Java 中的四种引用类型
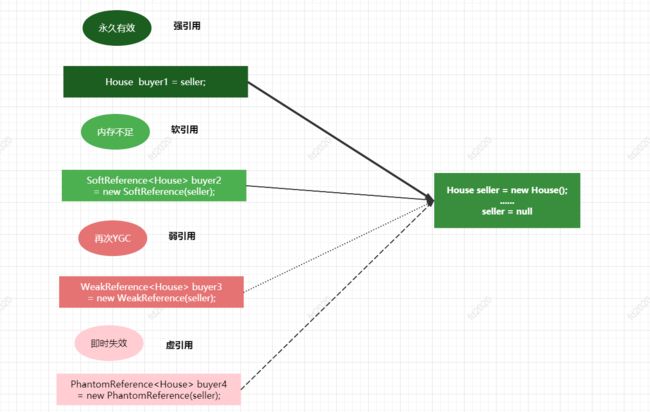
对象的引用类型如下图:
举个例子,在房产交易市场中,某个卖家有一套房子,成功出售给某个买家后引用置为null,
这里有4个买家使用4种不同的引用关系指向这套房子。
-
买家是强引用: 如果把seller引用赋值给它,则永久有效,系统不会因为seller= null 就触发对这套房子的回收,这时房屋交易市场最常见的交付方式。
-
买家buyer2是软引用,只要不产生OOM,buyer2.get() 就可以获取房子对象,就像房子是租来的一样。
-
买家buyer3是弱引用,一旦过户后,seller置为null, buyer3的房子持有时间估计只有几秒钟,卖家只是给买家做了一张假的房产证,买家高兴了几秒钟后没发现房子已经不是自己的了。
-
buyer4 是虚引用,定义完成后无法访问到房子对象,卖家只是虚构的房源,是空手套白狼的诈骗术。
强引用是最常用的,而虚引用在业务中几乎很难用到,下面我们举例介绍一下软引用和弱引用
先来说一下软引用的回收机制。首先设置JVM参数: -Xms20m -Xmx20m , 即只有20MB的堆空间内容。在下面代码中不断地往集合中添加House对象,而每个House有2000个Door的成员变量,狭小的堆空间加上大对象的产生,就为了尽快触达内存耗尽的临界状态。
强引用
public class SoftReferenceHouse {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List houses = new ArrayList<>();
int i =0;
while (true){
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
houses.add(new House());
System.out.println(“i==”+(++i));
}
}
}
class House{
private static final Integer DOOR_NUMBER = 2000;
public Door[] doors = new Door[DOOR_NUMBER];
class Door{}
}
上面代码会一直执行,直到报OOM,因为强引用不会释放。
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
at com.yaspeed2.House.(SoftReferenceHouse.java:26)
at com.yaspeed2.SoftReferenceHouse.main(SoftReferenceHouse.java:17)
软引用
public class SoftReferenceHouse {
public
static void main(String[] args) {
List
int i =0;
while (true){
SoftReference buyer2 = new SoftReference(new House());
houses.add(buyer2);
System.out.println(“i==”+(++i));
}
}
}
class House{
private static final Integer DOOR_NUMBER = 4000;
public Door[] doors = new Door[DOOR_NUMBER];
class Door{}
}
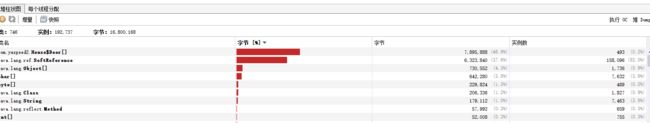
正常运行一段时间,内存到达耗尽的临近状态,House$Door 超过10MB左右,内存占比达到百分之七八十。
软引用的特性在数秒之后产生价值,House对象从千数量级迅速降到百数量级,内存容量迅速被释放出来。保证了程序的正常执行。
软引用SoftReference 的父类 Reference的属性: private T referent, 它指向new House()对象,而SoftReference 的get(),也是调用了super.get() 来访问父类这个私有属性。大量的House 在内存即将耗尽前,成功地一次次被清理掉。
对象buyer2虽然是引用类型,但其本身碍事占用一定内存空间的,它是被集合 ArrayList 强引用劫持的,在不断循环执行 houses.add() 后,终究会产生 OOM。
软引用、弱引用、虚引用均存在带有队列的构造方法
public SoftReference(T referent, ReferenceQueue q) {
super(referent, q);
this.timestamp = clock;
}
可以在队列中检查哪个软引用的对象被回收了,从而把失去House 的软引用对象清理掉。
软引用一般用于在同一服务器内缓存中间结果。如果命中缓存,则提取缓存结果,否则重新计算或获取。但是,软引用肯定不是用来缓存高频数据结构的,万一服务器重启或者软引用触发大规模回收,所有的访问将直接指向数据库,导致数据库压力时大时小,甚至崩溃。
弱引用
代码如下:
public class WeakReferenceWhenIdle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
House seller = new House();
WeakReference buyer3 = new WeakReference<>(seller);
seller = null;
long start = System.nanoTime();
long count = 0;
while (true){
if(buyer3.get() == null)
{
long duration = (System.nanoTime()- start)/(1000*1000);
System.out.println("house is null and exited time = "+duration +“ms”);
break;
}else{
System.out.println(“still there.count=”+count++);
}
}
}
}
执行结果如下:
house is null and exited time = 964ms
Heap
PSYoungGen total 75776K, used 2733K [0x000000076bf80000, 0x0000000771400000, 0x00000007c0000000)
eden space 65024K, 2% used [0x000000076bf80000,0x000000076c161470,0x000000076ff00000)
from space 10752K, 7% used [0x000000076ff00000,0x000000076ffca020,0x0000000770980000)
to space 10752K, 0% used [0x0000000770980000,0x0000000770980000,0x0000000771400000)
ParOldGen total 173568K, used 8K [0x00000006c3e00000, 0x00000006ce780000, 0x000000076bf80000)
object space 173568K, 0% used [0x00000006c3e00000,0x00000006c3e02000,0x00000006ce780000)
Metaspace used 3541K, capacity 4502K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K
class space used 388K, capacity 390K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
这个示例代码在YGC下,可以轻松回收 WeakReference指向的new House() 对象,WeakReference 典型的应用是WeakHashMap中。
在刚才的房源案例中,卖家的房子对应一些列房源资料,如果卖家的房源已经售出,则中介也不需要一直保存相关信息,自动回收存储空间即可,如下代码:
public class WeakHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
s space used 388K, capacity 390K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
这个示例代码在YGC下,可以轻松回收 WeakReference指向的new House() 对象,WeakReference 典型的应用是WeakHashMap中。
在刚才的房源案例中,卖家的房子对应一些列房源资料,如果卖家的房源已经售出,则中介也不需要一直保存相关信息,自动回收存储空间即可,如下代码:
public class WeakHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {