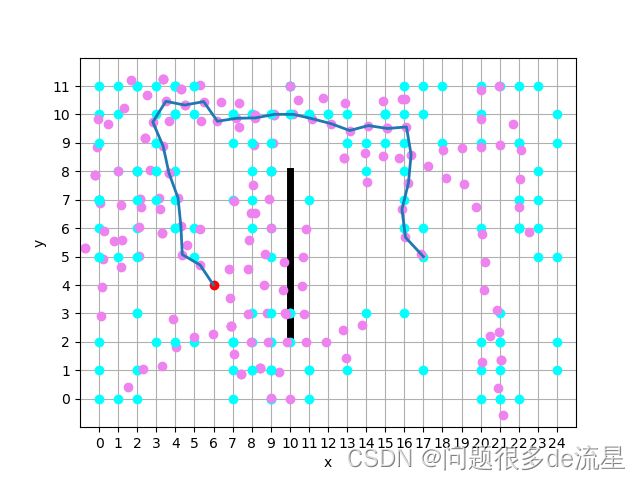
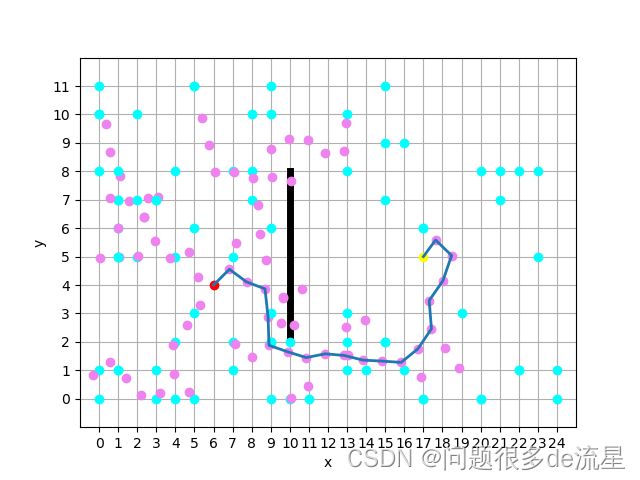
RRT与RRT*算法具体步骤与程序详解(python)
提示:前面写了A*、Dijkstra算法
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、RRT的原理与步骤
- 二、RRT算法编写的步骤
-
- 1.算法步骤
- 2.算法的实现
- 三、RRT*算法编写的步骤
-
- 1.算法的步骤
- 2.算法的实现
- 三、所有程序附录
-
- RRT算法
- RRT*算法
前言
RRT和RRT*的区别:
RRT的中文名为快速随机探索树,它的原理很简单,实际上就是维护一棵路径树:从起点开始,在空间中随机采样,并找到路径树上与采样点最接近且能与它无障碍地连接的点,连接这个点与采样点,将采样点加入路径树,直至终点附近区域被探索到。这种方式无法保证得到的路径是最优的。
RRT* 在RRT基础上做了改进,主要是进行了重新选择父节点和重布线的操作。试想在RRT中,我们的采样点最终与整棵树上和它最近的点连了起来,但这未必是最好的选择,我们的最终目的是让这个点与起点的距离尽可能近。RRT* 便对此做了改进,它在采样点加入路径树以后,以其为圆心画了一个小圈,考虑是否有更好的父节点,连到那些节点上能使起点到该点的距离更短(尽管那些节点并不是离采样点最近的点)。如果选择了更加合适的父节点,那么就把它们连接起来,并去除原来的连线(重布线)。
一、RRT的原理与步骤
我的原理启蒙:RRT算法原理图解
根据这篇文章,班门弄斧自己推导一遍这个过程,加强理解:

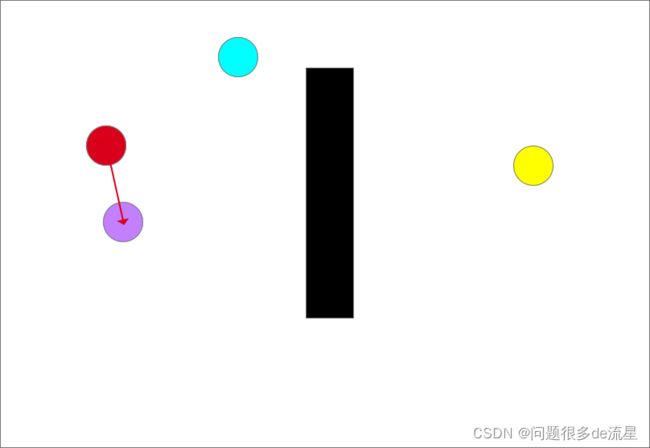
如图所示,红色的圆是起点,黄色的圆是终点,黑色代表障碍物
RRT的原理如下:
- 在空间中随机采样
如图中的蓝色圆,将其作为目标点

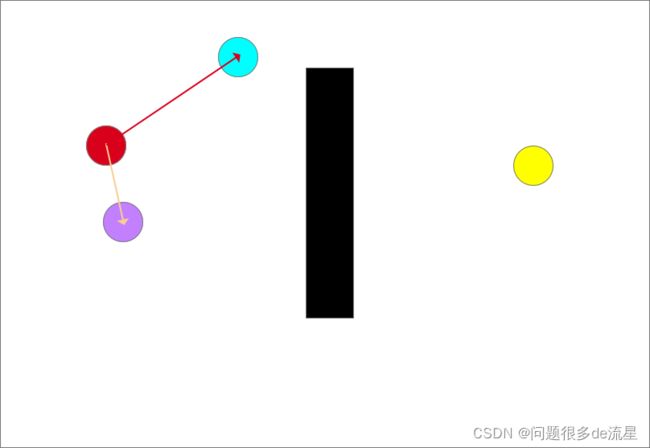
- 确定生长树的生长方向
以刚刚生成的随机点为目标,遍历生长树上的现存节点,计算每个节点到该随机点的距离,筛选出距离最小的节点作为最近点。此时树上仅存在起点(一颗没发芽的种子),所以直接选取起点为最近点。以最近点和随机点的连线为生长方向,如图中红色箭头所示

- 向目标点生长
生长步长是固定的,可由程序决定,但不宜太大也不宜太小,太小的话路径规划时间长,太大则会略过目标点。从此时的最近点也就是起点沿着生长方向生长一个步长得到一个生长点(紫色圆)

- 循环1~2步
随机采样(蓝色圆形)
确定生长树的生长方向,图中共有两个点,红色和紫色圆,离目标点(蓝色)最近的是红色点,以最近点和随机点的连线为生长方向,如图中红色箭头所示
从此时的最近点也就是起点沿着生长方向生长一个步长得到一个生长点(紫色圆)
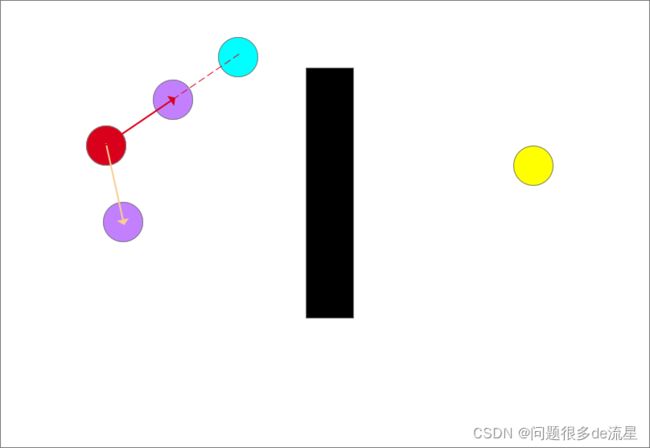
随机采样(蓝色圆形)
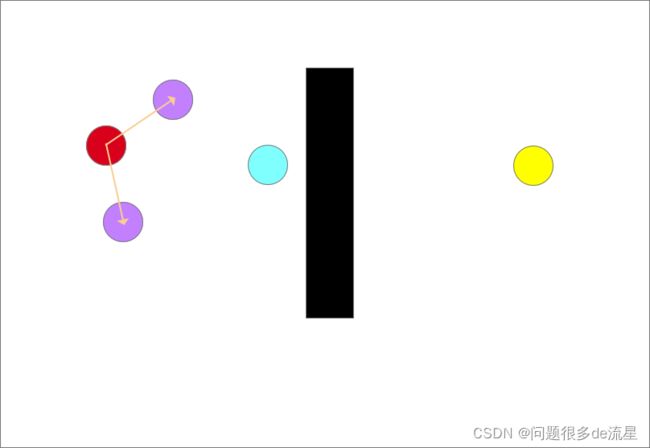
确定生长树的生长方向,以图中离目标点(蓝色)最近的点和随机点的连线为生长方向,如图中红色箭头所示,从此时的最近点也就是起点沿着生长方向生长一个步长得到一个生长点(紫色圆)
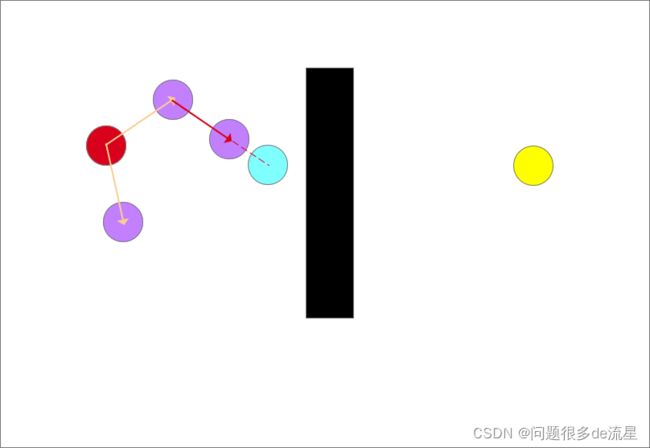
随机采样(蓝色圆形)

确定生长树的生长方向,以图中离目标点(蓝色)最近的点和随机点的连线为生长方向,如图中红色箭头所示

从此时的最近点也就是起点沿着生长方向生长一个步长得到一个生长点(紫色圆),但是生长点都长障碍物里面去了会发生碰撞,生长失败!

剔除该生长节点,此次生长作废,不合格,树不接受。

重复以上的步骤,直到有生长节点进入终点的设定邻域

不断追溯它们的父节点,可找到一条从起点到终点的安全路径。如图中绿色线所示

二、RRT算法编写的步骤
1.算法步骤
- 初始化整个空间,定义初始点、终点、采样点数、点与点之间的步长t等信息
- 在空间中随机产生一个点xrand
- 在已知树的点集合中找到距离这个随机点最近的点xnear
- 在xnear到xrand的直线方向上从xnear以步长t截取点xnew
- 判断从xnear到xnew之间是否存在障碍物,若存在则舍弃该点
- 将new点加入到树集合中
- 循环2~6,循环结束条件:有一个new点在终点的设定邻域内
2.算法的实现
- 初始化整个空间,定义初始点、终点、采样点数、点与点之间的步长t等信息
from math import sqrt
import numpy as np
import random
import itertools
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 初始化整个空间,定义初始点、终点、采样点数、点与点之间的步长t等信息
x_width = 25 # 空间的长度
y_width = 12 # 空间的宽度
error_list = [[0 for i in range(0, x_width)] for j in range(0, y_width)]
error_list[2][10] = 1
error_list[3][10] = 1
error_list[4][10] = 1
error_list[5][10] = 1
error_list[6][10] = 1
error_list[7][10] = 1
error_list[8][10] = 1
x0 = 6 # 定义初始点的x坐标
y0 = 4 # 定义初始点的y坐标
xn = 17 # 定义终点的x坐标
yn = 5 # 定义终点的y坐标
t = 1 # 点与点之间的步长
error_list[y0][x0] = 4
error_list[yn][xn] = 3
error_list = np.array(error_list)
# print(error_list)
plt.figure()
plt.xlim((-1, x_width))
plt.ylim((-1, y_width))
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.xticks(np.arange(x_width))
plt.yticks(np.arange(y_width))
plt.grid()
tree_list = []
tree_list.append([x0, y0, x0, y0]) # 把起点作为树的点放入列表,避免随机点与起点重合
plt.plot(x0, y0, 'ro')
plt.plot(xn, yn, marker='o', color='yellow')
plt.plot([10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10], [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 'k-', linewidth='5')
- 在空间中随机产生一个点xrand,这个点不能在tree_list里面,构建一个函数
# 在空间中随机产生一个点xrand ->这个点不能是起点
def product_rand(tree_list):
x_width = 25 # 空间的长度
y_width = 12 # 空间的宽度
random_point = list(itertools.product(range(0, x_width), range(0, y_width)))
xrand = random.sample(random_point, 1)
xrand = list(xrand[0]) # 将随机点转换成list形式
tree_list = np.array(tree_list)
tree = tree_list[:, 0:2]
while xrand in tree: # 如果随机点在树的点列表里,重新生成随机点
xrand = random.sample(random_point, 1)
xrand = list(xrand[0]) # 将随机点转换成list形式
return xrand
- 在已知树的点集合中找到距离这个随机点最近的点xnear,构建一个函数
# 在已知树的点集合中找到距离这个随机点最近的点xnear
def product_near(tree_list, xrand):
m = np.inf
for i in range(0, len(tree_list)):
if abs(tree_list[i][0] - xrand[0]) + abs(tree_list[i][1] - xrand[1]) < m:
m = abs(tree_list[i][0] - xrand[0]) + abs(tree_list[i][1] - xrand[1])
xnear = [tree_list[i][0], tree_list[i][1]]
return xnear
- 确定方向:在xnear到xrand的直线方向上从xnear以步长t截取点xnew,构建一个函数
def decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t):
z_value = sqrt((xnear[0] - xrand[0]) ** 2 + (xnear[1] - xrand[1]) ** 2) # 斜边长度
cos_value = (xrand[0] - xnear[0]) / z_value
sin_value = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / z_value
xnew = [(xnear[0] + t * cos_value), (xnear[1] + t * sin_value)]
return xnew
- 判断从xnear到xnew之间是否存在障碍物,若存在则舍弃该点
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xnear[0] != xrand[0]:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
else:
y = 0
while 10 <= max(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 10 <= min(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 2 <= y <= 8:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xrand[0] - xnear[0] != 0:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
tree_list.append([xnew[0], xnew[1], xnear[0], xnear[1]])
plt.plot(xrand[0], xrand[1], marker='o', color='cyan')
plt.plot(xnew[0], xnew[1], color='violet', marker='o')
- 循环,循环结束条件:有树节点在终点的设定固定邻域之内
# 循环
while ((xnew[0] - xn) ** 2 + (xnew[1] - yn) ** 2) > 1:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xnear[0] != xrand[0]:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
else:
y = 0
while 10 <= max(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 10 <= min(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 2 <= y <= 8:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xrand[0] - xnear[0] != 0:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
tree_list.append([xnew[0], xnew[1], xnear[0], xnear[1]])
plt.plot(xrand[0], xrand[1], marker='o', color='cyan')
plt.plot(xnew[0], xnew[1], color='violet', marker='o')
- 循环以找到父节点,将这些点保存在routine_list列表中,并可视化
tree_list = np.array(tree_list)
routine_list = [[xn,yn]]
n = len(tree_list)-1
x = tree_list[n,0]
y = tree_list[n,1]
f_x = tree_list[n,2]
f_y = tree_list[n,3]
routine_list.append([x,y])
search_list=[]
while [x0,y0] not in routine_list:
search_list = tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:,0]==f_x) & (tree_list[:,1]==f_y))][0]
search_list = search_list.tolist()
routine_list.append([search_list[0],search_list[1]])
f_x = search_list[2]
f_y = search_list[3]
print(routine_list)
routine_list = np.array(routine_list)
plt.plot(routine_list[:,0], routine_list[:,1], '-', linewidth='2')
plt.show()
三、RRT*算法编写的步骤
RRT算法只能找到一条可行路径,并不能保证找到一条最优路径,RRT* 算法在RRT算法的基础上增加了两步:rewrite和random relink。也就是重写和随机重连。
重写就是在新节点xnew加入到树种之后,重新为它选择父节点,好让它到起始点的路径长度(代价)更小。
随机重连就是在重写完成之后,对新节点xnew附近一定范围内的节点进行重连。重连就是,检查一下如果把xnew附近的这些节点的父节点设置为xnew,这些节点的代价会不会减小。如果能够减小,就把这些节点的父节点更改为xnew;否则,就不更改。RRT* 算法考虑每一个节点到出发点的距离,为此每一个节点会增加一个属性:distance_to_start,即到出发点的距离。相应地在每一个节点选择父节点地时候,新节点的距离等于父节点的距离加上父节点到子节点的直线距离。
1.算法的步骤
在RRT的基础上增加两个功能:
①rewrite重写
遍历整个树,
获得到新节点xnew的距离小于一定阈值(比如1.5倍的步长,也就是1.5*t)的所有节点
将这些节点加入到一个名为candidate_parent_of_newpoint的列表中,
为了方便,这些节点的distance不再用来存储到出发点的距离,而是用来存储如果把该节点设置为xnew的父节点的话,xnew到出发点的距离。
找到candidate_parent_of_newpoint列表中具有最小distance的那个节点,返回他的索引index,将新节点newpoint的父节点设置为index。
②random relink
遍历整个列表,对每一个节点执行如下动作{
if(该节点到xnew的距离小于一定的阈值,比如1.6倍的步长,也就是1.6*t){
if(该节点现在的distance>把该节点的父节点更新为newpoint之后的distance){
把该节点的父节点设置为xnew,并更新该节点的distance值
更新以该节点为根节点的子树中的每个节点的distance。
}
}
2.算法的实现
rewrite(重写):
# rewrite重写
def rewrite(tree_list, t, xnew):
# 遍历整个树
candidate_parent_of_xnew = []
for i in range(0, len(tree_list)):
