Android Application Programming with OpenCV——识别与跟踪图片
这篇文章按照之前文章的约定,给大家简单解读一下《Android Application Programming with OpenCV》这本书第四章的内容。
这一章主要介绍OpenCV中图像检测算法的应用,通过图像检测、描述和匹配算法,获取最优的匹配对,再计算出单应性矩阵,从而可以准确定位到标志图片在获取的视频帧中的位置,并使用线框将其框选出来,如下图所示:
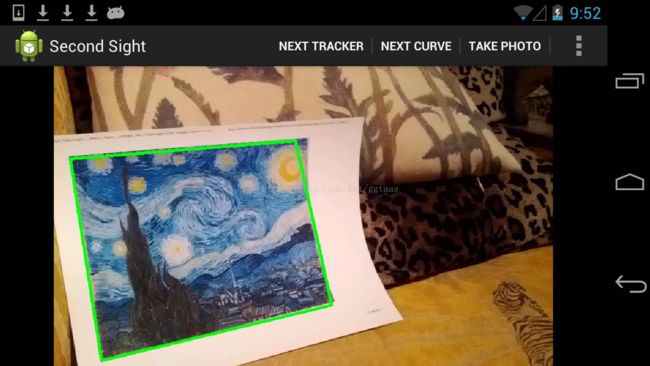
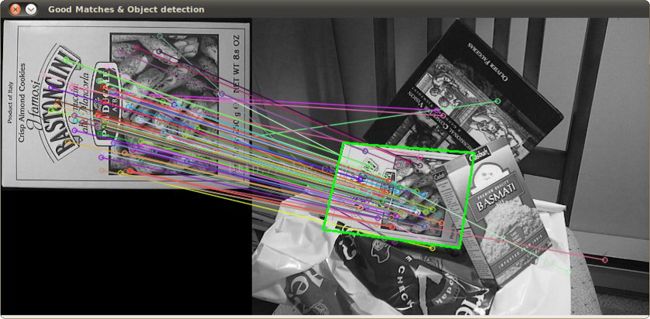
下面这个图是在opencv官方教程feature 2d module中的sample,和本书所讲的内容很相似。一个是在Android系统环境下实现,一个是使用C++实现,但是其中的算法思想是一致。我之前写得方法是使用NDK编程,可以参考官方教程编写C++程序,然后使用NDK编译出动态链接库so文件,再使用JNI在java层对其调用,实现算法。而本书有个特点就是,在Android系统下实现的该算法并没有使用NDK编程,完全利用OpenCV4Android提供函数库进行编写(纯java),这个也是吸引我学习这本书的地方之一吧。
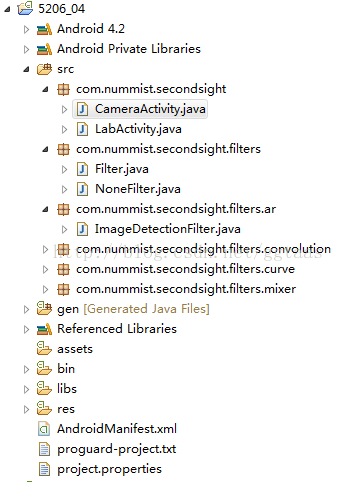
主要看我展开的包中的内容,第一个包是程序的入口,第二包是Filter的接口类,实现这个接口需要复写apply方法。第三个包是实现AR的filter的配置和实现。
其中CameraActivity为程序主类,有OpenCV4Android的接口的标准化调用方法,Filter的实例化。
privateBaseLoaderCallbackmLoaderCallback =
new BaseLoaderCallback(this) {
@Override
publicvoid onManagerConnected(finalint status) {
switch (status) {
case LoaderCallbackInterface.SUCCESS:
Log.d(TAG,"OpenCV loaded successfully");
mCameraView.enableView();
mBgr =new Mat();
final Filter starryNight;
try {
//设定过滤器以及模版图片
starryNight =new ImageDetectionFilter(
CameraActivity.this,
R.drawable.starry_night);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"Failed to load drawable: " +
"starry_night");
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
……(省略其他filter的实例化)
}
}
};需要实现这个接口,CvCameraViewListener2,并且需要复写接口方法,如下图所示:
这个可以参看OpenCV4Android的api介绍
http://docs.opencv.org/java/2.4.4/
最主要就是onCameraFrame这个方法了:
@Override
publicMat onCameraFrame(final CvCameraViewFrame inputFrame) {
final Mat rgba = inputFrame.rgba();
// Apply the active filters.
//主要看target检测效果,其他过滤效果可以不用看
if (mImageDetectionFilters !=null){
mImageDetectionFilters[mImageDetectionFilterIndex].apply(
rgba, rgba);
}
if (mCurveFilters !=null){
mCurveFilters[mCurveFilterIndex].apply(rgba,rgba);
}
if (mMixerFilters !=null){
mMixerFilters[mMixerFilterIndex].apply(rgba,rgba);
}
if (mConvolutionFilters !=null){
mConvolutionFilters[mConvolutionFilterIndex].apply(
rgba, rgba);
}
if (mIsPhotoPending) {
mIsPhotoPending =false;
takePhoto(rgba);
}
if (mIsCameraFrontFacing) {
// Mirror (horizontally flip) the preview.
