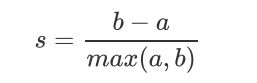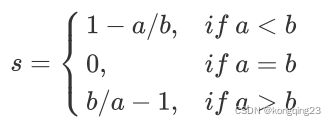机器学习sklearn-KNN
目录
1 概述
2 sklearn中的聚类算法
2.1 聚类算法的模型评估指标
2.2 重要参数init & random_state & n_init 初始化质心
2.3 重要参数max_iter & tol:让迭代停下来
3 Kmeans做矢量量化
1 概述
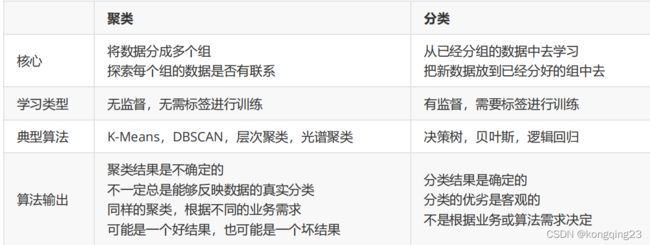
机器学习当中,有相当一部分算法属于“ 无监督学习 ” ,无监督的算法在训练的时候只需要特征矩阵 X ,不需要标签。 PCA 降维算法就是无监督学习中的一种,聚类算法,也是无监督学习的代表算法之一。
聚类算法又叫做 “ 无监督分类 ” ,其目的是将数据划分成有意义或有用的组(或簇)。这种划分可以基于我们的业务 需求或建模需求来完成,也可以单纯地帮助我们探索数据的自然结构和分布。
KMeans 算法将一组 N 个样本的特征矩阵 X 划分为 K 个无交集的簇,直观上来看是簇是一组一组聚集在一起的数据,在一个簇中的数据就认为是同一类。簇就是聚类的结果表现。
簇中所有数据的均值通常被称为这个簇的 “ 质心 ” ( centroids )。在一个二维平面中,一簇数据点的质心的横坐标就是这一簇数据点的横坐标的均值,质心的纵坐标就是这一簇数据点的纵坐标的均值。同理可推广至高维空间。
2 sklearn中的聚类算法
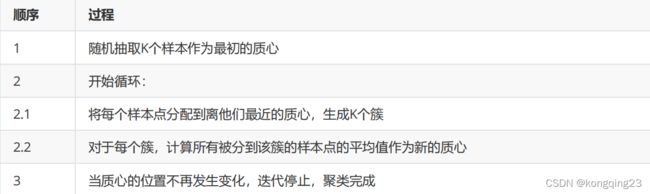
在 KMeans 算法中,簇的个数 K 是一个超参数,需要我们人为输入来确定。 KMeans 的核心任务就是根据我们设定好的K ,找出 K 个最优的质心,并将离这些质心最近的数据分别分配到这些质心代表的簇中去。
那什么情况下,质心的位置会不再变化呢?当我们找到一个质心,在每次迭代中被分配到这个质心上的样本都是一致的,即每次新生成的簇都是一致的,所有的样本点都不会再从一个簇转移到另一个簇,质心就不会变化了。
我们认为, 被分在同一个簇中的数据是有相似性的,而 不同簇中的数据是不同的 ,当聚类完毕之后,我们就要分别去研究每个簇中的样本都有什么样的性质,从而根据业务需求制定不同的商业或者科技策略。
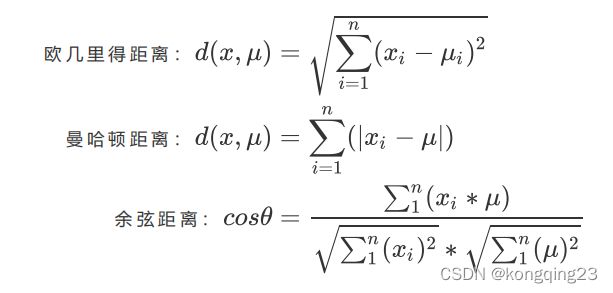
我们追求“ 簇内差异小,簇外差异大” 。而这个 “ 差异 “ ,由 样本点到其所在簇的质心的距离 来衡量。
对于一个簇来说,所有样本点到质心的距离之和越小,我们就认为这个簇中的样本越相似,簇内差异就越小。而距离的衡量方法有多种,令 表示簇中的一个样本点, 表示该簇中的质心,n 表示每个样本点中的特征数目, i 表示组成点 的每个特征,则该样本点到质心的距离可以由以下距离来度量:
如我们采用欧几里得距离,则一个簇中所有样本点到质心的距离的平方和为:
其中, m 为一个簇中样本的个数, j 是每个样本的编号。这个公式被称为 簇内平方和 ( cluster Sum of Square ),又叫做Inertia 。而将一个数据集中的所有簇的簇内平方和相加,就得到了整体平方和( Total Cluster Sum of Square),又叫做 total inertia 。 Total Inertia 越小,代表着每个簇内样本越相似,聚类的效果就越好。 因此 KMeans 追求的是,求解能够让 Inertia 最小化的质心 。实际上,在质心不断变化不断迭代的过程中,总体平方和是越来越小的。我们可以使用数学来证明,当整体平方和最小的时候,质心就不再发生变化了。如此,K-Means 的求解过程,就变成了一个最优化问题。
损失函数本质是用来衡量模型的拟合效果的,只有有着求解参数需求的算法,才会有损失函数。Kmeans 不求解什么参数,它的模型本质也没有在拟合数据,而是在对数据进行一种探索。
K-Means 不存在什么损失函数,Inertia 更像是 Kmeans 的模型评估指标,而非损失函数。
重要参数 n_clusters
n_clusters是 KMeans 中的 k ,表示着我们告诉模型我们要分几类。这是 KMeans 当中唯一一个必填的参数,默认为 8类,但通常我们的聚类结果会是一个小于8 的结果。通常,在开始聚类之前,我们并不知道 n_clusters 究竟是多少,因此我们要对它进行探索。
kmeans之前的数据分布。
进行kmeans之后数据分布
2.1 聚类算法的模型评估指标
KMeans 的目标是确保 “ 簇内差异小,簇外差异大 ” ,我们就可以通过 衡量簇内差异来衡量聚类的效
果 。我们刚才说过, Inertia 是用距离来衡量簇内差异的指标,因此,我们是否可以使用 Inertia 来作为聚类的衡量指标呢?Inertia 越小模型越好嘛。
可以,但是这个指标的缺点和极限太大。
首先,它不是有界的。我们只知道, Inertia 是越小越好,是 0 最好,但我们不知道,一个较小的 Inertia 究竟有没有达到模型的极限,能否继续提高。
第二,它的计算太容易受到特征数目的影响,数据维度很大的时候, Inertia 的计算量会陷入维度诅咒之中,计算量会爆炸,不适合用来一次次评估模型。
第三,它会受到超参数 K 的影响,在我们之前的常识中其实我们已经发现,随着 K 越大, Inertia 注定会越来越小,但这并不代表模型的效果越来越好了。
第四, Inertia 对数据的分布有假设,它假设数据满足凸分布(即数据在二维平面图像上看起来是一个凸函数的样子),并且它假设数据是各向同性的(isotropic ),即是说数据的属性在不同方向上代表着相同的含义。但是现实中的数据往往不是这样。所以使用Inertia 作为评估指标,会让聚类算法在一些细长簇,环形簇,或者不规则形状的流形时表现不佳。
如果我们有样本真实聚类情况的数据,我们可以对于聚类算法的结果和真实结果来衡量聚类的效果。常用的有以下三种方法:
在 99% 的情况下,我们是对没有真实标签的数据进行探索,也就是对不知道真正答案的数据进行聚类。这样的聚类,是完全依赖于评价簇内的稠密程度(簇内差异小)和簇间的离散程度(簇外差异大)来评估聚类的效果。其中轮廓系数是最常用的聚类算法的评价指标。它是对每个样本来定义的,它能够同时衡量:
1 )样本与其自身所在的簇中的其他样本的相似度 a ,等于样本与同一簇中所有其他点之间的平均距离
2 )样本与其他簇中的样本的相似度 b ,等于样本与下一个最近的簇中的所有点之间的平均距离
根据聚类的要求 ” 簇内差异小,簇外差异大 “ ,我们希望 b 永远大于 a ,并且大得越多越好。
单个样本的轮廓系数计算为
很容易理解轮廓系数范围是 (-1,1) ,其中值越接近 1 表示样本与自己所在的簇中的样本很相似,并且与其他簇中的样本不相似,当样本点与簇外的样本更相似的时候,轮廓系数就为负。当轮廓系数为0 时,则代表两个簇中的样本相似度一致,两个簇本应该是一个簇。可以总结为轮廓系数越接近于1越好,负数则表示聚类效果非常差。
如果一个簇中的大多数样本具有比较高的轮廓系数,则簇会有较高的总轮廓系数,则整个数据集的平均轮廓系数越高,则聚类是合适的。如果许多样本点具有低轮廓系数甚至负值,则聚类是不合适的,聚类的超参数K 可能设定得太大或者太小。
在 sklearn 中,我们使用模块 metrics 中的类 silhouette_score 来计算轮廓系数,它返回的是一个数据集中所有样本的轮廓系数的均值。但我们还有同在metrics 模块中的 silhouette_sample ,它的参数与轮廓系数一致,但返回的是数据集中每个样本自己的轮廓系数。
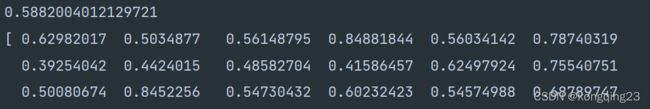
查看当前轮廓系数。
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score #所有样本轮廓系数均值