distance = sqrt((xnew[0] - tree_list[i][0]) ** 2 + (xnew[1] - tree_list[i][1]) ** 2)
# 获得新节点xnew的距离小于一定阈值(比如1.5倍步长,也就是1.5*t)所有节点
if distance < 1.5 * t and (xnew[0] != tree_list[i][0] or xnew[1] != tree_list[i][1]):
distance = tree_list[i][4] + distance
candidate_parent_of_xnew.append([tree_list[i][0], tree_list[i][1], distance])
candidate_parent_of_xnew = np.array(candidate_parent_of_xnew)
# 将这些节点加入到candidate_parent_of_xnew列表中
parent_point = candidate_parent_of_xnew[np.where(candidate_parent_of_xnew[:, 2] == candidate_parent_of_xnew[:, 2].min())]
tree_list.append([xnew[0], xnew[1], parent_point[0][0], parent_point[0][1], parent_point[0][2]])
# 找到candidate_parent_of_xnew列表中具有最小distance的那个节点,将新节点xnew的父节点设置为该节点
return tree_list
random relink:
# random relink
def random_relink(tree_list, t, xnew):
# 遍历整个列表,对每一个节点执行如下动作:
tree_list = np.array(tree_list)
for i in range(0, len(tree_list)):
parent_distance = sqrt((xnew[0] - tree_list[i, 0]) ** 2 + (xnew[1] - tree_list[i, 1]) ** 2)
if parent_distance < 1.6 * t:
child_distance = parent_distance + tree_list[
np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == xnew[0]) & (tree_list[:, 1] == xnew[1])), 4]
if tree_list[i][4] > child_distance:
tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == xnew[0]) & (tree_list[:, 1] == xnew[1])), 2] = xnew[0]
tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == xnew[0]) & (tree_list[:, 1] == xnew[1])), 3] = xnew[1]
tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == xnew[0]) & (tree_list[:, 1] == xnew[1])), 4] = child_distance
for j in range(0, len(tree_list)):
if tree_list[j, 2] == tree_list[i, 0] and tree_list[j, 3] == tree_list[i, 1]:
d = sqrt((tree_list[i, 0] - tree_list[j, 0]) ** 2 + (tree_list[i, 1] - tree_list[j, 1]) ** 2)
tree_list[j, 4] = child_distance + d
return tree_list.tolist()
三、所有程序附录
RRT算法
from math import sqrt
import numpy as np
import random
import itertools
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 初始化整个空间,定义初始点、终点、采样点数、点与点之间的步长t等信息
x_width = 25 # 空间的长度
y_width = 12 # 空间的宽度
error_list = [[0 for i in range(0, x_width)] for j in range(0, y_width)]
error_list[2][10] = 1
error_list[3][10] = 1
error_list[4][10] = 1
error_list[5][10] = 1
error_list[6][10] = 1
error_list[7][10] = 1
error_list[8][10] = 1
x0 = 6 # 定义初始点的x坐标
y0 = 4 # 定义初始点的y坐标
xn = 17 # 定义终点的x坐标
yn = 5 # 定义终点的y坐标
t = 1 # 点与点之间的步长
error_list[y0][x0] = 4
error_list[yn][xn] = 3
error_list = np.array(error_list)
# print(error_list)
plt.figure()