Core.flip(rgba, rgba, 1);
}
return rgba;
}看到这个主要需要研究其中aplly方法的实现。好的,再去看看包下的这个类。
/**
* 图像检测的类,大概思路如下所示
* 1、对参考图片和实时获取的视频帧数据的处理(特征点的检测描述)
* 2、对描述的特征点进行匹配运算
* 3、根据匹配结果判断特征点之间距离,在根据距离拾取最佳的点
* 4、根据拾取的点计算出单应性矩阵
* 5、根据单应性矩阵对模版图片进行透视变换,
* 6、再提取变化之后的角点坐标,使用线框连接四个角点即可
* @author scy
*
*/
public class ImageDetectionFilter implements Filter {
// 参考图片帧
private final Mat mReferenceImage;
private final MatOfKeyPoint mReferenceKeypoints =
new MatOfKeyPoint();
private final Mat mReferenceDescriptors = new Mat();
// CVType defines the color depth, number of channels, and
// channel layout in the image.
private final Mat mReferenceCorners =
new Mat(4, 1, CvType.CV_32FC2);
// 场景图片帧
private final MatOfKeyPoint mSceneKeypoints =
new MatOfKeyPoint();
private final Mat mSceneDescriptors = new Mat();
private final Mat mCandidateSceneCorners =
new Mat(4, 1, CvType.CV_32FC2);
private final Mat mSceneCorners = new Mat(4, 1, CvType.CV_32FC2);
private final MatOfPoint mIntSceneCorners = new MatOfPoint();
// 灰度图片
private final Mat mGraySrc = new Mat();
// 获取匹配对
private final MatOfDMatch mMatches = new MatOfDMatch();
/**
*
* 定义检测、描述和匹配相关算法
* 使用star、freak和汉明距离的强制匹配算法
*/
private final FeatureDetector mFeatureDetector =
FeatureDetector.create(FeatureDetector.STAR);
private final DescriptorExtractor mDescriptorExtractor =
DescriptorExtractor.create(DescriptorExtractor.FREAK);
private final DescriptorMatcher mDescriptorMatcher =
DescriptorMatcher.create(
DescriptorMatcher.BRUTEFORCE_HAMMING);
// 设置line绘制的颜色,绿色
private final Scalar mLineColor = new Scalar(0, 255, 0);
/**
* 构造方法,类的初始化,以及对模板(参考)图片的一些处理
* @param context
* @param referenceImageResourceID
* @throws IOException
*/
public ImageDetectionFilter(final Context context,
final int referenceImageResourceID) throws IOException {
//加载图片
mReferenceImage = Utils.loadResource(context,
referenceImageResourceID,
Highgui.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
// 对图片进行格式转换
final Mat referenceImageGray = new Mat();
Imgproc.cvtColor(mReferenceImage, referenceImageGray,
Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Imgproc.cvtColor(mReferenceImage, mReferenceImage,
Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2RGBA);
// 定义参考图片的上下左右角点,为后面 的仿射变化做准备
mReferenceCorners.put(0, 0,
new double[] {0.0, 0.0});
mReferenceCorners.put(1, 0,
new double[] {referenceImageGray.cols(), 0.0});
mReferenceCorners.put(2, 0,
new double[] {referenceImageGray.cols(),
referenceImageGray.rows()});
mReferenceCorners.put(3, 0,
new double[] {0.0, referenceImageGray.rows()});
// 对特征点进行检测和描述
mFeatureDetector.detect(referenceImageGray,
mReferenceKeypoints);
mDescriptorExtractor.compute(referenceImageGray,
mReferenceKeypoints, mReferenceDescriptors);
}
/**
*
* 对场景图片帧进行相关处理
* 其中在这里获取匹配对
* 然后绘制获取的线框
*/
@Override
public void apply(final Mat src, final Mat dst) {
Imgproc.cvtColor(src, mGraySrc, Imgproc.COLOR_RGBA2GRAY);
mFeatureDetector.detect(mGraySrc, mSceneKeypoints);
mDescriptorExtractor.compute(mGraySrc, mSceneKeypoints,
mSceneDescriptors);
mDescriptorMatcher.match(mSceneDescriptors,
mReferenceDescriptors, mMatches);
findSceneCorners();
draw(src, dst);
}
private void findSceneCorners() {
List matchesList = mMatches.toList();
// 匹配对太少
if (matchesList.size() < 4) {
// There are too few matches to find the homography.
return;
}
// 将MatOfKeyPoint数据结构存储的特征点数据转换成List,便于后面获取
List referenceKeypointsList =
mReferenceKeypoints.toList();
List sceneKeypointsList =
mSceneKeypoints.toList();
// Calculate the max and min distances between keypoints.
