提取图像感兴趣区域
Welcome to the second post in this series where we talk about extracting regions of interest (ROI) from images using OpenCV and Python.
欢迎来到本系列的第二篇文章,我们讨论使用OpenCV和Python从图像中提取感兴趣区域(ROI)。
As a recap, in the first post of this series we went through the steps to extract balls and table edges from an image of a pool table. We used simple OpenCV functions like inRange, findContours, boundingRect, minAreaRect, minEnclosingCircle, circle, HoughLines, line etc to achieve our objective.
回顾一下,在本系列的第一篇文章中,我们完成了从台球桌图像中提取球和桌边的步骤。 我们使用了简单的OpenCV函数(例如inRange,findContours,boundingRect,minAreaRect, minEnclosingCircle,circle,HoughLines,line等)来实现我们的目标。
For beginners in OpenCV, I would recommend to go through that post in order to get familiar with the usage of the above functions.
对于OpenCV初学者,我建议您仔细阅读该文章 ,以熟悉上述功能的用法。
In this post we will look at a somewhat more complex problem and explore some methods which we can use to obtain the desired results.
在这篇文章中,我们将研究一个更为复杂的问题,并探索一些可用于获得所需结果的方法。
Our task today is to extract the desired segments from an image which contains a snapshot of a patients brain activity map. The extracted segments can then be used in numerous applications e.g. in a Machine Learning model which can diagnose any health anomalies.
今天的任务是从包含患者大脑活动图快照的图像中提取所需的片段。 然后,可以将提取的段用于多种应用程序,例如可以诊断任何健康异常的机器学习模型。
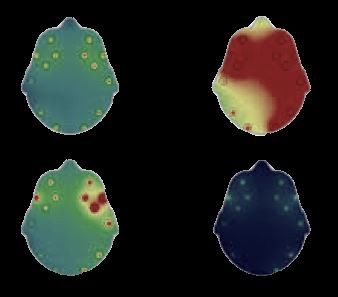
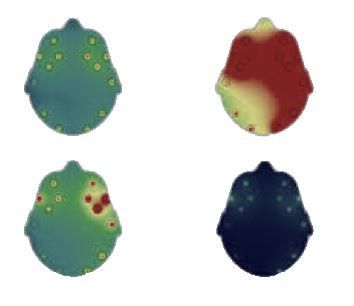
So let us start by looking at the input image itself. It is a typical report generated by medical instruments used in the field of Neurological Science which use sensors to detect signals from a patients brain and display them as colored maps. Typically there are four maps, all of which depict a certain feature and are analyzed together for diagnosis (further details are out of current scope).
因此,让我们从查看输入图像本身开始。 这是由神经科学领域的医疗仪器生成的典型报告,该仪器使用传感器检测来自患者大脑的信号并将其显示为彩色地图。 通常,有四张地图,所有地图都描绘了某个特征并一起分析以进行诊断(更多详细信息不在当前范围内)。
From the above image, we want to extract only the regions corresponding to the four maps (head scans) leaving everything else out. So lets get going.
从上面的图像中,我们只想提取与四个地图(头部扫描)相对应的区域,而将其他所有内容都排除在外。 因此,让我们开始吧。
The first step is detecting the edges of the segments we want to extract. This is a multi step process as mentioned below:
第一步是检测我们要提取的片段的边缘。 这是一个多步骤过程,如下所述:
Convert the RGB image to gray-scale using “cvtColor()”
使用“ cvtColor()”将RGB图像转换为灰度
Remove noise from the gray-scale image by applying a blurring function “GaussianBlur()”
通过应用模糊函数“ GaussianBlur()”来消除灰度图像中的噪声
Finally applying the “Canny()” function to the blurred image to obtain the edges
最后将“ Canny()”函数应用于模糊图像以获得边缘
The output of the edge detection process looks something like this:
边缘检测过程的输出如下所示:
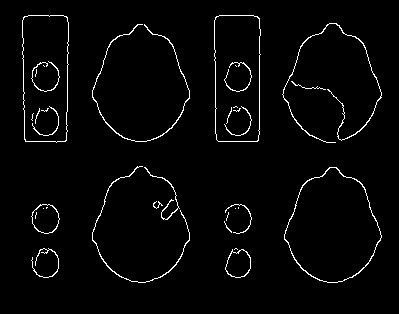
Edge detection output using Canny algorithm (image source author) 使用Canny算法的边缘检测输出(图像源作者)Notice that although the brain map segments are identified, there are a lot of unwanted edges which need to be eliminated and some of the edges have gaps in between which need to be closed.
请注意,尽管已识别出脑图片段,但仍有许多不需要的边缘需要消除,并且某些边缘之间有间隙需要封闭。
A common method applied for such purpose is Morphological Transformation which involves using a succession of dilations and erosions on the image to remove unwanted edges and close gaps.
用于此目的的常用方法是形态转换 ,它涉及在图像上使用一系列的扩张和腐蚀来去除不需要的边缘和闭合间隙。
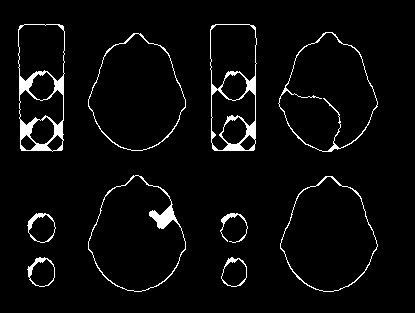
We use OpenCV functions “dilate()” and “erode()” over multiple iterations to get an output as below.
我们通过多次迭代使用OpenCV函数“ dilate()”和“ erode()”来获得如下输出。
Some enhancements in the edges using OpenCV (image source author) 使用OpenCV(图像源作者)对边缘进行了一些增强As you can see, the edges are now complete and much smoother than before.
如您所见,边缘现在已经完成并且比以前光滑得多。
Now we can extract the contours in this image using OpenCV function “findContours()” and select only those contours which have the following properties:
现在,我们可以使用OpenCV函数“ findContours()”提取该图像中的轮廓,并仅选择具有以下属性的轮廓:
- Geometry is circle or oval shaped 几何形状是圆形或椭圆形
- Area is above a certain threshold (the value 7000 works fine for this example). 面积大于某个阈值(在此示例中,值7000可以正常工作)。
For the first part, we will detect the bounding rectangle of each contour using OpenCV “boundingRect()” and check whether the aspect ratio (height to width ratio) is close to 1.
对于第一部分,我们将使用OpenCV“ boundingRect()”检测每个轮廓的边界矩形,并检查纵横比(高宽比)是否接近1。
It may appear that our task is finished but there is a little bit of fine tuning required.
看来我们的任务已经完成,但需要进行一些微调。
It is often the case that multiple overlapping contours are detected over a segment whereas we are interested in only one.
通常情况是在一个片段上检测到多个重叠的轮廓,而我们只对一个感兴趣。
This problem is solved using Non Maxima Suppression, i.e. we look at all overlapping contours and select the one with the maximum area as the final candidate. The logic is pretty straightforward hence we do not need any inbuilt OpenCV or Python functions.
使用非最大抑制可以解决此问题,即,我们查看所有重叠的轮廓,然后选择面积最大的轮廓作为最终候选轮廓。 逻辑非常简单,因此我们不需要任何内置的OpenCV或Python函数。
Another important logic is to identify the four segments separately i.e. Top-Left, Top-Right, Bottom-Left and Bottom-Right.
另一个重要的逻辑是分别识别四个段,即左上,右上,左下和右下。
This is also pretty straightforward and involves identifying the image center coordinates as well as the centroid of each of our detected segments. Centroid detection of a segment contour requires applying the OpenCV “moments()” function on the contour and then calculating the center X, Y coordinates using the formula below: center_x, center_y = (int(M[“m10”] / M[“m00”]), int(M[“m01”] / M[“m00”]))
这也非常简单,涉及识别图像中心坐标以及每个检测到的片段的质心。 对段轮廓进行质心检测需要在轮廓上应用OpenCV “ moments()”函数,然后使用以下公式计算中心 X,Y坐标: center_x,center_y =(int(M [“ m10”] / M [” m00”]),int(M [“ m01”] / M [“ m00”]))
Comparing the segment centroid coordinates with the image center coordinates lets us place the four segments in their respective positions.
