tensorflow基础知识总结+线性回归实战
目录
- 一、Tensorflow介绍
-
- 1.2 图与tensorBoard
-
- 1) 数据序列化-events文件
- 2) 启动TensorBoard
- 2.op
-
- 2.1 修改张量的命名
- 3.会话
-
- 3.1 __ init __
- 3.2 会话中的run()
- 4 张量
-
- 4.1 张量的类型
- 4.2 张量形状的变换
- 4.3 形状改变
- 4.4 张量的数学运算
- 4.5 变量OP
- 二、利用TensorFlow实现线性回归案例
-
- 2.1 基础代码
- 2.2 命名空间
- 2.3 收集变量
- 2.4 模型保存与加载
- 2.4 命令行参数
一、Tensorflow介绍
1.2 图与tensorBoard
实现程序可视化的需要两步:
1) 数据序列化-events文件
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant(20)
b = tf.constant(22)
c = tf.add(a, b)
# 获取默认图
g = tf.get_default_graph()
print("图", g)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 1、写入到events文件中
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./temp/summary", graph=sess.graph)
sum_t = sess.run(c)
print(sum_t)
2) 启动TensorBoard
tensorboard --logdir="./ai/temp/summary/" --host=127.0.0.1 # 在cmd中输入自己的events文件所在目录
> TensorBoard 1.12.2 at http://127.0.0.1:6006 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
在浏览器中输入: http://127.0.0.1:6006,即可打开TensorBoard
2.op
2.1 修改张量的命名
a = tf.constant(20, name="a")
b = tf.constant(20, name="b")
3.会话
3.1 __ init __
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant(20, name="a")
b = tf.constant(22, name="b")
d = tf.constant(22.2)
c = tf.add(a, b)
# 获取默认图
g = tf.get_default_graph()
print("图", g)
print("a:", a)
print("d:", d)
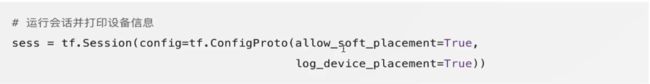
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
# 1、写入到events文件中
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./temp/summary", graph=sess.graph)
sum_t = sess.run(c)
print(sum_t)
>
图 <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000001D2D0B02470>
a: Tensor("a:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
d: Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
Device mapping: no known devices.
Add: (Add): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
a: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
b: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
Const: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
42
3.2 会话中的run()
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant(20, name="a")
b = tf.constant(22, name="b")
d = tf.constant(22.2)
c = tf.add(a, b)
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
# 1、写入到events文件中
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./temp/summary", graph=sess.graph)
a, b, c = sess.run([a, b, c])
print(a, b, c)
feed_dict:能够在运行时控制变量的赋值
import tensorflow as tf
# 定义placeholder
plat_a = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
plat_b = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
plat_add = tf.add(plat_a, plat_b)
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
# 1、写入到events文件中
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./temp/summary", graph=sess.graph)
ret = sess.run(plat_add, feed_dict={plat_a: 5.0, plat_b: 6.0})
print(ret)
4 张量
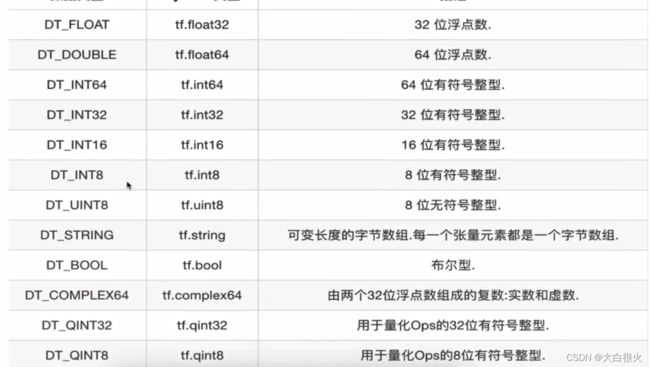
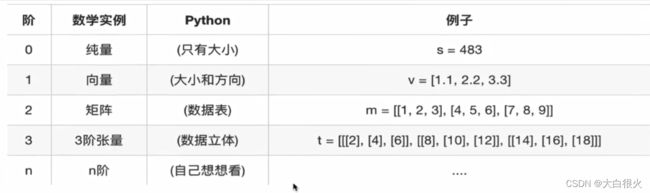
TensorFlow的张量就是一个n维数组,类型为tf.Tensor。Tensor具有两个重要属性:
type:数据类型shape:形状(阶)
4.1 张量的类型
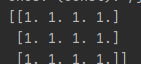
ones = tf.ones([3, 4])
print(ones.eval())
4.2 张量形状的变换
4.3 形状改变
TensorFlow的张量具有两种形状变换,动态形状和静态形状:
# 定义placeholder
plat_a = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
plat_b = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
plat_add = tf.add(plat_a, plat_b)
plat_c = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, None])
print(plat_c.shape)
plat_c.set_shape([5, 6])
print("c.shape:", plat_c.shape)
plat_c.set_shape([4, 3]) # 不能再次设置静态形状,否则会报错!!!,也不能跨阶数修改!!!!
