智能车巡线python-opencv
背景:2022智能车比赛百度提高组
思路:先拿赛道通过HSV调阈值,然后得到二值化图片,对二值化图像进行巡线;
巡线的思路:从图片最后一行的中央开始往左右两边扫线:分扫左线与扫右线;
以左线为例子:(图片大小为480*640)
图片以最后一行开始往第一行循环作为外循环(设为i),以中线开始往左减一作为内循环(设为j);记录该行的跳变点:即如果该行的该列为白色(255),下一列为黑色(0)则记录其列标(j),如果不满足该条件则说明无跳变点即该行无线,记录为0;记录到一个数组内(采用append的方法)。
右边线一样的思路,只不过如果没有线就记录为右最大列标(639)
赛道元素处理:
赛道有十字,锐角转弯,连着的双十字,以及因为摄像头安装的位置导致的缺角与缺赛道
锐角:
双十字:
十字:
缺角等:
......就不一 一展示了。
处理思路:1.锐角元素:
因为锐角出现,导致扫线方法不适用;然而锐角只会在图片上方出现,要么左锐角,要么右锐角,我们这个赛道只会出现左锐角,且占比较小,所以直接判断锐角,然后不扫锐角的线;
代码:如果当前行的最左边为非车道(0),下一行(往上)为车道(非0),右边线为非车道,则中断循环;因为锐角只会出现在左转,我们赛道十字都出现在左转,所以这样做不会出漏扫(如果十字处右转,则可能会出现漏扫现象)。
2.十字与缺角:
思路:先计算拐点,然后通过拐点来判断补线;补线直接将上下拐点连接起来:斜截式方程。
拐点的计算:计算左(右)边线的跳跃点:从0(黑)变到非0(白)即为左(右)上拐点, 从非0(白)变到0(黑)即为左(右)下拐点。(用四个变量标志记录是否存在拐点,如果有就再用四个变量存拐点坐标)
A.先补拐点,即如果左(右)边只有一个拐点,则另一个拐点就通过该拐点赋值,具体看程序:只有上拐点就把下拐点记为最下面一行同一列的点...
B.通过拐点标志判断如何补线
补线判断:只要出现拐点就补线
拐点的位置可以通过代码里面的 sm 这个变量调整
代码:(函数里对照片进行展示比较耗时,返回值为巡得的中线数组)
import cv2
import numpy
import numpy as np
def nothing(*arg):
pass
icol = (18, 0, 196, 36, 255, 255)
#path = "test/cruise/"
# Show the original image.
#frame = path+str(961)+'.jpg'
#frame = cv2.imread(frame)
l = [16, 45, 65] # [17, 55, 128]#阈值
h = [44, 255, 255] # [24, 255, 255]#阈值
def zh_ch(string):
return string.encode("gbk").decode('UTF-8', errors='ignore')
# mm = 320
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
def XunX(img,SX):
cv2.imshow('frame', img)
# Blur methods available, comment or uncomment to try different blur methods.
frameBGR = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (7, 7), 0)
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frameBGR, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# HSV values to define a colour range.
colorLow = numpy.array([16, 45, 65] ) # [17, 55, 128]
colorHigh = numpy.array([44, 225, 225]) # [24, 225, 225]
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, colorLow, colorHigh)
# Show the first mask
cv2.imshow('mask-plain', mask)
kernal = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (7, 7))
mask = cv2.morphologyEx(mask, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernal)
mask = cv2.morphologyEx(mask, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernal)
cv2.imshow('mask-plain', mask)
# Find_Line(mask)
left = np.array([])
right = np.array([])
leftb = np.array([])
rightb = np.array([])
medim = np.array([])
# len = []#记录边线丢失
le = [[]]
ri = [[]]
zz = 0 # 记录左缺陷时上一个坐标
yy = 639
SX = SX # 开始扫线时的y坐标
SXp = np.array([])
SS = 0
left_up = left_down = right_up = right_down = 0
for i in range(480, 1, -1):
# 扫左线
for j in range(SX + 1, 0, -1):
# 中线:319
if (mask[i - 1][j] == 0) and (mask[i - 1][j - 1] == 255):
# 记录左跳变点的列值
left = np.append(left, j)
leftb = np.append(leftb, j)
zz = j
break
# 现在缺线
elif (j == 1):
lk = 0
left = np.append(left, lk)
leftb = np.append(leftb, lk)
# 扫右线
for j1 in range(SX + 2, 639, 1):
if (mask[i - 1][j1] == 0) and (mask[i - 1][j1 + 1] == 255):
# 记录右跳变点的列值
right = np.append(right, j1)
rightb = np.append(rightb, j1)
yy = j1
break
# 缺线
elif (j1 == 638):
lk = 639
rightb = np.append(rightb, lk)
right = np.append(right, lk)
if (left[480 - i] == 0 and right[480 - i] != 639 and mask[i - 2][0] != 0 ):
break
# if (right[480 - i] == 639 and left[480 - i] != 0 and mask[i - 2][639] != 255 ):
# break
SX = int((left[480 - i] + right[480 - i]) / 2)