plt.xlim((-1, x_width))
plt.ylim((-1, y_width))
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.xticks(np.arange(x_width))
plt.yticks(np.arange(y_width))
plt.grid()
tree_list = []
tree_list.append([x0, y0, x0, y0]) # 把起点作为树的点放入列表,避免随机点与起点重合
plt.plot(x0, y0, 'ro')
plt.plot(xn, yn, marker='o', color='yellow')
plt.plot([10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10], [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 'k-', linewidth='5')
# 在空间中随机产生一个点xrand ->这个点不能是起点
def product_rand(tree_list):
x_width = 25 # 空间的长度
y_width = 12 # 空间的宽度
random_point = list(itertools.product(range(0, x_width), range(0, y_width)))
xrand = random.sample(random_point, 1)
xrand = list(xrand[0]) # 将随机点转换成list形式
tree_list = np.array(tree_list)
tree = tree_list[:, 0:2]
while xrand in tree: # 如果随机点在树的点列表里,重新生成随机点
xrand = random.sample(random_point, 1)
xrand = list(xrand[0]) # 将随机点转换成list形式
return xrand
# 在已知树的点集合中找到距离这个随机点最近的点xnear
def product_near(tree_list, xrand):
m = np.inf
for i in range(0, len(tree_list)):
if abs(tree_list[i][0] - xrand[0]) + abs(tree_list[i][1] - xrand[1]) < m:
m = abs(tree_list[i][0] - xrand[0]) + abs(tree_list[i][1] - xrand[1])
xnear = [tree_list[i][0], tree_list[i][1]]
return xnear
# 确定方向:在xnear到xrand的直线方向上从xnear以步长t截取点xnew
# tree_list.append(xrand)
def decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t):
z_value = sqrt((xnear[0] - xrand[0]) ** 2 + (xnear[1] - xrand[1]) ** 2) # 斜边长度
cos_value = (xrand[0] - xnear[0]) / z_value
sin_value = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / z_value
xnew = [(xnear[0] + t * cos_value), (xnear[1] + t * sin_value)]
return xnew
# 判断从xnear到xnew之间是否存在障碍物,若存在则舍弃该点
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xnear[0] != xrand[0]:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
else:
y = 0
while 10 <= max(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 10 <= min(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 2 <= y <= 8:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xrand[0] - xnear[0] != 0:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
tree_list.append([xnew[0], xnew[1], xnear[0], xnear[1]])
plt.plot(xrand[0], xrand[1], marker='o', color='cyan')
plt.plot(xnew[0], xnew[1], color='violet', marker='o')
# 循环
while ((xnew[0] - xn) ** 2 + (xnew[1] - yn) ** 2) > 1:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xnear[0] != xrand[0]:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
