python计算iou以及nms
python计算iou以及nms
iou
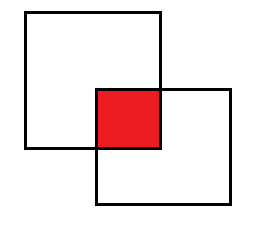
iou即交并比,如下图所示:
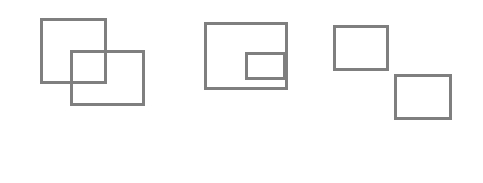
就是拿两个矩形的交集/并集,我们设交集为inner_area,矩形1面积为area1,矩形1面积为area2,则对应iou为inner_area/(area1+area2-inner_area) ,而两个矩形的面积很好计算,这里关键是计算两个矩形的交集,因为这个交集可能的情况有多种,比如:
具体可以参考这篇文章 https://blog.csdn.net/u014061630/article/details/82818112 ,所以我们如果写代码,则要对应很多个if-else,显然不优美,所以考虑能不能找到一个更加泛化的式子来表示,所以这里就先用了一个线段来演示:
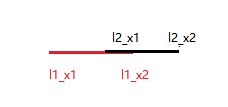
我们可以看到线段l1和线段l2会有一个交,这个交我们可以用以下式子表示:
inner_x1 = max(l1_x1,l2_x1)
inner_x2 = min(l1_x2,l2_x2)
inner_l = max((inner_x2 - inner_x1),0)
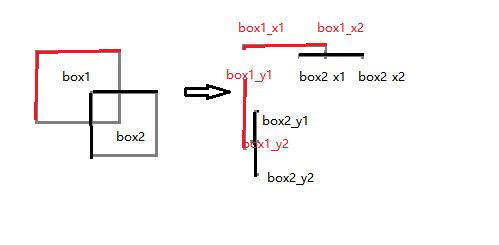
因为线段比较简单,所以我们可以分析得到上面的式子能够将所有情况概括。而矩形是由多个线段组成,所以很自然的将上述公式扩展到矩形上面,我们可以将矩形看作下面的情况:
可以看出我们把矩形变成了两个线段,而线段的交我们上面是计算过的,所以对于矩形而言,我们可以用下面的式子表示,其中x1,y1,x2,y2代表左上角和右下角的坐标:
inner_x1 = max(box1_x1,box2_x1)
inner_x2 = min(box1_x2,box2_x2)
w = max((inner_x2 - inner_x1),0)
inner_y1 = max(box1_y1,box2_y1)
inner_y2 = min(box1_y2,box2_y2)
h = max((inner_y2 - inner_y1),0)
上面的inner_x1,inner_y1,inner_x2,inner_y2 代表的是交的左上角和右下角坐标,通过上面的式子,我们得到inner_area = w*h,并且涵盖了所有情况。
对应代码如下:
def iou(box1, box2):
'''
box:[x1, y1, x2, y2]
'''
in_h = min(box1[3], box2[3]) - max(box1[1], box2[1])
in_w = min(box1[2], box2[2]) - max(box1[0], box2[0])
inner = 0 if in_h<0 or in_w<0 else in_h*in_w
union = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1]) + \
(box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1]) - inner
print(inner)
iou = inner / union
return iou
box1 = [0,0,10,10]
box2 = [5,5,15,15]
print(iou(box1,box2))
nms
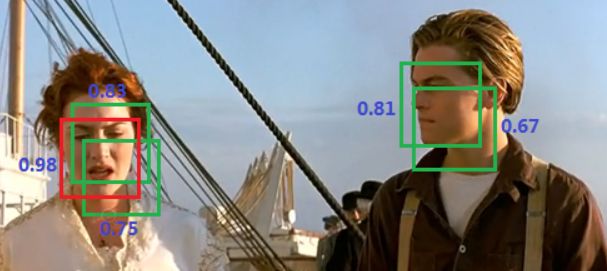
nms是非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression, NMS),也就是将那些不是最大值的给抑制下去,比如下面图片:
ross面部有很多框,但是我们最终只保留得分最大的,对于jack也是一样,但是目前有一个难点,我们程序接受的是这个图片里面的所有框,但是我们并不知道每个框代表是谁,所以这里就用到iou了,我们将iou的值比较大的就归于同一个物体,这样我们只需要计算iou即可。
nms算法的流程如下:
- 1.我们先将所有候选框的置信度排序,因为我们最终是要最大的
- 2.将置信度最大的加入到最终的返回值中
- 3.将其他的候选框和当前的最大的那个计算iou
- 4.如果iou大于一个阈值,则可删除(说明和置信度大的那个是重叠的)
- 5.将剩下的框重复以上过程
里面的iou计算上面已经提到过了,这里因为使用numpy,所以一次计算多个,所以剩下的就是选框,删框。
对应的代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
# x1 y1 x2 y2 score
boxes=np.array([[100,100,210,210,0.72],
[250,250,420,420,0.8],
[220,220,320,330,0.92],
[100,100,210,210,0.72],
[230,240,325,330,0.81],
[220,230,315,340,0.9]])
def nms(bboxes,threshold):
# 计算所有候选框面积,为了iou做准备(因为numpy可以一次算多个,所以这里一次算完)
x1 = bboxes[:, 0]
y1 = bboxes[:, 1]
x2 = bboxes[:, 2]
y2 = bboxes[:, 3]
score = bboxes[:, 4]
areas =(x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) # areas.shape [6,]
# 对置信度进行排序, argsort最终得到的是对应index, 默认从小到大排序,所以最后一个是最大(-1
order = np.argsort(score)
