Android音频框架之一 详解audioPolicy流程及HAL驱动加载与配置
前言
此音频架构梳理笔记、主要是因工作上需要在 Android8.1 以上版本中,增加 snd-aloop 虚拟声卡做前期准备工作,
本篇文章提纲挈领的把音频框架主线梳理清晰,通过这篇文章能够清晰如下内容:
1>. 声卡服务框架是什么时间产生、如何引发?
2>. 声卡框架主要模块都是什么,他们基本功能如何分配? audioFlinger、audioService、audioPolicyMannager等
3>. audio_policy_configuration.xml 与 audio_policy.conf 文件,是如何配置管理Android音频系统?
xml文件解析一般规则。
4>. 厂家 audio_hw_hal 驱动是如何被加载至系统的,由谁加载的、加载到哪里去了?
5>. 安卓 AUDIO-HAL 与 Linux snd-driver 是如何关联起来的,如果管理不同声卡?
希望您阅读此文章时,带着上述 5 点内容,能够快速全面的对安卓音频系统有框架认知。
由于本篇内容是走读 android7.0 源码梳理的内容,建议阅读时能够一起走读一下相关代码。
后面将分享 android 添加虚拟声卡实战系列笔记内容,敬请阅读共同探讨。
一、 AndroidRuntime.so 引发思考
android 系统 framework 代码起点, frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp 文件,
此文件是android系统主线程代码,代码内容涉及系统很多模块,此程序主要是注册模块的JNI接口方法。
其中涉及到模块 native、sensorHal、media、audioflinger、displayflinger、camera、serialport、bindler等模块
从各模块名称上、可看出是 android 系统核心组件内容,由此可见 AndroidRuntime 是系统框架的入口。
启动注册 audioRecodd、audioSystem、audioTrack 模块,此模块注册是在 mediaService 模块启动之前。
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
安卓源码中大量使用 sm 对象来管理系统的各种服务,添加、释放服务。用户 app 通过反射的方式获取系统的各种服务,
由此可以对安卓系统服务概念理解会更加深刻。
二、 Android 音频框架
Android音频系统有两大服务:一是AudioFlinger,二是AudioPolicyService。 AudioFlinger负责向下 访问AudioHardwareInterface,
实现音频PCM数据的混音/输入/输出,实现音量调节;
AudioPolicyService负责音 频输入输出设备的连接状态,音频策略调度即音频设备(如本地CODEC、Bluetooth A2DP、Headset)的切换
策略(注意它只是负责策略,真正的切换操作是在AudioFlinger中的openOutput,毕竟 AudioFlinger负责操作底层音频硬件)。
2.0> mediaserver 和 audioserver 本地服务
@ frameworks/av/media/mediaserver/main_mediaserver.cpp
此程序是入口函数,在 android 系统初始化 init.rc 中,
service media /system/bin/mediaserver
class main
user system
group audio camera inet net_bt net_bt_admin net_bw_acct drmrpc mediadrm radio
ioprio rt 4
启动 mediaserver 服务, 线程名称: /system/bin/mediaserver ,启动多媒体服务。
#define LOG_TAG "mediaserver"
//#define LOG_NDEBUG 0
#include @ frameworks/av/media/audioserver/main_audioserver.cpp
此程序是入口函数,程序加载编译和启动过程分析如下:
在文件 @build/target/product/core_tiny.mk 中把 init.zygote32.rc内容拷贝至系统根目录下
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES += \
system/core/rootdir/init.zygote32.rc:root/init.zygote32.rc
文件 @system/core/rootdir/init.zygote32.rc 中启动 audioserver 服务,内容如下:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver ## 启动 audioserver 服务
onrestart restart cameraserver ## 启动 cameraserver 服务
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
安卓系统初始化时、根据 init.zygote32.rc 中条目,会以次启动 audioserver、cameraserver 服务,
线程名称: /system/bin/audioserver。
#define LOG_TAG "audioserver"
//#define LOG_NDEBUG 0
#include 此线程启动服务有:AudioFlinger\AudioPolicyService\RadioService\SoundTriggerHwService 服务;
其中 RadioService 是电话服务,不是本次讨论内容略过。
2.1> audioflinger 本地混音管理框架
AudioFlinger(下面简称AF)是整个音频系统的核心与难点。作为 Android 系统中的音频中枢,它同时也是一个系统服务,
启到承上(为上层提供访问接口)启下(通过HAL来管理音频设备)的作用。 AudioFlinger 向下访问 AudioHardware,
实现输出音频数据,控制音频参数。
首先看 AudioFlinger 的继承关系及父类内容,在 audioserver 函数中调用 AudioFlinger::instantiate() 函数.
@frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/audioFlinger.hpp
class AudioFlinger :
public BinderService<AudioFlinger>,
public BnAudioFlinger
{
friend class BinderService<AudioFlinger>; // for AudioFlinger()
}
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
@frameworks/native/include/binder/BingderService.h
namespace android {
template<typename SERVICE>
class BinderService
{
public:
static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
return sm->addService(
String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()),
new SERVICE(), allowIsolated); //> 添加 AudioFlinger 服务.
}
static void publishAndJoinThreadPool(bool allowIsolated = false) {
publish(allowIsolated);
joinThreadPool();
}
static void instantiate() { publish(); }
static status_t shutdown() { return NO_ERROR; }
private:
static void joinThreadPool() {
sp<ProcessState> ps(ProcessState::self());
ps->startThreadPool();
ps->giveThreadPoolName();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}
};
}; // namespace android
在 系统服务中添加 audioService 服务内容,供用户通过服务的方式使用音频设备。
AudioFlinger 构造函数内容如下:
AudioFlinger::AudioFlinger()
: BnAudioFlinger(),
mPrimaryHardwareDev(NULL),
mAudioHwDevs(NULL),
mHardwareStatus(AUDIO_HW_IDLE),
mMasterVolume(1.0f),
mMasterMute(false),
// mNextUniqueId(AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_MAX),
mMode(AUDIO_MODE_INVALID),
mBtNrecIsOff(false),
mIsLowRamDevice(true),
mIsDeviceTypeKnown(false),
mGlobalEffectEnableTime(0),
mSystemReady(false)
{
// unsigned instead of audio_unique_id_use_t, because ++ operator is unavailable for enum
for (unsigned use = AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_UNSPECIFIED; use < AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_MAX; use++) {
// zero ID has a special meaning, so unavailable
mNextUniqueIds[use] = AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_MAX;
}
getpid_cached = getpid();
const bool doLog = property_get_bool("ro.test_harness", false);
if (doLog) {
mLogMemoryDealer = new MemoryDealer(kLogMemorySize, "LogWriters",
MemoryHeapBase::READ_ONLY);
}
// reset battery stats.
// if the audio service has crashed, battery stats could be left
// in bad state, reset the state upon service start.
BatteryNotifier::getInstance().noteResetAudio();
}
C++ 中智能指针创建对象时,第一次创建会调用onFirstRef()函数,在本例中将调用 AudioFlinger::onFirstRef() 函数,
内容如下:
@frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/audioFlinger.cpp
void AudioFlinger::onFirstRef()
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
/* TODO: move all this work into an Init() function */
char val_str[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = { 0 };
if (property_get("ro.audio.flinger_standbytime_ms", val_str, NULL) >= 0) {
uint32_t int_val;
if (1 == sscanf(val_str, "%u", &int_val)) {
mStandbyTimeInNsecs = milliseconds(int_val);
ALOGI("Using %u mSec as standby time.", int_val);
} else {
mStandbyTimeInNsecs = kDefaultStandbyTimeInNsecs;
ALOGI("Using default %u mSec as standby time.",
(uint32_t)(mStandbyTimeInNsecs / 1000000));
}
}
mPatchPanel = new PatchPanel(this); //> 构建的 audioFlinger 对象、传递给 pathPanel
mMode = AUDIO_MODE_NORMAL;
ALOGW(" %s , %d debug display.. \n ", __func__, __LINE__);
}
至此 audioFlinger 对象构建完成。
2.1.1> AudioPatch 模块
AudioPatch 模块是 AudioFlinger 的一个子类,封装了音频输入与输出端口对象、可以理解为一个逻辑的音频设备,
是音频输入规则、输出规则、混音规则具体实现;各模块之间关系参考下图:
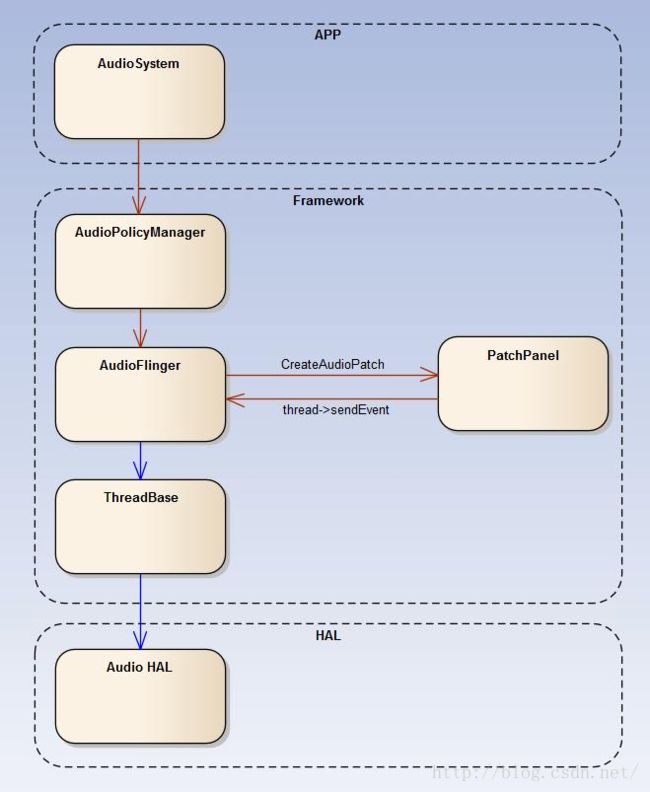
此图文章末尾有此博友连接。
接下来我们将对这部分代码进行走读和简单分析,旨在捋顺音频设备创建、管理、销毁与底层 hardware_hal 间接口
对应关系。
先认识以下 audio_patch 的数据结构:
@ system/media/audio/include/system/audio.h
/* An audio patch represents a connection between one or more source ports and
* one or more sink ports. Patches are connected and disconnected by audio policy manager or by
* applications via framework APIs.
* Each patch is identified by a handle at the interface used to create that patch. For instance,
* when a patch is created by the audio HAL, the HAL allocates and returns a handle.
* This handle is unique to a given audio HAL hardware module.
* But the same patch receives another system wide unique handle allocated by the framework.
* This unique handle is used for all transactions inside the framework.
*/
typedef enum {
AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE = 0,
} audio_patch_handle_t;
#define AUDIO_PATCH_PORTS_MAX 16
struct audio_patch {
audio_patch_handle_t id; /* patch unique ID */
unsigned int num_sources; /* number of sources in following array */
struct audio_port_config sources[AUDIO_PATCH_PORTS_MAX];
unsigned int num_sinks; /* number of sinks in following array */
struct audio_port_config sinks[AUDIO_PATCH_PORTS_MAX];
};
/* audio port configuration structure used to specify a particular configuration of
* an audio port */
struct audio_port_config {
audio_port_handle_t id; /* port unique ID */
audio_port_role_t role; /* sink or source */
audio_port_type_t type; /* device, mix ... */
unsigned int config_mask; /* e.g AUDIO_PORT_CONFIG_ALL */
unsigned int sample_rate; /* sampling rate in Hz */
audio_channel_mask_t channel_mask; /* channel mask if applicable */
audio_format_t format; /* format if applicable */
struct audio_gain_config gain; /* gain to apply if applicable */
union {
struct audio_port_config_device_ext device; /* device specific info */
struct audio_port_config_mix_ext mix; /* mix specific info */
struct audio_port_config_session_ext session; /* session specific info */
} ext;
};
/* extension for audio port structure when the audio port is a hardware device */
struct audio_port_device_ext {
audio_module_handle_t hw_module; /* module the device is attached to */
audio_devices_t type; /* device type (e.g AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER) */
char address[AUDIO_DEVICE_MAX_ADDRESS_LEN];
};
通过上面数据结构内容和注解,我们先把此形成框架认识,底层硬件 HAL 接口管理是通过 audio_port_device_ext 结构体管理,
此部分是衔接底层与安卓系统音频管理框架 wrapper , 是捋顺音频系统关键节点。
@ \src\frameworks\av\services\audioflinger\PatchPanel.cpp
/* Connect a patch between several source and sink ports */
status_t AudioFlinger::createAudioPatch(const struct audio_patch *patch,
audio_patch_handle_t *handle)
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
if (mPatchPanel != 0) {
return mPatchPanel->createAudioPatch(patch, handle);
}
return NO_INIT;
}
/* Connect a patch between several source and sink ports */
status_t AudioFlinger::PatchPanel::createAudioPatch(const struct audio_patch *patch, audio_patch_handle_t *handle)
{
audio_patch_handle_t halHandle = AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE;
// 1. 获得 AudioFlinger 对象
sp<AudioFlinger> audioflinger = mAudioFlinger.promote();
ALOGV("createAudioPatch() num_sources %d num_sinks %d handle %d", patch->num_sources, patch->num_sinks, *handle);
// 2. 只允许创建一个 souces , 只有 AudioPolicyManger 才能创建 2 Souces
// limit number of sources to 1 for now or 2 sources for special cross hw module case.
// only the audio policy manager can request a patch creation with 2 sources.
if (patch->num_sources > 2) {
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
// 3. 如果当前已经有现成的 Patch 则依次遍历,并且释放删除它 (释放 Audio Playback 或 Capture 线程,释放 Audio Hardware 接口)
if (*handle != AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE) {
for (size_t index = 0; *handle != 0 && index < mPatches.size(); index++) {
if (*handle == mPatches[index]->mHandle) {
ALOGV("createAudioPatch() removing patch handle %d", *handle);
halHandle = mPatches[index]->mHalHandle;
Patch *removedPatch = mPatches[index];
// free resources owned by the removed patch if applicable
// 释放 Audio Playback 或 Capture 线程
// 1) if a software patch is present, release the playback and capture threads and
// tracks created. This will also release the corresponding audio HAL patches
if ((removedPatch->mRecordPatchHandle != AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE) ||
(removedPatch->mPlaybackPatchHandle != AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE)) {
clearPatchConnections(removedPatch);
}
// 释放 Audio Hardware 接口
// 2) if the new patch and old patch source or sink are devices from different
// hw modules, clear the audio HAL patches now because they will not be updated
// by call to create_audio_patch() below which will happen on a different HW module
if (halHandle != AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE) {
audio_module_handle_t hwModule = AUDIO_MODULE_HANDLE_NONE;
if ((removedPatch->mAudioPatch.sources[0].type == AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_DEVICE) &&
((patch->sources[0].type != AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_DEVICE) ||
(removedPatch->mAudioPatch.sources[0].ext.device.hw_module !=
patch->sources[0].ext.device.hw_module))) {
hwModule = removedPatch->mAudioPatch.sources[0].ext.device.hw_module;
} else if ((patch->num_sinks == 0) ||
((removedPatch->mAudioPatch.sinks[0].type == AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_DEVICE) &&
((patch->sinks[0].type != AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_DEVICE) ||
(removedPatch->mAudioPatch.sinks[0].ext.device.hw_module !=
patch->sinks[0].ext.device.hw_module)))) {
// Note on (patch->num_sinks == 0): this situation should not happen as
// these special patches are only created by the policy manager but just
// in case, systematically clear the HAL patch.
// Note that removedPatch->mAudioPatch.num_sinks cannot be 0 here because
// halHandle would be AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE in this case.
hwModule = removedPatch->mAudioPatch.sinks[0].ext.device.hw_module;
}
if (hwModule != AUDIO_MODULE_HANDLE_NONE) {
ssize_t index = audioflinger->mAudioHwDevs.indexOfKey(hwModule);
if (index >= 0) {
sp<DeviceHalInterface> hwDevice =
audioflinger->mAudioHwDevs.valueAt(index)->hwDevice();
hwDevice->releaseAudioPatch(halHandle);
}
}
}
mPatches.removeAt(index);
delete removedPatch;
break;
}
}
}
// 4. 新建一个 patch 对象
Patch *newPatch = new Patch(patch);
==============>
| 在 patch 对象中主要包含了audiopatch 和 对应的 thread 信息:
|
| class Patch {
| public:
| explicit Patch(const struct audio_patch *patch) :
| mAudioPatch(*patch), mHandle(AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE),
| mHalHandle(AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE), mRecordPatchHandle(AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE),
| mPlaybackPatchHandle(AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE) {}
| ~Patch() {}
|
| struct audio_patch mAudioPatch;
| audio_patch_handle_t mHandle;
| // handle for audio HAL patch handle present only when the audio HAL version is >= 3.0
| audio_patch_handle_t mHalHandle;
| // below members are used by a software audio patch connecting a source device from a
| // given audio HW module to a sink device on an other audio HW module.
| sp<PlaybackThread> mPlaybackThread;
| sp<PlaybackThread::PatchTrack> mPatchTrack;
| sp<RecordThread> mRecordThread;
| sp<RecordThread::PatchRecord> mPatchRecord;
| // handle for audio patch connecting source device to record thread input.
| audio_patch_handle_t mRecordPatchHandle;
| // handle for audio patch connecting playback thread output to sink device
| audio_patch_handle_t mPlaybackPatchHandle;
| }
<==============
switch (patch->sources[0].type) {
// 5. 如果端口类型是 Device 的话
case AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_DEVICE: {
audio_module_handle_t srcModule = patch->sources[0].ext.device.hw_module;
ssize_t index = audioflinger->mAudioHwDevs.indexOfKey(srcModule);
AudioHwDevice *audioHwDevice = audioflinger->mAudioHwDevs.valueAt(index);
// manage patches requiring a software bridge
// - special patch request with 2 sources (reuse one existing output mix) OR Device to device AND
// - source HW module != destination HW module OR audio HAL does not support audio patches creation
if ((patch->num_sources == 2) || ((patch->sinks[0].type == AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_DEVICE) &&
((patch->sinks[0].ext.device.hw_module != srcModule) || !audioHwDevice->supportsAudioPatches()))) {
// (1)如果判断是有两个设备,则说明调用者是 AudioPolicyManger
// 其中 设备 0:AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_DEVICE , 设备 1:AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_MIX
if (patch->num_sources == 2) {
if (patch->sources[1].type != AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_MIX ||
(patch->num_sinks != 0 && patch->sinks[0].ext.device.hw_module !=
patch->sources[1].ext.mix.hw_module)) {
ALOGW("createAudioPatch() invalid source combination");
status = INVALID_OPERATION;
goto exit;
}
// 获得 playback 的线程
sp<ThreadBase> thread = audioflinger->checkPlaybackThread_l(patch->sources[1].ext.mix.handle);
// 将 playback 线程保存在 mPlaybackThread 中。
newPatch->mPlaybackThread = (MixerThread *)thread.get();
} else {
// (2)如果判断只有一个设备,则将config 配置为 AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER,output 配置为 AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE。
audio_config_t config = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
audio_devices_t device = patch->sinks[0].ext.device.type;
String8 address = String8(patch->sinks[0].ext.device.address);
audio_io_handle_t output = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
// 调用 openOutput_l() 创建 output 线程,mPlaybackThreads,保存在 mPlaybackThread 中。
sp<ThreadBase> thread = audioflinger->openOutput_l(
patch->sinks[0].ext.device.hw_module,
&output,
&config,
device,
address,
AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_NONE);
newPatch->mPlaybackThread = (PlaybackThread *)thread.get();
ALOGV("audioflinger->openOutput_l() returned %p", newPatch->mPlaybackThread.get());
}
// 获得输入设备类型 及 对应的输出设备地址
audio_devices_t device = patch->sources[0].ext.device.type;
String8 address = String8(patch->sources[0].ext.device.address);
audio_config_t config = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
// 获得source 的采样率、声道数、数据格式
// open input stream with source device audio properties if provided or
// default to peer output stream properties otherwise.
if (patch->sources[0].config_mask & AUDIO_PORT_CONFIG_SAMPLE_RATE) {
config.sample_rate = patch->sources[0].sample_rate;
} else {
config.sample_rate = newPatch->mPlaybackThread->sampleRate();
}
if (patch->sources[0].config_mask & AUDIO_PORT_CONFIG_CHANNEL_MASK) {
config.channel_mask = patch->sources[0].channel_mask;
} else {
config.channel_mask =
audio_channel_in_mask_from_count(newPatch->mPlaybackThread->channelCount());
}
if (patch->sources[0].config_mask & AUDIO_PORT_CONFIG_FORMAT) {
config.format = patch->sources[0].format;
} else {
config.format = newPatch->mPlaybackThread->format();
}
audio_io_handle_t input = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
// 创建输入设备的线程,保存在 newPatch->mRecordThread 中
sp<ThreadBase> thread = audioflinger->openInput_l(srcModule,
&input,
&config,
device,
address,
AUDIO_SOURCE_MIC,
AUDIO_INPUT_FLAG_NONE);
newPatch->mRecordThread = (RecordThread *)thread.get();
ALOGV("audioflinger->openInput_l() returned %p inChannelMask %08x",
newPatch->mRecordThread.get(), config.channel_mask);
// 调用 createPatchConnections 函数,创建patch 连接
status = createPatchConnections(newPatch, patch);
} else {
// 如果,输出源是 MIX 的话,则获得 record thread 线程
if (patch->sinks[0].type == AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_MIX) {
sp<ThreadBase> thread = audioflinger->checkRecordThread_l( patch->sinks[0].ext.mix.handle);
if (thread == 0) {
thread = audioflinger->checkMmapThread_l(patch->sinks[0].ext.mix.handle);
}
// 发送消息,创建 AudioPatch 事件
status = thread->sendCreateAudioPatchConfigEvent(patch, &halHandle);
} else {
// 否则,调用 createAudioPatch 创建 audio patch
sp<DeviceHalInterface> hwDevice = audioHwDevice->hwDevice();
status = hwDevice->createAudioPatch(patch->num_sources,
patch->sources,
patch->num_sinks,
patch->sinks,
&halHandle);
}
}
} break;
// 6. 如果端口类型是 MIX 的话
case AUDIO_PORT_TYPE_MIX: {
// 获得输入模块的 hardware Module
audio_module_handle_t srcModule = patch->sources[0].ext.mix.hw_module;
ssize_t index = audioflinger->mAudioHwDevs.indexOfKey(srcModule);
// limit to connections between devices and output streams
audio_devices_t type = AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE;
// 获得 输出源 playback 的类型
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < patch->num_sinks; i++) {
type |= patch->sinks[i].ext.device.type;
}
// 检查 输出源 playback 线程
sp<ThreadBase> thread = audioflinger->checkPlaybackThread_l(patch->sources[0].ext.mix.handle);
if (thread == 0) {
thread = audioflinger->checkMmapThread_l(patch->sources[0].ext.mix.handle);
}
// 如果 获得的 thread 线程 是系统主线程的话,则获得 audio param 参数,将参数发送到 record 线程中。
if (thread == audioflinger->primaryPlaybackThread_l()) {
AudioParameter param = AudioParameter();
param.addInt(String8(AudioParameter::keyRouting), (int)type);
audioflinger->broacastParametersToRecordThreads_l(param.toString());
}
status = thread->sendCreateAudioPatchConfigEvent(patch, &halHandle);// 发送消息,创建 AudioPatch 事件
} break;
}
exit:
// 如果创建成功,则给新建的 patch 分析一个 UID,并添加到 mPatchs 中。
ALOGV("createAudioPatch() status %d", status);
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
*handle = (audio_patch_handle_t) audioflinger->nextUniqueId(AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_PATCH);
newPatch->mHandle = *handle;
newPatch->mHalHandle = halHandle;
mPatches.add(newPatch);
ALOGV("createAudioPatch() added new patch handle %d halHandle %d", *handle, halHandle);
} else {
clearPatchConnections(newPatch);
delete newPatch;
}
return status;
}
@ frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Threads.cpp
status_t AudioFlinger::ThreadBase::sendCreateAudioPatchConfigEvent(
const struct audio_patch *patch,
audio_patch_handle_t *handle)
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
sp<ConfigEvent> configEvent = (ConfigEvent *)new CreateAudioPatchConfigEvent(*patch, *handle);
status_t status = sendConfigEvent_l(configEvent);
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
CreateAudioPatchConfigEventData *data =
(CreateAudioPatchConfigEventData *)configEvent->mData.get();
*handle = data->mHandle;
}
return status;
}
// sendConfigEvent_l() must be called with ThreadBase::mLock held
// Can temporarily release the lock if waiting for a reply from processConfigEvents_l().
