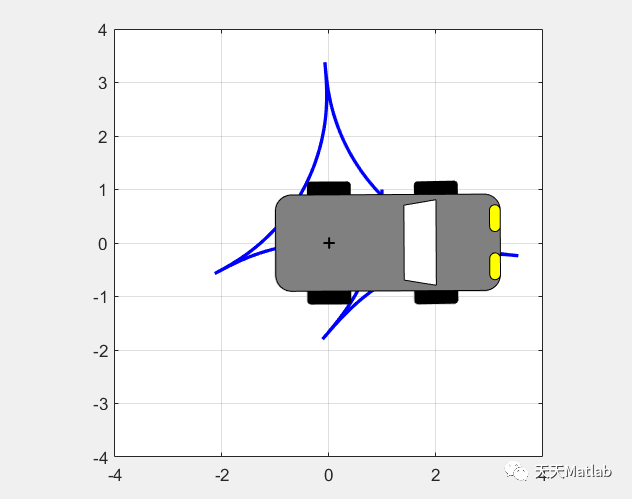
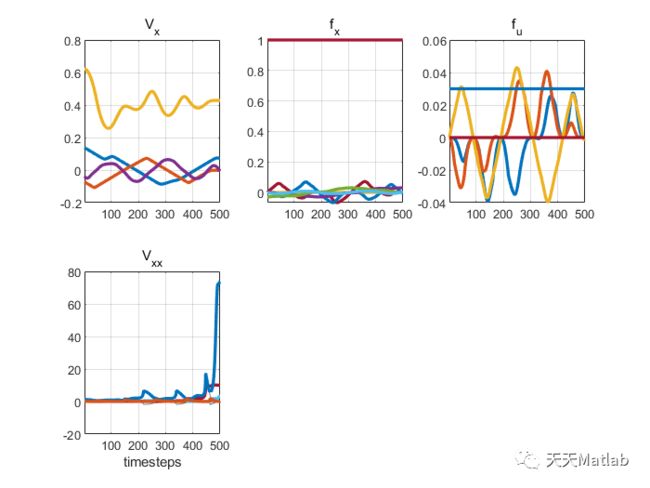
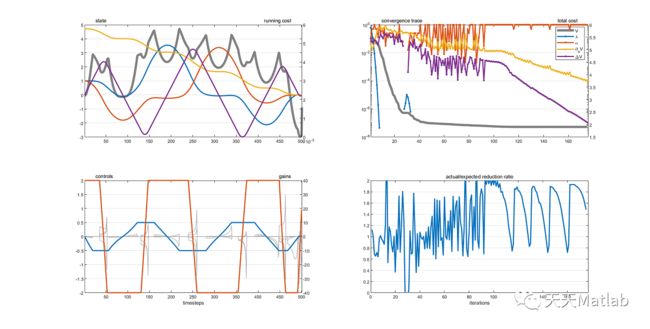
【车辆动力】基于Matlab模拟停车动力学
✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击
智能优化算法 神经网络预测 雷达通信 无线传感器
信号处理 图像处理 路径规划 元胞自动机 无人机 电力系统
⛄ 内容介绍
对影响汽车行驶安全的各方面因素进行了较为深入的分析和研究,建立停车动力学数学模型;该汽车数学模型不需引入很多的人为假设;.利用MATLAB语言开发了一个模块化的仿真软件,该软件能够满足所建模型的校验和在特殊工况下的仿真研究;也可以进一步完善该软件使之服务于汽车运行的其他方面的仿真研究.