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_samples #每一个样本的轮廓系数
#自己创建数据集
X,y=make_blobs(n_samples=500,n_features=2,centers=4,random_state=1)#规定randomstate是让数据稳定
#基于这个分布进行聚类
#kmeans 并不需要建立模型或预测结果 只需要fit就可以得到聚类结果
#kmeans 有接口predict和fit_predict 表示学习数据X并对X的类别进行预测
#但得到结果后一般不调用predict 直接fit之后调用熟悉labels_一模一样
#一般当数据量大时,才使用predict
n_cluster=3
cluster=KMeans(n_clusters=n_cluster,random_state=1).fit(X)
#查看聚好的类别 每个样本对应的类
y_pred=cluster.labels_
#查看质心
centroid=cluster.cluster_centers_
#查看总距离平方和
inertia=cluster.inertia_
# print(centroid)
# print(inertia)
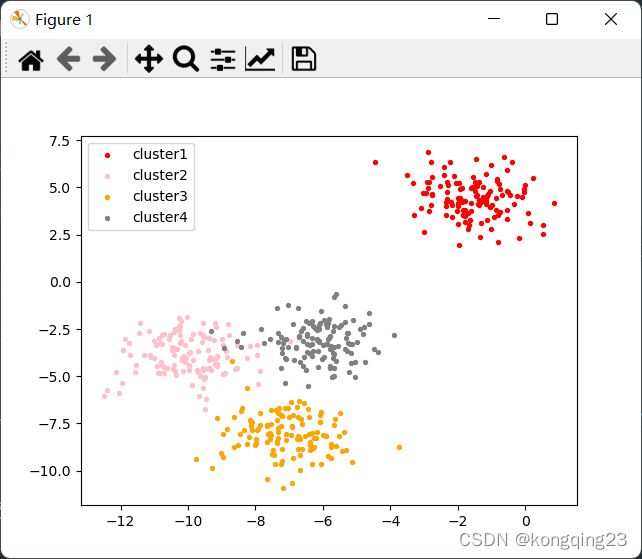
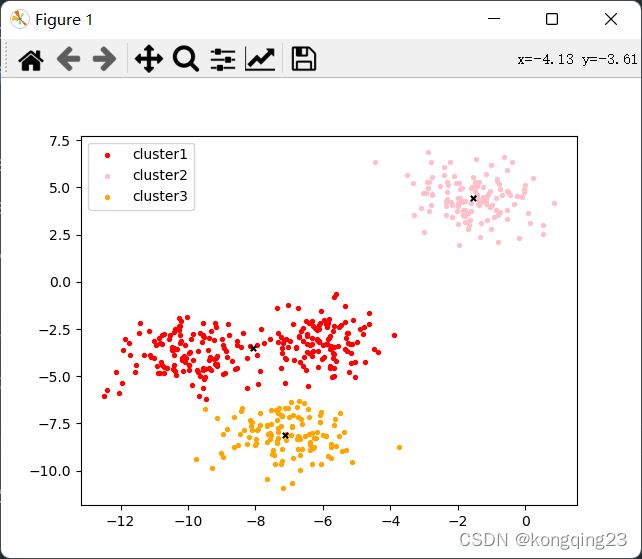
color = ["red","pink","orange"]
label=['cluster1','cluster2','cluster3']
fig,ax1=plt.subplots(1)
for i in range(len(color)):
ax1.scatter(X[y_pred==i,0],X[y_pred==i,1],
marker='o',#点的形状
s=8,#点的大小
label=label[i],
c=color[i])
#画出质心
ax1.scatter(centroid[:,0],centroid[:,1],
marker='x',s=15,c='black')
plt.legend(loc=0)
# plt.show()
#查看轮廓系数
print(silhouette_score(X,y_pred))
print(silhouette_samples(X,y_pred))
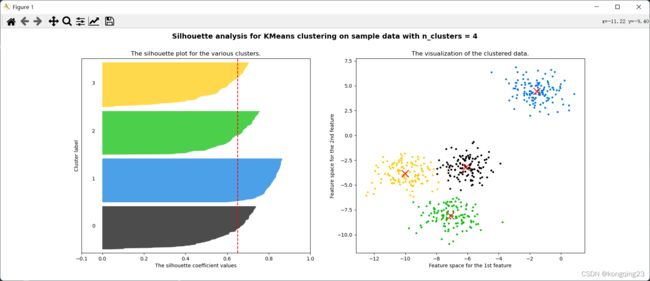
分析n_cluster=4时,分簇效果
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score #所有样本轮廓系数均值
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_samples #每一个样本的轮廓系数
"""
基于轮廓系数调整n_cluster
求每一个聚出来的类的轮廓系数
各个类之间轮廓系数的对比
聚类后图像的分布情况
绘制学习曲线
"""
#创建数据
X,y=make_blobs(n_samples=500,n_features=2,centers=4,random_state=1)#规定randomstate是让数据稳定
n_clusters=4
fig,(ax1,ax2)=plt.subplots(1,2)
fig.set_size_inches(18,7)#设置画布尺寸
#第一个图是轮廓系数图像(横向条形图) 横坐标为轮廓系数 纵坐标为每一个样本
ax1.set_xlim([-0.1,1])#设置轮廓系数范围
ax1.set_ylim([0,X.shape[0]+(n_clusters+1)*10])#加上后面的数是为了显示时有一定的间隔
clusterer=KMeans(n_clusters=n_clusters,random_state=10).fit(X)
cluster_labels=clusterer.labels_ #聚类后每一个样本对应的类
silhouette_avg = silhouette_score(X, cluster_labels)#平均轮廓系数
print("For n_clusters ={} The average silhouette_score is :{}".format(n_clusters, silhouette_avg))
#每个样本的轮廓系数 用作横坐标
sample_silhouette_values = silhouette_samples(X, cluster_labels)
y_lower=10 #设置y轴初始取值 避免贴着x轴开始画图
#对每一个簇进行循环
for i in range(n_clusters):
#从每个样本的轮廓系数取出第i个簇的轮廓系数
ith_cluster_silhouette_values = sample_silhouette_values[cluster_labels == i]
ith_cluster_silhouette_values.sort()
size_cluster_i=ith_cluster_silhouette_values.shape[0] #查看这个簇里有多少样本
y_upper=y_lower+size_cluster_i #这个簇在y轴的上界
color=cm.nipy_spectral(float(i)/n_clusters) #输入任意一个浮点数 会返回该浮点数对应的函数 保证不同簇的颜色不同
#fill_between是一个让范围中的柱状图都统一颜色的函数
#fill_betweenx的范围在纵坐标上 fill_betweeny的范围在横坐标上
#fill_betweenx 纵坐标下限 纵坐标上限 x取值 颜色
ax1.fill_betweenx(np.arange(y_lower,y_upper),
ith_cluster_silhouette_values,
facecolor=color,
alpha=0.7
)
#为每个簇的轮廓系数写上编号 并让编号显示在中间位置
ax1.text(-0.05,
y_lower + 0.5 * size_cluster_i
, str(i))
#更新y_lower 保证每一个簇直接存在间隔
y_lower = y_upper + 10
ax1.set_title("The silhouette plot for the various clusters.")
ax1.set_xlabel("The silhouette coefficient values")
ax1.set_ylabel("Cluster label")
#把轮廓系数均值用虚线形式放入图中
ax1.axvline(x=silhouette_avg, color="red", linestyle="--")
ax1.set_yticks([])
ax1.set_xticks([-0.1, 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1])
#画第二个图
colors = cm.nipy_spectral(cluster_labels.astype(float) / n_clusters)#利用分簇结果取n_clusters个颜色
centers = clusterer.cluster_centers_
ax2.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1],marker='o',s=8,c=colors)#画分簇图
ax2.scatter(centers[:, 0], centers[:, 1], marker='x',c="red", alpha=1, s=200) #画质心
ax2.set_title("The visualization of the clustered data.")
ax2.set_xlabel("Feature space for the 1st feature")