status_t AudioFlinger::ThreadBase::sendConfigEvent_l(sp<ConfigEvent>& event)
{
status_t status = NO_ERROR;
if (event->mRequiresSystemReady && !mSystemReady) {
event->mWaitStatus = false;
mPendingConfigEvents.add(event);
return status;
}
mConfigEvents.add(event);
ALOGV("sendConfigEvent_l() num events %zu event %d", mConfigEvents.size(), event->mType);
mWaitWorkCV.signal();
mLock.unlock();
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(event->mLock);
while (event->mWaitStatus) {
if (event->mCond.waitRelative(event->mLock, kConfigEventTimeoutNs) != NO_ERROR) {
event->mStatus = TIMED_OUT;
event->mWaitStatus = false;
}
}
status = event->mStatus;
}
mLock.lock();
return status;
}
事件解析处理
@ frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Threads.cpp
// post condition: mConfigEvents.isEmpty()
void AudioFlinger::ThreadBase::processConfigEvents_l()
{
bool configChanged = false;
while (!mConfigEvents.isEmpty()) {
ALOGV("processConfigEvents_l() remaining events %zu", mConfigEvents.size());
sp<ConfigEvent> event = mConfigEvents[0];
mConfigEvents.removeAt(0);
switch (event->mType) {
case CFG_EVENT_PRIO: {
PrioConfigEventData *data = (PrioConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
// FIXME Need to understand why this has to be done asynchronously
int err = requestPriority(data->mPid, data->mTid, data->mPrio,
true /*asynchronous*/);
if (err != 0) {
ALOGW("Policy SCHED_FIFO priority %d is unavailable for pid %d tid %d; error %d",
data->mPrio, data->mPid, data->mTid, err);
}
} break;
case CFG_EVENT_IO: {
IoConfigEventData *data = (IoConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
ioConfigChanged(data->mEvent, data->mPid);
} break;
case CFG_EVENT_SET_PARAMETER: {
SetParameterConfigEventData *data = (SetParameterConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
if (checkForNewParameter_l(data->mKeyValuePairs, event->mStatus)) {
configChanged = true;
}
} break;
case CFG_EVENT_CREATE_AUDIO_PATCH: {
CreateAudioPatchConfigEventData *data =
(CreateAudioPatchConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
event->mStatus = createAudioPatch_l(&data->mPatch, &data->mHandle);
} break;
case CFG_EVENT_RELEASE_AUDIO_PATCH: {
ReleaseAudioPatchConfigEventData *data =
(ReleaseAudioPatchConfigEventData *)event->mData.get();
event->mStatus = releaseAudioPatch_l(data->mHandle);
} break;
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false, "processConfigEvents_l() unknown event type %d", event->mType);
break;
}
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(event->mLock);
if (event->mWaitStatus) {
event->mWaitStatus = false;
event->mCond.signal();
}
}
ALOGV_IF(mConfigEvents.isEmpty(), "processConfigEvents_l() DONE thread %p", this);
}
if (configChanged) {
cacheParameters_l();
}
}
在解析 CFG_EVENT_CREATE_AUDIO_PATCH 事件时,调用函数
event->mStatus = createAudioPatch_l(&data->mPatch, &data->mHandle);
当前线程属于 MixerThread、PlaybackThread、RecordThread 就具有执行对应的方法。
@ frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Threads.cpp
status_t AudioFlinger::MixerThread::createAudioPatch_l(const struct audio_patch *patch,
audio_patch_handle_t *handle)
{
status_t status;
if (property_get_bool("af.patch_park", false /* default_value */)) {
// Park FastMixer to avoid potential DOS issues with writing to the HAL
// or if HAL does not properly lock against access.
AutoPark<FastMixer> park(mFastMixer);
status = PlaybackThread::createAudioPatch_l(patch, handle);
} else {
status = PlaybackThread::createAudioPatch_l(patch, handle);
}
return status;
}
此 PlaybackThread::createAudioPatch_l() 会检查 mOutput->audioHwDev->supportsAudioPatches()是否支持,
如果支持就调用 hwDevice->createAudioPatch() 方法创建,否则走另一个分支.
智能指针 sp hwDevice 的对象是 mOutput->audioHwDev->hwDevice() 传递过来,把 mOutput
对象创建过程搞清楚,我们就指导函数调用关系。
@ frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/Threads.cpp
status_t AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::createAudioPatch_l(const struct audio_patch *patch,
audio_patch_handle_t *handle)
{
status_t status = NO_ERROR;
// store new device and send to effects
audio_devices_t type = AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < patch->num_sinks; i++) {
type |= patch->sinks[i].ext.device.type;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < mEffectChains.size(); i++) {
mEffectChains[i]->setDevice_l(type);
}
// mPrevOutDevice is the latest device set by createAudioPatch_l(). It is not set when
// the thread is created so that the first patch creation triggers an ioConfigChanged callback
bool configChanged = mPrevOutDevice != type;
mOutDevice = type;
mPatch = *patch;
if (mOutput->audioHwDev->supportsAudioPatches()) {
sp<DeviceHalInterface> hwDevice = mOutput->audioHwDev->hwDevice();
status = hwDevice->createAudioPatch(patch->num_sources,
patch->sources,
patch->num_sinks,
patch->sinks,
handle);
} else {
char *address;
if (strcmp(patch->sinks[0].ext.device.address, "") != 0) {
//FIXME: we only support address on first sink with HAL version < 3.0
address = audio_device_address_to_parameter(
patch->sinks[0].ext.device.type,
patch->sinks[0].ext.device.address);
} else {
address = (char *)calloc(1, 1);
}
AudioParameter param = AudioParameter(String8(address));
free(address);
param.addInt(String8(AudioParameter::keyRouting), (int)type);
status = mOutput->stream->setParameters(param.toString());
*handle = AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE;
}
if (configChanged) {
mPrevOutDevice = type;
sendIoConfigEvent_l(AUDIO_OUTPUT_CONFIG_CHANGED);
}
return status;
}
通过 RecordThread::createAudioPatch_l() 方法能够看出,create_audio_patch() 需要3.0及以上版本才能够支持,
也就是说 mInput->stream->common.set_parameters(&mInput->stream->common, param.toString().string());
也是可以创建patch对象,根据源码版本自行对应源码分支路线,安卓7.0版本应该是3.0以下版本,没有支持create_audio_patch。
status_t AudioFlinger::RecordThread::createAudioPatch_l(const struct audio_patch *patch,
audio_patch_handle_t *handle)
{
status_t status = NO_ERROR;
// store new device and send to effects
mInDevice = patch->sources[0].ext.device.type;
mPatch = *patch;
for (size_t i = 0; i < mEffectChains.size(); i++) {
mEffectChains[i]->setDevice_l(mInDevice);
}
// disable AEC and NS if the device is a BT SCO headset supporting those
// pre processings
if (mTracks.size() > 0) {
bool suspend = audio_is_bluetooth_sco_device(mInDevice) &&
mAudioFlinger->btNrecIsOff();
for (size_t i = 0; i < mTracks.size(); i++) {
sp<RecordTrack> track = mTracks[i];
setEffectSuspended_l(FX_IID_AEC, suspend, track->sessionId());
setEffectSuspended_l(FX_IID_NS, suspend, track->sessionId());
}
}
// store new source and send to effects
if (mAudioSource != patch->sinks[0].ext.mix.usecase.source) {
mAudioSource = patch->sinks[0].ext.mix.usecase.source;
for (size_t i = 0; i < mEffectChains.size(); i++) {
mEffectChains[i]->setAudioSource_l(mAudioSource);
}
}
if (mInput->audioHwDev->version() >= AUDIO_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_0) {
audio_hw_device_t *hwDevice = mInput->audioHwDev->hwDevice();
status = hwDevice->create_audio_patch(hwDevice,
patch->num_sources,
patch->sources,
patch->num_sinks,
patch->sinks,
handle);
} else {
char *address;
if (strcmp(patch->sources[0].ext.device.address, "") != 0) {
address = audio_device_address_to_parameter(
patch->sources[0].ext.device.type,
patch->sources[0].ext.device.address);
} else {
address = (char *)calloc(1, 1);
}
AudioParameter param = AudioParameter(String8(address));
free(address);
param.addInt(String8(AUDIO_PARAMETER_STREAM_ROUTING),
(int)patch->sources[0].ext.device.type);
param.addInt(String8(AUDIO_PARAMETER_STREAM_INPUT_SOURCE),
(int)patch->sinks[0].ext.mix.usecase.source);
status = mInput->stream->common.set_parameters(&mInput->stream->common,
param.toString().string());
*handle = AUDIO_PATCH_HANDLE_NONE;
}
if (mInDevice != mPrevInDevice) {
sendIoConfigEvent_l(AUDIO_INPUT_CONFIG_CHANGED);
mPrevInDevice = mInDevice;
}
return status;
}
我先看看 audio_hw_device_t 结构体定义及相关方法,create_audio_patch() 就是方法之一。
@ hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/audio.h
struct audio_hw_device {
/**
* Common methods of the audio device. This *must* be the first member of audio_hw_device
* as users of this structure will cast a hw_device_t to audio_hw_device pointer in contexts
* where it's known the hw_device_t references an audio_hw_device.
*/
struct hw_device_t common;
/**
* used by audio flinger to enumerate what devices are supported by
* each audio_hw_device implementation.
*
* Return value is a bitmask of 1 or more values of audio_devices_t
*
* NOTE: audio HAL implementations starting with
* AUDIO_DEVICE_API_VERSION_2_0 do not implement this function.
* All supported devices should be listed in audio_policy.conf
* file and the audio policy manager must choose the appropriate
* audio module based on information in this file.
*/
uint32_t (*get_supported_devices)(const struct audio_hw_device *dev);
/**
* check to see if the audio hardware interface has been initialized.
* returns 0 on success, -ENODEV on failure.
*/
int (*init_check)(const struct audio_hw_device *dev);
/** set the audio volume of a voice call. Range is between 0.0 and 1.0 */
int (*set_voice_volume)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, float volume);
/**
* set the audio volume for all audio activities other than voice call.
* Range between 0.0 and 1.0. If any value other than 0 is returned,
* the software mixer will emulate this capability.
*/
int (*set_master_volume)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, float volume);
/**
* Get the current master volume value for the HAL, if the HAL supports
* master volume control. AudioFlinger will query this value from the
* primary audio HAL when the service starts and use the value for setting
* the initial master volume across all HALs. HALs which do not support
* this method may leave it set to NULL.
*/
int (*get_master_volume)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, float *volume);
/**
* set_mode is called when the audio mode changes. AUDIO_MODE_NORMAL mode
* is for standard audio playback, AUDIO_MODE_RINGTONE when a ringtone is
* playing, and AUDIO_MODE_IN_CALL when a call is in progress.
*/
int (*set_mode)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, audio_mode_t mode);
/* mic mute */
int (*set_mic_mute)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, bool state);
int (*get_mic_mute)(const struct audio_hw_device *dev, bool *state);
/* set/get global audio parameters */
int (*set_parameters)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, const char *kv_pairs);
/*
* Returns a pointer to a heap allocated string. The caller is responsible
* for freeing the memory for it using free().
*/
char * (*get_parameters)(const struct audio_hw_device *dev,
const char *keys);
/* Returns audio input buffer size according to parameters passed or
* 0 if one of the parameters is not supported.
* See also get_buffer_size which is for a particular stream.