⛄ 部分代码
function [x,result,Hfree,free,trace] = boxQP(H,g,lower,upper,x0,options)
% Minimize 0.5*x'*H*x + x'*g s.t. lower<=x<=upper
%
% inputs:
% H - positive definite matrix (n * n)
% g - bias vector (n)
% lower - lower bounds (n)
% upper - upper bounds (n)
%
% optional inputs:
% x0 - initial state (n)
% options - see below (7)
%
% outputs:
% x - solution (n)
% result - result type (roughly, higher is better, see below)
% Hfree - subspace cholesky factor (n_free * n_free)
% free - set of free dimensions (n)
if nargin==0
demoQP(); % run the built-in demo
return;
end
n = size(H,1);
clamped = false(n,1);
free = true(n,1);
oldvalue = 0;
result = 0;
gnorm = 0;
nfactor = 0;
trace = [];
Hfree = zeros(n);
clamp = @(x) max(lower, min(upper, x));
% initial state
if nargin > 4 && numel(x0)==n
x = clamp(x0(:));
else
LU = [lower upper];
LU(~isfinite(LU)) = nan;
x = nanmean(LU,2);
end
x(~isfinite(x)) = 0;
% options
if nargin > 5
options = num2cell(options(:));
[maxIter, minGrad, minRelImprove, stepDec, minStep, Armijo, print] = deal(options{:});
else % defaults
maxIter = 100; % maximum number of iterations
minGrad = 1e-8; % minimum norm of non-fixed gradient
minRelImprove = 1e-8; % minimum relative improvement
stepDec = 0.6; % factor for decreasing stepsize
minStep = 1e-22; % minimal stepsize for linesearch
Armijo = 0.1; % Armijo parameter (fraction of linear improvement required)
print = 0; % verbosity
end
% initial objective value
value = x'*g + 0.5*x'*H*x;
if print > 0
fprintf('==========\nStarting box-QP, dimension %-3d, initial value: %-12.3f\n',n, value);
end
% main loop
for iter = 1:maxIter
if result ~=0
break;
end
% check relative improvement
if( iter>1 && (oldvalue - value) < minRelImprove*abs(oldvalue) )
result = 4;
break;
end
oldvalue = value;
% get gradient
grad = g + H*x;
% find clamped dimensions
old_clamped = clamped;
clamped = false(n,1);
clamped((x == lower)&(grad>0)) = true;
clamped((x == upper)&(grad<0)) = true;
free = ~clamped;
% check for all clamped
if all(clamped)
result = 6;
break;
end
% factorize if clamped has changed
if iter == 1
factorize = true;
else
factorize = any(old_clamped ~= clamped);
end
if factorize
[Hfree, indef] = chol(H(free,free));
if indef
result = -1;
break
end
nfactor = nfactor + 1;
end
% check gradient norm
gnorm = norm(grad(free));
if gnorm < minGrad
result = 5;
break;
end
% get search direction
grad_clamped = g + H*(x.*clamped);
search = zeros(n,1);
search(free) = -Hfree\(Hfree'\grad_clamped(free)) - x(free);
% check for descent direction
sdotg = sum(search.*grad);
if sdotg >= 0 % (should not happen)
break
end
% armijo linesearch
step = 1;
nstep = 0;
xc = clamp(x+step*search);
vc = xc'*g + 0.5*xc'*H*xc;
while (vc - oldvalue)/(step*sdotg) < Armijo
step = step*stepDec;
nstep = nstep+1;
xc = clamp(x+step*search);
vc = xc'*g + 0.5*xc'*H*xc;
if step result = 2; break end end if print > 1 fprintf('iter %-3d value % -9.5g |g| %-9.3g reduction %-9.3g linesearch %g^%-2d n_clamped %d\n', ... iter, vc, gnorm, oldvalue-vc, stepDec, nstep, sum(clamped)); end if nargout > 4 trace(iter).x = x; %#ok<*AGROW> trace(iter).xc = xc; trace(iter).value = value; trace(iter).search = search; trace(iter).clamped = clamped; trace(iter).nfactor = nfactor; end % accept candidate x = xc; value = vc; end if iter >= maxIter result = 1; end results = { 'Hessian is not positive definite',... % result = -1 'No descent direction found',... % result = 0 SHOULD NOT OCCUR 'Maximum main iterations exceeded',... % result = 1 'Maximum line-search iterations exceeded',... % result = 2 'No bounds, returning Newton point',... % result = 3 'Improvement smaller than tolerance',... % result = 4 'Gradient norm smaller than tolerance',... % result = 5 'All dimensions are clamped'}; % result = 6 if print > 0 fprintf('RESULT: %s.\niterations %d gradient %-12.6g final value %-12.6g factorizations %d\n',... results{result+2}, iter, gnorm, value, nfactor); end function demoQP() options = [100 1e-8 1e-8 0.6 1e-22 0.1 2]; % defaults with detailed printing n = 500; g = randn(n,1); H = randn(n,n); H = H*H'; lower = -ones(n,1); upper = ones(n,1); tic boxQP(H, g, lower, upper, randn(n,1), options); toc [1]张勇, 殷承良, 熊伟威. 基于Matlab的车辆动力学控制交互式硬件在环仿真系统研究[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2006, 25(7):4. [2]郑战光, 汪兆亮, 王佳祥,等. 基于matlab的汽车动力学仿真计算[J]. 装备制造技术, 2015(11):3. ❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除 ❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
⛄ Matlab代码关注