ax2.set_ylabel("Feature space for the 2nd feature")
#设置整张图片标题
plt.suptitle(("Silhouette analysis for KMeans clustering on sample data "
"with n_clusters = {}".format(n_clusters)),
fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
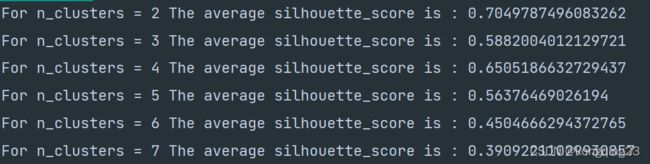
plt.show()包装成循环之后查看n_cluster取不同值下的轮廓系数,并以图片形式显示。
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.metrics import silhouette_samples, silhouette_score
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import numpy as np
#自己创建数据集
X,y=make_blobs(n_samples=500,n_features=2,centers=4,random_state=1)#规定randomstate是让数据稳定
for n_clusters in [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]:
n_clusters = n_clusters
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
fig.set_size_inches(18, 7)
ax1.set_xlim([-0.1, 1])
ax1.set_ylim([0, X.shape[0] + (n_clusters + 1) * 10])
clusterer = KMeans(n_clusters=n_clusters, random_state=10).fit(X)
cluster_labels = clusterer.labels_
silhouette_avg = silhouette_score(X, cluster_labels)
print("For n_clusters =", n_clusters,
"The average silhouette_score is :", silhouette_avg)
sample_silhouette_values = silhouette_samples(X, cluster_labels)
y_lower = 10
for i in range(n_clusters):
ith_cluster_silhouette_values = sample_silhouette_values[cluster_labels == i]
ith_cluster_silhouette_values.sort()
size_cluster_i = ith_cluster_silhouette_values.shape[0]
y_upper = y_lower + size_cluster_i
color = cm.nipy_spectral(float(i) / n_clusters)
ax1.fill_betweenx(np.arange(y_lower, y_upper)
, ith_cluster_silhouette_values
, facecolor=color
, alpha=0.7
)
ax1.text(-0.05
, y_lower + 0.5 * size_cluster_i
, str(i))
y_lower = y_upper + 10
ax1.set_title("The silhouette plot for the various clusters.")