*/
size_t (*get_input_buffer_size)(const struct audio_hw_device *dev,
const struct audio_config *config);
/** This method creates and opens the audio hardware output stream.
* The "address" parameter qualifies the "devices" audio device type if needed.
* The format format depends on the device type:
* - Bluetooth devices use the MAC address of the device in the form "00:11:22:AA:BB:CC"
* - USB devices use the ALSA card and device numbers in the form "card=X;device=Y"
* - Other devices may use a number or any other string.
*/
int (*open_output_stream)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
struct audio_config *config,
struct audio_stream_out **stream_out,
const char *address);
void (*close_output_stream)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
struct audio_stream_out* stream_out);
/** This method creates and opens the audio hardware input stream */
int (*open_input_stream)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
struct audio_config *config,
struct audio_stream_in **stream_in,
audio_input_flags_t flags,
const char *address,
audio_source_t source);
void (*close_input_stream)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
struct audio_stream_in *stream_in);
/** This method dumps the state of the audio hardware */
int (*dump)(const struct audio_hw_device *dev, int fd);
/**
* set the audio mute status for all audio activities. If any value other
* than 0 is returned, the software mixer will emulate this capability.
*/
int (*set_master_mute)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, bool mute);
/**
* Get the current master mute status for the HAL, if the HAL supports
* master mute control. AudioFlinger will query this value from the primary
* audio HAL when the service starts and use the value for setting the
* initial master mute across all HALs. HALs which do not support this
* method may leave it set to NULL.
*/
int (*get_master_mute)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, bool *mute);
/**
* Routing control
*/
/* Creates an audio patch between several source and sink ports.
* The handle is allocated by the HAL and should be unique for this
* audio HAL module. */
int (*create_audio_patch)(struct audio_hw_device *dev, //> 创建 audio_patch() 方法
unsigned int num_sources,
const struct audio_port_config *sources,
unsigned int num_sinks,
const struct audio_port_config *sinks,
audio_patch_handle_t *handle);
/* Release an audio patch */
int (*release_audio_patch)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
audio_patch_handle_t handle);
/* Fills the list of supported attributes for a given audio port.
* As input, "port" contains the information (type, role, address etc...)
* needed by the HAL to identify the port.
* As output, "port" contains possible attributes (sampling rates, formats,
* channel masks, gain controllers...) for this port.
*/
int (*get_audio_port)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
struct audio_port *port);
/* Set audio port configuration */
int (*set_audio_port_config)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
const struct audio_port_config *config);
};
typedef struct audio_hw_device audio_hw_device_t; //> 结构体定义
调用 sp 指向对象->createAudioPatch() 方法,在 DeviceHalInterface 类声明中createAudioPatch是虚函数,
DeviceHalLocal 类继承 DeviceHalInterface 类,并实现createAudioPatch方法,内容如下:
@ frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/DeviceHalLocal.cpp
status_t DeviceHalLocal::createAudioPatch(
unsigned int num_sources,
const struct audio_port_config *sources,
unsigned int num_sinks,
const struct audio_port_config *sinks,
audio_patch_handle_t *patch) {
if (version() >= AUDIO_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_0) {
return mDev->create_audio_patch(
mDev, num_sources, sources, num_sinks, sinks, patch);
} else {
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
}
类 DeviceHalLocal 中声明 audio_hw_device_t *mDev 变量,即存放着 struct audio_module{} 硬件设备管理接口集对象,
@ frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/DeviceHalLocal.h
class DeviceHalLocal : public DeviceHalInterface
{
public:
// Sets the value of 'devices' to a bitmask of 1 or more values of audio_devices_t.
virtual status_t getSupportedDevices(uint32_t *devices);
// Called when the audio mode changes.
virtual status_t setMode(audio_mode_t mode);
// Set global audio parameters.
virtual status_t setParameters(const String8& kvPairs);
// Get global audio parameters.
virtual status_t getParameters(const String8& keys, String8 *values);
// Returns audio input buffer size according to parameters passed.
virtual status_t getInputBufferSize(const struct audio_config *config,
size_t *size);
// Creates and opens the audio hardware output stream. The stream is closed
// by releasing all references to the returned object.
virtual status_t openOutputStream(
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
struct audio_config *config,
const char *address,
sp<StreamOutHalInterface> *outStream);
// Creates and opens the audio hardware input stream. The stream is closed
// by releasing all references to the returned object.
virtual status_t openInputStream(
audio_io_handle_t handle,
audio_devices_t devices,
struct audio_config *config,
audio_input_flags_t flags,
const char *address,
audio_source_t source,
sp<StreamInHalInterface> *inStream);
// Returns whether createAudioPatch and releaseAudioPatch operations are supported.
virtual status_t supportsAudioPatches(bool *supportsPatches);
// Creates an audio patch between several source and sink ports.
virtual status_t createAudioPatch(
unsigned int num_sources,
const struct audio_port_config *sources,
unsigned int num_sinks,
const struct audio_port_config *sinks,
audio_patch_handle_t *patch);
// Set audio port configuration.
virtual status_t setAudioPortConfig(const struct audio_port_config *config);
virtual status_t dump(int fd);
void closeOutputStream(struct audio_stream_out *stream_out);
void closeInputStream(struct audio_stream_in *stream_in);
private:
audio_hw_device_t *mDev;
friend class DevicesFactoryHalLocal; //> 在此类中构造了mDev 指向的 audio_hw_device_t device 对象
// Can not be constructed directly by clients.
explicit DeviceHalLocal(audio_hw_device_t *dev);
// The destructor automatically closes the device.
virtual ~DeviceHalLocal();
uint32_t version() const { return mDev->common.version; }
};
根据 DeviceHalLocal 构建方法为线索,查找 mDev 内容都初始化什么呢?
@ frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/DevicesFactoryHalLocal.cpp
#include 由此 hw_get_module_by_class(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, if_name, &mod) 函数, 建立与硬件设备驱动 HAL 层之间关系。如下:
@hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
/**
* Get the module info associated with a module by id.
*
* @return: 0 == success, <0 == error and *module == NULL
*/
int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module);
/**
* Get the module info associated with a module instance by class 'class_id'
* and instance 'inst'.
*
* Some modules types necessitate multiple instances. For example audio supports
* multiple concurrent interfaces and thus 'audio' is the module class
* and 'primary' or 'a2dp' are module interfaces. This implies that the files
* providing these modules would be named audio.primary..so and
* audio.a2dp..so
*
* @return: 0 == success, <0 == error and *module == NULL
*/
int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
const struct hw_module_t **module);
//-----------------------------
@hardware/libhardware/hardware.c
int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
int i = 0;
char prop[PATH_MAX] = {0};
char path[PATH_MAX] = {0};
char name[PATH_MAX] = {0};
char prop_name[PATH_MAX] = {0};
if (inst)
snprintf(name, PATH_MAX, "%s.%s", class_id, inst);
else
strlcpy(name, class_id, PATH_MAX);
/*
* Here we rely on the fact that calling dlopen multiple times on
* the same .so will simply increment a refcount (and not load
* a new copy of the library).
* We also assume that dlopen() is thread-safe.
*/
/* First try a property specific to the class and possibly instance */
snprintf(prop_name, sizeof(prop_name), "ro.hardware.%s", name);
if (property_get(prop_name, prop, NULL) > 0) {
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}
/* Loop through the configuration variants looking for a module */
for (i=0 ; i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT; i++) {
if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}
/* Nothing found, try the default */
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, "default") == 0) {
goto found;
}
return -ENOENT;
found:
/* load the module, if this fails, we're doomed, and we should not try
* to load a different variant. */
return load(class_id, path, module);
}
int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
return hw_get_module_by_class(id, NULL, module);
}
由 hw_get_module_by_class() 函数,把 struct hw_module_t **module 内容填充即 audio_hw.c 中相关内容,
源码请参考 3.1> 部分内容,由 tinyalsa_hal 源码可见,此驱动并没有支持 create_audio_patch() 方法。
总结:
1>. audioServer 和 mediaServer 都是android系统服务,在系统启动时就启动这两个服务;
2>. audioServer 服务启动中,构建 audioFlinger、audioPolicyService、RadioService、SoundTriggerHwService
对象;
3>. audioFlinger 构建中、创建 patchpanel 对象,并实例化 MixerThread、RecordThread 和 PlaybackThread 线程,
做系统服务执行者,存活于内存中;
4>. 在 打开输出流、输入流或设备时,将触发执行 createAudioPatch_l() 方法执行,由此条路径梳理 audioFlinger 是
如何构建 audio_hw_device_t *mDev 对象;
5>. 由 DevicesFactoryHalLocal::openDevice() 方法实现的代码,调用 hw_get_module_by_class() 函数,梳理出
驱动程序加载方法。
第一部分 audioFlinger 内容告一段落,
此篇内容太长,这也是没有办法的、android 声卡框架就这么安排的,大家一起休息一下,在开启下面两部分。
2.2> AudioPolicyService 本地服务的创建
@ frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/service/AudioPolicyService.cpp
此 AudioPolicyService::instantiate(),在系统中注册 media.audio_policy 服务,并构建 audioPolicyManager 实例;
调用 onFirstRef() 函数,如下:
void AudioPolicyService::onFirstRef()
{
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
// start tone playback thread
mTonePlaybackThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmTone"), this);
// start audio commands thread
mAudioCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmAudio"), this);
// start output activity command thread
mOutputCommandThread = new AudioCommandThread(String8("ApmOutput"), this);
#ifdef USE_LEGACY_AUDIO_POLICY
ALOGI("AudioPolicyService CSTOR in legacy mode");
/* instantiate the audio policy manager */
const struct hw_module_t *module;
int rc = hw_get_module(AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module); //> 获取 AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID 的 module 内容
if (rc) {
return;
}
rc = audio_policy_dev_open(module, &mpAudioPolicyDev); //> 打开 AudioPolicyDevice 逻辑设备
ALOGE_IF(rc, "couldn't open audio policy device (%s)", strerror(-rc));
if (rc) {
return;
}
rc = mpAudioPolicyDev->create_audio_policy(mpAudioPolicyDev, &aps_ops, this,
&mpAudioPolicy); //> 调用 create_legacy_ap() 函数创建路由策略
ALOGE_IF(rc, "couldn't create audio policy (%s)", strerror(-rc));
if (rc) {
return;
}
rc = mpAudioPolicy->init_check(mpAudioPolicy);
ALOGE_IF(rc, "couldn't init_check the audio policy (%s)", strerror(-rc));
if (rc) {
return;
}
ALOGI("Loaded audio policy from %s (%s)", module->name, module->id);
#else
ALOGI("AudioPolicyService CSTOR in new mode"); //> 采用 XML 配置文件模式
mAudioPolicyClient = new AudioPolicyClient(this);
mAudioPolicyManager = createAudioPolicyManager(mAudioPolicyClient); //> 此函数创建 AudioPolicyManager() 对象。
#endif
}
// load audio processing modules
sp<AudioPolicyEffects>audioPolicyEffects = new AudioPolicyEffects();
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
mAudioPolicyEffects = audioPolicyEffects;
}
}
2.2.1 legacy 模式、创建策略与声卡
@ hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/audio_policy.h
audio_policy 宏定义
/**
* The id of this module
*/
#define AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID "audio_policy"
@ hardware/rockchip/audio/legacy_hal/audio_policy_hal.cpp
static int legacy_ap_dev_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
hw_device_t** device)
{
struct legacy_ap_device *dev;
if (strcmp(name, AUDIO_POLICY_INTERFACE) != 0)
return -EINVAL;
dev = (struct legacy_ap_device *)calloc(1, sizeof(*dev));
if (!dev)
return -ENOMEM;
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = 0;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast<hw_module_t*>(module);
dev->device.common.close = legacy_ap_dev_close;
dev->device.create_audio_policy = create_legacy_ap;
dev->device.destroy_audio_policy = destroy_legacy_ap;
*device = &dev->device.common;
return 0;
}
static struct hw_module_methods_t legacy_ap_module_methods = {
.open = legacy_ap_dev_open
};
struct legacy_ap_module HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.module = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "LEGACY Audio Policy HAL",
.author = "The Android Open Source Project",
.methods = &legacy_ap_module_methods,
.dso = NULL,
.reserved = {0},
},
},
};
@ hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/audio.h
/**
* The id of this module
*/
#define AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID "audio"
/**
* List of known audio HAL modules. This is the base name of the audio HAL
* library composed of the "audio." prefix, one of the base names below and
* a suffix specific to the device.
