST API 。
from flask import Flask, request
import json
from TextClassification.TextClassification import create_text_classification_model, predict_category
from TextClassification import create_text_classification_model
app=Flask(__name__)
result={}
@app.route ("/textClassification", methods=['POST'])
def textClassification ():
try:
json_data = request.get_json(force=True)
input_text = json_data['query']
classification_model, trans = create_text_classification_model()
category = predict_category(classification_model, trans, input_text)
result = {}
result['query'] = input_text
result['category'] = category
result = json.dumps(result)
return result
except Exception as e:
error = {"Error": str(e)}
error = json.dumps(error)
return error
if __name__ == "__main__" :
app.run(port="5000")网址: http: //127.0.0.1 :5000/textClassification
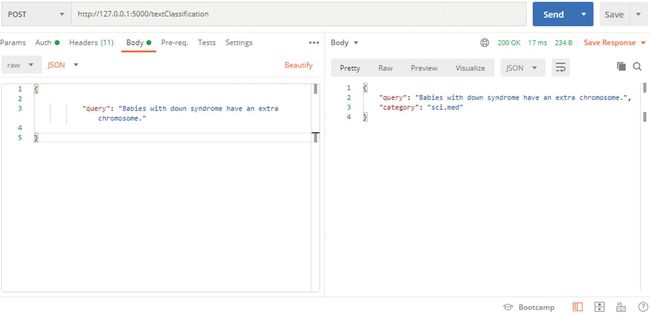
{
"query": "Babies with down syndrome have an extra chromosome."
}
{
"query": "Babies with down syndrome have an extra chromosome.",
"category": "sci.med"
}
可以从 GitHub 下载此练习的代码库,网址为Python_code/Chapter6/TextClassification at master · bertbook/Python_code · GitHub。
文本摘要
-
提取摘要:在提取摘要 中,生成的摘要中的句子将仅来自文档本身。摘要中的句子不会有任何修改。这也可以定义为根据句子与文档主题的相关性对句子进行重新排列。TF-IDF、余弦相似度、基于图的方法、实体提取、标记化等几种方法已被用于积极开发文档摘要系统。
-
抽象摘要:在抽象摘要 中,生成的摘要中的句子不会是文档本身的实际句子。这些句子将根据文档中使用的语言语义进行修改。各种基于神经网络的方法,如 LSTM、GRU 等已被用于实现这一点。
from summarizer import Summarizer3.这个库实现了 HuggingFace Pytorch 转换器来运行提取摘要。它的工作原理是生成句子的嵌入,然后使用聚类算法(例如基于密度的算法等)对最接近质心的句子进行聚类,形成一个高度密集的区域。来自最高密度区域的句子将被用来形成摘要。接下来,创建一个Summarizer实例,如此处所示。
text_summarization_model = Summarizer()from summarizer import Summarizer
def text_summary(text):
model=Summarizer()
return model(text)
if __ name__=='__main__':
text = "Machine learning (ML) is the study of computer algorithms that improve automatically through experience. It is seen as a subset of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a mathematical model based on sample data, known as "training data", in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as email filtering and computer vision, where it is difficult or infeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks."
print(text_summary(text))此示例中的文本片段来自维基百科关于机器学习的文章。
Machine learning (ML) is the study of computer algorithms that improve automatically through experience. It is seen as a subset of artificial intelligence.此输出显示文档的摘要,摘要中的所有句子都是文档本身的实际句子。文档可以是任意长度(例如,100 或 200 页),REST API 无法在单个 API 调用中接收如此大量的数据。因此,作为最佳实践,文档摘要系统应该仅用作后端应用程序或具有父系统(例如搜索引擎)的系统,其中作为搜索结果的一部分返回的每个文档也应该具有文档摘要。
可以从 GitHub 下载此练习的代码库,网址为Python_code/Chapter6/TextSummarization at master · bertbook/Python_code · GitHub 。
结论
本章涵盖了 BERT 在各种 NLP 任务中的适用性,例如情感分析、文本分类、实体识别和文档摘要。我们利用基于 BERT 的模型来构建基于 NLP 的系统。在下一章中,我们将讨论 BERT 中发生的最新研究。