将线段质心坐标与图像中心坐标进行比较,可以将四个线段放置在各自的位置。
Now that we have the four segments identified, we need to build the image mask which will allow us to pull out the desired features from the original image.
现在我们已经确定了四个部分,我们需要构建图像蒙版,这将使我们能够从原始图像中提取所需的特征。
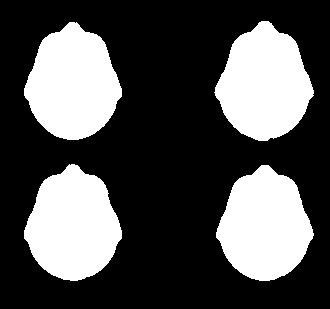
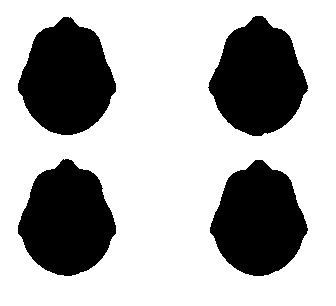
We will use the OpenCV function “drawContours()” using color as White (R,G,B=255,2555,255) and thickness as FILLED (-1) to draw all four segment contours over a black background. The result looks like below:
我们将使用OpenCV函数“ drawContours()”,将颜色用作白色(R,G,B = 255,2555,255),将厚度用作FILLED(-1)在黑色背景上绘制所有四个线段轮廓。 结果如下所示:
Mask for extracting our ROIs (image source author) 用于提取我们的ROI的蒙版(图像来源作者)Applying this mask on the original image gets us the desired segments over a background of our choice (e.g. Black or White).
在原始图像上应用此蒙版可以在我们选择的背景(例如黑色或白色)上为我们提供所需的分段。
For a black background we create a black canvas and then draw upon it using the OpenCV function “bitwise_and()” with the previously obtained mask.
对于黑色背景,我们创建一个黑色画布,然后使用OpenCV函数“ bitwise_and()”以及先前获得的蒙版在其上进行绘制。
Extracted ROIs over a black background (image source author) 在黑色背景上提取的ROI(图像源作者)For a white background we first create a white canvas and then create a color inverted mask as below by drawing contours with OpenCV function “drawContours()” in black color (R,G,B = 0,0,0) and thickness as FILLED (-1).
对于白色背景,我们首先创建一个白色画布,然后通过使用OpenCV函数“ drawContours()”绘制轮廓为黑色(R,G,B = 0,0,0)并且厚度为FILLED的颜色,如下所示创建颜色反转的蒙版(-1)。
An alternative Inverted mask for ROI extraction (image source author) 用于ROI提取的备用倒置掩模(图像源作者)We then add this inverted mask with the previously obtained black background using OpenCV “add()” function and achieve the same result but with white background.
然后,我们使用OpenCV “ add()”函数将此反向蒙版添加到先前获得的黑色背景中,并获得相同的结果,但使用白色背景。
Extracted ROIs over a white background (image source author) 在白色背景上提取的ROI(图像源作者)This concludes the current post in which we looked at few methods using which we can easily extract regions of interest from images.
到此为止,我们在当前文章中总结了几种方法,可以轻松地从图像中提取感兴趣区域。
It should be noted that the methods used above may undergo modifications in case of other images with varying complexity. However the basics discussed above would lay the groundwork for any advanced techniques that may be required to solve such problems.
应当注意,在具有变化的复杂度的其他图像的情况下,上面使用的方法可以进行修改。 但是,以上讨论的基础将为解决此类问题所需的任何高级技术奠定基础。
翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/extracting-regions-of-interest-from-images-dacfd05a41ba
提取图像感兴趣区域