* e.g: audio.primary.goldfish.so or audio.a2dp.default.so
*/
#define AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_PRIMARY "primary"
#define AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_A2DP "a2dp"
#define AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_USB "usb"
#define AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_REMOTE_SUBMIX "r_submix"
#define AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_CODEC_OFFLOAD "codec_offload"
@ hardware/rockchip/audio/legacy_hal/audio_hw_hal.cpp
#define LOG_TAG "legacy_audio_hw_hal"
//#define LOG_NDEBUG 0
#include Android7.0 以前版本采用 legacy 接口, 通过 AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID、AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID 方式、
查找声卡路由策略和声卡hal层驱动。
2.2.2 采用 XML 配置文件方法
在 Android7.0 使用 XML 配置文件方法,需要在编译配置文件 @ device/rockchip/rk3288/device.mk
中增加如下内容:
## config audio policy by ljb
USE_XML_AUDIO_POLICY_CONF := 1 ## 配置采用 XML 配置文件方式
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES += frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/config/audio_policy_configuration.xml:system/etc/audio_policy_configuration.xml\
frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/config/a2dp_audio_policy_configuration.xml:system/etc/a2dp_audio_policy_configuration.xml\
frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/config/usb_audio_policy_configuration.xml:system/etc/usb_audio_policy_configuration.xml\
frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/config/r_submix_audio_policy_configuration.xml:system/etc/r_submix_audio_policy_configuration.xml\
frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/config/audio_policy_volumes.xml:system/etc/audio_policy_volumes.xml\
frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/config/default_volume_tables.xml:system/etc/default_volume_tables.xml
同时把缺省 xml 配置文件拷贝至系统system/etc 文件夹下,驱动程序将会从此目录下加载配置文件,
在 audioserver 函数中调用 AudioPolicyService::instantiate() 构建函数,该函数调用
createAudioPolicyManager() 函数,由此函数引发 AudioPolicyManager() 对象被创建。
@ av/services/audiopolicy/manager/AudioPolicyFactory.cpp
#include "managerdefault/AudioPolicyManager.h"
namespace android {
extern "C" AudioPolicyInterface* createAudioPolicyManager(
AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
{
return new AudioPolicyManager(clientInterface); //> 此函数创建 2.3> 的 AudioPolicyManager 对象。
}
}
AudioPolicyManager 实例加载并解析文件如下:
@ frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/managerdefault/AudioPolicyManager.cpp
AudioPolicyManager::AudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
:
#ifdef AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
Thread(false),
#endif //AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
mLimitRingtoneVolume(false), mLastVoiceVolume(-1.0f),
mA2dpSuspended(false),
mAudioPortGeneration(1),
mBeaconMuteRefCount(0),
mBeaconPlayingRefCount(0),
mBeaconMuted(false),
mTtsOutputAvailable(false),
mMasterMono(false)
{
mUidCached = getuid();
mpClientInterface = clientInterface;
// TODO: remove when legacy conf file is removed. true on devices that use DRC on the
// DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER path to boost soft sounds, used to adjust volume curves accordingly.
// Note: remove also speaker_drc_enabled from global configuration of XML config file.
bool speakerDrcEnabled = false;
#ifdef USE_XML_AUDIO_POLICY_CONF
mVolumeCurves = new VolumeCurvesCollection();
AudioPolicyConfig config(mHwModules, mAvailableOutputDevices, mAvailableInputDevices,
mDefaultOutputDevice, speakerDrcEnabled,
static_cast<VolumeCurvesCollection *>(mVolumeCurves));
PolicySerializer serializer;
ALOGD(" \n %s xml_config: %s \n", __FILE__, AUDIO_POLICY_XML_CONFIG_FILE); //> debug printf by ljb
if (serializer.deserialize(AUDIO_POLICY_XML_CONFIG_FILE, config) != NO_ERROR) { //> XML 文件解析
#else
mVolumeCurves = new StreamDescriptorCollection();
AudioPolicyConfig config(mHwModules, mAvailableOutputDevices, mAvailableInputDevices,
mDefaultOutputDevice, speakerDrcEnabled);
if ((ConfigParsingUtils::loadConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_VENDOR_CONFIG_FILE, config) != NO_ERROR) &&
(ConfigParsingUtils::loadConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_CONFIG_FILE, config) != NO_ERROR)) {
#endif
ALOGE("could not load audio policy configuration file, setting defaults");
config.setDefault();
}
// must be done after reading the policy (since conditionned by Speaker Drc Enabling)
mVolumeCurves->initializeVolumeCurves(speakerDrcEnabled);
// Once policy config has been parsed, retrieve an instance of the engine and initialize it.
audio_policy::EngineInstance *engineInstance = audio_policy::EngineInstance::getInstance();
if (!engineInstance) {
ALOGE("%s: Could not get an instance of policy engine", __FUNCTION__);
return;
}
mHDMIOutputDevice = NULL;
mSPDIFOutputDevice = NULL;
#ifdef BOX_STRATEGY
mHDMIOutputDevice = new DeviceDescriptor(AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL);
mSPDIFOutputDevice = new DeviceDescriptor(AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPDIF);
mHDMIOutputDevice->mAddress = "";
mSPDIFOutputDevice->mAddress = "";
#define CARDSDEFAULT 0
#define CARDSTRATEGYSPDIF 1
#define CARDSTRATEGYBOTH 9
#define CARDSTRATEGYSPDIFPR 8
#define CARDSTRATEGYHDMIMUL 7
#define CARDSTRATEGYHDMIBS 6
#define CARDSTRATEGYBOTHSTR "9"
#define MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_BYPASS "media.cfg.audio.bypass"
#define MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_MUL "media.cfg.audio.mul"
#define MEDIA_AUDIO_CURRENTPB "persist.audio.currentplayback"
#define MEDIA_AUDIO_LASTPB "persist.audio.lastsocplayback"
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = "";
int cardStrategy= 0;
property_get(MEDIA_AUDIO_CURRENTPB, value, "-1");
cardStrategy = atoi(value);
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_BYPASS, "false");
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_MUL, "false");
ALOGD("cardStrategy = %d , hasSpdif() = %d", cardStrategy,hasSpdif());
if(hasSpdif())
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mSPDIFOutputDevice);
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mHDMIOutputDevice);
switch (cardStrategy) {
case CARDSDEFAULT:
if(hasSpdif())
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mSPDIFOutputDevice);
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mHDMIOutputDevice);
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_BYPASS, "false");
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_MUL, "false");
break;
case CARDSTRATEGYHDMIMUL:
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mHDMIOutputDevice);
mAvailableOutputDevices.remove(mSPDIFOutputDevice);
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_MUL, "true");
break;
case CARDSTRATEGYSPDIF:
case CARDSTRATEGYSPDIFPR:
if(hasSpdif())
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mSPDIFOutputDevice);
mAvailableOutputDevices.remove(mHDMIOutputDevice);
if(cardStrategy==CARDSTRATEGYSPDIFPR)
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_BYPASS, "true");
else
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_BYPASS, "false");
break;
case CARDSTRATEGYHDMIBS:
if(hasSpdif())
mAvailableOutputDevices.remove(mSPDIFOutputDevice);
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mHDMIOutputDevice);
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_BYPASS, "true");
property_set(MEDIA_CFG_AUDIO_MUL, "false");
break;
default:
if(hasSpdif())
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mSPDIFOutputDevice);
mAvailableOutputDevices.add(mHDMIOutputDevice);
property_set(MEDIA_AUDIO_CURRENTPB, "0");
property_set(MEDIA_AUDIO_LASTPB, "0");
break;
}
system("sync");
#endif
// Retrieve the Policy Manager Interface
mEngine = engineInstance->queryInterface<AudioPolicyManagerInterface>();
if (mEngine == NULL) {
ALOGE("%s: Failed to get Policy Engine Interface", __FUNCTION__);
return;
}
mEngine->setObserver(this);
status_t status = mEngine->initCheck();
(void) status;
ALOG_ASSERT(status == NO_ERROR, "Policy engine not initialized(err=%d)", status);
// mAvailableOutputDevices and mAvailableInputDevices now contain all attached devices
// open all output streams needed to access attached devices
audio_devices_t outputDeviceTypes = mAvailableOutputDevices.types();
audio_devices_t inputDeviceTypes = mAvailableInputDevices.types() & ~AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN;
for (size_t i = 0; i < mHwModules.size(); i++) {
mHwModules[i]->mHandle = mpClientInterface->loadHwModule(mHwModules[i]->getName()); //> 获取 tinyalsa_hal 的 handle
if (mHwModules[i]->mHandle == 0) {
ALOGW("could not open HW module %s", mHwModules[i]->getName());
continue;
}
// open all output streams needed to access attached devices
// except for direct output streams that are only opened when they are actually
// required by an app.