SXp = np.append(SXp, SX)
# 找拐点
sm = 30
for i in range(len(left) - 10):
if (left[i] == 0 and left[i + 3] == 0 and left[i + 5] > 0 and left[i + 10] > 0):
left_up = 1
left_up1 = (i + min(len(left[i+2:]),sm), left[i + min(len(left[i+2:]),sm)]) # 480 - i-sm
if (left[i] > 0 and left[i + 3] > 0 and left[i + 5] == 0 and left[i + 10] == 0):
left_down = 1
left_down1 = (i - min(i,sm), left[i - min(i,sm)]) # 480 - i+sm
if (right[i] == 639 and right[i + 3] == 639 and right[i + 5] < 639 and right[i + 10] <= 639):
right_up = 1
right_up1 = (i + min(len(left[i+2:]),sm), right[i + min(len(left[i+2:]),sm)])
if (right[i] < 639 and right[i + 3] < 639 and right[i + 5] == 639 and right[i + 10] == 639):
right_down = 1
right_down1 = (i - min(i,sm), right[i - min(i,sm)]) # -1
# 判断元素:补线操作
print(left_up, left_down, right_up, right_down)
if (left_up and not left_down):
left_down1 = (0, left_up1[1])
elif (not left_up and left_down):
left_up1 = (479, left_down1[1])
if (right_up and not right_down):
right_down1 = (0, right_up1[1])
elif (not right_up and right_down):
right_up1 = (479, right_down1[1])
# 左右的上下拐点同时出现
#if (left_up and right_up) or (left_down and right_down):
if (left_up or right_up) or (left_down or right_down):
# if(right_up1[0] - left_up1[0] <= 20):
for k in range(len(leftb)):
if (k >= left_down1[0] and k <= left_up1[0]) or (k <= left_down1[0] and k >= left_up1[0]):
leftb[k] = ((left_up1[1] - left_down1[1]) / (left_up1[0] -
left_down1[0])) * (k - left_up1[0]) + left_up1[1]
if (k >= right_down1[0] and k <= right_up1[0]) or (k <= right_down1[0] and k >= right_up1[0]):
rightb[k] = ((right_up1[1] - right_down1[1]) / (right_up1[0] -
right_down1[0])) * (k - right_up1[0]) + right_up1[1]
# # 同时出现左上下,或右上下:
# if (left_up and left_down) or (right_up and right_down):
# # if(right_up1[0] - left_up1[0] <= 20):
# for k in range(len(leftb)):
# if (k >= left_down1[0] and k <= left_up1[0]) or (k <= left_down1[0] and k >= left_up1[0]):
# leftb[k] = ((left_up1[1] - left_down1[1]) / (left_up1[0] -
# left_down1[0])) * (k - left_up1[0]) + left_up1[1]
# if (k >= right_down1[0] and k <= right_up1[0]) or (k <= right_down1[0] and k >= right_up1[0]):
# rightb[k] = ((right_up1[1] - right_down1[1]) / (right_up1[0] -
# right_down1[0])) * (k - right_up1[0]) + right_up1[1]
# left_up = left_down = right_up = right_down = 0
# if
medim = (leftb + rightb) / 2
# img = [mask,mask3,mask4,mask5]
pl = ['left', 'right', 'l&r', 'no']
o = 0
img = mask
cg = len(left)-1
print(cg,len(leftb),len(right))
for k in range(cg, -1, -1):
point = (int(medim[k]), 479 - k) # 左
# point2 = (SXp[k], 478-k)
point3 = (int(leftb[k]), 479 - k) # 中
point1 = (int(rightb[k]), 479 - k) # 右
cv2.circle(img, point, 1, (255, 0, 255), 0)
cv2.circle(img, point1, 1, (255, 0, 255), 0)
cv2.circle(img, point3, 1, (255, 0, 255), 0)
cv2.imshow(pl[o], img)
cv2.waitKey(100000)
return SX,(leftb + rightb) / 2,SXp
mm = 320#扫线开始的坐标
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
test, frame = cap.read()
print(frame.shape)
mm,XB,SXp = XunX(frame, mm)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
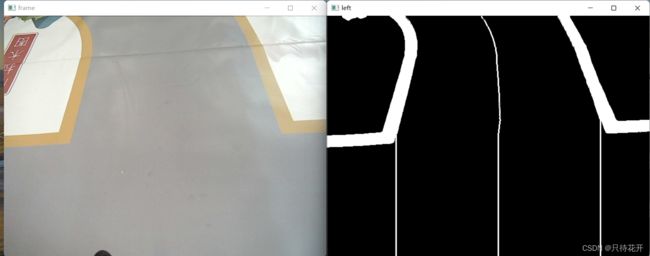
效果:
附录(阈值调试代码与文章):
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35831978/article/details/106988028?spm=1001.2014.3001.5506
持续更新