Triton部署YOLOV5笔记(二)
直达链接
Triton部署YOLOV5笔记(一)
Triton部署YOLOV5笔记(二)
triton部署yolov5笔记(三)
triton部署yolov5笔记(四)
参考
我不会用 Triton 系列:Python Backend 的使用
官方github[triton-inference-server]
人脸识别例程
目录结构
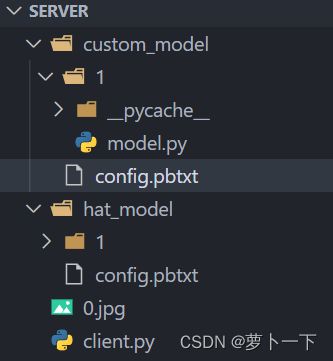
server/
└── hat_model # 模型名字,需要和 config.txt 中的名字对上
├── 1 # 模型版本号
│ └── model.onnx # 这个是你自己训练好保存的模型
├── config.pbtxt # 模型配置文件
custom_model # 模型名字,需要和 config.txt 中的名字对上
├── 1 # 模型版本号
│ └── model.py # python backend服务端代码
├── config.pbtxt # 模型配置文件
client.py # 客户端脚本,可以不放在这里
0.jpg # 测试图片
服务端配置
输入是一张图片,输出是一张图片
name: "custom_model"
backend: "python"
input [
{
name: "input0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [-1, -1, 3]
}
]
output [
{
name: "output0"
data_type: TYPE_FP32
dims: [-1, -1, 3 ]
}
]
服务端
model.py 中需要提供三个接口:initialize, execute, finalize。其中 initialize 和 finalize 是模型实例初始化、模型实例清理的时候会调用的。如果有 n 个模型实例,那么会调用 n 次这两个函数。
#model.py
import json
import numpy as np
import triton_python_backend_utils as pb_utils
import cv2
import torch
import torchvision
import random
import math
from torch.utils.dlpack import from_dlpack
class TritonPythonModel:
def initialize(self, args):
self.model_config = model_config = json.loads(args['model_config'])
output0_config = pb_utils.get_output_config_by_name(model_config, "output0")
self.output0_dtype = pb_utils.triton_string_to_numpy(output0_config['data_type'])
def execute(self, requests):
output0_dtype = self.output0_dtype
responses = []
for request in requests:
in_0 = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(request, 'input0')
img = self._recognize(in_0.as_numpy())
out_tensor_0 = pb_utils.Tensor('output0', img.astype(output0_dtype))
# out_tensor_0, out_tensor_1, out_tensor_2 = self._recognize(in_0.as_numpy())
inference_response = pb_utils.InferenceResponse(output_tensors=[out_tensor_0])
# inference_response = pb_utils.InferenceResponse(output_tensors=[out_tensor_0,out_tensor_1,out_tensor_2])
responses.append(inference_response)
return responses
def finalize(self):
print('Cleaning up...')
# def _recognize(self,draw):
# return draw
def _recognize(self,draw):
# 超参数的设置
img_size=(640,640) #图片缩放大小
conf_thres=0.25 #置信度阈值
iou_thres=0.45 #iou阈值
class_num=2 #类别数
stride=[8,16,32]
anchor_list= [[10,13, 16,30, 33,23],[30,61, 62,45, 59,119], [116,90, 156,198, 373,326]]
anchor = np.array(anchor_list).astype(np.float).reshape(3,-1,2)
area = img_size[0] * img_size[1]
size = [int(area / stride[0] ** 2), int(area / stride[1] ** 2), int(area / stride[2] ** 2)]
feature = [[int(j / stride[i]) for j in img_size] for i in range(3)]
draw = draw.copy()
# print(draw)
# draw = cv2.cvtColor(draw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# height, width, _ = np.shape(draw)
# src_size = [height, width]
src_size = draw.shape[:2]
# 图片填充并进行归一化
img = self.letterbox(draw,img_size,stride=32)[0]
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
# 归一化
img=img.astype(dtype=np.float32)
img/=255.0
# 维度扩张
img=np.expand_dims(img,axis=0).astype(np.float32)
# print(img.shape)
inference_request = pb_utils.InferenceRequest(
model_name='hat_model',
requested_output_names=['output0','output1','output2'],
inputs=[pb_utils.Tensor('images', img)]
)
inference_response = inference_request.exec()
out_tensor_0 = self.pb_tensor_to_numpy(pb_utils.get_output_tensor_by_name(inference_response, 'output0'))[0]
out_tensor_1 = self.pb_tensor_to_numpy(pb_utils.get_output_tensor_by_name(inference_response, 'output1'))[0]
out_tensor_2 = self.pb_tensor_to_numpy(pb_utils.get_output_tensor_by_name(inference_response, 'output2'))[0]
output = [out_tensor_0,out_tensor_1,out_tensor_2]
#提取出特征
y = []
y.append(torch.tensor(output[0].reshape(-1,size[0]*3,5+class_num)).sigmoid())
y.append(torch.tensor(output[1].reshape(-1,size[1]*3,5+class_num)).sigmoid())
y.append(torch.tensor(output[2].reshape(-1,size[2]*3,5+class_num)).sigmoid())
grid = []
for k, f in enumerate(feature):
grid.append([[i, j] for j in range(f[0]) for i in range(f[1])])
z = []
for i in range(3):
src = y[i]
xy = src[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5
wh = (src[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2
dst_xy = []
dst_wh = []
for j in range(3):
dst_xy.append((xy[:, j * size[i]:(j + 1) * size[i], :] + torch.tensor(grid[i])) * stride[i])
dst_wh.append(wh[:, j * size[i]:(j + 1) * size[i], :] * anchor[i][j])
src[..., 0:2] = torch.from_numpy(np.concatenate((dst_xy[0], dst_xy[1], dst_xy[2]), axis=1))
src[..., 2:4] = torch.from_numpy(np.concatenate((dst_wh[0], dst_wh[1], dst_wh[2]), axis=1))
z.append(src.view(1, -1, 5+class_num))
results = torch.cat(z, 1)
results = self.nms(results, conf_thres, iou_thres)
#映射到原始图像
img_shape=img.shape[2:]
# print(img_size)
for det in results: # detections per image
if det is not None and len(det):
det[:, :4] = self.scale_coords(img_shape, det[:, :4],src_size).round()
if det is not None and len(det):
draw = self.draw(draw, det)
return draw