keep = [] # 返回值
while order.size > 0:
# 将当前置信度最大的框加入返回值列表中 对应的1 2步
index = order[-1]
keep.append(index)
# 对应第3步 计算其他框和当前选定的框的iou,因为这里数据类型是np,所以一次是计算的多个
inner_x1 = np.maximum(x1[index], x1[order[:-1]])
inner_x2 = np.minimum(x2[index], x2[order[:-1]])
inner_y1 = np.maximum(y1[index], y1[order[:-1]])
inner_y2 = np.minimum(y2[index], y2[order[:-1]])
in_w = np.maximum(0.0, inner_x2 - inner_x1 + 1)
in_h = np.maximum(0.0, inner_y2 - inner_y1 + 1)
inner = in_w * in_h
# 利用相交的面积和两个框自身的面积计算框的交并比, 将交并比大于阈值的框删除 对应第4步
ratio = inner / (areas[index] + areas[order[:-1]] - inner)
left = np.where(ratio < threshold) # left里面对应的就是
order = order[left] # 将所有
return keep
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_bbox(dets, c='k'):
x1 = dets[:,0]
y1 = dets[:,1]
x2 = dets[:,2]
y2 = dets[:,3]
plt.plot([x1,x2], [y1,y1], c)
plt.plot([x1,x1], [y1,y2], c)
plt.plot([x1,x2], [y2,y2], c)
plt.plot([x2,x2], [y1,y2], c)
plt.title(" nms")
plt.figure(1)
ax1 = plt.subplot(1,2,1)
ax2 = plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.sca(ax1)
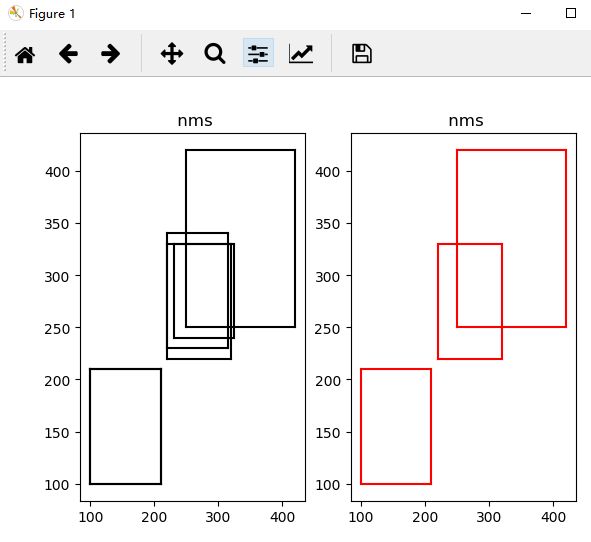
plot_bbox(boxes,'k') # before nms
keep = nms(boxes,0.7)
plt.sca(ax2)
plot_bbox(boxes[keep], 'r')# after nm
plt.show()
代码数据来源于https://blog.csdn.net/a1103688841/article/details/89711120 最后效果如下:
因为用python可能速度比较慢, 而在目标检测中这个算法又是比较耗时的,所以一般都是用c直接写,或者cuda。可以参考https://hellozhaozheng.github.io/z_post/%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA%E8%A7%86%E8%A7%89-NMS-Implementation/
#include
#include
#include
struct Bbox {
int x1;
int y1;
int x2;
int y2;
float score;
Bbox(int x1_, int y1_, int x2_, int y2_, float s):
x1(x1_), y1(y1_), x2(x2_), y2(y2_), score(s) {};
};
float iou(Bbox box1, Bbox box2) {
float area1 = (box1.x2 - box1.x1 + 1) * (box1.y2 - box1.y1 + 1);
float area2 = (box2.x2 - box2.x1 + 1) * (box2.y2 - box2.y1 + 1);
int x11 = std::max(box1.x1, box2.x1);
int y11 = std::max(box1.y1, box2.y1);
int x22 = std::min(box1.x2, box2.x2);
int y22 = std::min(box1.y2, box2.y2);
float intersection = (x22 - x11 + 1) * (y22 - y11 + 1);
return intersection / (area1 + area2 - intersection);
}
std::vector nms(std::vector &vecBbox, float threshold) {
auto cmpScore = [](Bbox box1, Bbox box2) {
return box1.score < box2.score; // 升序排列, 令score最大的box在vector末端
};
std::sort(vecBbox.begin(), vecBbox.end(), cmpScore);
std::vector pickedBbox;
while (vecBbox.size() > 0) {
pickedBbox.emplace_back(vecBbox.back());
vecBbox.pop_back();
for (size_t i = 0; i < vecBbox.size(); i++) {
if (iou(pickedBbox.back(), vecBbox[i]) >= threshold) {
vecBbox.erase(vecBbox.begin() + i);
}
}
}
return pickedBbox;
}