print("c.shape:", plat_c.shape)
动态形状的设置:会生成一个新的张量值
plat_c = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, None])
print(plat_c.shape)
c_shape = tf.reshape(plat_c, [12, 12])
c_shape = tf.reshape(c_shape, [2, 12, 6])
print("c.shape:", c_shape.get_shape())
4.4 张量的数学运算
4.5 变量OP
二、利用TensorFlow实现线性回归案例
2.1 基础代码
import tensorflow as tf
# 1.准备数据
X = tf.random_normal(shape=(100, 1), mean=2, stddev=2)
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + [[0.7]]
# 2.构建模型
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)))
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)))
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
# 3. 确定损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict-y_true))
# 4.梯度下降优化损失
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 5.训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
print("随机初始化的权重%f, 偏置为%f" % (weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 训练模型
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(optimizer)
print("第%d步的误差为%f, 权重为%f, 偏置为%f" % (i, error.eval(), weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
2.2 命名空间
添加模块的命名
import tensorflow as tf
# 1.准备数据
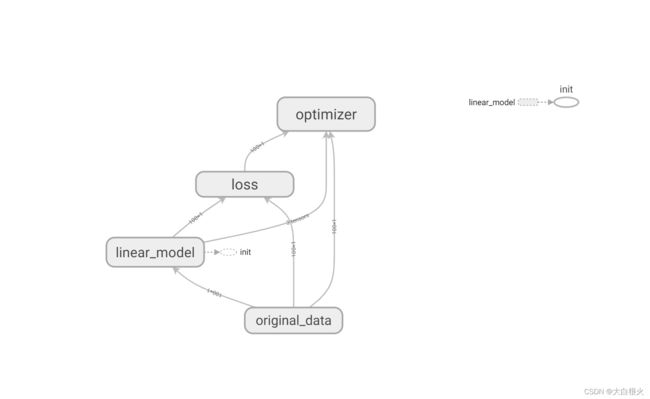
with tf.variable_scope("original_data"):
X = tf.random_normal(shape=(100, 1), mean=2, stddev=2, name="original_data_x")
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + [[0.7]]
# 2.构建模型
with tf.variable_scope("linear_model"):
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="w")
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="b")
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
# 3. 确定损失函数
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict-y_true))
# 4.梯度下降优化损失
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 5.训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 5.1运行初始化变量
sess.run(init)
print("随机初始化的权重%f, 偏置为%f" % (weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 5.2 创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir="./temp/summary/", graph=sess.graph)
# 5.3训练模型
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(optimizer)
print("第%d步的误差为%f, 权重为%f, 偏置为%f" % (i, error.eval(), weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
2.3 收集变量
import tensorflow as tf
# 1.准备数据
with tf.variable_scope("original_data"):
X = tf.random_normal(shape=(100, 1), mean=2, stddev=2, name="original_data_x")
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + [[0.7]]
# 2.构建模型
with tf.variable_scope("linear_model"):
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="w")
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="b")
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
# 3. 确定损失函数
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict-y_true))
# 4.梯度下降优化损失
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 11.手机观察的变量
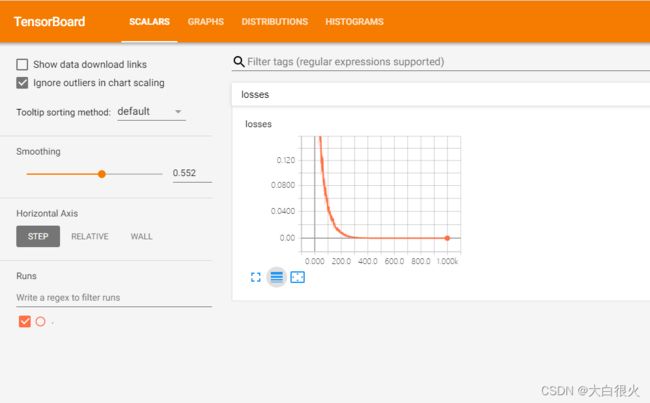
tf.summary.scalar("losses", error)
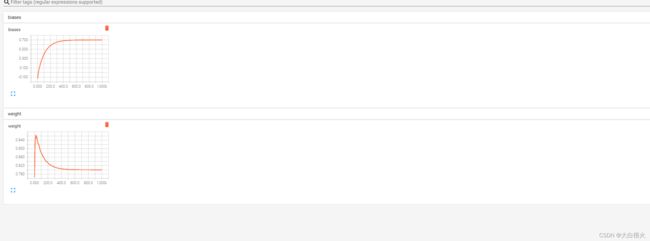