// 计算特征点之间的最大和最小距离
double maxDist = 0.0;
double minDist = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for(DMatch match : matchesList) {
double dist = match.distance;
if (dist < minDist) {
minDist = dist;
}
if (dist > maxDist) {
maxDist = dist;
}
}
// The thresholds for minDist are chosen subjectively
// based on testing. The unit is not related to pixel
// distances; it is related to the number of failed tests
// for similarity between the matched descriptors.
// 根据距离对角点进行取舍
if (minDist > 50.0) {
// The target is completely lost.
// Discard any previously found corners.
mSceneCorners.create(0, 0, mSceneCorners.type());
return;
} else if (minDist > 25.0) {
// The target is lost but maybe it is still close.
// Keep any previously found corners.
return;
}
// Identify "good" keypoints based on match distance.
ArrayList goodReferencePointsList =
new ArrayList();
ArrayList goodScenePointsList =
new ArrayList();
// 最佳距离极限为minDist的1.75倍,然后拾取在此范围的点到ArrayList中
double maxGoodMatchDist = 1.75 * minDist;
for(DMatch match : matchesList) {
if (match.distance < maxGoodMatchDist) {
goodReferencePointsList.add(
referenceKeypointsList.get(match.trainIdx).pt);
goodScenePointsList.add(
sceneKeypointsList.get(match.queryIdx).pt);
}
}
// 如果在范围内的(拾取到的)点数小于4,则表示没有发现标志
if (goodReferencePointsList.size() < 4 ||
goodScenePointsList.size() < 4) {
// There are too few good points to find the homography.
return;
}
// 再从ArrayList转换成MatOfPoint2f数据结构(OpenCV中),同样是为了后面的处理
// 一个是参考图片的点数据,一个是图像帧的点数据
MatOfPoint2f goodReferencePoints = new MatOfPoint2f();
goodReferencePoints.fromList(goodReferencePointsList);
MatOfPoint2f goodScenePoints = new MatOfPoint2f();
goodScenePoints.fromList(goodScenePointsList);
// 计算单应性矩阵,根据最佳参考图像和场景图片的特征点(需要描述)
Mat homography = Calib3d.findHomography(
goodReferencePoints, goodScenePoints);
/**
* 根据单应性矩阵对参考图像帧进行透视变换,将2D场景转换成3D
* 保存在mCandidateSceneCorners
*/
Core.perspectiveTransform(mReferenceCorners,
mCandidateSceneCorners, homography);
// 对mCandidateSceneCorners进行类型转换
mCandidateSceneCorners.convertTo(mIntSceneCorners,
CvType.CV_32S);
// 输入数据(四边形)必须是凸面
if (Imgproc.isContourConvex(mIntSceneCorners)) {
mCandidateSceneCorners.copyTo(mSceneCorners);
}
}
protected void draw(Mat src, Mat dst) {
if (dst != src) {
src.copyTo(dst);
}
// 如果没有找到标志,在左上角绘制标志图片的缩影
if (mSceneCorners.height() < 4) {
// The target has not been found.
// Draw a thumbnail of the target in the upper-left
// corner so that the user knows what it is.
int height = mReferenceImage.height();
int width = mReferenceImage.width();
int maxDimension = Math.min(dst.width(),
dst.height()) / 2;
double aspectRatio = width / (double)height;
if (height > width) {
height = maxDimension;
width = (int)(height * aspectRatio);
} else {
width = maxDimension;
height = (int)(width / aspectRatio);
}
Mat dstROI = dst.submat(0, height, 0, width);
Imgproc.resize(mReferenceImage, dstROI, dstROI.size(),
0.0, 0.0, Imgproc.INTER_AREA);
return;
}
// 找到标志之后绘制标志边框,参考图片四个角点经过透视变换转换成模版图片中的四个角点
// 这样就完成了!
// Outline the found target in green.
Core.line(dst, new Point(mSceneCorners.get(0, 0)),
new Point(mSceneCorners.get(1, 0)), mLineColor, 4);
Core.line(dst, new Point(mSceneCorners.get(1, 0)),
new Point(mSceneCorners.get(2, 0)), mLineColor, 4);
Core.line(dst, new Point(mSceneCorners.get(2, 0)),
new Point(mSceneCorners.get(3, 0)), mLineColor, 4);
Core.line(dst, new Point(mSceneCorners.get(3,0)),
new Point(mSceneCorners.get(0, 0)), mLineColor, 4);
}
}
通过这些就可以得到开始的效果图了。
声明:本人水平有限,如果有什么地方描述欠妥,欢迎指正。同时也欢迎大家有什么疑问可以在文章后面提,谢谢!
AR研发团队招募有梦想的年轻人,有兴趣可以私信我,最好是在深圳。