else:
y = 0
while 10 <= max(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 10 <= min(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 2 <= y <= 8:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xrand[0] - xnear[0] != 0:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
tree_list.append([xnew[0], xnew[1], xnear[0], xnear[1]])
plt.plot(xrand[0], xrand[1], marker='o', color='cyan')
plt.plot(xnew[0], xnew[1], color='violet', marker='o')
tree_list = np.array(tree_list)
routine_list = [[xn,yn]]
n = len(tree_list)-1
x = tree_list[n,0]
y = tree_list[n,1]
f_x = tree_list[n,2]
f_y = tree_list[n,3]
routine_list.append([x,y])
search_list=[]
while [x0,y0] not in routine_list:
search_list = tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:,0]==f_x) & (tree_list[:,1]==f_y))][0]
search_list = search_list.tolist()
routine_list.append([search_list[0],search_list[1]])
f_x = search_list[2]
f_y = search_list[3]
print(routine_list)
routine_list = np.array(routine_list)
plt.plot(routine_list[:,0], routine_list[:,1], '-', linewidth='2')
plt.show()
RRT*算法
from math import sqrt
import numpy as np
import random
import itertools
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 初始化整个空间,定义初始点、终点、采样点数、点与点之间的步长t等信息
x_width = 25 # 空间的长度
y_width = 12 # 空间的宽度
error_list = [[0 for i in range(0, x_width)] for j in range(0, y_width)]
error_list[2][10] = 1
error_list[3][10] = 1
error_list[4][10] = 1
error_list[5][10] = 1
error_list[6][10] = 1
error_list[7][10] = 1
error_list[8][10] = 1
x0 = 6 # 定义初始点的x坐标
y0 = 4 # 定义初始点的y坐标
xn = 17 # 定义终点的x坐标
yn = 5 # 定义终点的y坐标
t = 1 # 点与点之间的步长
error_list[y0][x0] = 4
error_list[yn][xn] = 3
error_list = np.array(error_list)
# print(error_list)
plt.figure()
plt.xlim((-1, x_width))
plt.ylim((-1, y_width))
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.xticks(np.arange(x_width))
plt.yticks(np.arange(y_width))
plt.grid()
tree_list = []
tree_list.append([x0, y0, x0, y0, 0]) # 把起点作为树的点放入列表,避免随机点与起点重合
plt.plot(x0, y0, 'ro')
plt.plot(xn, yn, marker='o', color='yellow')
plt.plot([10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10], [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], 'k-', linewidth='5')
# 在空间中随机产生一个点xrand ->这个点不能是起点
def product_rand(tree_list):
x_width = 25 # 空间的长度
y_width = 12 # 空间的宽度
random_point = list(itertools.product(range(0, x_width), range(0, y_width)))
xrand = random.sample(random_point, 1)
xrand = list(xrand[0]) # 将随机点转换成list形式
tree_list = np.array(tree_list)
tree = tree_list[:, 0:2]
while xrand in tree: # 如果随机点在树的点列表里,重新生成随机点
xrand = random.sample(random_point, 1)
xrand = list(xrand[0]) # 将随机点转换成list形式
return xrand
# 在已知树的点集合中找到距离这个随机点最近的点xnear
def product_near(tree_list, xrand):
m = np.inf
for i in range(0, len(tree_list)):
if abs(tree_list[i][0] - xrand[0]) + abs(tree_list[i][1] - xrand[1]) < m:
m = abs(tree_list[i][0] - xrand[0]) + abs(tree_list[i][1] - xrand[1])
xnear = [tree_list[i][0], tree_list[i][1]]
return xnear
# 确定方向:在xnear到xrand的直线方向上从xnear以步长t截取点xnew
# tree_list.append(xrand)
def decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t):
z_value = sqrt((xnear[0] - xrand[0]) ** 2 + (xnear[1] - xrand[1]) ** 2) # 斜边长度
cos_value = (xrand[0] - xnear[0]) / z_value
sin_value = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / z_value
xnew = [(xnear[0] + t * cos_value), (xnear[1] + t * sin_value)]
return xnew
# 判断从xnear到xnew之间是否存在障碍物,若存在则舍弃该点
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xnear[0] != xrand[0]:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
else:
y = 0
while 10 <= max(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 10 <= min(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 2 <= y <= 8:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xrand[0] - xnear[0] != 0:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
else:
y = 0
tree_list.append([xnew[0], xnew[1], xnear[0], xnear[1], t])
plt.plot(xrand[0], xrand[1], marker='o', color='cyan')
plt.plot(xnew[0], xnew[1], color='violet', marker='o')
# rewrite重写
def rewrite(tree_list, t, xnew):
# 遍历整个树
candidate_parent_of_xnew = []
for i in range(0, len(tree_list)):
distance = sqrt((xnew[0] - tree_list[i][0]) ** 2 + (xnew[1] - tree_list[i][1]) ** 2)
# 获得新节点xnew的距离小于一定阈值(比如1.5倍步长,也就是1.5*t)所有节点
if distance < 1.5 * t and (xnew[0] != tree_list[i][0] or xnew[1] != tree_list[i][1]):
distance = tree_list[i][4] + distance
candidate_parent_of_xnew.append([tree_list[i][0], tree_list[i][1], distance])
candidate_parent_of_xnew = np.array(candidate_parent_of_xnew)
# 将这些节点加入到candidate_parent_of_xnew列表中
parent_point = candidate_parent_of_xnew[np.where(candidate_parent_of_xnew[:, 2] == candidate_parent_of_xnew[:, 2].min())]
tree_list.append([xnew[0], xnew[1], parent_point[0][0], parent_point[0][1], parent_point[0][2]])
# 找到candidate_parent_of_xnew列表中具有最小distance的那个节点,将新节点xnew的父节点设置为该节点
return tree_list
# random relink
def random_relink(tree_list, t, xnew):
# 遍历整个列表,对每一个节点执行如下动作:
tree_list = np.array(tree_list)
for i in range(0, len(tree_list)):
parent_distance = sqrt((xnew[0] - tree_list[i, 0]) ** 2 + (xnew[1] - tree_list[i, 1]) ** 2)
if parent_distance < 1.6 * t:
child_distance = parent_distance + tree_list[
np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == xnew[0]) & (tree_list[:, 1] == xnew[1])), 4]
if tree_list[i][4] > child_distance:
tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == xnew[0]) & (tree_list[:, 1] == xnew[1])), 2] = xnew[0]
tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == xnew[0]) & (tree_list[:, 1] == xnew[1])), 3] = xnew[1]
tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == xnew[0]) & (tree_list[:, 1] == xnew[1])), 4] = child_distance
for j in range(0, len(tree_list)):
if tree_list[j, 2] == tree_list[i, 0] and tree_list[j, 3] == tree_list[i, 1]:
d = sqrt((tree_list[i, 0] - tree_list[j, 0]) ** 2 + (tree_list[i, 1] - tree_list[j, 1]) ** 2)
tree_list[j, 4] = child_distance + d
return tree_list.tolist()
# 循环
while ((xnew[0] - xn) ** 2 + (xnew[1] - yn) ** 2) > 1:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xnear[0] != xrand[0]:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
else:
y = 0
while 10 <= max(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 10 <= min(xnear[0], xnew[0]) and 2 <= y <= 8:
xrand = product_rand(tree_list) # 随机生成点
xnear = product_near(tree_list, xrand)
xnew = decide_direction(xrand, xnear, t)
if xrand[0] - xnear[0] != 0:
k = (xrand[1] - xnear[1]) / (xrand[0] - xnear[0])
y = k * (10 - xnear[0]) + xnear[1]
tree_list = rewrite(tree_list, t, xnew)
tree_list = random_relink(tree_list, t, xnew)
plt.plot(xrand[0], xrand[1], marker='o', color='cyan')
plt.plot(xnew[0], xnew[1], color='violet', marker='o')
tree_list = np.array(tree_list)
routine_list = [[xn, yn]]
n = len(tree_list) - 1
x = tree_list[n, 0]
y = tree_list[n, 1]
f_x = tree_list[n, 2]
f_y = tree_list[n, 3]
routine_list.append([x, y])
search_list = []
while [x0, y0] not in routine_list:
search_list = tree_list[np.where((tree_list[:, 0] == f_x) & (tree_list[:, 1] == f_y))][0]
search_list = search_list.tolist()
routine_list.append([search_list[0], search_list[1]])
f_x = search_list[2]
f_y = search_list[3]
print(routine_list)
routine_list = np.array(routine_list)
plt.plot(routine_list[:, 0], routine_list[:, 1], '-', linewidth='2')
plt.show()