// This also validates mAvailableOutputDevices list
for (size_t j = 0; j < mHwModules[i]->mOutputProfiles.size(); j++)
{
const sp<IOProfile> outProfile = mHwModules[i]->mOutputProfiles[j];
if (!outProfile->hasSupportedDevices()) {
ALOGW("Output profile contains no device on module %s", mHwModules[i]->getName());
continue;
}
if ((outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_TTS) != 0) {
mTtsOutputAvailable = true;
}
if ((outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT) != 0) {
continue;
}
audio_devices_t profileType = outProfile->getSupportedDevicesType();
if ((profileType & mDefaultOutputDevice->type()) != AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) {
profileType = mDefaultOutputDevice->type();
} else {
// chose first device present in profile's SupportedDevices also part of
// outputDeviceTypes
profileType = outProfile->getSupportedDeviceForType(outputDeviceTypes);
}
if ((profileType & outputDeviceTypes) == 0) {
continue;
}
sp<SwAudioOutputDescriptor> outputDesc = new SwAudioOutputDescriptor(outProfile,
mpClientInterface);
const DeviceVector &supportedDevices = outProfile->getSupportedDevices();
const DeviceVector &devicesForType = supportedDevices.getDevicesFromType(profileType);
String8 address = devicesForType.size() > 0 ? devicesForType.itemAt(0)->mAddress
: String8("");
outputDesc->mDevice = profileType;
audio_config_t config = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
config.sample_rate = outputDesc->mSamplingRate;
config.channel_mask = outputDesc->mChannelMask;
config.format = outputDesc->mFormat;
audio_io_handle_t output = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
status_t status = mpClientInterface->openOutput(outProfile->getModuleHandle(),
&output,
&config,
&outputDesc->mDevice,
address,
&outputDesc->mLatency,
outputDesc->mFlags);
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGW("Cannot open output stream for device %08x on hw module %s",
outputDesc->mDevice,
mHwModules[i]->getName());
} else {
outputDesc->mSamplingRate = config.sample_rate;
outputDesc->mChannelMask = config.channel_mask;
outputDesc->mFormat = config.format;
for (size_t k = 0; k < supportedDevices.size(); k++) {
ssize_t index = mAvailableOutputDevices.indexOf(supportedDevices[k]);
// give a valid ID to an attached device once confirmed it is reachable
if (index >= 0 && !mAvailableOutputDevices[index]->isAttached()) {
mAvailableOutputDevices[index]->attach(mHwModules[i]);
}
}
if (mPrimaryOutput == 0 &&
outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY) {
mPrimaryOutput = outputDesc;
}
addOutput(output, outputDesc);
setOutputDevice(outputDesc,
outputDesc->mDevice,
true,
0,
NULL,
address.string());
}
}
// open input streams needed to access attached devices to validate
// mAvailableInputDevices list
for (size_t j = 0; j < mHwModules[i]->mInputProfiles.size(); j++)
{
const sp<IOProfile> inProfile = mHwModules[i]->mInputProfiles[j];
if (!inProfile->hasSupportedDevices()) {
ALOGW("Input profile contains no device on module %s", mHwModules[i]->getName());
continue;
}
// chose first device present in profile's SupportedDevices also part of
// inputDeviceTypes
audio_devices_t profileType = inProfile->getSupportedDeviceForType(inputDeviceTypes);
if ((profileType & inputDeviceTypes) == 0) {
continue;
}
sp<AudioInputDescriptor> inputDesc =
new AudioInputDescriptor(inProfile);
inputDesc->mDevice = profileType;
// find the address
DeviceVector inputDevices = mAvailableInputDevices.getDevicesFromType(profileType);
// the inputs vector must be of size 1, but we don't want to crash here
String8 address = inputDevices.size() > 0 ? inputDevices.itemAt(0)->mAddress
: String8("");
ALOGV(" for input device 0x%x using address %s", profileType, address.string());
ALOGE_IF(inputDevices.size() == 0, "Input device list is empty!");
audio_config_t config = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
config.sample_rate = inputDesc->mSamplingRate;
config.channel_mask = inputDesc->mChannelMask;
config.format = inputDesc->mFormat;
audio_io_handle_t input = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
status_t status = mpClientInterface->openInput(inProfile->getModuleHandle(),
&input,
&config,
&inputDesc->mDevice,
address,
AUDIO_SOURCE_MIC,
AUDIO_INPUT_FLAG_NONE);
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
const DeviceVector &supportedDevices = inProfile->getSupportedDevices();
for (size_t k = 0; k < supportedDevices.size(); k++) {
ssize_t index = mAvailableInputDevices.indexOf(supportedDevices[k]);
// give a valid ID to an attached device once confirmed it is reachable
if (index >= 0) {
sp<DeviceDescriptor> devDesc = mAvailableInputDevices[index];
if (!devDesc->isAttached()) {
devDesc->attach(mHwModules[i]);
devDesc->importAudioPort(inProfile);
}
}
}
mpClientInterface->closeInput(input);
} else {
ALOGW("Cannot open input stream for device %08x on hw module %s",
inputDesc->mDevice,
mHwModules[i]->getName());
}
}
}
// make sure all attached devices have been allocated a unique ID
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAvailableOutputDevices.size();) {
if (!mAvailableOutputDevices[i]->isAttached()) {
ALOGW("Output device %08x unreachable", mAvailableOutputDevices[i]->type());
mAvailableOutputDevices.remove(mAvailableOutputDevices[i]);
continue;
}
// The device is now validated and can be appended to the available devices of the engine
mEngine->setDeviceConnectionState(mAvailableOutputDevices[i],
AUDIO_POLICY_DEVICE_STATE_AVAILABLE);
i++;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAvailableInputDevices.size();) {
if (!mAvailableInputDevices[i]->isAttached()) {
ALOGW("Input device %08x unreachable", mAvailableInputDevices[i]->type());
mAvailableInputDevices.remove(mAvailableInputDevices[i]);
continue;
}
// The device is now validated and can be appended to the available devices of the engine
mEngine->setDeviceConnectionState(mAvailableInputDevices[i],
AUDIO_POLICY_DEVICE_STATE_AVAILABLE);
i++;
}
// make sure default device is reachable
if (mDefaultOutputDevice == 0 || mAvailableOutputDevices.indexOf(mDefaultOutputDevice) < 0) {
ALOGE("Default device %08x is unreachable", mDefaultOutputDevice->type());
}
ALOGE_IF((mPrimaryOutput == 0), "Failed to open primary output");
updateDevicesAndOutputs();
#ifdef AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
if (mPrimaryOutput != 0) {
AudioParameter outputCmd = AudioParameter();
outputCmd.addInt(String8("set_id"), 0);
mpClientInterface->setParameters(mPrimaryOutput->mIoHandle, outputCmd.toString());
mTestDevice = AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER;
mTestSamplingRate = 44100;
mTestFormat = AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT;
mTestChannels = AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO;
mTestLatencyMs = 0;
mCurOutput = 0;
mDirectOutput = false;
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_TEST_OUTPUTS; i++) {
mTestOutputs[i] = 0;
}
const size_t SIZE = 256;
char buffer[SIZE];
snprintf(buffer, SIZE, "AudioPolicyManagerTest");
run(buffer, ANDROID_PRIORITY_AUDIO);
}
#endif //AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
}
总结:
在 构建函数中区分 *.conf 与 *.xml 配置管理方法,分别使用不同程序解析生成 HwModule[]、输入、输出接口及路由策略内容.
Android 7.0以上的版本弃用了 audio_policy.conf,使用 XML 文件格式来定义音频拓扑的支持,这种文件格式更通俗易懂,
具有多种编辑和解析工具,并且足够灵活,可以描述复杂的音频拓扑。
2.3> audio_policy_configuration.xml 策略管理方法
驱动程序获取 audio_policy_configuration.xml 生成音频设备管理对象,根据 xml 定义构建 audio policy 对象和 input、output 设备,
通过 dumpsys media.audio_policy 可以看到本机声卡设备和路由策略。
2.3.1> XML 配置内容
此 audio_policy_configuration.xml 包含 usb、a2dp 和 r_submix 策略配置文件 xml , 这些文件会拷贝至 system/etc/ 文件夹中。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<audioPolicyConfiguration version="1.0" xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude">
<!-- version section contains a “version” tag in the form “major.minor” e.g version=”1.0” -->
<!-- Global configuration Decalaration -->
<globalConfiguration speaker_drc_enabled="true"/>
<modules>
<!-- Primary Audio HAL -->
<module name="primary" halVersion="3.0">
<attachedDevices>
<item>Speaker</item>
<item>Built-In Mic</item>
<item>Built-In Back Mic</item>
</attachedDevices>
<defaultOutputDevice>Speaker</defaultOutputDevice>
<mixPorts>
<mixPort name="primary output" role="source" flags="AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="48000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO"/>
</mixPort>
<mixPort name="deep_buffer" role="source"
flags="AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DEEP_BUFFER">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="48000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO"/>
</mixPort>
<mixPort name="compressed_offload" role="source"
flags="AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT|AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD|AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_NON_BLOCKING">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_MP3"
samplingRates="8000,11025,12000,16000,22050,24000,32000,44100,48000"
channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_MONO"/>
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_AAC"
samplingRates="8000,11025,12000,16000,22050,24000,32000,44100,48000"
channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_MONO"/>
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_AAC_LC"
samplingRates="8000,11025,12000,16000,22050,24000,32000,44100,48000"
channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_MONO"/>
</mixPort>
<mixPort name="voice_tx" role="source">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,16000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_MONO"/>
</mixPort>
<mixPort name="primary input" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,11025,12000,16000,22050,24000,32000,44100,48000"
channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_MONO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_STEREO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_FRONT_BACK"/>
</mixPort>
<mixPort name="voice_rx" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,16000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_MONO"/>
</mixPort>
</mixPorts>
<devicePorts>
<!-- Output devices declaration, i.e. Sink DEVICE PORT -->
<devicePort tagName="Earpiece" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_EARPIECE" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="48000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_MONO"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="Speaker" role="sink" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER" address="">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="48000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO"/>
<gains>
<gain name="gain_1" mode="AUDIO_GAIN_MODE_JOINT"
minValueMB="-8400"
maxValueMB="4000"
defaultValueMB="0"
stepValueMB="100"/>
</gains>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="Wired Headset" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADSET" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="48000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="Wired Headphones" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="48000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="BT SCO" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,16000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_MONO"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="BT SCO Headset" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO_HEADSET" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,16000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_MONO"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="BT SCO Car Kit" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO_CARKIT" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,16000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_MONO"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="Telephony Tx" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_TELEPHONY_TX" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,16000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_MONO"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="Built-In Mic" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC" role="source">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,11025,12000,16000,22050,24000,32000,44100,48000"
channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_MONO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_STEREO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_FRONT_BACK"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="Built-In Back Mic" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BACK_MIC" role="source">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,11025,12000,16000,22050,24000,32000,44100,48000"
channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_MONO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_STEREO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_FRONT_BACK"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="Wired Headset Mic" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_WIRED_HEADSET" role="source">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,11025,12000,16000,22050,24000,32000,44100,48000"
channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_MONO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_STEREO,AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_FRONT_BACK"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="BT SCO Headset Mic" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BLUETOOTH_SCO_HEADSET" role="source">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,16000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_MONO"/>
</devicePort>
<devicePort tagName="Telephony Rx" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_TELEPHONY_RX" role="source">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="8000,16000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_MONO"/>
</devicePort>
</devicePorts>
<!-- route declaration, i.e. list all available sources for a given sink -->
<routes>
<route type="mix" sink="Earpiece"
sources="primary output,deep_buffer,BT SCO Headset Mic"/>
<route type="mix" sink="Speaker"
sources="primary output,deep_buffer,compressed_offload,BT SCO Headset Mic,Telephony Rx"/>
<route type="mix" sink="Wired Headset"
sources="primary output,deep_buffer,compressed_offload,BT SCO Headset Mic,Telephony Rx"/>
<route type="mix" sink="Wired Headphones"
sources="primary output,deep_buffer,compressed_offload,BT SCO Headset Mic,Telephony Rx"/>
<route type="mix" sink="Telephony Tx"
sources="voice_tx"/>
<route type="mix" sink="primary input"
sources="Built-In Mic,Built-In Back Mic,Wired Headset Mic,BT SCO Headset Mic"/>
<route type="mix" sink="Telephony Tx"
sources="Built-In Mic,Built-In Back Mic,Wired Headset Mic,BT SCO Headset Mic"/>
<route type="mix" sink="voice_rx"
sources="Telephony Rx"/>
</routes>
</module>
<!-- HDMI Audio HAL -->
<module description="HDMI Audio HAL" name="hdmi" version="2.0">
<mixPorts>
<mixPort name="hdmi output" role="source">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT" samplingRates="48000"/>