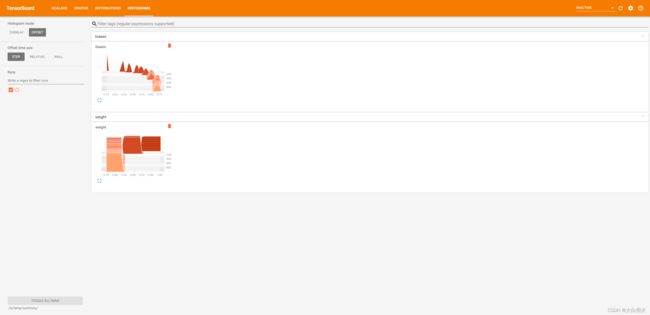
tf.summary.histogram("weight", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("biases", bias)
# 22.合并收集的张量
merge = tf.summary.merge_all()
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 5.训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 5.1运行初始化变量
sess.run(init)
print("随机初始化的权重%f, 偏置为%f" % (weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 5.2 创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir="./temp/summary/", graph=sess.graph)
# 5.3训练模型
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(optimizer)
print("第%d步的误差为%f, 权重为%f, 偏置为%f" % (i, error.eval(), weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 写入收集的变量
summary = sess.run(merge)
file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
2.4 模型保存与加载
保存的文件格式为ckpt
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.save(sess, "./temp/ckpt/linearregression")
saver.restore(sess, "./temp/ckpt/linearregression")
保存代码
import tensorflow as tf
# 1.准备数据
with tf.variable_scope("original_data"):
X = tf.random_normal(shape=(100, 1), mean=2, stddev=2, name="original_data_x")
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + [[0.7]]
# 2.构建模型
with tf.variable_scope("linear_model"):
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="w")
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="b")
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
# 3. 确定损失函数
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict-y_true))
# 4.梯度下降优化损失
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 11.手机观察的变量
tf.summary.scalar("losses", error)
tf.summary.histogram("weight", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("biases", bias)
# 22.合并收集的张量
merge = tf.summary.merge_all()
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 创建saver
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# 5.训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 5.1运行初始化变量
sess.run(init)
print("随机初始化的权重%f, 偏置为%f" % (weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 5.2 创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir="./temp/summary/", graph=sess.graph)
# 5.3训练模型
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(optimizer)
print("第%d步的误差为%f, 权重为%f, 偏置为%f" % (i, error.eval(), weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 写入收集的变量
summary = sess.run(merge)
file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
saver.save(sess, "./temp/ckpt/linearregression")
读取
import tensorflow as tf
# 1.准备数据
with tf.variable_scope("original_data"):
X = tf.random_normal(shape=(100, 1), mean=2, stddev=2, name="original_data_x")
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + [[0.7]]
# 2.构建模型
with tf.variable_scope("linear_model"):
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="w")
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="b")
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
