Rabbitmq消息发布确认机制
消息的确认,是指生产者投递消息后,如果 Broker(消息实体) 收到消息,则会给我们生产者一个应答。生产者进行接收应答,用来确定这条消息是否正常的发送到 Broker ,这种方式也是消息的可靠性投递的核心保障!
单个确认
这是一种简单的确认方式,它是一种同步确认发布的方式,也就是发布一个消息之后只有它
被确认发布,后续的消息才能继续发布,waitForConfirms()这个方法只有在消息被确认
的时候才返回,如果在指定时间范围内这个消息没有被确认那么它将抛出异常。
这种确认方式有一个最大的缺点就是:发布速度特别的慢,因为如果没有确认发布的消息就会
阻塞所有后续消息的发布,这种方式最多提供每秒不超过数百条发布消息的吞吐量。当然对于某
些应用程序来说这可能已经足够了。
批量确认
单个确认的方式非常慢,与单个等待确认消息相比,先发布一批消息然后一起确认可以极大地提高吞吐量,当然这种方式的缺点就是:当发生故障导致发布出现问题时,不知道是哪个消息出现问题了,我们必须将整个批处理保存在内存中,以记录重要的信息而后重新发布消息。当然这种方案仍然是同步的,也一样会阻塞消息的发布。
异步确认
Channel对象提供的ConfirmListener()回调方法只包含deliverTag(当前Channel发出的消息序列号),需要自己为每一个Channel维护一个cunconfirm的消息序列号集合,每个publish数据,集合中元素+1,回调一次handleAck方法,unconfirm集合删除相应的一条(multiple=false)或多条(multiple=true)记录。从程序效率上看,这个unconfirm集合最好采用有序集合SortedSet存储结构
public class Test {
private static final long MESSAGE_COUNT=1000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//单个确认
// Test.danGeQueRen(); //发布1000个单独确认消息,耗时991ms
//批量确认
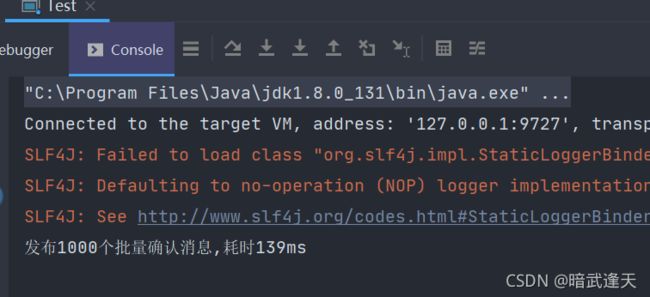
Test.piLiangQueRen(); //发布1000个批量确认消息,耗时139ms
//异步确认
// Test.yiBuQueRen(); //发布1000个异步确认消息,耗时56ms
}
// 单个确认
static void danGeQueRen() throws Exception {
Channel channel = Rabbitmqutil.getChannel();
//队列的声明 使用uuid生成随机队列名
String queueName = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
channel.queueDeclare(queueName,false,false,false,null);
//开启发布确认
channel.confirmSelect();
//开始时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//批量发消息
for (int i = 1; i < MESSAGE_COUNT ; i++) {
String message = i+"";
channel.basicPublish("",queueName,null,message.getBytes());
//单个发布确认
boolean flag = channel.waitForConfirms();
if(flag){
System.out.println("消息发送成功");
}
}
//结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("发布"+MESSAGE_COUNT+"个单独确认消息,耗时"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}
//批量确认
static void piLiangQueRen() throws Exception{
Channel channel = Rabbitmqutil.getChannel();
//队列的声明 使用uuid生成随机队列名
String queueName = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
channel.queueDeclare(queueName,false,false,false,null);
//开启发布确认
channel.confirmSelect();
//开始时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//批量发消息
//批量确认消息大小
int batchSize = 100;
for (int i = 1; i < MESSAGE_COUNT ; i++) {
String message = i+"";
channel.basicPublish("",queueName,null,message.getBytes());
//判断达到100条消息的时候 批量确认一次
if(i%batchSize==0){
//发布确认
channel.waitForConfirms();
}
}
//结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("发布"+MESSAGE_COUNT+"个批量确认消息,耗时"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}
//异步确认
static void yiBuQueRen() throws Exception{
Channel channel = Rabbitmqutil.getChannel();
//队列的声明 使用uuid生成随机队列名
String queueName = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
channel.queueDeclare(queueName,false,false,false,null);
//开启发布确认
channel.confirmSelect();
/*
* 线程安全有序的一个哈希表 适用于高并发的情况
* 1 轻松的将序号与消息进行关联
* 2 轻松批量删除条目 只要给到序号
* 3 支持高并发(多线程)
* */
ConcurrentSkipListMap<Long,String> outstandingConfirms=
new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
//消息确认成功 回调函数
ConfirmCallback ackCallback = (deliveryTag,multiple)->{
if(multiple){
//2 删除掉已经确认的消息 剩下的就是未确认的消息
ConcurrentNavigableMap<Long,String> confirmed=
outstandingConfirms.headMap(deliveryTag);
}else{
outstandingConfirms.remove(deliveryTag);
}
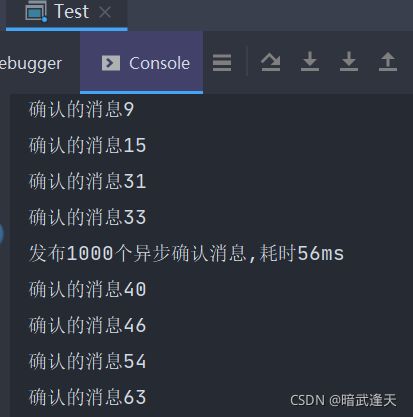
System.out.println("确认的消息"+deliveryTag);
};
/*
* 1 消息的标记
* 2 是否为批量确认
* */
//消息确认失败 回调函数
ConfirmCallback nackCallback = (deliveryTag,multiple)->{
//3 打印下未确认的消息都有哪些
String message = outstandingConfirms.get(deliveryTag);
System.out.println("未确认的消息是"+message+"-->未确认消息的tag:"+deliveryTag);
};
//准备消息的监听器 监听哪些消息成功了 哪些消息失败了
/*
* 1 监听成功的消息
* 2 监听失败的消息
* */
channel.addConfirmListener(ackCallback,nackCallback);
//开始时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i < MESSAGE_COUNT ; i++) {
String message = i+"";
channel.basicPublish("",queueName,null,message.getBytes());
// 1 记录下所有要发送的消息 消息的总和
outstandingConfirms.put(channel.getNextPublishSeqNo(), message);
}
//结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("发布"+MESSAGE_COUNT+"个异步确认消息,耗时"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}