</mixPort>
</mixPorts>
<devicePorts>
<devicePort tagName="HDMI Out" type="AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL" role="sink">
<profile name="" format="AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT"
samplingRates="48000" channelMasks="AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO"/>
</devicePort>
</devicePorts>
<routes>
<route type="mix" sink="HDMI Out"
sources="hdmi output"/>
</routes>
</module>
<!-- A2dp Audio HAL --> <xi:include href="a2dp_audio_policy_configuration.xml"/>
<!-- Usb Audio HAL --> <xi:include href="usb_audio_policy_configuration.xml"/>
<!-- Remote Submix Audio HAL --> <xi:include href="r_submix_audio_policy_configuration.xml"/>
</modules> <!-- End of Modules section -->
<!-- Volume section -->
<xi:include href="audio_policy_volumes.xml"/>
<xi:include href="default_volume_tables.xml"/>
<!-- End of Volume section -->
</audioPolicyConfiguration>
总结:
(1). 在 AudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface) 构建函数中,根据 xml 配置文件 module 生成
mHwModules[] 设备对象,多个 moduel 就生成多个 mHwModules[] 对象;
(2). 把 mHwModules[] 模块中的端口 ,添加到所有 mAvailableOutputDevices 和 mAvailableInputDevices 实例中;
(3). 把 mHwModules[] 模块中设备,添加到 DeviceVector[] 设备描述符集中;
(4). 把 mHwModules[] 模块的 route 属性,提取路由策略信息并生成系统的路由策略;
(5). 在 建立设备连接关系中,创建 audioPatch 模块,在此过程调用 audioFlinger->createAudioPatch() 函数,
此函数流程可参考 2.1 部分中内容。
2.3.2> XML 解析结果
解析后在系统中生成的设备及策略内容如下:
rk3288:/ # dumpsys media.audio_policy
AudioPolicyManager Dump: 0xb4d3e200
Primary Output: 13
Phone state: 0
Force use for communications 0
Force use for media 0
Force use for record 0
Force use for dock 8
Force use for system 0
Force use for hdmi system audio 0
Force use for encoded surround output 0
TTS output not available
Master mono: off
- Available output devices:
Device 1:
- id: 1
- tag name: Speaker
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
- gains:
Gain 1:
- mode: 00000001
- channel_mask: 00000000
- min_value: 0 mB
- max_value: 4000 mB
- default_value: 0 mB
- step_value: 100 mB
- min_ramp_ms: 0 ms
- max_ramp_ms: 0 ms
- Available input devices:
Device 1:
- id: 4
- tag name: Built-In Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x000c, 0x0010, 0x0030
Device 2:
- id: 5
- tag name: Built-In Back Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BACK_MIC
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x000c, 0x0010, 0x0030
Device 3:
- id: 6
- tag name: Remote Submix In
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_REMOTE_SUBMIX
- address: 0
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x000c
HW Modules dump:
- HW Module 1:
- name: primary
- handle: 10
- version: 2.5
- outputs:
output 0:
- name: primary output
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
- flags: 0x0002
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: Earpiece
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_EARPIECE
Device 2:
- id: 1
- tag name: Speaker
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
Device 3:
- tag name: Wired Headset
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADSET
Device 4:
- tag name: Wired Headphones
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE
output 1:
- name: deep_buffer
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
- flags: 0x0008
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: Earpiece
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_EARPIECE
Device 2:
- id: 1
- tag name: Speaker
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
Device 3:
- tag name: Wired Headset
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADSET
Device 4:
- tag name: Wired Headphones
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE
output 2:
- name: compressed_offload
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_MP3
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x0001, 0x0003
Profile 1:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_AAC
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x0001, 0x0003
Profile 2:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_AAC_LC
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x0001, 0x0003
- flags: 0x0031
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- id: 1
- tag name: Speaker
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
Device 2:
- tag name: Wired Headset
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADSET
Device 3:
- tag name: Wired Headphones
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE
output 3:
- name: voice_tx
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 16000
- channel masks:0x0001
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: Telephony Tx
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_TELEPHONY_TX
- inputs:
input 0:
- name: primary input
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x000c, 0x0010, 0x0030
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- id: 4
- tag name: Built-In Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC
Device 2:
- id: 5
- tag name: Built-In Back Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BACK_MIC
Device 3:
- tag name: Wired Headset Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_WIRED_HEADSET
Device 4:
- tag name: BT SCO Headset Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BLUETOOTH_SCO_HEADSET
input 1:
- name: voice_rx
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 16000
- channel masks:0x0010
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: Telephony Rx
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_TELEPHONY_RX
- Declared devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: Earpiece
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_EARPIECE
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0010
Device 2:
- id: 1
- tag name: Speaker
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
- gains:
Gain 1:
- mode: 00000001
- channel_mask: 00000000
- min_value: 0 mB
- max_value: 4000 mB
- default_value: 0 mB
- step_value: 100 mB
- min_ramp_ms: 0 ms
- max_ramp_ms: 0 ms
Device 3:
- tag name: Wired Headset
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADSET
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
Device 4:
- tag name: Wired Headphones
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
Device 5:
- tag name: BT SCO
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 16000
- channel masks:0x0001
Device 6:
- tag name: BT SCO Headset
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO_HEADSET
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 16000
- channel masks:0x0001
Device 7:
- tag name: BT SCO Car Kit
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_SCO_CARKIT
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 16000
- channel masks:0x0001
Device 8:
- tag name: Telephony Tx
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_TELEPHONY_TX
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 16000
- channel masks:0x0001
Device 9:
- id: 4
- tag name: Built-In Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x000c, 0x0010, 0x0030
Device 10:
- id: 5
- tag name: Built-In Back Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BACK_MIC
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x000c, 0x0010, 0x0030
Device 11:
- tag name: Wired Headset Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_WIRED_HEADSET
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x000c, 0x0010, 0x0030
Device 12:
- tag name: BT SCO Headset Mic
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BLUETOOTH_SCO_HEADSET
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 16000
- channel masks:0x0010
Device 13:
- tag name: Telephony Rx
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_TELEPHONY_RX
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:8000, 16000
- channel masks:0x0010
Audio Routes (8):
- Route 1:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: Earpiece
- Sources:
primary output
deep_buffer
BT SCO Headset Mic
- Route 2:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: Speaker
- Sources:
primary output
deep_buffer
compressed_offload
BT SCO Headset Mic
Telephony Rx
- Route 3:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: Wired Headset
- Sources:
primary output
deep_buffer
compressed_offload
BT SCO Headset Mic
Telephony Rx
- Route 4:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: Wired Headphones
- Sources:
primary output
deep_buffer
compressed_offload
BT SCO Headset Mic
Telephony Rx
- Route 5:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: Telephony Tx
- Sources:
voice_tx
- Route 6:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: primary input
- Sources:
Built-In Mic
Built-In Back Mic
Wired Headset Mic
BT SCO Headset Mic
- Route 7:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: Telephony Tx
- Sources:
Built-In Mic
Built-In Back Mic
Wired Headset Mic
BT SCO Headset Mic
- Route 8:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: voice_rx
- Sources:
Telephony Rx
- HW Module 2:
- name: hdmi
- handle: 0
- version: 2.0
- outputs:
output 0:
- name: hdmi output
- Profiles:
Profile 0:[dynamic channels]
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: HDMI Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL
- Declared devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: HDMI Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
Audio Routes (1):
- Route 1:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: HDMI Out
- Sources:
hdmi output
- HW Module 3:
- name: a2dp
- handle: 18
- version: 2.3
- outputs:
output 0:
- name: a2dp output
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:44100
- channel masks:0x0003
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: BT A2DP Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP
Device 2:
- tag name: BT A2DP Headphones
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP_HEADPHONES
Device 3:
- tag name: BT A2DP Speaker
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP_SPEAKER
- inputs:
input 0:
- name: a2dp input
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x000c, 0x0010
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: BT A2DP In
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BLUETOOTH_A2DP
- Declared devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: BT A2DP Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:44100
- channel masks:0x0003
Device 2:
- tag name: BT A2DP Headphones
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP_HEADPHONES
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:44100
- channel masks:0x0003
Device 3:
- tag name: BT A2DP Speaker
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP_SPEAKER
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:44100
- channel masks:0x0003
Device 4:
- tag name: BT A2DP In
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BLUETOOTH_A2DP
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:44100, 48000
- channel masks:0x000c, 0x0010
Audio Routes (4):
- Route 1:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: BT A2DP Out
- Sources:
a2dp output
- Route 2:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: BT A2DP Headphones
- Sources:
a2dp output
- Route 3:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: BT A2DP Speaker
- Sources:
a2dp output
- Route 4:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: a2dp input
- Sources:
BT A2DP In
- HW Module 4:
- name: usb
- handle: 26
- version: 2.2
- outputs:
output 0:
- name: usb_accessory output
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:44100
- channel masks:0x0003
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: USB Host Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_USB_ACCESSORY
output 1:
- name: usb_device output
- Profiles:
Profile 0:[dynamic format][dynamic channels][dynamic rates]
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: USB Device Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_USB_DEVICE
- inputs:
input 0:
- name: usb_device input
- Profiles:
Profile 0:[dynamic format][dynamic channels][dynamic rates]
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: USB Device In
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_USB_DEVICE
- Declared devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: USB Host Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_USB_ACCESSORY
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:44100
- channel masks:0x0003
Device 2:
- tag name: USB Device Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_USB_DEVICE
- Profiles:
Profile 0:[dynamic format][dynamic channels][dynamic rates]
Device 3:
- tag name: USB Device In
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_USB_DEVICE
- Profiles:
Profile 0:[dynamic format][dynamic channels][dynamic rates]
Audio Routes (3):
- Route 1:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: USB Host Out
- Sources:
usb_accessory output
- Route 2:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: USB Device Out
- Sources:
usb_device output
- Route 3:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: usb_device input
- Sources:
USB Device In
- HW Module 5:
- name: r_submix
- handle: 34
- version: 2.1
- outputs:
output 0:
- name: r_submix output
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: Remote Submix Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_REMOTE_SUBMIX
- address: 0
- inputs:
input 0:
- name: r_submix input
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x000c
- flags: 0x0000
- Supported devices:
Device 1:
- id: 6
- tag name: Remote Submix In
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_REMOTE_SUBMIX
- address: 0
- Declared devices:
Device 1:
- tag name: Remote Submix Out
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_REMOTE_SUBMIX
- address: 0
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x0003
Device 2:
- id: 6
- tag name: Remote Submix In
- type: AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_REMOTE_SUBMIX
- address: 0
- Profiles:
Profile 0:
- format: AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT
- sampling rates:48000
- channel masks:0x000c
Audio Routes (2):
- Route 1:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: Remote Submix Out
- Sources:
r_submix output
- Route 2:
- Type: Mix
- Sink: r_submix input
- Sources:
Remote Submix In
Outputs dump:
- Output 13 dump:
Latency: 115
Flags 00000002
ID: 2
Sampling rate: 48000
Format: 00000001
Channels: 00000003
Devices 00000002
Stream volume refCount muteCount
00 -24.000 00 00
01 -758.000 00 00
02 -758.000 00 00
03 -758.000 00 00
04 -758.000 00 00
05 -758.000 00 00
06 -1.000 00 00
07 -758.000 00 00
08 -758.000 00 00
09 0.000 00 01
10 -758.000 00 00
11 0.000 00 00
12 -1.000 00 00
- Output 21 dump:
Latency: 743
Flags 00000008
ID: 3
Sampling rate: 48000
Format: 00000001
Channels: 00000003
Devices 00000002
Stream volume refCount muteCount
00 -24.000 00 00
01 -758.000 00 00
02 -758.000 00 00
03 -758.000 00 00
04 -758.000 00 00
05 -758.000 00 00
06 -1.000 00 00
07 -758.000 00 00
08 -758.000 00 00
09 0.000 00 01
10 -758.000 00 00
11 0.000 00 00
12 -1.000 00 00
Inputs dump:
Streams dump:
Stream Can be muted Index Min Index Max Index Cur [device : index]...