# 3. 确定损失函数
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict-y_true))
# 4.梯度下降优化损失
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 11.手机观察的变量
tf.summary.scalar("losses", error)
tf.summary.histogram("weight", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("biases", bias)
# 22.合并收集的张量
merge = tf.summary.merge_all()
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 创建saver
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# 5.训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 5.1运行初始化变量
sess.run(init)
print("随机初始化的权重%f, 偏置为%f" % (weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 5.2 创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir="./temp/summary/", graph=sess.graph)
saver.restore(sess, "./temp/ckpt/linearregression")
print(weights.eval(), bias.eval())
# # 5.3训练模型
# for i in range(1000):
# sess.run(optimizer)
# print("第%d步的误差为%f, 权重为%f, 偏置为%f" % (i, error.eval(), weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
#
# # 写入收集的变量
# summary = sess.run(merge)
# file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
#
# saver.save(sess, "./temp/ckpt/linearregression")
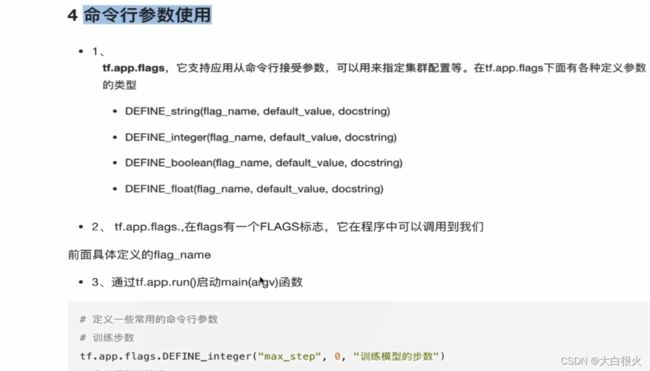
2.4 命令行参数
import tensorflow as tf
# 1.准备数据
with tf.variable_scope("original_data"):
X = tf.random_normal(shape=(100, 1), mean=2, stddev=2, name="original_data_x")
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + [[0.7]]
# 2.构建模型
with tf.variable_scope("linear_model"):
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="w")
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal((1, 1)), name="b")
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
# 3. 确定损失函数
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict-y_true))
# 4.梯度下降优化损失
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 11.手机观察的变量
tf.summary.scalar("losses", error)
tf.summary.histogram("weight", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("biases", bias)
# 22.合并收集的张量
merge = tf.summary.merge_all()
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 创建saver
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# #################### 定义命令行参数
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer("max_step", 1000, "train_ step number")
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
# 5.训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 5.1运行初始化变量
sess.run(init)
print("随机初始化的权重%f, 偏置为%f" % (weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 5.2 创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir="./temp/summary/", graph=sess.graph)
# saver.restore(sess, "./temp/ckpt/linearregression")
print(weights.eval(), bias.eval())
# 5.3训练模型
for i in range(FLAGS.max_step):
sess.run(optimizer)
print("第%d步的误差为%f, 权重为%f, 偏置为%f" % (i, error.eval(), weights.eval(), bias.eval()))
# 写入收集的变量
summary = sess.run(merge)
file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
saver.save(sess, "./temp/ckpt/linearregression")