def letterbox(self, img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=False, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True,
stride=32):
'''图片归一化'''
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def pb_tensor_to_numpy(self,pb_tensor):
'''pb_tensor转换为numpy格式'''
if pb_tensor.is_cpu():
return pb_tensor.as_numpy()
else:
pytorch_tensor = from_dlpack(pb_tensor.to_dlpack())
return pytorch_tensor.cpu().numpy()
def xywh2xyxy(self,x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def nms(self,prediction, conf_thres=0.1, iou_thres=0.6, agnostic=False):
if prediction.dtype is torch.float16:
prediction = prediction.float() # to FP32
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_det = 300 # maximum number of detections per image
output = [None] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
box = self.xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((torch.tensor(box), conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n:
continue
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.boxes.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres)
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
output[xi] = x[i]
return output
def clip_coords(self,boxes, img_shape):
'''查看是否越界'''
# Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)
boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y2
def scale_coords(self,img1_shape, coords, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
'''
坐标对应到原始图像上,反操作:减去pad,除以最小缩放比例
:param img1_shape: 输入尺寸
:param coords: 输入坐标
:param img0_shape: 映射的尺寸
:param ratio_pad:
:return:
'''
# Rescale coords (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new,计算缩放比率
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (
img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding ,计算扩充的尺寸
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding,减去x方向上的扩充
coords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding,减去y方向上的扩充
coords[:, :4] /= gain # 将box坐标对应到原始图像上
self.clip_coords(coords, img0_shape) # 边界检查
return coords
def sigmoid(self,x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def plot_one_box(self,x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=None):
# Plots one bounding box on image img
tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
return img
def draw(self,img, boxinfo):
colors = [[0, 0, 255],[0,255,0]]
class_id =['hat','no_hat']
for *xyxy, conf, cls in boxinfo:
label = '%s %.2f' % (class_id[int(cls)], conf)
# print('xyxy: ', xyxy)
self.plot_one_box(xyxy, img, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=1)
return img
客户端
接下来,写一个脚本调用一下服务。
#client.py
import numpy as np
import cv2
import tritonclient.http as httpclient
import time
if __name__ == '__main__':
triton_client = httpclient.InferenceServerClient(url='192.168.188.108:8000')
img = cv2.imread('0.jpg').astype(np.float32)
inputs = []
inputs.append(httpclient.InferInput('input0', [*img.shape], "FP32"))
# binary_data 默认是 True, 表示传输的时候使用二进制格式, 否则使用 JSON 文本(大小不一样)
inputs[0].set_data_from_numpy(img, binary_data=True)
outputs = []
outputs.append(httpclient.InferRequestedOutput('output0', binary_data=False))
t1 = time.time()
results = triton_client.infer('custom_model', inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
t2 = time.time()
print('inference time is: {}ms'.format(1000 * (t2 - t1)))
output_data0 = results.as_numpy('output0')
print(img.shape)
print(output_data0.shape)
cv2.imwrite('out.jpg', output_data0.astype(np.uint8))
输出结果,效果不太好,不过跑通了。

注意事项
需要配置python环境
进入docker容器根目录
docker exec xxxxxxx /bin/bash
或者直接在docker客户端,进入容器,运行终端

可以看到models目录,models目录下即为模型目录,映射到本地server下
安装model.py所需要的包
pip3 install opencv-python-headless
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio
清华镜像源地址
pip install xxx -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
也可以根据官方的教程,Packaging the Conda Environment具体实现过程我没有试,大家可以试试
使用本地环境
在创建环境之前运行
export PYTHONNOUSERSITE=True
创建一个虚拟环境,安装服务端需要的包
conda create -n triton python=3.8
pip install opencv-python # conda 安装不了,用 pip,如果有问题安装opencv-python-headless
pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio
# 清华镜像源
# pip install xxx -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
conda install conda-pack
conda-pack # 运行打包程序,将会打包到运行的目录下面
如果需要,安装opencv的依赖
apt update
apt install ffmpeg libsm6 libxext6 -y --fix-missing # 安装 opencv 的依赖, -y 表示 yes
将打包的triton.tar.gz文件放到cuetom_model路径下
具体路径如下
.
├── deploy
│ ├── custom_model
│ │ ├── 1
│ │ │ ├── model.py
│ │ │ └── __pycache__
│ │ │ ├── hat_utils.cpython-38.pyc
│ │ │ └── model.cpython-38.pyc
│ │ ├── config.pbtxt
│ │ └── triton.tar.gz
│ ├── model_0
│ │ ├── 1
│ │ │ └── model.onnx
│ │ └── config.pbtxt
│ └── model_1
│ ├── 1
│ │ └── model.onnx
│ └── config.pbtxt
└── images
├── input_img
│ └── 4.jpg
└── output_img
└── 111.png
修改配置文件
最后一行加上
parameters: {
key: "EXECUTION_ENV_PATH",
value: {string_value: "$$TRITON_MODEL_DIRECTORY/triton.tar.gz"}
}