00 true 01 05 0002 : 05, 0004 : 05, 0008 : 05, 0400 : 05, 40000000 : 04,
01 true 00 07 0002 : 07, 0004 : 07, 0008 : 07, 0400 : 07, 40000000 : 05,
02 true 00 07 0002 : 07, 0004 : 07, 0008 : 07, 0400 : 07, 40000000 : 05,
03 true 00 15 0002 : 15, 0004 : 15, 0008 : 15, 0400 : 15, 40000000 : 11,
04 true 00 07 0002 : 07, 0004 : 07, 0008 : 07, 0400 : 07, 40000000 : 06,
05 true 00 07 0002 : 07, 0004 : 07, 0008 : 07, 0400 : 07, 40000000 : 05,
06 true 00 15 0002 : 15, 0004 : 15, 0008 : 15, 0400 : 15, 40000000 : 07,
07 true 00 07 0002 : 07, 0004 : 07, 0008 : 07, 0400 : 07, 40000000 : 05,
08 true 00 15 0002 : 15, 0004 : 15, 0008 : 15, 0400 : 15, 40000000 : 11,
09 true 00 15 0002 : 15, 0004 : 15, 0008 : 15, 0400 : 15, 40000000 : 11,
10 true 00 15 0002 : 15, 0004 : 15, 0008 : 15, 0400 : 15, 40000000 : 11,
11 true 00 01 40000000 : 00,
12 true 00 01 40000000 : 00,
Volume Curves for Use Cases (aka Stream types) dump:
AUDIO_STREAM_VOICE_CALL (00): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 0, -4200), ( 33, -2800), ( 66, -1400), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 0, -2400), ( 33, -1600), ( 66, -800), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 0, -2400), ( 33, -1600), ( 66, -800), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
AUDIO_STREAM_SYSTEM (01): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 1, -3000), ( 33, -2600), ( 66, -2200), (100, -1800) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 1, -2400), ( 33, -1800), ( 66, -1200), (100, -600) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 1, -2400), ( 33, -1800), ( 66, -1200), (100, -600) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -2100), (100, -1000) }
AUDIO_STREAM_RING (02): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 1, -4950), ( 33, -3350), ( 66, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 1, -2970), ( 33, -2010), ( 66, -1020), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 1, -4950), ( 33, -3350), ( 66, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -2100), (100, -1000) }
AUDIO_STREAM_MUSIC (03): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
AUDIO_STREAM_ALARM (04): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 1, -4950), ( 33, -3350), ( 66, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 1, -2970), ( 33, -2010), ( 66, -1020), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 1, -4950), ( 33, -3350), ( 66, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -2100), (100, -1000) }
AUDIO_STREAM_NOTIFICATION (05): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 1, -4950), ( 33, -3350), ( 66, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 1, -2970), ( 33, -2010), ( 66, -1020), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 1, -4950), ( 33, -3350), ( 66, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -2100), (100, -1000) }
AUDIO_STREAM_BLUETOOTH_SCO (06): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 0, -4200), ( 33, -2800), ( 66, -1400), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 0, -2400), ( 33, -1600), ( 66, -800), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 0, -4200), ( 33, -2800), ( 66, -1400), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
AUDIO_STREAM_ENFORCED_AUDIBLE (07): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 1, -3000), ( 33, -2600), ( 66, -2200), (100, -1800) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 1, -2400), ( 33, -1800), ( 66, -1200), (100, -600) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 1, -2400), ( 33, -1800), ( 66, -1200), (100, -600) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -2100), (100, -1000) }
AUDIO_STREAM_DTMF (08): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 1, -3000), ( 33, -2600), ( 66, -2200), (100, -1800) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 1, -2400), ( 33, -1800), ( 66, -1200), (100, -600) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 1, -2400), ( 33, -1800), ( 66, -1200), (100, -600) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -2100), (100, -1000) }
AUDIO_STREAM_TTS (09): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 0, -9600), (100, -9600) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 0, -9600), (100, -9600) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 0, -9600), (100, -9600) }
AUDIO_STREAM_ACCESSIBILITY (10): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 1, -5800), ( 20, -4000), ( 60, -1700), (100, 0) }
AUDIO_STREAM_REROUTING (11): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
AUDIO_STREAM_PATCH (12): Curve points for device category (index, attenuation in millibel)
DEVICE_CATEGORY_HEADSET : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EARPIECE : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
DEVICE_CATEGORY_EXT_MEDIA : {( 0, 0), (100, 0) }
Total Effects CPU: 0.000000 MIPS, Total Effects memory: 0 KB, Max memory used: 0 KB
Registered effects:
Audio Patches:
Audio patch 1:
- handle: 1
- audio flinger handle: 12
- owner uid: 1041
- 1 sources:
- Mix ID 2 I/O handle 13
- 1 sinks:
- Device ID 1 AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
Audio patch 2:
- handle: 2
- audio flinger handle: 20
- owner uid: 1041
- 1 sources:
- Mix ID 3 I/O handle 21
- 1 sinks:
- Device ID 1 AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER
此部分纪实内容较多,读者可仔细对比生成对象与 XML 配置对应关系,以及 AudioPolicyManager 程序构建解析实现,
当对应关系就代码摆在面前后、我认为代码阅读就简单很多了。
2.3.3> 如何通过 xml 配置文件对应 hw_hal 驱动?
mpClientInterface 是入口参数传递过来,此 loadHwModule() 是虚函数,在 AudioPolicyClientImpl.cpp 中被实现;
/* implementation of the client interface from the policy manager */
audio_module_handle_t AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyClient::loadHwModule(const char *name) //> name = primary 在配置文件中
{
sp<IAudioFlinger> af = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger(); //> @ framework/av/media/libmeida/AudioSystem.cpp 中
if (af == 0) {
ALOGW("%s: could not get AudioFlinger", __func__);
return AUDIO_MODULE_HANDLE_NONE;
}
return af->loadHwModule(name); //> 通过 AudioFlinger 服务的 loadHwModule() 方法装载 audio.primary.rk30xx.so 库
} //> 就是 rockchip 实现的 audio_tinyalsa_hal 驱动程序库文件。
@ AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger() 函数内容如下
// establish binder interface to AudioFlinger service
const sp<IAudioFlinger> AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger()
{
sp<IAudioFlinger> af;
sp<AudioFlingerClient> afc;
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(gLock);
if (gAudioFlinger == 0) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager(); //> sm 对象
sp<IBinder> binder;
do {
binder = sm->getService(String16("media.audio_flinger")); //> 系统服务
if (binder != 0)
break;
ALOGW("AudioFlinger not published, waiting...");
usleep(500000); // 0.5 s
} while (true);
if (gAudioFlingerClient == NULL) {
gAudioFlingerClient = new AudioFlingerClient(); //> AudioFlingerClient 实例
} else {
if (gAudioErrorCallback) {
gAudioErrorCallback(NO_ERROR);
}
}
binder->linkToDeath(gAudioFlingerClient); //> 绑定 client 与 gAudioFlinger 对象关系
gAudioFlinger = interface_cast<IAudioFlinger>(binder);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(gAudioFlinger == 0);
afc = gAudioFlingerClient;
}
af = gAudioFlinger;
}
if (afc != 0) {
af->registerClient(afc); //> 注册 AudioFlingerClient 对象
}
return af;
}
@ hardware/rockchip/tinyalsa_hal/Android.mk
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := audio.primary.$(TARGET_BOARD_HARDWARE) //> tinyalsa_hal 的程序编译生成结果,audio.primary.rk30.so 文件
LOCAL_PROPRIETARY_MODULE := true
LOCAL_MODULE_RELATIVE_PATH := hw
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
audio_setting.c \
audio_bitstream.c \
audio_hw.c \
alsa_route.c \
alsa_mixer.c \
voice_preprocess.c \
audio_hw_hdmi.c
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += \
external/tinyalsa/include \
$(call include-path-for, audio-utils) \
$(call include-path-for, audio-route) \
$(call include-path-for, speex)
至此为止,我们捋顺 AudioPolicyManager 是如何装载厂商编写 HAL 驱动程序。
在 AudioPolicyManager::AudioPolicyManager() 构造函数中, 解析 xml 配置文件将生成 4 个 HwModule[] 对象,分别是:
primary、a2dp、usb 和 r_submix 模块。
总结:
-
AudioPolicyService继承了IAudioPolicyService接口,这样AudioPolicyService就可以基于Android的Binder机制,向外部提供服务;
-
AudioPolicyService同时也继承了AudioPolicyClientInterface类,他有一个AudioPolicyInterface类的成员指针mpPolicyManager,
实际上就是指向了AudioPolicyManager; -
AudioPolicyManager类继承了AudioPolicyInterface类以便向AudioPolicyService提供服务,反过来同时还有一个AudioPolicyClientInterface指针,
该指针在构造函数中被初始化,指向了AudioPolicyService,实际上,AudioPolicyService是通过成员指针mpPolicyManager访问AudioPolicyManager,
而AudioPolicyManager则通过AudioPolicyClientInterface(mpClientInterface)访问AudioPolicyService; -
AudioPolicyService有一个内部线程类AudioCommandThread,顾名思义,所有的命令(音量控制,输入、输出的切换等)最终都会在该线程中排队执行;
-
音频系统为音频设备定义了一个枚举:AudioSystem::audio_devices,例如:DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER,DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE,
DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP,DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC,DEVICE_IN_VOICE_CALL等等,每一个枚举值其实对应一个32bit整数的某一个位,
所以这些值是可以进行位或操作的,例如我希望同时打开扬声器和耳机,可以这样配置:
newDevice = DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER | DEVICE_OUT_WIRED_HEADPHONE;
setOutputDevice(mHardwareOutput, newDevice);
- AudioPolicyManager中有两个成员变量:mAvailableOutputDevices和mAvailableInputDevices,他们记录了当前可用的输入和输出设备,
当系统检测到耳机或者蓝牙已连接好时,会调用AudioPolicyManager的成员函数;
status_t AudioPolicyManager::setDeviceConnectionState(AudioSystem::audio_devices device,
AudioSystem::device_connection_state state,
const char *device_address)
- AudioSystem::stream_type 音频流的类型,一共有10种类型;AudioSystem::audio_devices 音频输入输出设备,xml 文件中可配置;
AudioPolicyManager::routing_strategy 音频路由策略,可以有4种策略;
2.4> SoundTringer
@frameworks/av/services/soundtriger/SoundTriggerHwService.cpp
此模块是音频动态管理服务,本地音频设备动态调整时将产生 uevent 事件,程序根据音频设备变化自动改变音频路由策略。
/* 装载声卡模块
* Load a sound model. Once loaded, recognition of this model can be started and stopped.
* Only one active recognition per model at a time. The SoundTrigger service will handle
* concurrent recognition requests by different users/applications on the same model.
* The implementation returns a unique handle used by other functions (unload_sound_model(),
* start_recognition(), etc...
*/
virtual int loadSoundModel(struct sound_trigger_sound_model *sound_model,
sound_model_callback_t callback,
void *cookie,
sound_model_handle_t *handle);
/*
* Unload a sound model. A sound model can be unloaded to make room for a new one to overcome
* implementation limitations.
*/
virtual int unloadSoundModel(sound_model_handle_t handle);
void convertTriggerPhraseToHal(
ISoundTriggerHw::Phrase *halTriggerPhrase,
const struct sound_trigger_phrase *triggerPhrase);
ISoundTriggerHw::SoundModel *convertSoundModelToHal(
const struct sound_trigger_sound_model *soundModel);
三、audio HAL 硬件抽象层接口
3.1> Android 对 Audio HAL 的框架定义
@ hardware/rockchip/audio/tinyalsa_hal/aduio_hw.cpp
rk3288 实现的 tinyalsa 接口实例代码如下:
//#define LOG_NDEBUG 0
#define LOG_TAG "AudioHardwareTiny"
#include "alsa_audio.h"
#include "audio_hw.h"
#include "audio_hw_hdmi.h"
#include 此代码是 rockchip 实现 tinyalsa_hal 源码,此库会在 AudioPolicyManager.cpp 源码中调用并装载至 AudioFlinger 封装对象中。
此 tinyalsa_hal 在 audio_hw.h 中包含 #include
audio_hw.cpp 中使用的 open_pcm() 函数就是 libtinyalsa.so 库函数。直接操作linux内核 dev/snd/ 声卡设备。此部分内容是连接
android frameware 与 linux 内核间的衔接点。
3.2> Linux tinyalsa 库部分
extern/tinyalsa/README.MD
tinyalsa: a small library to interface with ALSA in the Linux kernel
此部分通过源码 mixer.c与pcm.c 产生 libtinyalsa.so 库文件,在 tinyalsa_hal 中调用此库,来管理 linux 内核中声卡。
在此查看库接口,就能够分析处库提供功能及多声卡切换相关逻辑。
The aims are:
- Provide a basic pcm and mixer API
- If it’s not absolutely needed, don’t add it to the API
- Avoid supporting complex and unnecessary operations that could be
dealt with at a higher level
在startSource 函数中,如要是播放音乐的话,应用音乐的参数 ,调用 setOutputDevice( ) 配置输出设备,最后配置对应的音量;
在 AudioPolicyManager.cpp 的 setOutputDevice( ) 中过滤当前支持的设备,保存输出设备的类型,开始修改输出的设备类型,
如果没有现成的 patch 新建一个,有现成的则直接获得其索引号,调用 createAudioPatch( ) 创建新的 AudioPatch,
配置输出设备的 patch,并更新监听,调用 setParameters( ) 配置 audio 参数,更新音量。
//> 此处敲黑板了!!!
如我们所知,BluetoothA2DP 与 ALSA 设备并不走同一套接口,因此 Android 的设计者就把ALSA设备接口扔到A2DP接口里面管理了。
这又是如何管理呢?简单来说,就是根据上层传下来的参数 devices,判断 devices 是否是 DEVICE_OUT_BLUETOOTH_A2DP,
如果是则走A2DP接口,如果不是则走ALSA设备接口。 连接: https://blog.csdn.net/tronteng/article/details/8212641
参考链接:
此篇文章是声卡驱动相关知识集合,系统全面介绍 android 声卡。
https://blog.csdn.net/zyuanyun/article/details/59180272
此篇文章是 audio_system、audioService、audioPolicyManagern 内容。
https://blog.csdn.net/zyuanyun/article/details/60890534
此篇文章介绍 audio_patch 框架和功能。
https://ciellee.blog.csdn.net/article/details/102524866