李沐-深度学习 第七章-AlexNet代码
现代卷积网络主要模型:
1. AlexNet 第一个在大规模视觉竞赛中击败传统计算机视觉模型的大型神经网络
2. 使用重复块的网络(VCG) 利用许多重复的神经网络块
3. 网络中的网络(NiN) 重复使用由卷积层和1x1卷积层来构建深层网络
4. 含并行连结的网络(GoogLeNet) 使用并行连结的网络,通过不同窗口大小的卷积层和最大汇聚层来并行抽取信息
5. 残差网络(ResNet) 通过残差块构建跨层的数据通道,是计算机视觉中最流行的体系架构
6. 稠密连接网络(DenseNet) 计算成本高,但效果很好
AlexNet进步之处:
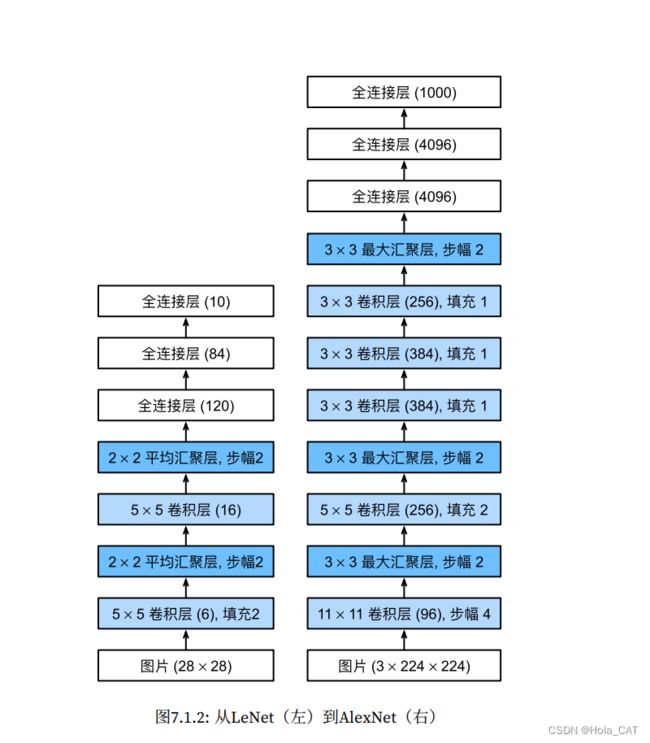
AlexNet由⼋层组成:五个卷积层、两个全连接隐藏层和⼀个全连接输出层。其次,AlexNet使⽤ReLU⽽不 是sigmoid作为其激活函数
LeNet与AlexNet架构:
#AlexNet
from audioop import lin2adpcm
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
#容量控制和预处理
net = nn.Sequential(
#使用11x11的更大窗口来捕捉对象,同时步幅为4,以减少输出高度和宽度,输出通道数目远大于LeNet
nn.Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
#减少卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使输入与输出高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
#使用三个连续的卷积层和较小的卷积窗口,除了最后的卷积层,输出通道数量进一步增强,在前两个卷积层之后,汇聚层不用减少输入的高度和宽度
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Flatten(), #将数据拉伸成一维
#全连接层的输出数量是LeNet中的好几倍,用dropout层来减轻过拟合
nn.Linear(6400, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
#输出层,使用的Fashion-MNIST,所以类别数为10
nn.Linear(4096, 10)
)
x = torch.randn(1, 1, 224, 224)
for layer in net:
x = layer(x)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t', x.shape)
#读取数据集
'''使用的Fashion-MNIST数据,但Fashion-MNIST图像分辨率(28x28)低于ImageNet图像,所以将其增加到224x224'''
batch_size = 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
#训练AlexNet
lr, num_epochs = 0.01, 10 #比LeNet使用更小学习率是因为AlexNet网络更深更广,图像分辨率更高,训练更昂贵
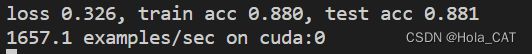
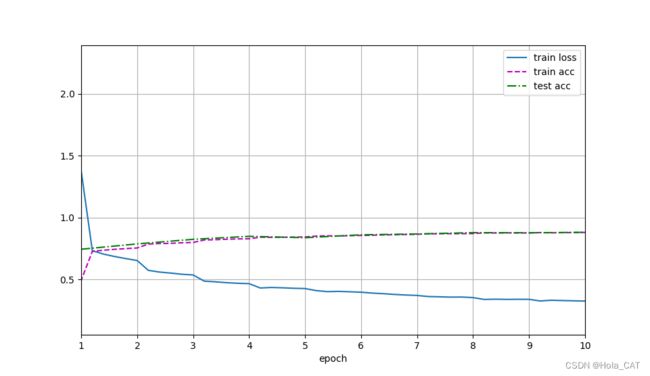
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())
d2l.plt.show()运行结果: