C++调用Python(Yolov5)
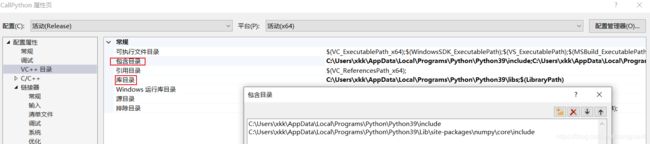
首先在VS中【项目】-【属性】进行环境配置:
1、【VC++目录】-【包含目录】加入python安装目录的include路径:C:\你的路径\Python\Python39\include
(代码中用到了numpy,所以同时加上numpy的include路径:C:\你的路径\Python\Python39\Lib\site-packages\numpy\core\include)
2、【VC++目录】-【库目录】加入python安装目录的libs路径:C:\你的路径\Python\Python39\libs
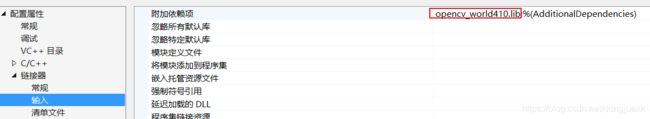
3、【链接器】-【输入】-【附加依赖项】加入库名:
python39.lib(Release模式下)
python39_d.lib(Debug模式下,如果没有此文件,复制python39.lib重命名为python39_d.lib)
项目中用C++调用yolov5,将图片直接传给函数,返回结果值。
C++
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int initNumpy()
{
//该宏Debug下编译不通过,python3.7需要将python-include路径下"object.h"文件中第56行"#define Py_TRACE_REFS"注释掉;
//python3.9需要将python-include路径下"pyconfig.h"文件中第316行"#define Py_DEBUG"注释掉
import_array();
return 1;
}
int main()
{
Py_SetPythonHome(L"D:/Anaconda/envs/py3/envs/yolov5");//安装的Python路径
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('F:/Yolov5/')");//要执行的Python文件路径
initNumpy();
//检查初始化是否成功
if (!Py_IsInitialized())
return 0;
/*直接执行Python脚本文件
wchar_t *argv[2];
argv[0] = L"python";
argv[1] = L"F:/Yolov5/test.py";
Py_Main(2, argv);
*/
PyObject * pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("detect001"); //detect001:要执行的Python文件名
PyObject * pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "detect"); //detect:Python文件中的函数名
PyObject *pReturn = NULL;
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("./source.jpg"); //图片作为参数传入Python
if (img.empty())
return 0;
PyObject *ArgList = PyTuple_New(1);//储存Python参数,参数个数为1
int x = img.size().width;
int y = img.size().height;
int z = img.channels();
uchar *CArrays = new uchar[x*y*z];//这一行申请的内存需要释放指针,否则存在内存泄漏的问题
int iChannels = img.channels();
int iRows = img.rows;
int iCols = img.cols * iChannels;
if (img.isContinuous())
{
iCols *= iRows;
iRows = 1;
}
uchar* p;
int id = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < iRows; i++)
{
// get the pointer to the ith row
p = img.ptr(i);
// operates on each pixel
for (int j = 0; j < iCols; j++)
CArrays[++id] = p[j];//连续空间
}
npy_intp Dims[3] = { y, x, z };
PyObject *PyArray = PyArray_SimpleNewFromData(3, Dims, NPY_UBYTE, CArrays);
PyTuple_SetItem(ArgList, 0, PyArray);//图片数据PyArray加入到ArgList的0位
pReturn = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, ArgList); //调用Python中detect(imgdata)函数
/*pReturn返回类型为tuple:5,其中array大小为n x 7
(221, 222, 222, 222, array([[ 2, 6112.1, 480, ..., 0.793, 0, 1],
[ 1026, 531.91, 1505, ..., 0.78835, 0, 3],
[ 2, 5348.8, 481, ..., 0.7863, 0, 1],
...,
[ 512, 5304.8, 994, ..., 0.46315, 0, 2],
[ 772, 2652.3, 994, ..., 0.46234, 0, 2],
[ 357, 5304.2, 483, ..., 0.45566, 0, 1]]))
*/
PyObject *pInt0 = PyTuple_GetItem(pReturn, 0);
PyObject *pInt1 = PyTuple_GetItem(pReturn, 1);
PyObject *pInt2 = PyTuple_GetItem(pReturn, 2);
PyObject *pInt3 = PyTuple_GetItem(pReturn, 3);
PyObject *pNdarray4 = PyTuple_GetItem(pReturn, 4);
//Python array 转C++
PyArrayIterObject *pIter = (PyArrayIterObject *)PyArray_IterNew(pNdarray4);
vector >ArrayVec4(pIter->size);
vector tmpVec(7);
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (pIter->index < pIter->size) {
tmpVec[i++ % 7] = *(double *)pIter->dataptr;
if (i % 7 == 0)
ArrayVec4[j++] = tmpVec;
PyArray_ITER_NEXT(pIter);
}
//Python int 转C++
int result;
PyArg_Parse(pInt0, "i", &result);
cout << "-------------------------" << result << "-------------------------" << endl;
PyArg_Parse(pInt1, "i", &result);
cout << "-------------------------" << result << "-------------------------" << endl;
PyArg_Parse(pInt2, "i", &result);
cout << "-------------------------" << result << "-------------------------" << endl;
PyArg_Parse(pInt3, "i", &result);
cout << "-------------------------" << result << "-------------------------" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < pIter->size / 7; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++)
cout << "----------array---------------" << ArrayVec4[i][j] << "-------------array------------" << endl;
}
delete[]CArrays;
CArrays = nullptr;
Py_Finalize();
system("pause");
return 0;
} Python
def detect(imgdata):
# cv2.imwrite("source.jpg",imgdata)
opt = argparse.Namespace()
opt.agnostic_nms = False
opt.augment = False
opt.classes = None
opt.conf_thres = 0.3
opt.device = ''
.
.
.