ax1.set_xlabel("The silhouette coefficient values")
ax1.set_ylabel("Cluster label")
ax1.axvline(x=silhouette_avg, color="red", linestyle="--")
ax1.set_yticks([])
ax1.set_xticks([-0.1, 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1])
colors = cm.nipy_spectral(cluster_labels.astype(float) / n_clusters)
ax2.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1]
, marker='o'
, s=8
, c=colors
)
centers = clusterer.cluster_centers_
# Draw white circles at cluster centers
ax2.scatter(centers[:, 0], centers[:, 1], marker='x',
c="red", alpha=1, s=200)
ax2.set_title("The visualization of the clustered data.")
ax2.set_xlabel("Feature space for the 1st feature")
ax2.set_ylabel("Feature space for the 2nd feature")
plt.suptitle(("Silhouette analysis for KMeans clustering on sample data "
"with n_clusters = %d" % n_clusters),
fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.show()2.2 重要参数init & random_state & n_init 初始化质心
在 K-Means 中有一个重要的环节,就是放置初始质心。如果有足够的时间, K-means 一定会收敛,但 Inertia 可能收敛到局部最小值。是否能够收敛到真正的最小值很大程度上取决于质心的初始化。init 就是用来帮助我们决定初始化方式的参数。
init :可输入 "k-means++" , "random" 或者一个 n 维数组。这是初始化质心的方法,默认 "k-means++" 。输入 "k-means++":一种为 K 均值聚类选择初始聚类中心的聪明的办法,以加速收敛。如果输入了 n 维数组,数组的形状应该是(n_clusters , n_features) 并给出初始质心。
random_state :控制每次质心随机初始化的随机数种子。
n_init :整数,默认 10 ,使用不同的质心随机初始化的种子来运行 k-means 算法的次数。最终结果会是基于 Inertia来计算的n_init 次连续运行后的最佳输出。
2.3 重要参数max_iter & tol:让迭代停下来
当质心不再移动, Kmeans 算法就会停下来。但在完全收敛之前,我们也可以使用max_iter ,最大迭代次数,或者 tol ,两次迭代间 Inertia 下降的量,这两个参数来让迭代提前停下来。有时候,当我们的n_clusters 选择不符合数据的自然分布,或者我们为了业务需求,必须要填入与数据的自然分布不合的n_clusters ,提前让迭代停下来反而能够提升模型的表现。
max_iter :整数,默认 300 ,单次运行的 k-means 算法的最大迭代次数。
tol :浮点数,默认 1e-4 ,两次迭代间 Inertia 下降的量,如果两次迭代之间 Inertia 下降的值小于 tol 所设定的值,迭代就会停下。
一般在模型数据比较大的时候,平时使用默认值就好。
3 Kmeans做矢量量化
K-Means 聚类最重要的应用之一是非结构数据(图像,声音)上的矢量量化( VQ )。非结构化数据往往占用比较 多的储存空间,文件本身也会比较大,运算非常缓慢,我们希望能够在保证数据质量的前提下,尽量地缩小非结构化数据的大小,或者简化非结构化数据的结构。矢量量化就可以帮助我们实现这个目的。KMeans 聚类的矢量量化本质是一种降维运用,但它与我们之前学过的任何一种降维算法的思路都不相同。特征选择的降维是直接选取对模型贡献最大的特征,PCA 的降维是聚合信息,而 矢量量化的降维是在同等样本量上压缩信息的大小 ,即不改变特征的数目也不改变样本的数目,只改变在这些特征下的样本上的信息量。
用 K-Means 聚类中获得的质心来替代原有的数据,可以把数据上的信息量压缩到非常小,但又不损失太多信息。我们接下来就通过一张图图片的矢量量化来看一看K-Means 如何实现压缩数据大小,却不损失太多信息量。
图像探索完毕,我们了解了,图像现在有 9W 多种颜色。我们希望来试试看,能否使用 K-Means 将颜色压缩到 64种,还不严重损耗图像的质量。为此,我们要使用K-Means 来将 9W 种颜色聚类成 64 类,然后使用 64 个簇的质心来替代全部的9W 种颜色,记得质心有着这样的性质:簇中的点都是离质心最近的样本点。
