READING NOTE: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation using Part Affinity Fields
TITLE: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation using Part Affinity Fields
AUTHOR: Zhe Cao, Tomas Simon, Shih-En Wei, Yaser Sheikh
ASSOCIATION: CMU
FROM: arXiv:1611.08050
CONTRIBUTIONS
- a method for multi-person pose estimation is proposed that approaches the problem in a bottom-up manner to maintain realtime performance and robustness to early commitment, but utilizes global contextual information in the detection of parts and their association.
- Part Affinity Fields (PAFs), a set of 2D vector fields, is presented, each of which encode the location and orientation of a particular limb at each position in the image domain.
METHOD
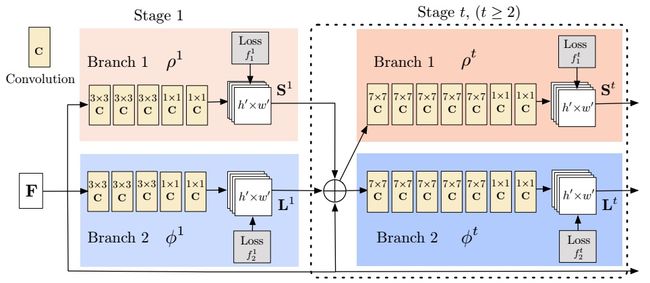
This work is the successor of Convolutional Pose Machines. The network structure, which predict the part emergence heatmap and part aafinity field jointly, is illustrated in the following figure. We can compare it with previous work.
Similar with previous work, the network works as sequence learning scheme. One of the branch predicts confidence maps for part detection, while the other one predicts part affinity fields for part association.
Confidence Maps for Part Detection
At each location P , the value of the confidence S∗j(P) for a part type j is defined as
It means that for every type of part, a heatmap is predicted with multiple highlight areas, indicating the emergence of a part instance.
Part Affinity Fields for Part Association
If we consider a single limb, let xj1,k and xj2,k be the position of body parts j1 and j2 from the limb class c for a person k on the image. lc,k=∥xj2,k−xj1,k∥2 is the length of the limb, and v=l−1c,k(xj2,k−xj1,k) is the unit vector in the direction of the limb. The ideal part affinity vector field, L∗c,k , at an image point P as
Similar to confidence maps for part detection, part affinity fields are also predicted for all persons
where np is the number of non-zero vectos at point P . The confidence score of each limb candidate is measured by
where dj1 and dj2 are two detected body parts.
Multi-Person Parsing using PAFs
The last problem is to select different limbs linked in PAFs to combine as one person’s skeleton. This is a classical generalized maximum clique problem. I think in additional to the method mentioned in this paper, many other optimiaztion algorithms can be tried. These algorithms are well discussed in multi-object tracking problem.