我们需要随机选取64个样本点作为随机质心,计算原数据中每个样本到它们的距离来找出离每个样本最近的随机质心,然后用每个样本所对应的随机质心来替换原本的样本。两种状况下,我们观察图像可视化之后的状况,以查看图片信息的损失。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.metrics import pairwise_distances_argmin #对两个序列中的点进行距离匹配的函数
from sklearn.datasets import load_sample_image #导入图片数据的库
from sklearn.utils import shuffle #打乱有序序列
#导入数据
china = load_sample_image("china.jpg")
# print(china.shape)
newimage = china.reshape((427 * 640,3))
# print(newimage.shape)
color_num=pd.DataFrame(newimage).drop_duplicates().shape
# print(color_num)
#图片可视化 imshow必须导入三维图片
# plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
# plt.imshow(china)
# plt.show()
n_clusters = 64
#plt.imshow在浮点数上表现很好 将china的数据归一化为浮点数
china = np.array(china, dtype=np.float64) / china.max()
#把图像格式转换为矩阵格式
w, h, d = original_shape = tuple(china.shape) #取出长 宽 通道数
assert d==3 #确保d=3 即3通道
image_array=np.reshape(china,(w*h,d))# 第一个参数为改变结构的对象 第二个参数为改变后的结构
#对数据进行矢量量化 此时数据量较大 先抽取一部分数据来进行拟合 再让全数据按照拟合出来的质心进行聚类
image_array_sample = shuffle(image_array, random_state=0)[:1000]#随机抽1000个质心
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=n_clusters, random_state=0).fit(image_array_sample)
labels = kmeans.predict(image_array)#按照找出的质心对所有数据进行聚类
image_kmeans = image_array.copy()#拷贝 避免破坏原有数据
#用64个质心代替所有数据
for i in range(w*h):
image_kmeans[i] = kmeans.cluster_centers_[labels[i]]
#还原为imshow可以使用的形式
# print(pd.DataFrame(image_kmeans).drop_duplicates().shape) #查看替换是否成功
image_kmeans = image_kmeans.reshape(w,h,d)
#随机选取64个质心
centroid_random = shuffle(image_array, random_state=0)[:n_clusters]
#计算第二个参数每一个样本到第一个参数每一个样本的距离 返回第一个参数中距离第二个参数最近的index 形状和第二个参数一致
labels_random = pairwise_distances_argmin(centroid_random,image_array,axis=0)
image_random = image_array.copy()
for i in range(w*h):
image_random[i] = centroid_random[labels_random[i]]
image_random = image_random.reshape(w,h,d)
fig,(ax1,ax2,ax3)=plt.subplots(1,3)
fig.set_size_inches(18, 7)
ax1.axis('off')
ax1.set_title('Original image (96,615 colors)')
ax1.imshow(china)
ax2.axis('off')
ax2.set_title('Quantized image (64 colors, K-Means)')
ax2.imshow(image_kmeans)
ax3.axis('off')
ax3.set_title('Quantized image (64 colors, Random)')
ax3.imshow(image_random)
plt.show()